spring boot项目08:切面(AOP)-基础使用
JAVA 8
Spring Boot 2.5.3
---
百度百科:
在软件业,AOP 为 Aspect Oriented Programming 的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
涉及注解:
@Aspect、@Pointcut、
@Around、@Before、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing、@AfterThrowing、@After
涉及接口:
JoinPoint
ProceedingJoinPoint
---
jar包:aspectjweaver-x.y.z.jar
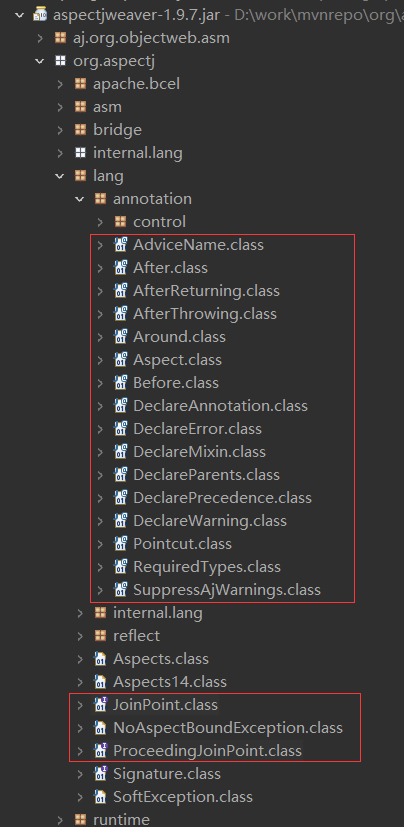
AOP 属于 Spring Framework的内容,在官文 Spring Framework Documentation->Core 可以找到 介绍。

在 本文的 Spring Boot 版本使用时,不需要使用 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解了。
找原因:
spring-boot-autoconfigure 包 的 META-INFO/spring.factories 中有下面的定义:AopAutoConfiguration
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\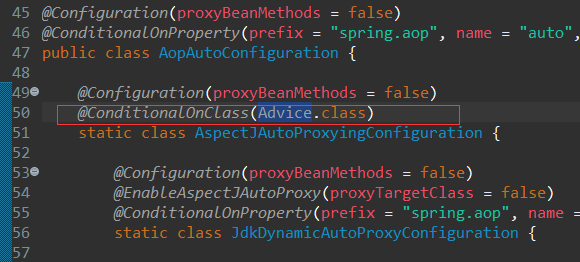
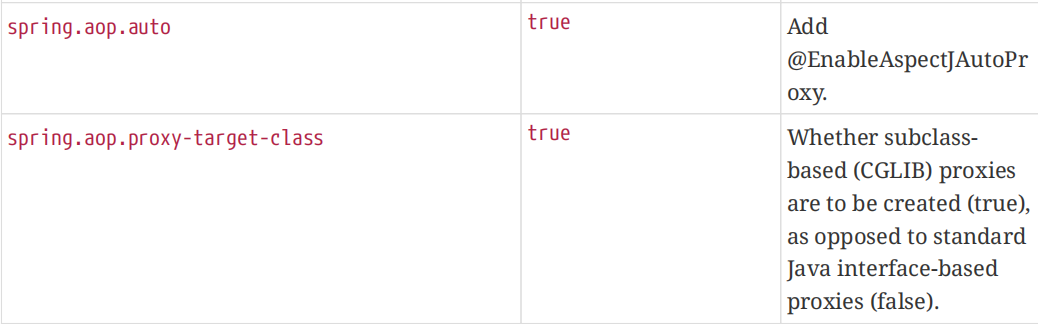
官文中 spring.aop.auto 默认为 true:
示例代码:
package org.lib.mysqlhello.common;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component // 必须
public class WebLogAspect {
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest req;
// @Autowired
// private HttpServletResponse resp;
// org.lib.mysqlhello.user.controller包下 所有public方法
// 注意通配符的使用!
@Pointcut(value="execution(public * org.lib.mysqlhello.user.controller..*.*(..))")
private void ptUserController() {
}
/**
* Before
* @author ben
* @date 2021-08-22 11:32:28 CST
* @param joinPoint
*/
// 等效
// @Before(value="execution(public * org.lib.mysqlhello.user.controller..*.*(..))")
@Before(value="ptUserController()")
public void logBeforeUserController(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("请求before:{}", req.getRequestURI());
}
/**
* Around
* @author ben
* @date 2021-08-22 11:32:21 CST
* @param pjp
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
// 等效
// @Around(value="execution(public * org.lib.mysqlhello.user.controller..*.*(..))")
@Around(value="ptUserController()")
public Object logAroundUserController(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
try {
// 在 @Before 之后执行
log.info("请求around: {}", req.getRequestURI());
return pjp.proceed();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("请求around发生异常:{}, e={}", req.getRequestURI(), e.getMessage());
throw e;
// return后,全局异常处理无效了!
// return ResultVO.getFailed(500, "发生异常-@Aspect-Around", e.getMessage());
} finally {
// 在 @After 之后执行
log.info("请求around-finally: {}", req.getRequestURI());
}
}
/**
* AfterReturning
* @author ben
* @date 2021-08-22 11:32:15 CST
*/
// 等效
// @AfterReturning(value="execution(public * org.lib.mysqlhello.user.controller..*.*(..))")
// @AfterReturning(value="ptUserController()")
@AfterReturning(pointcut="ptUserController()")
public void logAfterReturningUserController() {
log.info("请求afterReturning:{}", req.getRequestURI());
}
/**
* AfterThrowing 1-不抛出异常,没有throwing属性
* @author ben
* @date 2021-08-22 11:30:33 CST
*/
// 等效
// @AfterThrowing(value="execution(public * org.lib.mysqlhello.user.controller..*.*(..))")
// @AfterThrowing(value="ptUserController()")
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "ptUserController()")
public void logAfterThrowingUserController() {
log.info("请求afterThrowing:{}, nothing...", req.getRequestURI());
}
/**
* AfterThrowing 2-抛出异常,必须有throwing属性
* @author ben
* @date 2021-08-22 11:31:02 CST
* @param ex
*/
// 等效
// @AfterThrowing(value="execution(public * org.lib.mysqlhello.user.controller..*.*(..))", throwing = "ex")
// @AfterThrowing(value="ptUserController()", throwing = "ex")
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "ptUserController()", throwing = "ex")
public void logAfterThrowingUserController(Exception ex) {
log.info("请求afterThrowing:{}, ex.msg={}", req.getRequestURI(), ex.getMessage());
}
/**
* After
* @author ben
* @date 2021-08-22 11:31:59 CST
*/
// 等效
// @After(value="execution(public * org.lib.mysqlhello.user.controller..*.*(..))")
@After(value="ptUserController()")
public void logAfterUserController() {
log.info("请求after:{}", req.getRequestURI());
}
}
测试结果1:正常请求,,注意顺序
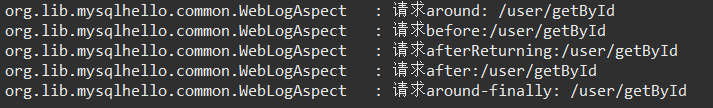
测试结果2:异常请求,,注意顺序
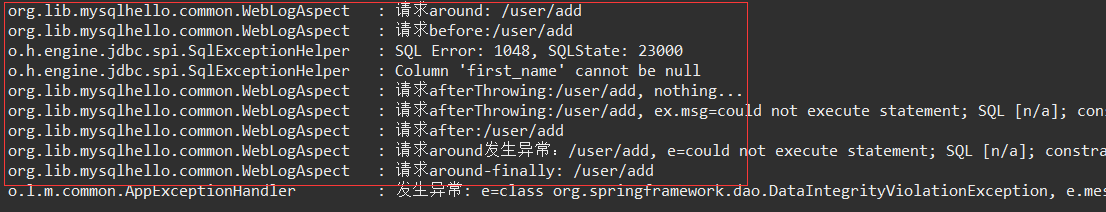
注,上图最后异常 是 全局异常处理 的日志——AOP 的 @Around 捕获异常后,没有return,直接throw,这才执行到 全局异常处理。
各个Advice注解的属性列举:
注解 @Around、@Before、@After 的属性——只有2个:
String value、
String argNames;
注解 @AfterReturning 、@AfterThrowing 的属性——各4个:
String value、
String pointcut
String returning —— 仅@AfterReturning
String throwing —— 仅@AfterThrowing
String argNames
AOP的实际使用中,还会涉及到 入参、响应 的一些处理,可以通过 各个Advice 的属性 或者 函数里面的参数 JoinPoint、ProceedingJoinPoint对象 获取。

参考文档
1、拦截机制中Aspect、ControllerAdvice、Interceptor、Fliter之间的区别详解
理解 这个顺序很重要。
2、在SpringBoot中用SpringAOP实现日志记录功能
讲了 Aspect内部各个Advice的顺序。
但其中介绍的 RequestContextHolder 在 本文的 S.B.版本中没有。
3、



