lambda表达式和函数式接口


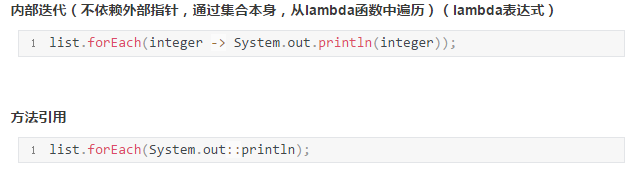
使用案例
package com.shengsiyuan; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; public class lambdaTest { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("My JFrame"); JButton jButton=new JButton("Button"); // 匿名函数 jButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { System.out.println("hello"); } }); /* //lambda表达式使用1: 最简(没定义类型,java编译系统去进行类型推断) jButton.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("hello"));*/ //lambda表达式使用2: 定义类了类型 jButton.addActionListener((ActionEvent event) -> System.out.println("hello") ); //lambda表达式使用3: 定义类了类型,多行使用花括号 jButton.addActionListener((ActionEvent event) ->{ System.out.println("hello"); System.out.println("hello"); System.out.println("hello"); } ); jFrame.add(jButton); jFrame.pack(); jFrame.setVisible(true); jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); } }

lambda为什么不需要写函数名?
因为实现函数式接口只有一个接口数量,所以不需要。
例:
package com.shengsiyuan; @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface { void test1(); String toString(); //使用toString()不会报错,因为toString是重写了Object的toString()方法 // String MyString(); //使用MyString()会报错 } public class Test2 { void test(MyInterface myInterface) { System.out.println("1"); myInterface.test1(); System.out.println("2"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Test2 test2 = new Test2(); // test2.test(new MyInterface() { // @Override // public void test1() { // System.out.println("ok"); // } // }); //当实现接口的方法参数为void时,类型的括号不能省略 test2.test(() -> { System.out.println("OK"); }); // 使用lambda表达式实现了 MyInterface接口 MyInterface myInterface = () -> { System.out.println("OK"); }; System.out.println(myInterface.getClass()); // class com.shengsiyuan.Test2$$Lambda$2/1418481495 System.out.println(myInterface.getClass().getSuperclass()); // class java.lang.Object System.out.println(myInterface.getClass().getInterfaces().length); // 1 System.out.println(myInterface.getClass().getInterfaces()[0]); // interface com.shengsiyuan.MyInterface } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号