java集合
一、集合框架图如下:
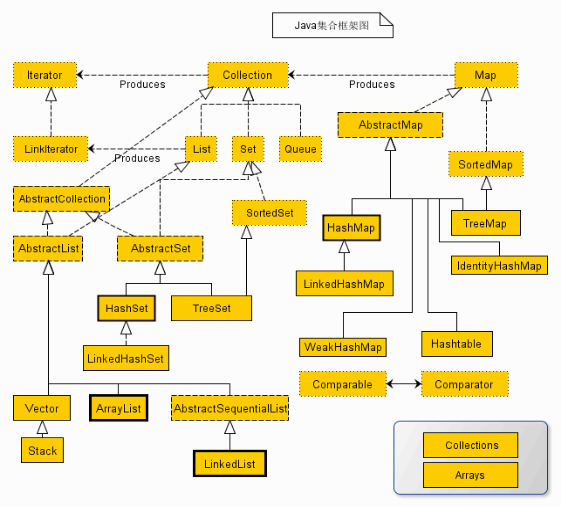
图:集合图
二、集合简单图
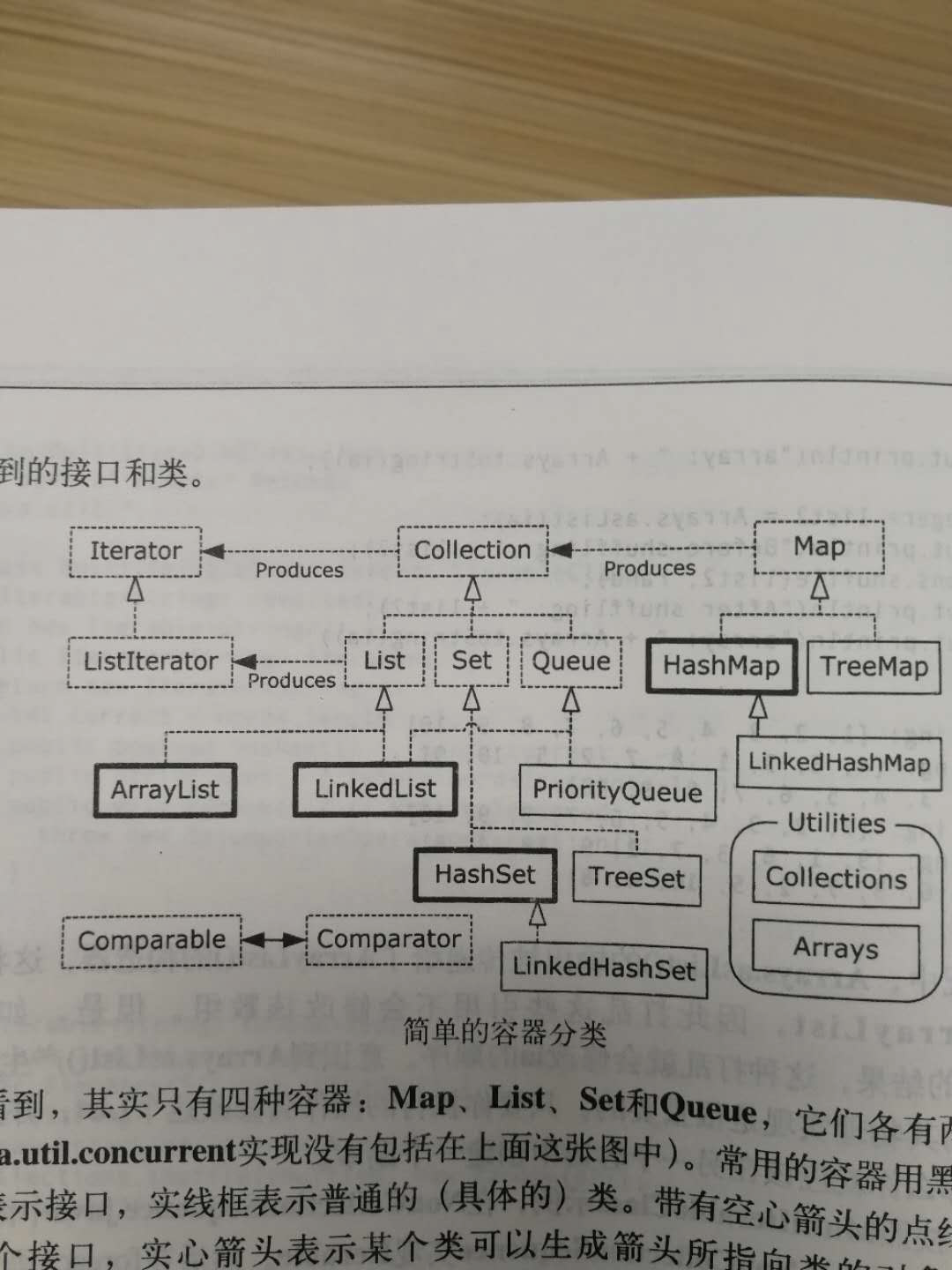
图:简单容器图。来自《thingKing in Java》
三、Java集合主要有三类:List,Map,Set,以下对用的比较多的,做下简单介绍。
1,List
如果涉及到“栈”、“队列”、“链表”等操作,应该考虑用List,具体的选择哪个List,根据下面的标准来取舍。
(01) 对于需要快速插入,删除元素,应该使用LinkedList。
(02) 对于需要快速随机访问元素,应该使用ArrayList。
(03) 对于“单线程环境” 或者 “多线程环境,但List仅仅只会被单个线程操作”,此时应该使用非同步的类(如ArrayList)。
对于“多线程环境,且List可能同时被多个线程操作”,此时,应该使用同步的类(如Vector)。
ArrayList:基于动态数组的数据结构
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
/** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }
new ArrayList的时候,会创建一个默认长度为10的数组。
public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
调用add方法的时候,会去判断数组的大小,当其长度 >=(容量 * 加载因子)时,动态扩大1.5倍。
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
LinkedList:基于链表的数据结构
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
/** * Constructs an empty list. */ public LinkedList() { }
2,map
HashMap:基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现。此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键。数组 + 链表.
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {}
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
- 构造一个具有默认初始容量 (16) 和默认加载因子 (0.75) 的空 HashMap。
如图所示
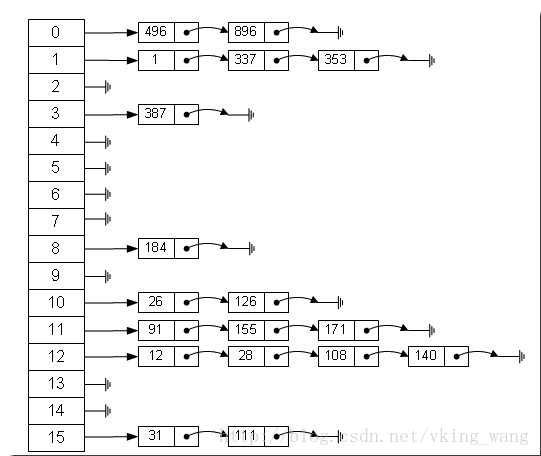
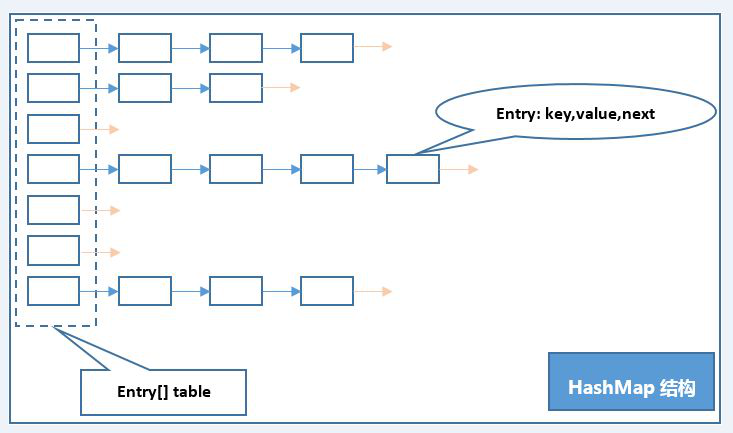
http://www.importnew.com/27043.html 其他文章的介绍。
遍历:
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("aa", "@sohu.com"); map.put("bb", "@163.com"); map.put("cc", "@sina.com"); System.out.println("普通的遍历方法,通过Map.keySet遍历key和value");// 普通使用,二次取值 for (String key : map.keySet()) { System.out.println("key= " + key + " and value= " + map.get(key)); } System.out.println("通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历key和value:"); Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = map.entrySet().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<String, String> entry = it.next(); System.out.println("key= " + entry.getKey() + " and value= " + entry.getValue()); } System.out.println("通过Map.entrySet遍历key和value"); // 推荐这种,特别是容量大的时候 for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { System.out.println("key= " + entry.getKey() + " and value= " + entry.getValue()); }
LinkedHashMap:Map 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。此实现与 HashMap 的不同之处在于,后者维护着一个运行于所有条目的双重链接列表。此链接列表定义了迭代顺序,该迭代顺序通常就是将键插入到映射中的顺序(插入顺序)。注意,如果在映射中重新插入 键,则插入顺序不受影响。可以说是HashMap和链表的结合。
可以用来做缓存:LinkedHashMap支持两种缓存策略。FIFO和LRU。大家应该也猜到控制策略的地方就是accessOrder。默认为false。就是FIFO。设置为true时就是LRU。
LinkedHashMap是有序的,按顺序插入的顺序输出。HashMap是无序的。见下面例子(accessOrder是默认false,按照插入顺序输出)
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {}
Map<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); hashMap.put("u", "5"); hashMap.put("a", "1"); hashMap.put("b", "3"); hashMap.put("x", "4"); hashMap.put("c", "2"); Map<String, String> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); linkedHashMap.put("y", "4"); linkedHashMap.put("h", "5"); linkedHashMap.put("a", "1"); linkedHashMap.put("b", "3"); linkedHashMap.put("c", "2"); System.out.println(hashMap);// {a=1, b=3, c=2, u=5, x=4} System.out.println(linkedHashMap);// {y=4, h=5, a=1, b=3, c=2}
TreeMap:基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)的 NavigableMap 实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
数据put进去之后,会自动做排序,然后按顺序输出:如下例子所示:
TreeMap tmap = new TreeMap<Integer, String>(); tmap.put(1, "1"); tmap.put(9, "9"); tmap.put(7, "7"); tmap.put(3, "3"); System.out.println("treemap: " + tmap);// treemap: {1=1, 3=3, 7=7, 9=9}
3,set 值不能重复
HashSet:无序
public class HashSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
/** * Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has * default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). */ public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); }
HashSet本质上是hashmap。
TreeSet:有序
public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
Set hs = new HashSet<>(); hs.add("ddd"); hs.add("rrr"); hs.add("ggg"); hs.add("kkk"); hs.add("ddd"); System.out.println(hs); Set ts = new TreeSet<>(); ts.add("ddd"); ts.add("rrr"); ts.add("ggg"); ts.add("kkk"); ts.add("qqq"); System.out.println(ts);
output:
[ddd, ggg, kkk, rrr]
[ddd, ggg, kkk, qqq, rrr]
几种集合效率对比:
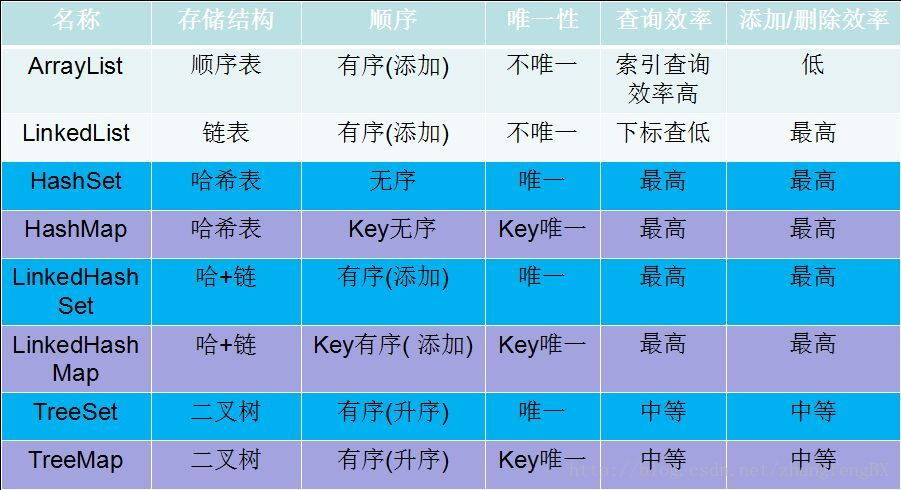
总结:数据结构是基础,熟悉数据结构,对掌握这些知识点很有帮助。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号