【栈】栈:链式栈,顺序栈,共享栈
简介
栈也是一种线性表结构,只不过栈的操作是受限的,它的特点就是在栈顶方向添加新的元素,且删除元素也只能从栈顶方向删除。因此栈是一种LIFO(后进先出)特性的数据结构。
压栈:新的元素放入栈的操作。
出栈:从栈中移除一个元素的操作。
因为栈是一种线性结构,所以可以通过前面所学的链表和顺序表作为内部实现。
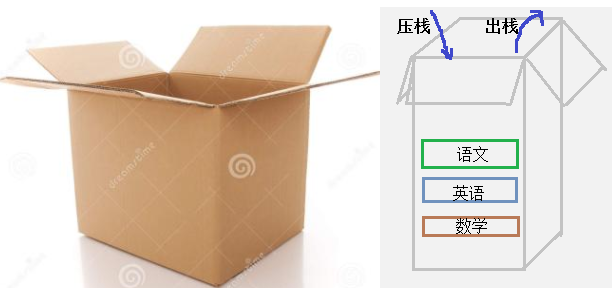
看图说栈
我们可以把一个栈看做是一个开口的箱子,箱子口就是栈顶,箱子底就是栈底。我们依次把 数学书,英语书,放进空箱子里,如果我们要再放一本语文书,则只能放在最顶层,如果我们要从箱子里拿出一本书,只能取出最顶层(栈顶)的语文书。这就是栈的标志性操作和特性。
栈的链式实现
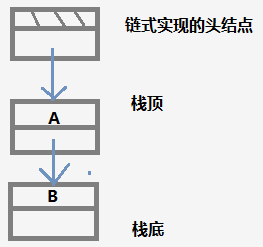
链式栈的优点是:不需要预先分配容量,也无需增加容量。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> #include<stdexcept> using namespace std; struct SNode { int element; SNode * next; SNode(int e=0,SNode*nxt = 0):element(e),next(nxt) { } }; class Stack { private: SNode headNode; //头结点 int size; //栈长度 public: Stack():headNode(),size(0) { } ~Stack() { SNode* p = headNode.next; SNode* t; while(p!=0){ t = p; p=p->next; delete t; } } /* *压栈操作 ,头插法 **/ bool push(int e) { SNode* new_node = new SNode(e,0); new_node->next = headNode.next; headNode.next = new_node; size++; return true; } bool pop() { SNode* del_node = headNode.next; //取出待删结点(也就是链表的首结点) if(del_node == 0) return false; //栈为空 headNode.next = del_node->next; delete del_node; size--; return true; } bool peek(int&e) const { SNode* peek_node = headNode.next; //取出栈顶结点(也就是链表的首结点) if(peek_node == 0) return false; //栈为空 e = peek_node->element; return true; } int length() const { return size; } bool empty() const{ return headNode.next == 0; } void clear() { SNode *p = headNode.next; SNode *t; while(p!=0){ t = p; p = p->next; delete t; } size =0; } }; int main() { using std::cout; using std::endl;; Stack s ; for(int i=0;i<20;++i) s.push(i); cout<<std::boolalpha<<"empty? "<<s.empty()<<endl; cout<<"length? "<<s.length()<<endl; for(int i=0;i<20;++i) { int e ; s.peek(e); cout<<e<<' '; s.pop(); } cout<<"\n---------------------"<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"empty? "<<s.empty()<<endl; cout<<"length? "<<s.length()<<endl; return 0; }
栈的顺序实现

#include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> #include<stdexcept> class Stack { private: enum{MAX_SIZE = 20}; int elements[MAX_SIZE]; //存储元素使用的数组 int top; //下一个栈顶元素的在数组中的索引。 public: Stack() { top = 0; //初始top为0 } bool peek(int &e) const { if(top <= 0) return false; e = elements[ top-1 ]; return true; } bool pop(){ if(top <= 0) return false; top--; return true; } bool push(int e){ if(top >=MAX_SIZE) return false; elements[ top++ ] = e; return true; } size_t length() const{ return top; } bool empty() const{ return top == 0; } bool full()const{ return top >=MAX_SIZE; } void clear(){ top = 0; } }; int main() { using std::cout; using std::endl;; Stack s ; for(int i=0;i<20;++i) s.push(i); cout<<std::boolalpha<<"empty? "<<s.empty()<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"full? "<<s.full()<<endl; cout<<"length? "<<s.length()<<endl; for(int i=0;i<20;++i) { int e ; s.peek(e); cout<<e<<' '; s.pop(); } cout<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"empty? "<<s.empty()<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"full? "<<s.full()<<endl; cout<<"length? "<<s.length()<<endl; return 0; }
共享顺序栈
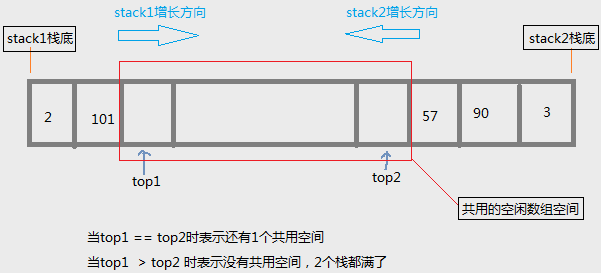
使用顺序栈时,要预先分配1个大的数组空间。共享顺序栈可以让2个栈共享同一个数组空间。
考试和面试常用,实际开发不常用。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> #include<stdexcept> class Stack { private: enum{MAX_SIZE = 20}; //内部数组的容量 int elements[MAX_SIZE]; //存储元素使用的数组,stack1和2共享 int top1; //stack1中 下一个栈顶元素的在数组中的索引。 int top2; //stack2中 下一个栈顶元素的在数组中的索引。 public: Stack() { top1 = 0; top2 = MAX_SIZE - 1; } /**** 用choose 代表stack1 和 stack2,默认是1 ****/ bool peek(int &e,int choose = 1) const { switch(choose) { case 1: { if(top1 <= 0) return false; e = elements[ top1-1 ]; return true; } case 2: { if(top2 >= MAX_SIZE-1) return false; e = elements[ top2 +1 ]; return true; } default: throw std::out_of_range(0); } } bool pop(int choose = 1)
{ switch(choose) { case 1: { if(top1 <= 0) return false; top1--; return true; } case 2: { if(top2 >= MAX_SIZE-1) return false; top2++; return true; } default: throw std::out_of_range(0); } } bool push(int e,int choose = 1){ switch(choose) { case 1: { if(top1 > top2) return false; elements[ top1++ ] = e; return true; } case 2: { if(top1 > top2) return false; elements[ top2-- ] = e; return true; } default: throw std::out_of_range(0); } } size_t length(int choose = 1) const { switch(choose) { case 1: return top1; case 2: return MAX_SIZE - 1 - top2; default: throw std::out_of_range(0); } } bool empty(int choose = 1) const { switch(choose) { case 1: return top1 == 0; case 2: return top2 == MAX_SIZE - 1 ; default: throw std::out_of_range(0); } } /*** 栈满的标志是: top1 > top2 ,数组还有1个空间的标志是 top1 == top2 ***/ bool full()const { return top1 > top2; } void clear(int choose = 1) { switch(choose) { case 1: top1 = 0; case 2: top2 = MAX_SIZE -1; default: throw std::out_of_range(0); } } }; int main() { using std::cout; using std::endl;; Stack s ; cout<<"put 15 elements to stack1"<<endl; for(int i=0;i<15;++i) s.push(i); cout<<"put 5 elements to stack2"<<endl; for(int i=0;i<5;++i) s.push(i,2); cout<<"---------stack1----------"<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"empty? "<<s.empty()<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"full? "<<s.full()<<endl; cout<<"length? "<<s.length()<<endl; cout<<"---------stack2----------"<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"empty? "<<s.empty(2)<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"full? "<<s.full()<<endl; cout<<"length? "<<s.length(2)<<endl; cout<<"----pop elements from stack1----"<<endl; for(int i=0;i<15;++i) { int e ; s.peek(e); cout<<e<<' '; s.pop(); } cout<<"\n----pop elements from stack2----"<<endl; for(int i=0;i<5;++i) { int e ; s.peek(e,2); cout<<e<<' '; s.pop(2); } cout<<"\n-----stack1 status-----"<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"empty? "<<s.empty()<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"full? "<<s.full()<<endl; cout<<"length? "<<s.length()<<endl; cout<<"\n-----stack2 status-----"<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"empty? "<<s.empty(2)<<endl; cout<<std::boolalpha<<"full? "<<s.full()<<endl; cout<<"length? "<<s.length(2)<<endl; return 0; }
栈的使用
进制转换:十进制转二进制输出
//使用递归将十进制转换为二进制输出 void toBinary(int x) { if(x/2) toBinary(x/2); cout<<x%2; } //使用栈做临时存储,进行 十进制转换为二进制输出 void toBin(int x) { Stack s; do{ s.push(x%2); }while(x/=2); while(s.length()!=0){ int e; s.peek(e); s.pop(); cout<<e; } }
括号匹配:如果输入的括号是成对匹配的,则输出true,否则输出false
bool braceMatch() { /** [ ] OK ( ) OK [()()[]] OK ()()()[][] OK [[[[()]]]] OK */ char token; std::stack<char> s; while(cin>>token && token!='#'){ if(s.empty()){ s.push(token); continue; } if(token == '(' || token == '['){ s.push(token); continue; } if(token == ')' && !s.empty()){ //如果是 ) ,则出栈匹配,直到匹配到 ( char out; do{ out = s.top(); s.pop(); }while(out != '(' && !s.empty()); continue; } if(token == ']' && !s.empty() ){ //如果是 ] ,则出栈匹配,直到匹配到 [ char out; do{ out = s.top(); s.pop(); }while(out != '[' && !s.empty() ); continue; } } return s.empty(); //如果栈为空则说明括号匹配 }
作者:lulipro-代码钢琴家
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lulipro/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载。限于本人水平,如果文章和代码有表述不当之处,还请不吝赐教。

