Python map()函数
一、Python map()函数的用法
map(function, iterable)
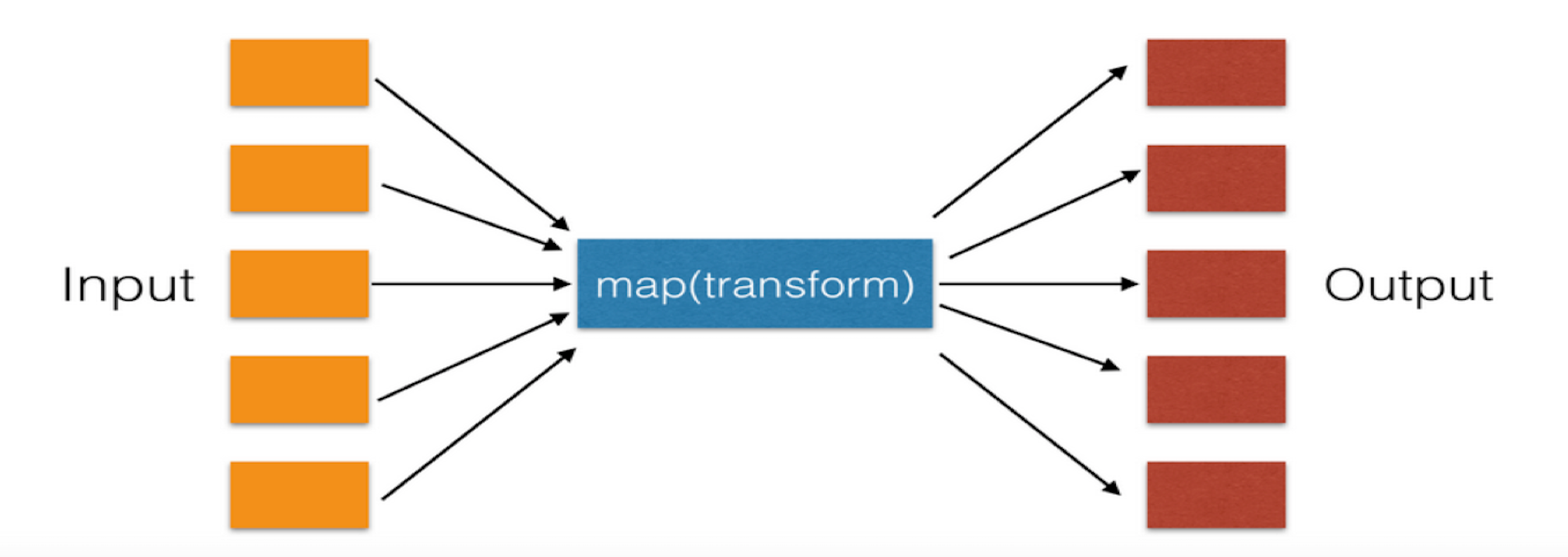
功能:遍历序列,对序列中每个元素进行操作,最终获取新的序列。
i = [11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
map(函数,可迭代的对象(可以for循环的东西))
def f2(a):
return a + 100
result = map(f2, li)
result = map(lambda a: a + 200, li)
print(list(result))
filter # 函数返回True,将元素添加到结果中
map # 将函数返回值添加到结果中
def f1(args):
result = []
for i in args:
result.append(100+i)
return result
r = f1(li)
print(list(r))
输出结构如下:
[211, 222, 233, 244, 255] [111, 122, 133, 144, 155]
应用场景:
1、每个元素增加100
2、两个列表对应元素相加
注意:map()函数不改变原有的 list,而是返回一个新的 list。
利用map()函数,可以把一个 list 转换为另一个 list,只需要传入转换函数。由于list包含的元素可以是任何类型,因此,map() 不仅仅可以处理只包含数值的 list,事实上它可以处理包含任意类型的 list,只要传入的函数f可以处理这种数据类型。任务假设用户输入的英文名字不规范,没有按照首字母大写,后续字母小写的规则,请利用map()函数,把一个list(包含若干不规范的英文名字)变成一个包含规范英文名字的list:输入:['adam', 'LISA', 'barT']输出:['Adam', 'Lisa', 'Bart']def format_name(s): s1=s[0:1].upper()+s[1:].lower(); return s1; print map(format_name, ['adam', 'LISA', 'barT'])
二、通过PyCharm查看源码
选中map函数右键Go To—Implementation代码如下
class map(object):
"""
map(func, *iterables) --> map object
Make an iterator that computes the function using arguments from
each of the iterables. Stops when the shortest iterable is exhausted.
"""
def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return getattr(self, name). """
pass
def __init__(self, func, *iterables): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
pass
def __iter__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Implement iter(self). """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass
def __next__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Implement next(self). """
pass
def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return state information for pickling. """
pass
三、查看源码里的FixMap.py
# Copyright 2007 Google, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
# Licensed to PSF under a Contributor Agreement.
"""Fixer that changes map(F, ...) into list(map(F, ...)) unless there
exists a 'from future_builtins import map' statement in the top-level
namespace.
As a special case, map(None, X) is changed into list(X). (This is
necessary because the semantics are changed in this case -- the new
map(None, X) is equivalent to [(x,) for x in X].)
We avoid the transformation (except for the special case mentioned
above) if the map() call is directly contained in iter(<>), list(<>),
tuple(<>), sorted(<>), ...join(<>), or for V in <>:.
NOTE: This is still not correct if the original code was depending on
map(F, X, Y, ...) to go on until the longest argument is exhausted,
substituting None for missing values -- like zip(), it now stops as
soon as the shortest argument is exhausted.
"""
# Local imports
from ..pgen2 import token
from .. import fixer_base
from ..fixer_util import Name, ArgList, Call, ListComp, in_special_context
from ..pygram import python_symbols as syms
from ..pytree import Node
class FixMap(fixer_base.ConditionalFix):
BM_compatible = True
PATTERN = """
map_none=power<
'map'
trailer< '(' arglist< 'None' ',' arg=any [','] > ')' >
[extra_trailers=trailer*]
>
|
map_lambda=power<
'map'
trailer<
'('
arglist<
lambdef< 'lambda'
(fp=NAME | vfpdef< '(' fp=NAME ')'> ) ':' xp=any
>
','
it=any
>
')'
>
[extra_trailers=trailer*]
>
|
power<
'map' args=trailer< '(' [any] ')' >
[extra_trailers=trailer*]
>
"""
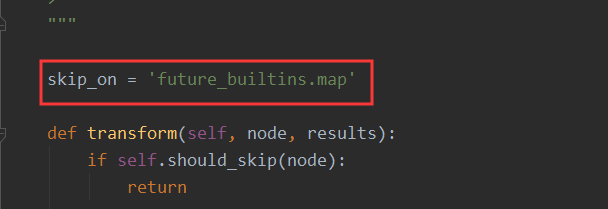
skip_on = 'future_builtins.map'
def transform(self, node, results):
if self.should_skip(node):
return
trailers = []
if 'extra_trailers' in results:
for t in results['extra_trailers']:
trailers.append(t.clone())
if node.parent.type == syms.simple_stmt:
self.warning(node, "You should use a for loop here")
new = node.clone()
new.prefix = ""
new = Call(Name("list"), [new])
elif "map_lambda" in results:
new = ListComp(results["xp"].clone(),
results["fp"].clone(),
results["it"].clone())
new = Node(syms.power, [new] + trailers, prefix="")
else:
if "map_none" in results:
new = results["arg"].clone()
new.prefix = ""
else:
if "args" in results:
args = results["args"]
if args.type == syms.trailer and \
args.children[1].type == syms.arglist and \
args.children[1].children[0].type == token.NAME and \
args.children[1].children[0].value == "None":
self.warning(node, "cannot convert map(None, ...) "
"with multiple arguments because map() "
"now truncates to the shortest sequence")
return
new = Node(syms.power, [Name("map"), args.clone()])
new.prefix = ""
if in_special_context(node):
return None
new = Node(syms.power, [Name("list"), ArgList([new])] + trailers)
new.prefix = ""
new.prefix = node.prefix
return new
重点在这
什么是fix呀?
# Copyright 2006 Google, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
# Licensed to PSF under a Contributor Agreement.
"""Base class for fixers (optional, but recommended)."""
# Python imports
import itertools
# Local imports
from .patcomp import PatternCompiler
from . import pygram
from .fixer_util import does_tree_import
class BaseFix(object):
"""Optional base class for fixers.
The subclass name must be FixFooBar where FooBar is the result of
removing underscores and capitalizing the words of the fix name.
For example, the class name for a fixer named 'has_key' should be
FixHasKey.
"""
PATTERN = None # Most subclasses should override with a string literal
pattern = None # Compiled pattern, set by compile_pattern()
pattern_tree = None # Tree representation of the pattern
options = None # Options object passed to initializer
filename = None # The filename (set by set_filename)
numbers = itertools.count(1) # For new_name()
used_names = set() # A set of all used NAMEs
order = "post" # Does the fixer prefer pre- or post-order traversal
explicit = False # Is this ignored by refactor.py -f all?
run_order = 5 # Fixers will be sorted by run order before execution
# Lower numbers will be run first.
_accept_type = None # [Advanced and not public] This tells RefactoringTool
# which node type to accept when there's not a pattern.
keep_line_order = False # For the bottom matcher: match with the
# original line order
BM_compatible = False # Compatibility with the bottom matching
# module; every fixer should set this
# manually
# Shortcut for access to Python grammar symbols
syms = pygram.python_symbols
def __init__(self, options, log):
"""Initializer. Subclass may override.
Args:
options: a dict containing the options passed to RefactoringTool
that could be used to customize the fixer through the command line.
log: a list to append warnings and other messages to.
"""
self.options = options
self.log = log
self.compile_pattern()
def compile_pattern(self):
"""Compiles self.PATTERN into self.pattern.
Subclass may override if it doesn't want to use
self.{pattern,PATTERN} in .match().
"""
if self.PATTERN is not None:
PC = PatternCompiler()
self.pattern, self.pattern_tree = PC.compile_pattern(self.PATTERN,
with_tree=True)
def set_filename(self, filename):
"""Set the filename.
The main refactoring tool should call this.
"""
self.filename = filename
def match(self, node):
"""Returns match for a given parse tree node.
Should return a true or false object (not necessarily a bool).
It may return a non-empty dict of matching sub-nodes as
returned by a matching pattern.
Subclass may override.
"""
results = {"node": node}
return self.pattern.match(node, results) and results
def transform(self, node, results):
"""Returns the transformation for a given parse tree node.
Args:
node: the root of the parse tree that matched the fixer.
results: a dict mapping symbolic names to part of the match.
Returns:
None, or a node that is a modified copy of the
argument node. The node argument may also be modified in-place to
effect the same change.
Subclass *must* override.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def new_name(self, template="xxx_todo_changeme"):
"""Return a string suitable for use as an identifier
The new name is guaranteed not to conflict with other identifiers.
"""
name = template
while name in self.used_names:
name = template + str(next(self.numbers))
self.used_names.add(name)
return name
def log_message(self, message):
if self.first_log:
self.first_log = False
self.log.append("### In file %s ###" % self.filename)
self.log.append(message)
def cannot_convert(self, node, reason=None):
"""Warn the user that a given chunk of code is not valid Python 3,
but that it cannot be converted automatically.
First argument is the top-level node for the code in question.
Optional second argument is why it can't be converted.
"""
lineno = node.get_lineno()
for_output = node.clone()
for_output.prefix = ""
msg = "Line %d: could not convert: %s"
self.log_message(msg % (lineno, for_output))
if reason:
self.log_message(reason)
def warning(self, node, reason):
"""Used for warning the user about possible uncertainty in the
translation.
First argument is the top-level node for the code in question.
Optional second argument is why it can't be converted.
"""
lineno = node.get_lineno()
self.log_message("Line %d: %s" % (lineno, reason))
def start_tree(self, tree, filename):
"""Some fixers need to maintain tree-wide state.
This method is called once, at the start of tree fix-up.
tree - the root node of the tree to be processed.
filename - the name of the file the tree came from.
"""
self.used_names = tree.used_names
self.set_filename(filename)
self.numbers = itertools.count(1)
self.first_log = True
def finish_tree(self, tree, filename):
"""Some fixers need to maintain tree-wide state.
This method is called once, at the conclusion of tree fix-up.
tree - the root node of the tree to be processed.
filename - the name of the file the tree came from.
"""
pass
class ConditionalFix(BaseFix):
""" Base class for fixers which not execute if an import is found. """
# This is the name of the import which, if found, will cause the test to be skipped
skip_on = None
def start_tree(self, *args):
super(ConditionalFix, self).start_tree(*args)
self._should_skip = None
def should_skip(self, node):
if self._should_skip is not None:
return self._should_skip
pkg = self.skip_on.split(".")
name = pkg[-1]
pkg = ".".join(pkg[:-1])
self._should_skip = does_tree_import(pkg, name, node)
return self._should_skip
作者:罗阿红
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/luoahong/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。


