java 并发 线程
thinking in java
Java是一种多线程语言。线程机制是抢占式的。
线程状态转化图:
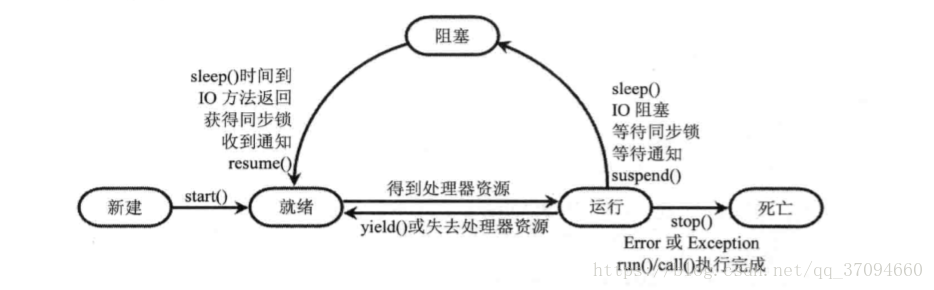
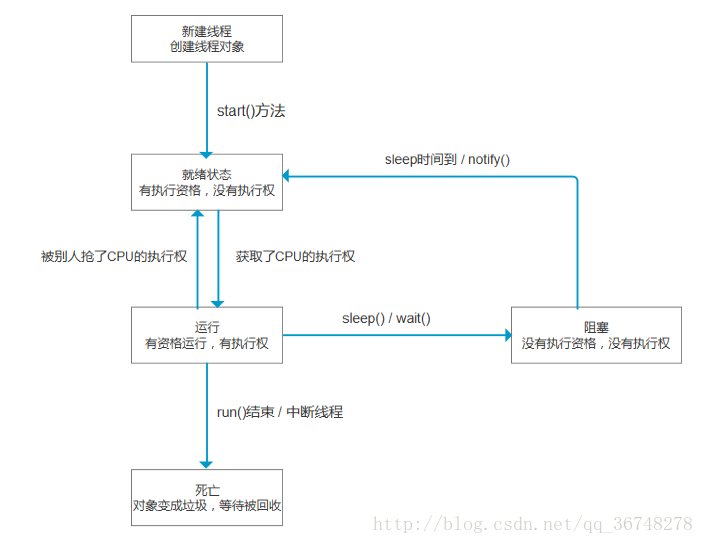
代码实现如下:
1,定义任务:
public class LiftOff implements Runnable { protected int countDown = 10; // Default private static int taskCount = 0; private final int id = taskCount++; public LiftOff() {} public LiftOff(int countDown) { this.countDown = countDown; } public String status() { return "#" + id + "(" + (countDown > 0 ? countDown : "Liftoff!") + "), "; } public void run() { while(countDown-- > 0) { System.out.print(status()); Thread.yield(); } }
public class MainThread { public static void main(String[] args) { LiftOff launch = new LiftOff(); launch.run(); }
/* Output:
#0(9), #0(8), #0(7), #0(6), #0(5), #0(4), #0(3), #0(2), #0(1), #0(Liftoff!),
*/
也可以继承Thread类,这样只能继承一个类。实现Runnable接口,还可以继承别的类。
2,提交给一个Thread构造器:
public class BasicThreads { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(new LiftOff()); t.start(); System.out.println("Waiting for LiftOff"); } }
/* Output: (90% match)
Waiting for LiftOff
#0(9), #0(8), #0(7), #0(6), #0(5), #0(4), #0(3), #0(2), #0(1), #0(Liftoff!),
*/
可以很容易的添加更多的线程去驱动更多的任务:
public class MoreBasicThreads { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) new Thread(new LiftOff()).start(); System.out.println("Waiting for LiftOff"); } }
3,使用Executor
java.util.concurrent包的Executor管理Thread对象,从而简化并发编程。方法首选。
public class CachedThreadPool { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) exec.execute(new LiftOff()); exec.shutdown(); } }
shutdown()方法防止新任务被提交给这个Executor。
Executors.newCachedThreadPool():在程序执行过程中通常会创建与所需数量相同的线程,在回收旧线程时停止创建新线程,因此是Executor的首选。
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);可以一次性预先执行代价高昂的线程分配,可以限制线程的数量。
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();就像是数量为1的newFixedThreadPool。
java core 核心技术卷I
每一个java对象都有一个锁,线程可以调用同步方法获得锁。
4、线程状态如下
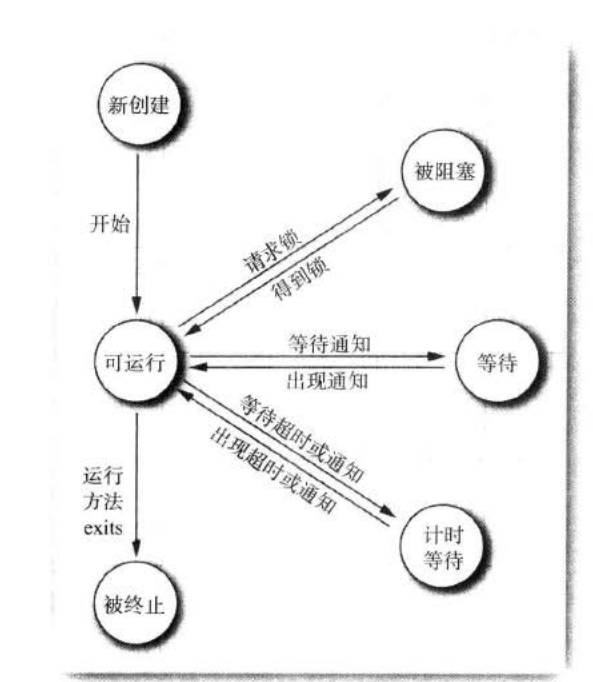
5、锁对象。有两种机制防止代码块受并发访问的干扰。一是:ReentrantLock;二是synchronized关键字。
ReentrantLock典型代码如下:
class X { private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // ... public void m() { lock.lock(); // block until condition holds try { // ... method body } finally { lock.unlock() } } }
还可以结合Conditon一起使用,来控制线程。
synchronized :
public synchronized void methodName(){
method body
}
volatile关键字为实例域的同步访问提供了一种免锁机制。
6,线程安全的集合,比如ConcurrentHashMap,ConcurrentSkipListSet



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号