上周五,公司的同事,从客户那边回来,说一个人员选择页面很慢,页面打开需要15s左右,后来自己也试了一下,也的确需要比较长的时间,客户反应比较强烈。

select * from (select id,objname,objno,station,orgid,seclevel, ROW_NUMBER() OVER
( order by seclevel desc,id desc) as pos from humres tbalias where isdelete=0
and id in (select h.id from humres h,orgunitlink o where o.col1 like '%4028b14f17578814011757e2bebf002a%'
and h.orgids like '%'+o.oid+'%')) as T where T.pos>0 and T.pos<=20

select count( id) as totalnum from humres tbalias where isdelete=0
and id in (select h.id from humres h,orgunitlink o where o.col1
like '%4028b14f17578814011757e2bebf002a%' and h.orgids like '%'+o.oid+'%')

--优化 by zping :2008年11月17日15:14:50
--建立humres中间表
create table humres_r
( id varchar(32),
orgid varchar(32)
)
--建立orgunitlink中间表
create table orgunitlink_r
( id varchar(32),
oid varchar(32),
orgid varchar(32)
)
--建立数据一列转多行数据
--@ids数据类型为:为32位id,中间用","号隔开, 如:'4028b14f175788140117581e030d00c7,4028b14f17578814011757f6131d0065'
--@id为数据表的唯一id
create function getCols(@id varchar(32),@ids varchar(8000))
returns @tb table (
id varchar(32),
orgid varchar(32)
)
as
begin
declare @num as int,@result varchar(8000);
set @result=replace(@ids,',','');
set @num=len(@result)/32 -- 因为数据格式为32固定字符加“,”
while @num<>0
begin
insert into @tb values(@id,substring(@result,(@num-1)*32+1,32));
set @num=@num-1;
end
return;
end
go
--建立表humres的触发器,用于同步中间表的数据
create TRIGGER trigger_humres
ON humres
for INSERT,update,delete
as
if @@rowcount = 0 --如果影响的行数为 0,则结束触发器运行,避免占用资源
return
begin tran
truncate table humres_r
insert into humres_r
select a.id,b.orgid from humres a cross apply dbo.getCols(id,orgids) b
commit tran
go
--建立表orgunitlink的触发器,用于同步中间表的数据
create TRIGGER trigger_orgunitlink
ON orgunitlink
for INSERT,update,delete
as
if @@rowcount = 0 --如果影响的行数为 0,则结束触发器运行,避免占用资源
return
begin tran
truncate table orgunitlink_r
insert into orgunitlink_r
select a.id,a.oid,b.orgid from orgunitlink a cross apply dbo.getCols(id,col1) b
commit tran
go
--修改后的SQL语句,计算总数
select count(id) as totalnum from humres tbalias where isdelete=0
and id in (
select h.id from
humres_r h,orgunitlink_r o where o.orgid='4028b14f17578814011757e2bebf002a' and
h.orgid=o.oid
)
--取语句的20条数据
select * from (select id,objname,objno,station,orgid,seclevel,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER ( order by seclevel desc,id desc) as pos from humres
tbalias where isdelete=0 and id in (select h.id from
humres_r h, orgunitlink_r o where o.orgid='4028b14f17578814011757e2bebf002a' and
h.orgid=o.oid))
as T where T.pos>0 and T.pos<=20
通过DMV查出缓慢的两个语句如下:
语句一:
select * from (select id,objname,objno,station,orgid,seclevel, ROW_NUMBER() OVER
( order by seclevel desc,id desc) as pos from humres tbalias where isdelete=0
and id in (select h.id from humres h,orgunitlink o where o.col1 like '%4028b14f17578814011757e2bebf002a%'
and h.orgids like '%'+o.oid+'%')) as T where T.pos>0 and T.pos<=20
语句二:
select count( id) as totalnum from humres tbalias where isdelete=0
and id in (select h.id from humres h,orgunitlink o where o.col1
like '%4028b14f17578814011757e2bebf002a%' and h.orgids like '%'+o.oid+'%')
查询的两个表的数据量: 表humres: 1920 行 , 191次 IO
表orgunitlink: 256 行, 11 次IO
最大表才不到2000行数据,查询为何如此慢。看看执行计划: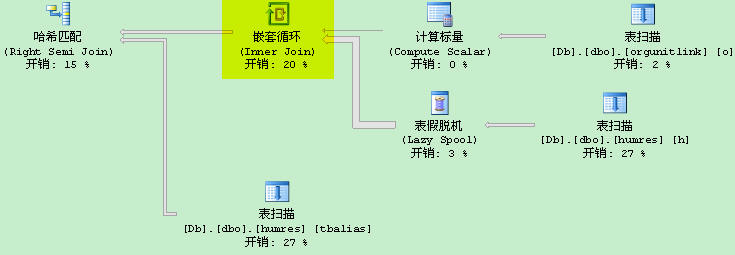
查询开销:
(20 行受影响)
表 'Worktable'。扫描计数 1,逻辑读取 8270 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。
表 'humres'。扫描计数 2,逻辑读取 382 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。
表 'orgunitlink'。扫描计数 1,逻辑读取 11 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。
表 'Worktable'。扫描计数 1,逻辑读取 8270 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。
表 'humres'。扫描计数 2,逻辑读取 382 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。
表 'orgunitlink'。扫描计数 1,逻辑读取 11 次,物理读取 0 次,预读 0 次,lob 逻辑读取 0 次,lob 物理读取 0 次,lob 预读 0 次。
这时发现:由于采用“%”来模糊查询,系统无法使用hash联结算法,采用嵌套循环算法。使得IO次数,多了8000个IO。
这里的col1,orgids :多个32位id,中间用","号隔开串, 如:'4028b14f175788140117581e030d00c7,4028b14f17578814011757f6131d0065'
一开始,我的思路是通过函数,将列col1,orgids中通过‘,’分开的函数隔离开来,将一行变多行,使其使用hash联结,但是后来发现虽然使用了hash联结
,但在系统在col1,orgids转换成多列时也很耗时间,最后想了一个更好的办法:
通过触发器建立中间表,将orgids,col1存放到另一个表中,由于这里都是一些基本数据,人员和机构,一般的变化的频率不高,也就一两天修改一次就很了不起了。建立触发器对数据库其他性能影响很小。全部代码和改写的SQL如下:
--优化 by zping :2008年11月17日15:14:50
--建立humres中间表
create table humres_r
( id varchar(32),
orgid varchar(32)
)
--建立orgunitlink中间表
create table orgunitlink_r
( id varchar(32),
oid varchar(32),
orgid varchar(32)
)
--建立数据一列转多行数据
--@ids数据类型为:为32位id,中间用","号隔开, 如:'4028b14f175788140117581e030d00c7,4028b14f17578814011757f6131d0065'
--@id为数据表的唯一id
create function getCols(@id varchar(32),@ids varchar(8000))
returns @tb table (
id varchar(32),
orgid varchar(32)
)
as
begin
declare @num as int,@result varchar(8000);
set @result=replace(@ids,',','');
set @num=len(@result)/32 -- 因为数据格式为32固定字符加“,”
while @num<>0
begin
insert into @tb values(@id,substring(@result,(@num-1)*32+1,32));
set @num=@num-1;
end
return;
end
go
--建立表humres的触发器,用于同步中间表的数据
create TRIGGER trigger_humres
ON humres
for INSERT,update,delete
as
if @@rowcount = 0 --如果影响的行数为 0,则结束触发器运行,避免占用资源
return
begin tran
truncate table humres_r
insert into humres_r
select a.id,b.orgid from humres a cross apply dbo.getCols(id,orgids) b
commit tran
go
--建立表orgunitlink的触发器,用于同步中间表的数据
create TRIGGER trigger_orgunitlink
ON orgunitlink
for INSERT,update,delete
as
if @@rowcount = 0 --如果影响的行数为 0,则结束触发器运行,避免占用资源
return
begin tran
truncate table orgunitlink_r
insert into orgunitlink_r
select a.id,a.oid,b.orgid from orgunitlink a cross apply dbo.getCols(id,col1) b
commit tran
go
--修改后的SQL语句,计算总数
select count(id) as totalnum from humres tbalias where isdelete=0
and id in (
select h.id from
humres_r h,orgunitlink_r o where o.orgid='4028b14f17578814011757e2bebf002a' and
h.orgid=o.oid
)
--取语句的20条数据
select * from (select id,objname,objno,station,orgid,seclevel,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER ( order by seclevel desc,id desc) as pos from humres
tbalias where isdelete=0 and id in (select h.id from
humres_r h, orgunitlink_r o where o.orgid='4028b14f17578814011757e2bebf002a' and
h.orgid=o.oid))
as T where T.pos>0 and T.pos<=20
通过以上的修改优化,点开页面速度很快。
总结:
- 这里,由于前期表设计的不合理,造成速度很慢,而且在业务逻辑不变,程序不变的情况下,是一个比较择中的优化方法。同时在后面设计表时要,注意让SQL优化器能使用到Hash联结,同时要注意符合第一设计范式啊,否则即使数据很小,速度也很慢。



