[Azure Load Balancer]Azure 内部负载均衡器工作原理
Default distribution algorithm
Azure Load Balancer is a Layer-4 (TCP, UDP) type load balancer that distributes incoming traffic among healthy service instances in cloud services or virtual machines defined in a load balancer set.
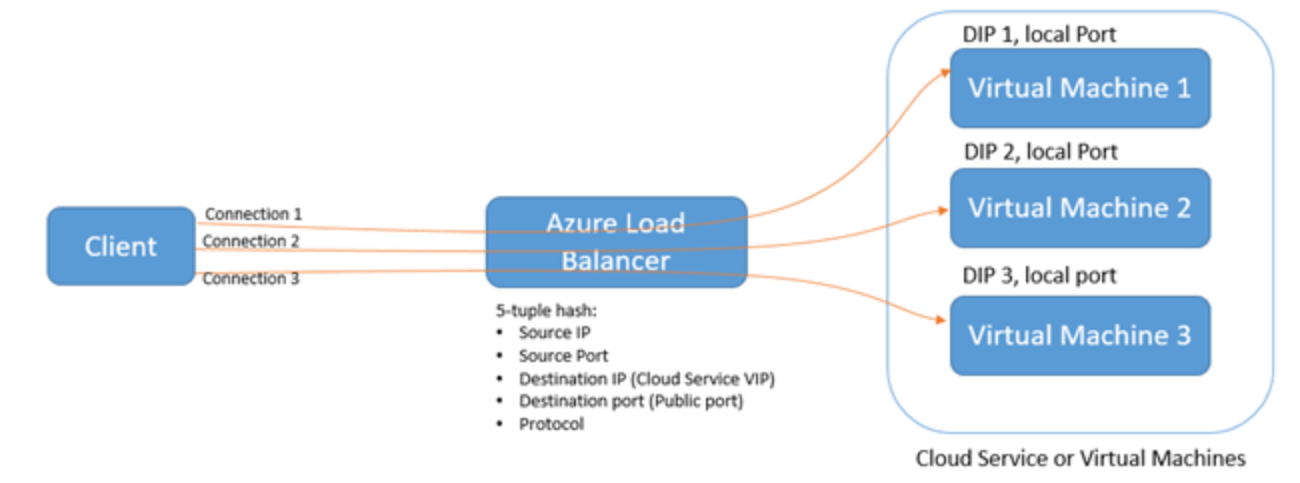
The distribution algorithm used is a 5 tuple (source IP, source port, destination IP, destination port, protocol type) hash to map traffic to available servers. It provides stickiness only within a transport session.
Packets in the same TCP or UDP session will be directed to the same datacenter IP (DIP) instance behind the load balanced endpoint. When the client closes and re-opens the connection or starts a new session from the same source IP, the source port changes and causes the traffic to go to a different DIP endpoint.
New Distribution Mode
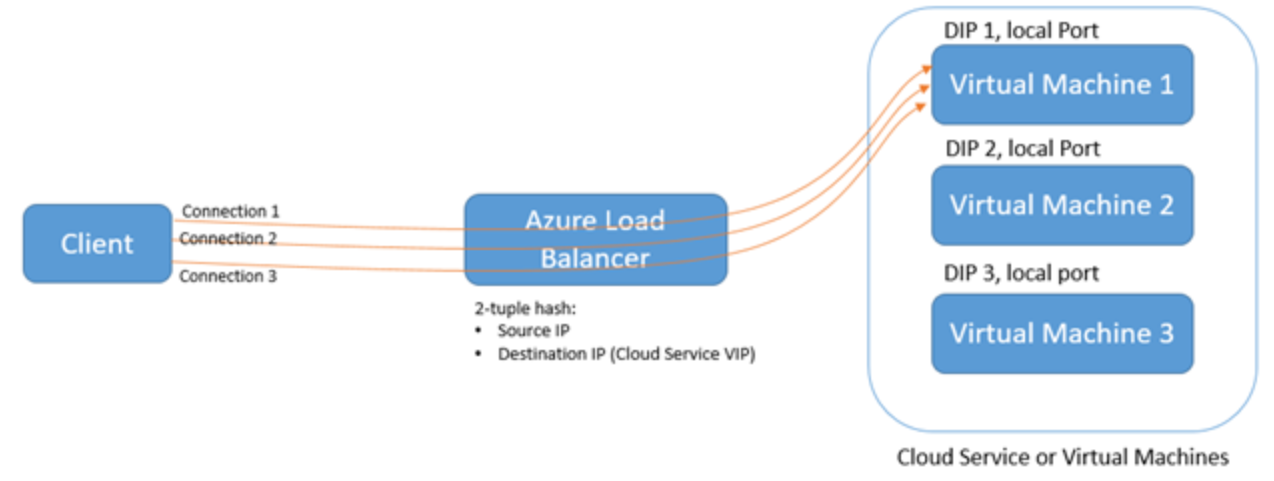
We have introduced a new distribution mode called Source IP Affinity (also known as session affinity or client IP affinity).
Azure Load Balancer can be configured to use a 2 tuple (Source IP, Destination IP) or 3 tuple (Source IP, Destination IP, Protocol) to map traffic to the available servers. By using Source IP affinity, connections initiated from the same client computer goes to the same DIP endpoint.
Source IP affinity solves an incompatibility between the Azure Load Balancer and RD Gateway.
Now you can build a RD gateway farm in a single cloud service. Another usage scenario is media upload where the real data upload happens through UDP but wherein the control plane is achieved through TCP:
- A client first initiates a TCP session to the load balanced public address, gets directed to a specific DIP, this channel is left active to monitor the connection health
- A new UDP session from the same client computer is initiated to the same load balanced public endpoint, the expectation here is that this connection is also directed to the same DIP endpoint as the previous TCP connection so that media upload can be executed at high throughput while also maintaining a control channel through TCP.
Note that if the load-balanced set changes (removing or adding a virtual machine), the distribution of client requests is recomputed. You cannot depend on new connections from existing client sessions ending up at the same server. Additionally, using source IP affinity distribution mode may cause an unequal distribution of traffic. Clients running behind proxies may be seen as one unique client application.
More content: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/azure-load-balancer-new-distribution-mode/
当在复杂的环境中面临问题,格物之道需:浊而静之徐清,安以动之徐生。 云中,恰是如此!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号