logsic 回归
logstic 回归 ,从本质上说,就是一个单层感知器,仅此而已。 一个输入层 ,一个层激活的神经网络。
SVM ,一个输入层 ,一个隐藏层(核函数),一个激活的神经网络。
所以,在当下所有的过往的机器学习算法,都无法与深度学习相提并论!,你们都过时了!
但是,经过logistic变换,自变量为负无穷到正无穷,并且输出值即是属于某一类的概率。数学概念清晰。在很多浅薄,SB的领域,智力水平的低的种族中还有一定的应用。
from numpy import *
def loadDataSet():
dataMat = []; labelMat = []
fr = open('testSet.txt')
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr = line.strip().split()
dataMat.append([1.0, float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])])
labelMat.append(int(lineArr[2]))
return dataMat,labelMat
def sigmoid(inX):
return 1.0/(1+exp(-inX))
def gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels):
dataMatrix = mat(dataMatIn) #convert to NumPy matrix
labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose() #convert to NumPy matrix
m,n = shape(dataMatrix)
alpha = 0.001
maxCycles = 5000
weights = ones((n,1))
for k in range(maxCycles): #heavy on matrix operations
h = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weights) #matrix mult
error = (labelMat - h) #vector subtraction
weights = weights + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose()* error #matrix mult
return weights
def plotBestFit(weights):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dataMat,labelMat=loadDataSet()
dataArr = array(dataMat)
n = shape(dataArr)[0]
xcord1 = []; ycord1 = []
xcord2 = []; ycord2 = []
for i in range(n):
if int(labelMat[i])== 1:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2])
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=30, c='red', marker='s')
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=30, c='green')
x = arange(-3.0, 3.0, 0.1)
y = (-weights[0]-weights[1]*x)/weights[2]
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('X1'); plt.ylabel('X2');
plt.show()
def stocGradAscent0(dataMatrix, classLabels):
m,n = shape(dataMatrix)
alpha = 0.2
weights = ones(n) #initialize to all ones
for i in range(m):
h = sigmoid(dataMatrix[i].T@ weights) # #h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[i]*weights))
error = classLabels[i] - h
weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[i]
return weights
def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter=150):
m,n = shape(dataMatrix)
weights = ones(n) #initialize to all ones
for j in range(numIter):
dataIndex = range(m)
for i in range(m):
alpha = 4/(1.0+j+i)+0.0001 #apha decreases with iteration, does not
randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))#go to 0 because of the constant
h = sigmoid(dataMatrix[randIndex].T@ weights) #h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[i]*weights))
error = classLabels[randIndex] - h
weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex]
del(randIndex)
return weights
def classifyVector(inX, weights):
prob = sigmoid(sum(inX*weights))
if prob > 0.5: return 1.0
else: return 0.0
def colicTest():
frTrain = open('horseColicTraining.txt'); frTest = open('horseColicTest.txt')
trainingSet = []; trainingLabels = []
for line in frTrain.readlines():
currLine = line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr =[]
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
trainingSet.append(lineArr)
trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21]))
trainWeights = stocGradAscent1(array(trainingSet), trainingLabels, 1000)
errorCount = 0; numTestVec = 0.0
for line in frTest.readlines():
numTestVec += 1.0
currLine = line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr =[]
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
if int(classifyVector(array(lineArr), trainWeights))!= int(currLine[21]):
errorCount += 1
errorRate = (float(errorCount)/numTestVec)
print ("the error rate of this test is: %f" % errorRate)
return errorRate
def multiTest():
numTests = 10; errorSum=0.0
for k in range(numTests):
errorSum += colicTest()
print ("after %d iterations the average error rate is: %f" % (numTests, errorSum/float(numTests)))
'''
import logRegres
dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet()
logRegres.gradAscent(dataArr,labelMat)
'''
'''
from numpy import *
weights=logRegres.gradAscent(dataArr,labelMat)
logRegres.plotBestFit(weights.getA())
'''
'''
from numpy import *
import logRegres
dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet()
weights=logRegres.stocGradAscent0(array(dataArr),labelMat)
logRegres.plotBestFit(weights)
'''
'''
from numpy import *
import logRegres
dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet()
weights=logRegres.stocGradAscent1(array(dataArr),labelMat)
logRegres.plotBestFit(weights)
'''
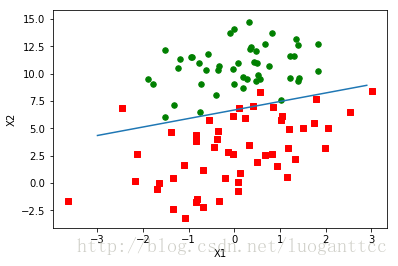
import logRegres
dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet()
logRegres.gradAscent(dataArr,labelMat)
matrix([[ 4.12414349],
[ 0.48007329],
[-0.6168482 ]])from numpy import *
weights=logRegres.gradAscent(dataArr,labelMat)
logRegres.plotBestFit(weights.getA())from numpy import *
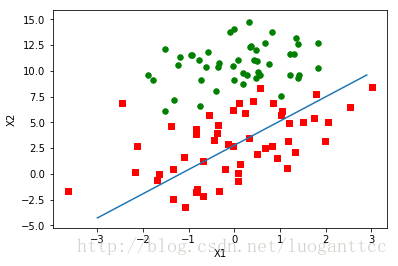
import logRegres
dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet()
weights=logRegres.stocGradAscent0(array(dataArr),labelMat)
logRegres.plotBestFit(weights.getA())from numpy import *
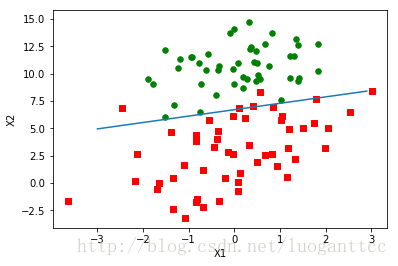
import logRegres
dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet()
weights=logRegres.stocGradAscent1(array(dataArr),labelMat)
logRegres.plotBestFit(weights)import logRegres
logRegres.multiTest()return 1.0/(1+exp(-inX))
the error rate of this test is: 0.283582
the error rate of this test is: 0.388060
the error rate of this test is: 0.313433
the error rate of this test is: 0.432836
the error rate of this test is: 0.358209
the error rate of this test is: 0.328358
the error rate of this test is: 0.208955
the error rate of this test is: 0.253731
the error rate of this test is: 0.373134
the error rate of this test is: 0.447761
after 10 iterations the average error rate is: 0.338806 我靠,这么好,如此有规律的数据集,你的误差这么大,%33.8啊!!!!
正确率只有%66.2,太搞笑了!
这是对如此完美数据集的无耻浪费!!!!!!