Opencv之LBP特征(算法)
LBP(Local Binary Pattern),即局部二进制模式,对一个像素点以半径r画一个圈,在圈上取K个点(一般为8),这K个点的值(像素值大于中心点为1,否则为0)组成K位二进制数。此即局部二进制模式,实际中使用的是LBP特征谱的直方统计图。在旧版的Opencv里,使用CvHaarClassifierCascade函数,只支持Harr特征。新版使用CascadeClassifier类,还可以支持LBP特征。Opencv的人脸识别使用的是Extended LBP(即circle_LBP),其LBP特征值的模式为256(0-255)种。
优点:
1,旋转不变性(局部二进制循环左移或右移其表示不变)
2,一定程度上消除了光照变化的问题
3,纹理特征维度低,计算速度快
缺点:
1,当光照变化不均匀时,各像素间的大小关系被破坏,对应的LBP算子也就发生了变化
2,通过引入旋转不变的定义,使LBP算子更具鲁棒性。但这也使得LBP算子丢失了方向信息(如使局部二进制左移或右移,结果是一样的,但是图像不一样)
以下介绍若干中LBP:
1,原始LBP。基于方框选取中心点周围8个像素,构成8位二进制
# 以下不再重复这个部分 import cv2 import numpy as np image_path=your_img_path
# 原始LBP算法:选取中心点周围的8个像素点,大于中心点为1,小于为0,将这些1或0顺时针串成8位二进制,即最终表示 def origin_LBP(img): dst = np.zeros(img.shape,dtype=img.dtype) h,w=img.shape start_index=1 for i in range(start_index,h-1): for j in range(start_index,w-1): center = img[i][j] code = 0 # 顺时针,左上角开始的8个像素点与中心点比较,大于等于的为1,小于的为0,最后组成8位2进制 code |= (img[i-1][j-1] >= center) << (np.uint8)(7) code |= (img[i-1][j ] >= center) << (np.uint8)(6) code |= (img[i-1][j+1] >= center) << (np.uint8)(5) code |= (img[i ][j+1] >= center) << (np.uint8)(4) code |= (img[i+1][j+1] >= center) << (np.uint8)(3) code |= (img[i+1][j ] >= center) << (np.uint8)(2) code |= (img[i+1][j-1] >= center) << (np.uint8)(1) code |= (img[i ][j-1] >= center) << (np.uint8)(0) dst[i-start_index][j-start_index]= code return dst # 读入灰度图 gray = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) # LBP处理 org_lbp = origin_LBP(gray)
cv2.imshow('img', gray) cv2.imshow('org_lbp', org_lbp) # 若针对视频取图片,delay=k时表示下一帧在kms后选取 cv2.waitKey(0)
2,Extended LBP
# 使用圆形选取框替代矩形框选:给定半径为r(半径越小,纹理越细),在此圆上选择K个点(选取点越多,亮度越高),同样,逆/顺时针组成K为二进制 # 称为extend LBP def circular_LBP(img, radius=3, neighbors=8): h,w=img.shape dst = np.zeros((h-2*radius, w-2*radius),dtype=img.dtype) for i in range(radius,h-radius): for j in range(radius,w-radius): # 获得中心像素点的灰度值 center = img[i,j] for k in range(neighbors): # 计算采样点对于中心点坐标的偏移量rx,ry rx = radius * np.cos(2.0 * np.pi * k / neighbors) ry = -(radius * np.sin(2.0 * np.pi * k / neighbors)) # 为双线性插值做准备 # 对采样点偏移量分别进行上下取整 x1 = int(np.floor(rx)) x2 = int(np.ceil(rx)) y1 = int(np.floor(ry)) y2 = int(np.ceil(ry)) # 将坐标偏移量映射到0-1之间 tx = rx - x1 ty = ry - y1 # 根据0-1之间的x,y的权重计算公式计算权重,权重与坐标具体位置无关,与坐标间的差值有关 w1 = (1-tx) * (1-ty) w2 = tx * (1-ty) w3 = (1-tx) * ty w4 = tx * ty # 根据双线性插值公式计算第k个采样点的灰度值 neighbor=img[i+y1,j+x1] * w1 + img[i+y2,j+x1] *w2 + img[i+y1,j+x2] * w3 +img[i+y2,j+x2] *w4 # LBP特征图像的每个邻居的LBP值累加,累加通过与操作完成,对应的LBP值通过移位取得 dst[i-radius,j-radius] |= (neighbor>center) << (np.uint8)(neighbors-k-1) return dst gray = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) circul_1_8 = circular_LBP(gray,1,8) circul_3_8 = circular_LBP(gray,3,8) circul_3_6 = circular_LBP(gray,3,6) # 最好是先计算完,统一显示 cv2.imshow('img', gray) cv2.imshow('r1k8', circul_1_8) cv2.imshow('r3k8', circul_3_8) cv2.imshow('r3k6', circul_3_6) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
其中,双线性插值公式为:
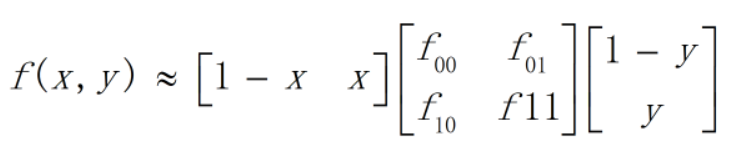
3,加入旋转不变性
# 在圆形选取框基础上,加入旋转不变操作 def rotation_invariant_LBP(img, radius=3, neighbors=8): h,w=img.shape dst = np.zeros((h-2*radius, w-2*radius),dtype=img.dtype) for i in range(radius,h-radius): for j in range(radius,w-radius): # 获得中心像素点的灰度值 center = img[i,j] for k in range(neighbors): # 计算采样点对于中心点坐标的偏移量rx,ry rx = radius * np.cos(2.0 * np.pi * k / neighbors) ry = -(radius * np.sin(2.0 * np.pi * k / neighbors)) # 为双线性插值做准备 # 对采样点偏移量分别进行上下取整 x1 = int(np.floor(rx)) x2 = int(np.ceil(rx)) y1 = int(np.floor(ry)) y2 = int(np.ceil(ry)) # 将坐标偏移量映射到0-1之间 tx = rx - x1 ty = ry - y1 # 根据0-1之间的x,y的权重计算公式计算权重,权重与坐标具体位置无关,与坐标间的差值有关 w1 = (1-tx) * (1-ty) w2 = tx * (1-ty) w3 = (1-tx) * ty w4 = tx * ty # 根据双线性插值公式计算第k个采样点的灰度值 neighbor = img[i+y1,j+x1] * w1 + img[i+y2,j+x1] *w2 + img[i+y1,j+x2] * w3 +img[i+y2,j+x2] *w4 # LBP特征图像的每个邻居的LBP值累加,累加通过与操作完成,对应的LBP值通过移位取得 dst[i-radius,j-radius] |= (neighbor>center) << (np.uint8)(neighbors-k-1) # 进行旋转不变处理 for i in range(dst.shape[0]): for j in range(dst.shape[1]): currentValue = dst[i,j] minValue = currentValue for k in range(1, neighbors): # 对二进制编码进行循环左移,意思即选取移动过程中二进制码最小的那个作为最终值 temp = (np.uint8)(currentValue>>(neighbors-k)) | (np.uint8)(currentValue<<k) if temp < minValue: minValue = temp dst[i,j] = minValue return dst gray = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) rotation_invariant = rotation_invariant_LBP(gray,3,8) cv2.imshow('img', gray) cv2.imshow('ri', rotation_invariant) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
4,等价模式
def get_shifts(data): ''' 计算跳变次数,即二进制码相邻2位不同,总共出现的次数 ''' count = 0 binaryCode = "{0:0>8b}".format(data) for i in range(1,len(binaryCode)): if binaryCode[i] != binaryCode[(i-1)]: count+=1 return count def create_table(img): # LBP特征值对应图像灰度编码表,直接默认采样点为8位 temp = 1 table =np.zeros((256),dtype=img.dtype) for i in range(256): # 跳变小于3定义为等价模式类,共58,混合类算做1种 if get_shifts(i)<3: table[i] = temp temp+=1 return table # 等价模式类:二进制码跳变次数小于3,8位二进制码共58种等价模式,其他256-58种为混合类。混合类的LBP特征将置为0,所以最终图像偏暗 def uniform_pattern_LBP(img,table,radius=3, neighbors=8): h,w=img.shape dst = np.zeros((h-2*radius, w-2*radius),dtype=img.dtype) for i in range(radius,h-radius): for j in range(radius,w-radius): # 获得中心像素点的灰度值 center = img[i,j] for k in range(neighbors): # 计算采样点对于中心点坐标的偏移量rx,ry rx = radius * np.cos(2.0 * np.pi * k / neighbors) ry = -(radius * np.sin(2.0 * np.pi * k / neighbors)) # 为双线性插值做准备 # 对采样点偏移量分别进行上下取整 x1 = int(np.floor(rx)) x2 = int(np.ceil(rx)) y1 = int(np.floor(ry)) y2 = int(np.ceil(ry)) # 将坐标偏移量映射到0-1之间 tx = rx - x1 ty = ry - y1 # 根据0-1之间的x,y的权重计算公式计算权重,权重与坐标具体位置无关,与坐标间的差值有关 w1 = (1-tx) * (1-ty) w2 = tx * (1-ty) w3 = (1-tx) * ty w4 = tx * ty # 根据双线性插值公式计算第k个采样点的灰度值 neighbor = img[i+y1,j+x1] * w1 + img[i+y2,j+x1] *w2 + img[i+y1,j+x2] * w3 +img[i+y2,j+x2] *w4 # LBP特征图像的每个邻居的LBP值累加,累加通过与操作完成,对应的LBP值通过移位取得 dst[i-radius,j-radius] |= (neighbor>center) << (np.uint8)(neighbors-k-1) # 进行LBP特征的UniformPattern编码 # 8位二进制码形成后,查表,对属于混合类的特征置0 if k==neighbors-1: dst[i-radius,j-radius] = table[dst[i-radius,j-radius]] return dst gray = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) table=create_table(gray) uniform_pattern = uniform_pattern_LBP(gray,table,3,8) cv2.imshow('img', gray) cv2.imshow('up', uniform_pattern) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
5,MB_LBP:先对像素做区域平均处理,再使用原始LBP
# 先对像素分割,用一个小区域的平均值代替这个区域,再用LBP特征处理 def multi_scale_block_LBP(img,scale): h,w= img.shape # cellSize表示一个cell大小 cellSize = int(scale / 3) offset = int(cellSize / 2) cellImage = np.zeros((h-2*offset, w-2*offset),dtype=img.dtype) for i in range(offset,h-offset): for j in range(offset,w-offset): temp = 0 for m in range(-offset,offset+1): for n in range(-offset,offset+1): temp += img[i+n,j+m] # 即取一个cell里所有像素的平均值 temp /= (cellSize*cellSize) cellImage[i-offset,j-offset] = np.uint8(temp) # 再对平均后的像素做LBP特征处理 dst = origin_LBP(cellImage) return dst gray = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) mb_3 = multi_scale_block_LBP(gray,3) mb_9 = multi_scale_block_LBP(gray,9) mb_15 = multi_scale_block_LBP(gray,15) cv2.imshow('img', gray) cv2.imshow('mb_3', mb_3) cv2.imshow('mb_9', mb_9) cv2.imshow('mb_15', mb_15) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
5,LBPH,Local Binary Patterns Histograms
此处基于等价模式,再使用像素各分割块的直方统计图,拼接为最后的特征向量
# 先使用等价模式预处理图像,降维。再分割图像,对每个分割块进行直方统计(降维后的类别为59),返回密度向量,再拼接各个分割块对应的密度向量 # 最终返回grid_x*grid_y*numPatterns维的特征向量,作为图像的LBPH特征向量 def getLBPH(img_lbp,numPatterns,grid_x,grid_y,density): ''' 计算LBP特征图像的直方图LBPH ''' h,w=img_lbp.shape width = int(w / grid_x) height = int(h / grid_y) # 定义LBPH的行和列,grid_x*grid_y表示将图像分割的块数,numPatterns表示LBP值的模式种类 result = np.zeros((grid_x * grid_y,numPatterns),dtype=float) resultRowIndex = 0 # 对图像进行分割,分割成grid_x*grid_y块,grid_x,grid_y默认为8 for i in range(grid_x): for j in range(grid_y): # 图像分块 src_cell = img_lbp[i*height:(i+1)*height,j*width:(j+1)*width] # 计算直方图 hist_cell = getLocalRegionLBPH(src_cell,0,(numPatterns-1),density) #将直方图放到result中 result[resultRowIndex]=hist_cell resultRowIndex+=1 return np.reshape(result,(-1)) def getLocalRegionLBPH(src,minValue,maxValue,density=True): ''' 计算一个LBP特征图像块的直方图 ''' data = np.reshape(src,(-1)) # 计算得到直方图bin的数目,直方图数组的大小 bins = maxValue - minValue + 1; # 定义直方图每一维的bin的变化范围 ranges = (float(minValue),float(maxValue + 1)) # density为True返回的是每个bin对应的概率值,bin为单位宽度时,概率总和为1 hist, bin_edges = np.histogram(src, bins=bins, range=ranges, density=density) return hist uniform_pattern = uniform_pattern_LBP(gray,table,3,8) #等价模式58种,混合模式算1种 lbph = getLBPH(uniform_pattern,59,8,8,True)
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/lk3030/article/details/84034963






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(六):基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类