趣谈Linux操作系统学习笔记:第二十八讲
一、引子
磁盘→盘片→磁道→扇区(每个 512 字节)
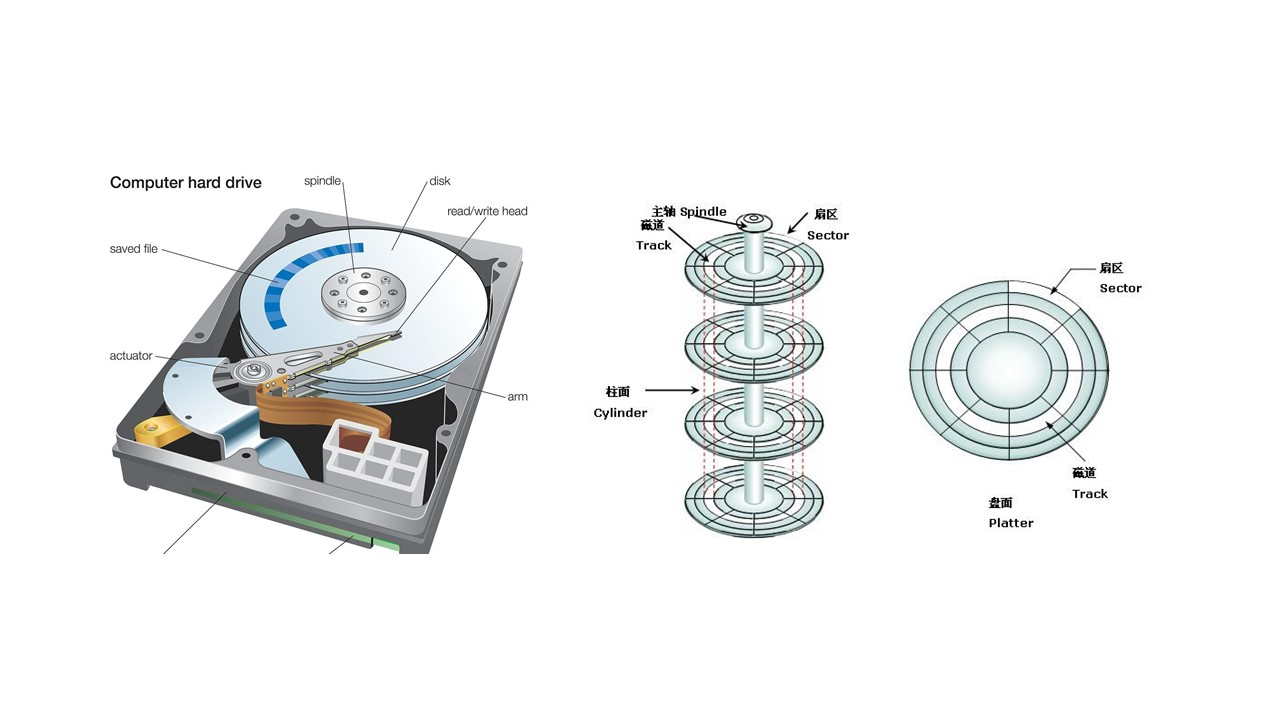
ext* 定义文件系统的格式
二、inode 与块的存储
1、块

2、不用给他分配一块连续的空间
我们可以分散成一个个小块进行存放
1、优点

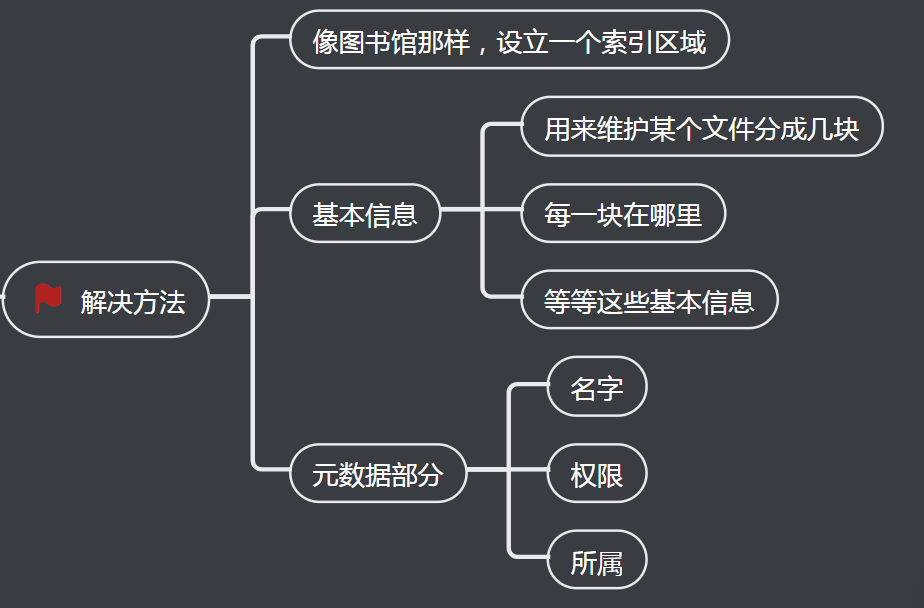
2、存在的问题

3、如何解决
3、inode里面有哪些信息?
至于 inode 里面有哪些信息,其实我们在内核中就有定义。你可以看下面这个数据结构。
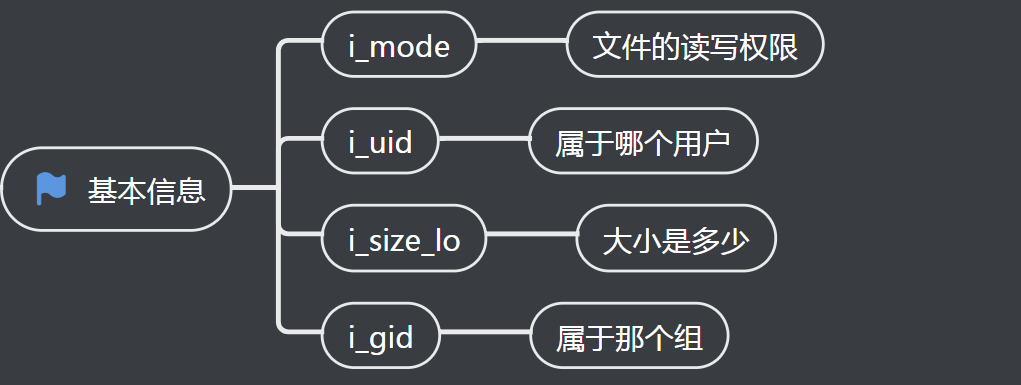
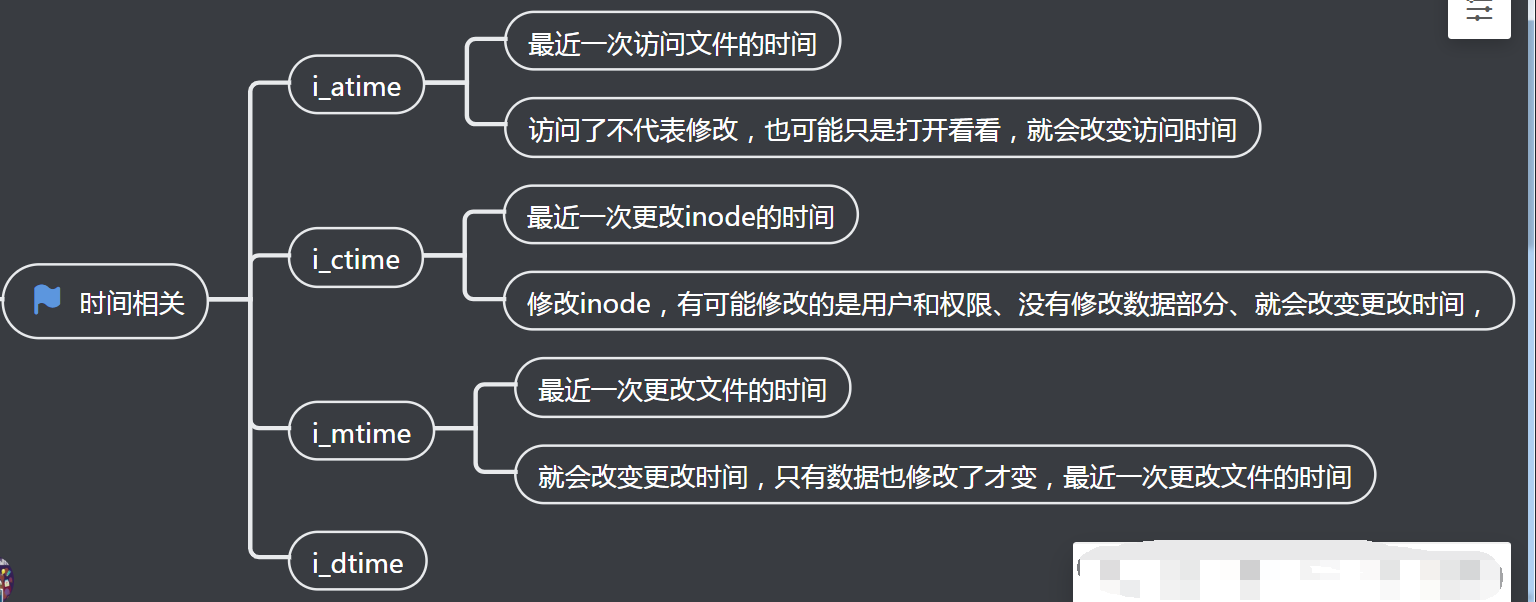
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | struct ext4_inode { __le16 i_mode; /* File mode */ __le16 i_uid; /* Low 16 bits of Owner Uid */ __le32 i_size_lo; /* Size in bytes */ __le32 i_atime; /* Access time */ __le32 i_ctime; /* Inode Change time */ __le32 i_mtime; /* Modification time */ __le32 i_dtime; /* Deletion Time */ __le16 i_gid; /* Low 16 bits of Group Id */ __le16 i_links_count; /* Links count */ __le32 i_blocks_lo; /* Blocks count */ __le32 i_flags; /* File flags */...... __le32 i_block[EXT4_N_BLOCKS];/* Pointers to blocks */ __le32 i_generation; /* File version (for NFS) */ __le32 i_file_acl_lo; /* File ACL */ __le32 i_size_high;......}; |
1、什么是inode?

2、基本信息
3、时间相关信息

4、i_blocks_lo

5、i_block
4、这些在 inode 里面,应该保存在 i_block 里面。
具体如何保存的呢?EXT4_N_BLOCKS 有如下的定义,
1 2 3 4 5 | #define EXT4_NDIR_BLOCKS 12#define EXT4_IND_BLOCK EXT4_NDIR_BLOCKS#define EXT4_DIND_BLOCK (EXT4_IND_BLOCK + 1)#define EXT4_TIND_BLOCK (EXT4_DIND_BLOCK + 1)#define EXT4_N_BLOCKS (EXT4_TIND_BLOCK + 1 |
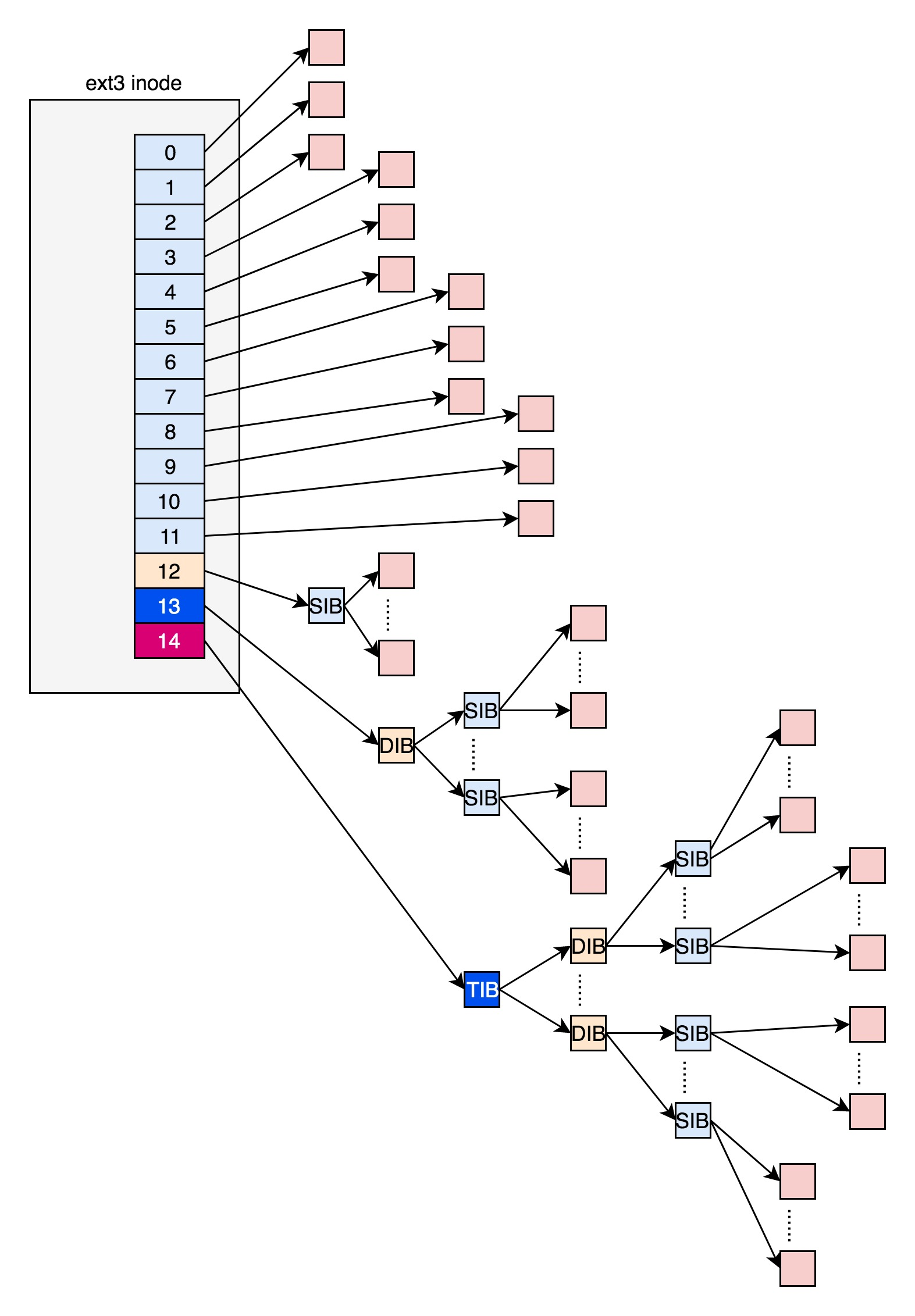
1、如何保存?
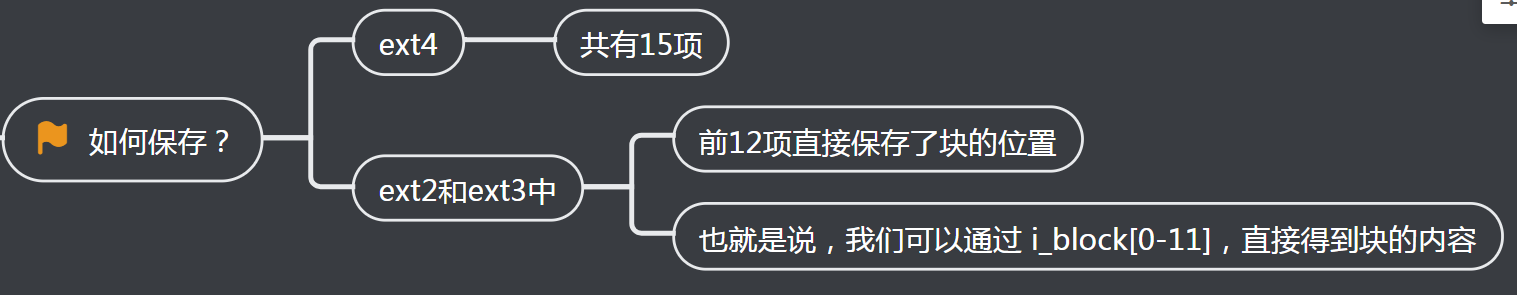
2、文件比较大12块放不下?
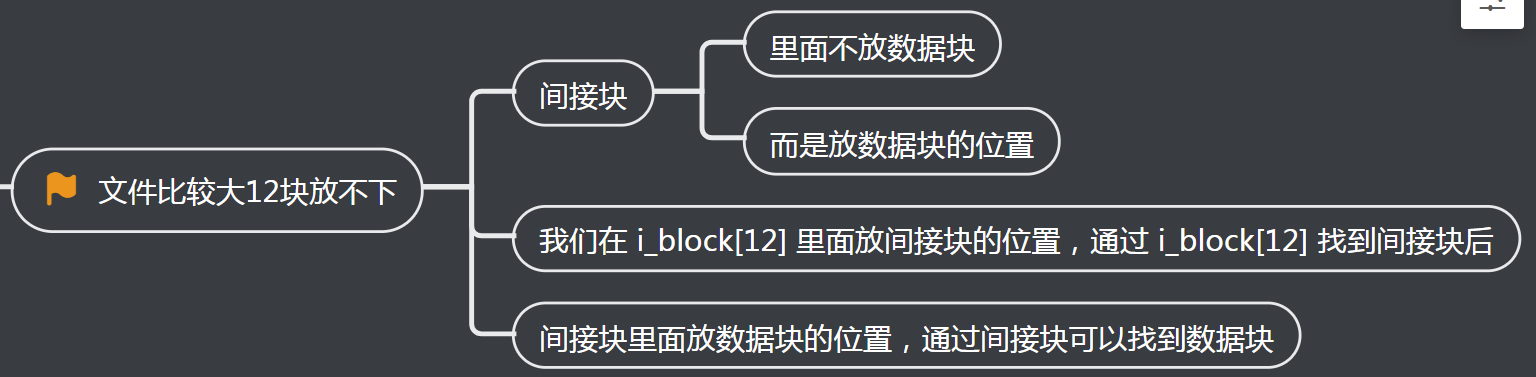
3、文件再大些

4、文件更大一些

5、存在问题

三、Extents
ext4 引入 Extents 概念, 可以用于存放连续的数据块
优点:对于大文件的读写性能提高了,文件碎片也减少了
1、Extents是如何存储?

ext4_extent_header
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | struct ext4_extent_header { __le16 eh_magic; /* probably will support different formats */ __le16 eh_entries; /* number of valid entries */ __le16 eh_max; /* capacity of store in entries */ __le16 eh_depth; /* has tree real underlying blocks? */ __le32 eh_generation; /* generation of the tree */}; |

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | /* * This is the extent on-disk structure. * It's used at the bottom of the tree. */struct ext4_extent { __le32 ee_block; /* first logical block extent covers */ __le16 ee_len; /* number of blocks covered by extent */ __le16 ee_start_hi; /* high 16 bits of physical block */ __le32 ee_start_lo; /* low 32 bits of physical block */};/* * This is index on-disk structure. * It's used at all the levels except the bottom. */struct ext4_extent_idx { __le32 ei_block; /* index covers logical blocks from 'block' */ __le32 ei_leaf_lo; /* pointer to the physical block of the next * * level. leaf or next index could be there */ __le16 ei_leaf_hi; /* high 16 bits of physical block */ __u16 ei_unused;}; |
三、inode 位图和块位图
要保存数据是, 应放在哪? 全扫一遍效率低
1、位图

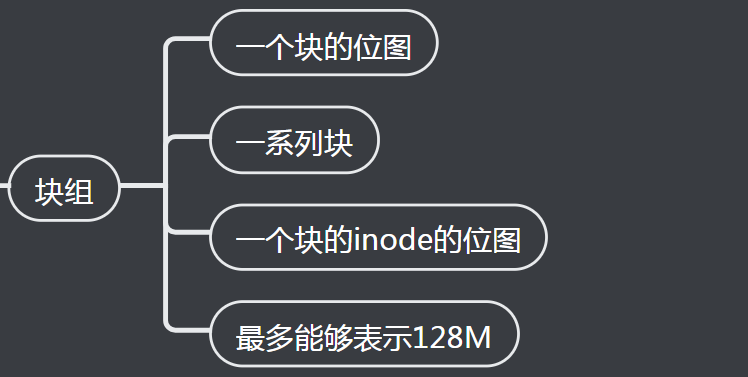
2、块组
上海虹桥火车站的厕位智能引导系统,不知道你有没有见过?这个系统很厉害,我们要想知道哪个位置有没有被占用,不用挨个拉门,从这样一个电子版上就能看到了

do_sys_open
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | SYSCALL_DEFINE3(open, const char __user *, filename, int, flags, umode_t, mode){ if (force_o_largefile()) flags |= O_LARGEFILE; return do_sys_open(AT_FDCWD, filename, flags, mode);} |
inode 操作的调用链

1、要打开一个文件,先要根据路径找到文件夹、如果发现文件夹下面没有这个文件,同时又设置了 O_CREAT
2、就说明我们要在这个文件夹下面创建一个文件,那我们就需要一个新inode
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | static int lookup_open(struct nameidata *nd, struct path *path, struct file *file, const struct open_flags *op, bool got_write, int *opened){...... if (!dentry->d_inode && (open_flag & O_CREAT)) {...... error = dir_inode->i_op->create(dir_inode, dentry, mode, open_flag & O_EXCL);...... }......} |
想要创建新的 inode,我们就要调用 dir_inode,
也就是文件夹的 inode 的 create 函数。它的具体定义是这样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | const struct inode_operations ext4_dir_inode_operations = { .create = ext4_create, .lookup = ext4_lookup, .link = ext4_link, .unlink = ext4_unlink, .symlink = ext4_symlink, .mkdir = ext4_mkdir, .rmdir = ext4_rmdir, .mknod = ext4_mknod, .tmpfile = ext4_tmpfile, .rename = ext4_rename2, .setattr = ext4_setattr, .getattr = ext4_getattr, .listxattr = ext4_listxattr, .get_acl = ext4_get_acl, .set_acl = ext4_set_acl, .fiemap = ext4_fiemap,}; |
接下来的调用链是这样

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | struct inode *__ext4_new_inode(handle_t *handle, struct inode *dir, umode_t mode, const struct qstr *qstr, __u32 goal, uid_t *owner, __u32 i_flags, int handle_type, unsigned int line_no, int nblocks){......inode_bitmap_bh = ext4_read_inode_bitmap(sb, group);......ino = ext4_find_next_zero_bit((unsigned long *) inode_bitmap_bh->b_data, EXT4_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb), ino);......} |
四、文件系统的格式
一个位图只能表示 2^15 个数据块, 即 128MB
1、块组
超级块 ext4_super_block

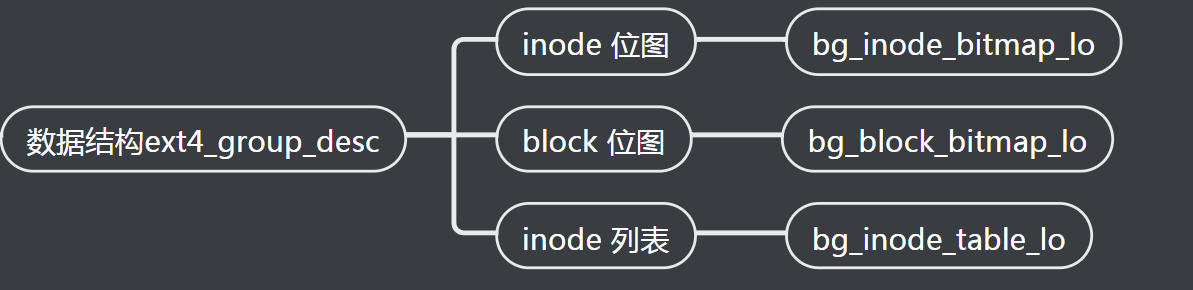
一个 inode 位图 + 一个 block 位图, 称为块组, 用数据结构 ext4_group_desc 表示, 里面包含 inode 位图, block 位图和 inode 列表

这些块组描述符构成列表, 另外用超级块 ext4_super_block 描述整个文件系统; 第一个块组前 1k 用于启动引导

文件系统的组成

文件系统由引导块 + N 个块组组成; 每个块组由: 超级块 + 块组描述符表 + 块位图 + inode 位图 + inode 列表 + 数据块构成
超级块和块组描述符表都是全局信息; 默认超级块和块组描述符表再灭个租客都有备份; 若开启 sparse_super, 则只在固定块组中备份
采用 Meta Block Groups 特性, 避免块组表浪费空间, 或限制文件系统的大小

- 将块组分成多个组(元块组) 块组描述符表只保存当前元块组中块组的信息, 并在元块组内备份
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | struct ext4_super_block {...... __le32 s_blocks_count_lo; /* Blocks count */ __le32 s_r_blocks_count_lo; /* Reserved blocks count */ __le32 s_free_blocks_count_lo; /* Free blocks count */...... __le32 s_blocks_count_hi; /* Blocks count */ __le32 s_r_blocks_count_hi; /* Reserved blocks count */ __le32 s_free_blocks_count_hi; /* Free blocks count */......} |
五、目录的存储格式
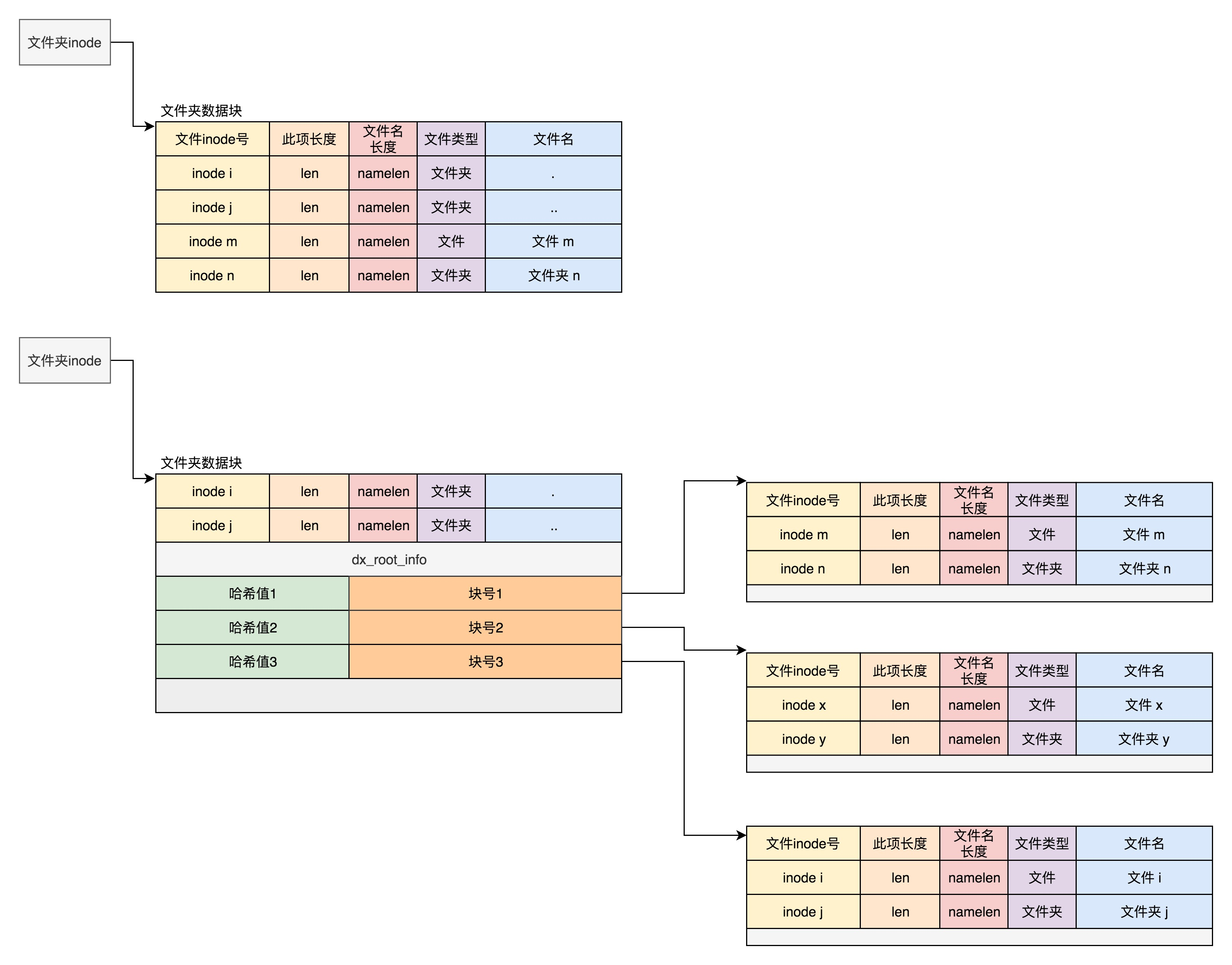
目录也是文件, 也有 inode, inode 指向一个块, 块中保存各个文件信息, ext4_dir_entry 包括文件名和 inode, 默认按列表存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | struct ext4_dir_entry { __le32 inode; /* Inode number */ __le16 rec_len; /* Directory entry length */ __le16 name_len; /* Name length */ char name[EXT4_NAME_LEN]; /* File name */};struct ext4_dir_entry_2 { __le32 inode; /* Inode number */ __le16 rec_len; /* Directory entry length */ __u8 name_len; /* Name length */ __u8 file_type; char name[EXT4_NAME_LEN]; /* File name */}; |
第一项 "." 当前目录; 第二项 ".." 上一级目录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | struct dx_root{ struct fake_dirent dot; char dot_name[4]; struct fake_dirent dotdot; char dotdot_name[4]; struct dx_root_info { __le32 reserved_zero; u8 hash_version; u8 info_length; /* 8 */ u8 indirect_levels; u8 unused_flags; } info; struct dx_entry entries[0];}; |
可添加索引, 加快文件查找
1 2 3 4 5 | struct dx_entry{ __le32 hash; __le32 block;}; |
需要改变目录块格式, 加入索引树: 用索引项 dx_entry 保存文件名哈希和块的映射, 若该块不是索引, 则里面保存 ext4_dir_enry 列表, 逐项查找
六、软链接和硬链接的存储格式
1、链接即文件的别名: ln -s 创建软链接; ln 创建硬链接
2、硬链接与原始文件共用一个 inode, 但不能跨文件系统
3、软链接是一个文件, 有自己的 inode, 该文件内容指向另一个文件, 可跨文件系统
七、总结时刻
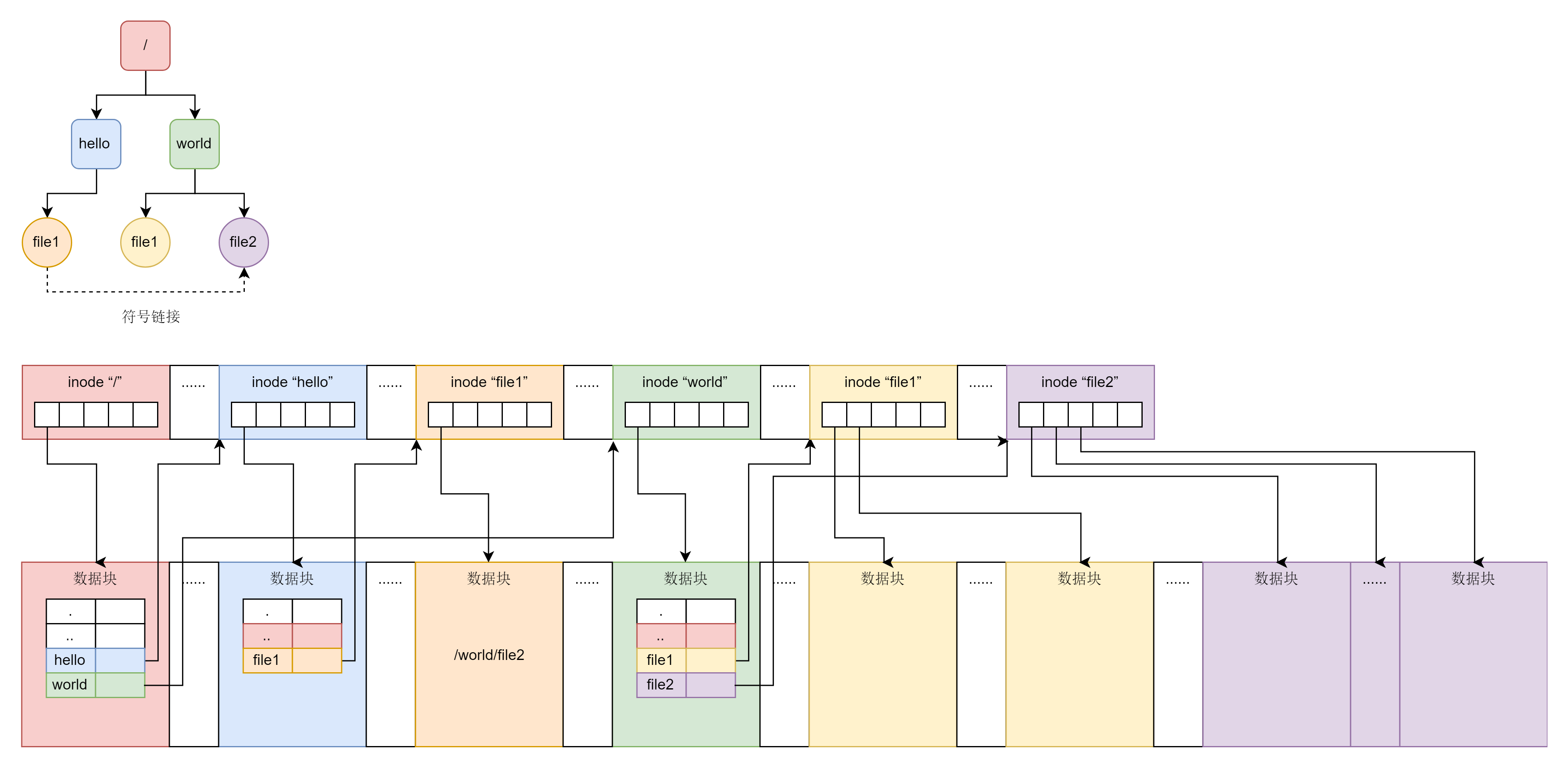
这一节,我们描述了复杂的应哦按上的文件系统,但是对于咱们平时的应用来讲,用的最多的是两个概念,一个是inode、一个是数据块
为了表示图中上半部分的那个简单的树形结构,在文件系统上的布局就像图的下半部分一样,无论是文件夹还是文件,都有一个inode,inode里面的会指向数据块,对于文件夹的数据块,里面是一个表,是下一层的文件和inode的对应关系,文件的数据块里面存放的是真正的数据



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构