深入浅出计算机组成原理学习笔记:第八讲
一、为什么会Permission denied
1、测试用例
不知道你注意到没,在过去的几节,我们通过gcc生成的文件和objdump获取到的汇编指令都有些小小的问题,我们先把前面的函数示例,拆分成两个文件add_lib.c 和 link_example.c。
1、创建示例文件
1、add_lib.c
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@luoahong c]# cat add_lib.cint add(int a, int b){ return a+b;} |
2、link_example.c
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | [root@luoahong c]# cat link_example.c#include <stdio.h>int main(){ int a = 10; int b = 5; int c = add(a, b); printf("c = %d\n", c);} |
2、我们通过 gcc 来编译这两个文件,然后通过objdump 命令看看它们的汇编代码。
1 | [root@luoahong c]# gcc -g -c add_lib.c link_example.c |
3、通过 objdump 命令看看它们的汇编代码。
objdump -d -M intel -S add_lib.o
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | [root@luoahong c]# objdump -d -M intel -S add_lib.oadd_lib.o: file format elf64-x86-64Disassembly of section .text:0000000000000000 <add>:int add(int a, int b){ 0: 55 push rbp 1: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 4: 89 7d fc mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],edi 7: 89 75 f8 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],esi return a+b; a: 8b 45 f8 mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8] d: 8b 55 fc mov edx,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4] 10: 01 d0 add eax,edx} 12: 5d pop rbp 13: c3 ret |
objdump -d -M intel -S link_example.o
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | [root@luoahong c]# objdump -d -M intel -S link_example.olink_example.o: file format elf64-x86-64Disassembly of section .text:0000000000000000 <main>:#include <stdio.h>int main(){ 0: 55 push rbp 1: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 4: 48 83 ec 10 sub rsp,0x10 int a = 10; 8: c7 45 fc 0a 00 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],0xa int b = 5; f: c7 45 f8 05 00 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],0x5 int c = add(a, b); 16: 8b 55 f8 mov edx,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8] 19: 8b 45 fc mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4] 1c: 89 d6 mov esi,edx 1e: 89 c7 mov edi,eax 20: b8 00 00 00 00 mov eax,0x0 25: e8 00 00 00 00 call 2a <main+0x2a> 2a: 89 45 f4 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0xc],eax printf("c = %d\n", c); 2d: 8b 45 f4 mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0xc] 30: 89 c6 mov esi,eax 32: bf 00 00 00 00 mov edi,0x0 37: b8 00 00 00 00 mov eax,0x0 3c: e8 00 00 00 00 call 41 <main+0x41>} 41: c9 leave 42: c3 ret |
2、文件没有执行权限
1 2 | [root@luoahong c]# ./link_example.o-bash: ./link_example.o: Permission denied |

3、通过chmod命令赋予文件可执行的权限,故障依旧
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@luoahong c]# chmod +x link_example.o[root@luoahong c]# ll link_example.o-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3408 May 16 17:06 link_example.o[root@luoahong c]# ./link_example.o-bash: ./link_example.o: cannot execute binary file |

我们再仔细看一下 objdump 出来的两个文件的代码,会发现两个程序的地址都是从 0 开始的。如果地址是一样的,程序如果需要通过 call 指令调用函数的话,它怎么知道应该跳转到哪一个文件里呢?
这么说吧,无论是这里的运行报错,还是 objdump 出来的汇编代码里面的重复地址,都是因为add_lib.o 以及 link_example.o 并不一个可执行文件(Executable Program),而是目标文
件(Object File)。只有通过链接器(Linker)把多个目标文件以及调用的各种函数库链接起来,我们才能得到一个可执行文件。
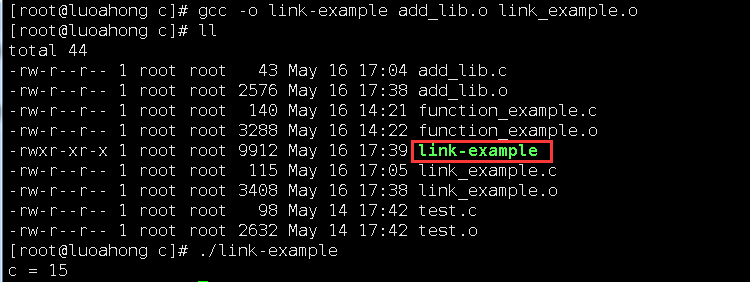
4、通过gcc的-o参数完美解决Permission denied
我们通过 gcc 的 -o 参数,可以生成对应的可执行文件,对应执行之后,就可以得到这个简单的加法调用函数的结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | [root@luoahong c]# gcc -o link-example add_lib.o link_example.o[root@luoahong c]# lltotal 44-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 43 May 16 17:04 add_lib.c-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2576 May 16 17:38 add_lib.o-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 140 May 16 14:21 function_example.c-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3288 May 16 14:22 function_example.o-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 9912 May 16 17:39 link-example-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 115 May 16 17:05 link_example.c-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3408 May 16 17:38 link_example.o-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 98 May 14 17:42 test.c-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2632 May 14 17:42 test.o[root@luoahong c]# ./link-examplec = 15 |
二、C 语言程序是如何变成一个可执行程序的。
实际上,“C 语言代码 - 汇编代码 - 机器码” 这个过,在我们的计算机上进行的时候是由两部分组成的。
第一个部分由编译(Compile)、汇编(Assemble)以及链接(Link)三个阶段组成。在这三个阶段完成之后,我们就生成了一个可执行文件。
第二部分,我们通过装载器(Loader)把可执行文件装载(Load)到内存中。CPU 从内存中读取指令和数据,来开始真正执行程序。

三、ELF 格式和链接:理解链接过程
1、用objdump查看执行文件内容
程序最终是通过装载器变成指令和数据的,所以其实我们生成的可执行代码也并不仅仅是一条条的指令。我们还是通过objdump指令,把可执行文件内容拿出来看看
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 | [root@luoahong c]# objdump -d -M intel -S link-examplelink-example: file format elf64-x86-64Disassembly of section .init:00000000004003c8 <_init>: 4003c8: 48 83 ec 08 sub rsp,0x8 4003cc: 48 8b 05 25 0c 20 00 mov rax,QWORD PTR [rip+0x200c25] # 600ff8 <__gmon_start__> 4003d3: 48 85 c0 test rax,rax 4003d6: 74 05 je 4003dd <_init+0x15> 4003d8: e8 43 00 00 00 call 400420 <.plt.got> 4003dd: 48 83 c4 08 add rsp,0x8 4003e1: c3 retDisassembly of section .plt:00000000004003f0 <.plt>: 4003f0: ff 35 12 0c 20 00 push QWORD PTR [rip+0x200c12] # 601008 <_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+0x8> 4003f6: ff 25 14 0c 20 00 jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x200c14] # 601010 <_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+0x10> 4003fc: 0f 1f 40 00 nop DWORD PTR [rax+0x0]0000000000400400 <printf@plt>: 400400: ff 25 12 0c 20 00 jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x200c12] # 601018 <printf@GLIBC_2.2.5> 400406: 68 00 00 00 00 push 0x0 40040b: e9 e0 ff ff ff jmp 4003f0 <.plt>0000000000400410 <__libc_start_main@plt>: 400410: ff 25 0a 0c 20 00 jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x200c0a] # 601020 <__libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.2.5> 400416: 68 01 00 00 00 push 0x1 40041b: e9 d0 ff ff ff jmp 4003f0 <.plt>Disassembly of section .plt.got:0000000000400420 <.plt.got>: 400420: ff 25 d2 0b 20 00 jmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x200bd2] # 600ff8 <__gmon_start__> 400426: 66 90 xchg ax,axDisassembly of section .text:0000000000400430 <_start>: 400430: 31 ed xor ebp,ebp 400432: 49 89 d1 mov r9,rdx 400435: 5e pop rsi 400436: 48 89 e2 mov rdx,rsp 400439: 48 83 e4 f0 and rsp,0xfffffffffffffff0 40043d: 50 push rax 40043e: 54 push rsp 40043f: 49 c7 c0 f0 05 40 00 mov r8,0x4005f0 400446: 48 c7 c1 80 05 40 00 mov rcx,0x400580 40044d: 48 c7 c7 31 05 40 00 mov rdi,0x400531 400454: e8 b7 ff ff ff call 400410 <__libc_start_main@plt> 400459: f4 hlt 40045a: 66 0f 1f 44 00 00 nop WORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0]0000000000400460 <deregister_tm_clones>: 400460: b8 37 10 60 00 mov eax,0x601037 400465: 55 push rbp 400466: 48 2d 30 10 60 00 sub rax,0x601030 40046c: 48 83 f8 0e cmp rax,0xe 400470: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 400473: 77 02 ja 400477 <deregister_tm_clones+0x17> 400475: 5d pop rbp 400476: c3 ret 400477: b8 00 00 00 00 mov eax,0x0 40047c: 48 85 c0 test rax,rax 40047f: 74 f4 je 400475 <deregister_tm_clones+0x15> 400481: 5d pop rbp 400482: bf 30 10 60 00 mov edi,0x601030 400487: ff e0 jmp rax 400489: 0f 1f 80 00 00 00 00 nop DWORD PTR [rax+0x0]0000000000400490 <register_tm_clones>: 400490: b8 30 10 60 00 mov eax,0x601030 400495: 55 push rbp 400496: 48 2d 30 10 60 00 sub rax,0x601030 40049c: 48 c1 f8 03 sar rax,0x3 4004a0: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 4004a3: 48 89 c2 mov rdx,rax 4004a6: 48 c1 ea 3f shr rdx,0x3f 4004aa: 48 01 d0 add rax,rdx 4004ad: 48 d1 f8 sar rax,1 4004b0: 75 02 jne 4004b4 <register_tm_clones+0x24> 4004b2: 5d pop rbp 4004b3: c3 ret 4004b4: ba 00 00 00 00 mov edx,0x0 4004b9: 48 85 d2 test rdx,rdx 4004bc: 74 f4 je 4004b2 <register_tm_clones+0x22> 4004be: 5d pop rbp 4004bf: 48 89 c6 mov rsi,rax 4004c2: bf 30 10 60 00 mov edi,0x601030 4004c7: ff e2 jmp rdx 4004c9: 0f 1f 80 00 00 00 00 nop DWORD PTR [rax+0x0]00000000004004d0 <__do_global_dtors_aux>: 4004d0: 80 3d 55 0b 20 00 00 cmp BYTE PTR [rip+0x200b55],0x0 # 60102c <_edata> 4004d7: 75 11 jne 4004ea <__do_global_dtors_aux+0x1a> 4004d9: 55 push rbp 4004da: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 4004dd: e8 7e ff ff ff call 400460 <deregister_tm_clones> 4004e2: 5d pop rbp 4004e3: c6 05 42 0b 20 00 01 mov BYTE PTR [rip+0x200b42],0x1 # 60102c <_edata> 4004ea: f3 c3 repz ret 4004ec: 0f 1f 40 00 nop DWORD PTR [rax+0x0]00000000004004f0 <frame_dummy>: 4004f0: 48 83 3d 28 09 20 00 cmp QWORD PTR [rip+0x200928],0x0 # 600e20 <__JCR_END__> 4004f7: 00 4004f8: 74 1e je 400518 <frame_dummy+0x28> 4004fa: b8 00 00 00 00 mov eax,0x0 4004ff: 48 85 c0 test rax,rax 400502: 74 14 je 400518 <frame_dummy+0x28> 400504: 55 push rbp 400505: bf 20 0e 60 00 mov edi,0x600e20 40050a: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 40050d: ff d0 call rax 40050f: 5d pop rbp 400510: e9 7b ff ff ff jmp 400490 <register_tm_clones> 400515: 0f 1f 00 nop DWORD PTR [rax] 400518: e9 73 ff ff ff jmp 400490 <register_tm_clones>000000000040051d <add>:int add(int a, int b){ 40051d: 55 push rbp 40051e: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 400521: 89 7d fc mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],edi 400524: 89 75 f8 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],esi return a+b; 400527: 8b 45 f8 mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8] 40052a: 8b 55 fc mov edx,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4] 40052d: 01 d0 add eax,edx} 40052f: 5d pop rbp 400530: c3 ret0000000000400531 <main>:#include <stdio.h>int main(){ 400531: 55 push rbp 400532: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 400535: 48 83 ec 10 sub rsp,0x10 int a = 10; 400539: c7 45 fc 0a 00 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],0xa int b = 5; 400540: c7 45 f8 05 00 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],0x5 int c = add(a, b); 400547: 8b 55 f8 mov edx,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8] 40054a: 8b 45 fc mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4] 40054d: 89 d6 mov esi,edx 40054f: 89 c7 mov edi,eax 400551: b8 00 00 00 00 mov eax,0x0 400556: e8 c2 ff ff ff call 40051d <add> 40055b: 89 45 f4 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0xc],eax printf("c = %d\n", c); 40055e: 8b 45 f4 mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0xc] 400561: 89 c6 mov esi,eax 400563: bf 10 06 40 00 mov edi,0x400610 400568: b8 00 00 00 00 mov eax,0x0 40056d: e8 8e fe ff ff call 400400 <printf@plt>} 400572: c9 leave 400573: c3 ret 400574: 66 2e 0f 1f 84 00 00 nop WORD PTR cs:[rax+rax*1+0x0] 40057b: 00 00 00 40057e: 66 90 xchg ax,ax0000000000400580 <__libc_csu_init>: 400580: 41 57 push r15 400582: 41 89 ff mov r15d,edi 400585: 41 56 push r14 400587: 49 89 f6 mov r14,rsi 40058a: 41 55 push r13 40058c: 49 89 d5 mov r13,rdx 40058f: 41 54 push r12 400591: 4c 8d 25 78 08 20 00 lea r12,[rip+0x200878] # 600e10 <__frame_dummy_init_array_entry> 400598: 55 push rbp 400599: 48 8d 2d 78 08 20 00 lea rbp,[rip+0x200878] # 600e18 <__init_array_end> 4005a0: 53 push rbx 4005a1: 4c 29 e5 sub rbp,r12 4005a4: 31 db xor ebx,ebx 4005a6: 48 c1 fd 03 sar rbp,0x3 4005aa: 48 83 ec 08 sub rsp,0x8 4005ae: e8 15 fe ff ff call 4003c8 <_init> 4005b3: 48 85 ed test rbp,rbp 4005b6: 74 1e je 4005d6 <__libc_csu_init+0x56> 4005b8: 0f 1f 84 00 00 00 00 nop DWORD PTR [rax+rax*1+0x0] 4005bf: 00 4005c0: 4c 89 ea mov rdx,r13 4005c3: 4c 89 f6 mov rsi,r14 4005c6: 44 89 ff mov edi,r15d 4005c9: 41 ff 14 dc call QWORD PTR [r12+rbx*8] 4005cd: 48 83 c3 01 add rbx,0x1 4005d1: 48 39 eb cmp rbx,rbp 4005d4: 75 ea jne 4005c0 <__libc_csu_init+0x40> 4005d6: 48 83 c4 08 add rsp,0x8 4005da: 5b pop rbx 4005db: 5d pop rbp 4005dc: 41 5c pop r12 4005de: 41 5d pop r13 4005e0: 41 5e pop r14 4005e2: 41 5f pop r15 4005e4: c3 ret 4005e5: 90 nop 4005e6: 66 2e 0f 1f 84 00 00 nop WORD PTR cs:[rax+rax*1+0x0] 4005ed: 00 00 0000000000004005f0 <__libc_csu_fini>: 4005f0: f3 c3 repz retDisassembly of section .fini:00000000004005f4 <_fini>: 4005f4: 48 83 ec 08 sub rsp,0x8 4005f8: 48 83 c4 08 add rsp,0x8 4005fc: c3 ret[root@luoahong c]# |
2、执行文件和目标代码的区别
1、和之前的目标代码长的差不多,但是长了很多,因为在linux下,可执行文件和目标文件所使用的都是一种叫ELF的文件格式,中文名字叫可执行与可链接文件格式,
2、这里面不仅存放了编译成汇编指令,还保留了很多别的数据
比如我们过去所有 objdump 出来的代码里,你都可以看到对应的函数名称,像 add、main 等等,乃至你自己定义的全局可以访问的变量名称,都存放在这个 ELF 格式文件里。
这些名字和它们对应的地址,在 ELF 文件里面,存储在一个叫作符号表的位置里。符号表相当于一个地址簿,把名字和地址关联了起来。
3、main 函数里调用add 的跳转地址,不再是下一条指令的地址了,而是 add 函数的入口地址了
我们先只关注和我们的 add 以及 main 函数相关的部分。你会发现,这里面,main 函数里调用add 的跳转地址,不再是下一条指令的地址了,
而是 add 函数的入口地址了,这就是 EFL 格式和链接器的功劳。
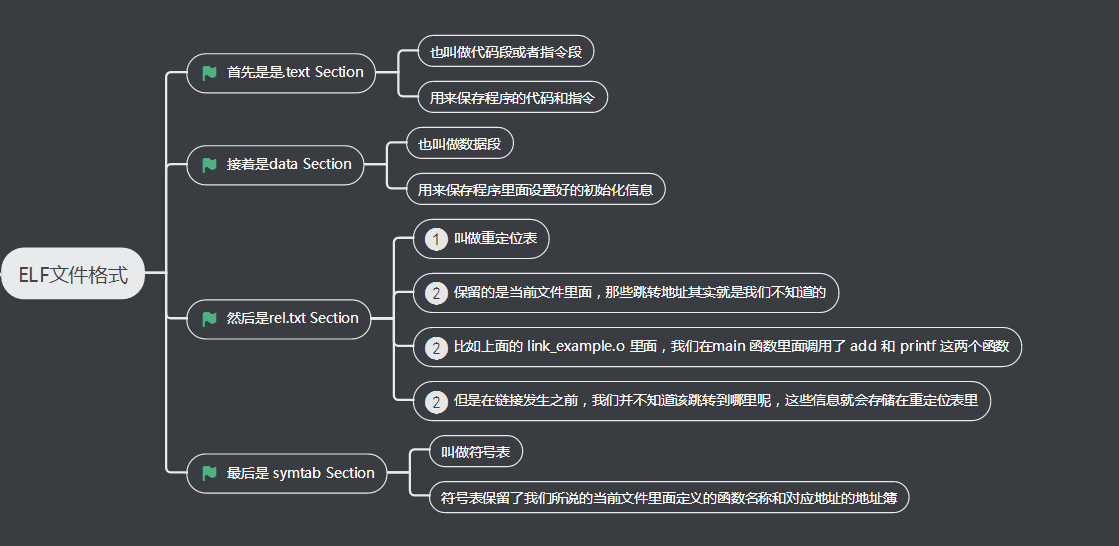
四、EFL文件格式

ELF 文件格式把各种信息,分成一个一个的 Section 保存起来。ELF 有一个基本的文件头(File Header),用来表示这个文件的基本属性,比如是否是可执行文件,对应的CPU、操作系统等等,除了这些基本属性之外,大部分程序还有这么一些Section:
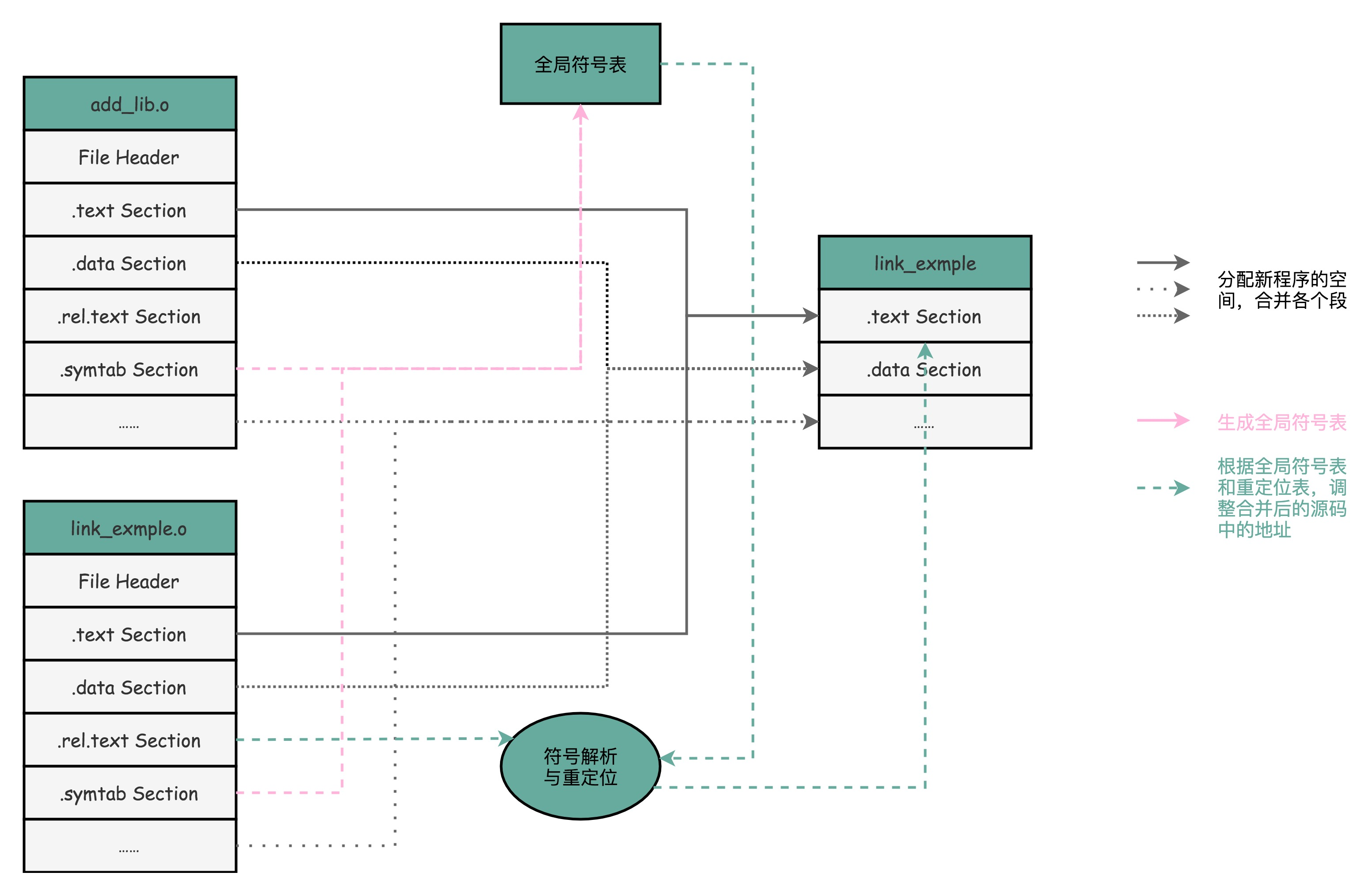
链接器会扫描所有输入的目标文件,然后把所有的符号表里的信息收集起来,构成一个全局的符号表,然后再根据重定位表把所有不确定要跳转地址的代码,
根据符号表里面的存储地址,进行一次修正,最后,把所有的目标文件的对应进行一次合并,变成了最终的可执行代码,这也是为什么,可执行文件里面的函数调用的地址都是正确的
在链接器把程序变成可执行文件之后,要装载器去执行程序就容易多了。装载器不再需要考虑地址跳转的问题,只需要解析 ELF 文件,把对应的指令和数据,加载到内存里面供 CPU 执行就可以了。
五、小结与延伸
讲到这里,相信你已经猜到,为什么同样一个程序,在Linux下可以执行而Windows下不能执行了?
1、其中一个非常重要的原因就是,两个操作系统下可执行文件的格式不一样
2、我们今天讲的事Linux下的ELF文件格式,而Windows的可执行文件格式是一种叫做PE的文件格式Linux下的装饰器只能解析ELF格式而不能解析PE格式而不能解析PE格式
3、如果我们有一个可以能够解析PE格式的装载器,我们就有可能在下Linux运行Windows里面也提供了WSL也就是Windows Subsystem for Linux,可以.解析和加载ELF格式的文件
我们去写可用的程序,也不仅仅是把所有代码放在一个文件里来编译执行,而是可以拆分成不同的函数库,最后通过一个静态链接的机制,
使得不同的文件之间既有分工有能通过静态链接来“合作“,变成了一个可执行的程序
4、对于ELF格式的文件,为了能够实现这样一个静态链接的机制,里面不只是简单罗列了程序所需要执行的指令,还会包括链接所需要的重定位表和符号表



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
2018-05-16 pycharm的一些快捷键