Python core part2
1. Comprehensions

2.

List Comprehensions
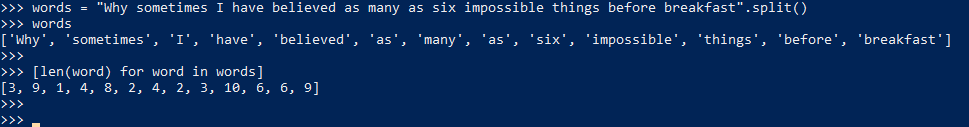
与上面的语句达到相同的效果,但是复杂的多
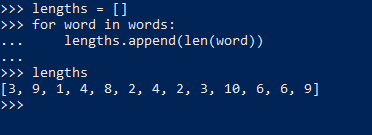
another example
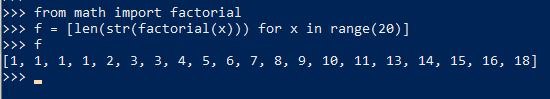
and another for set comprehensions
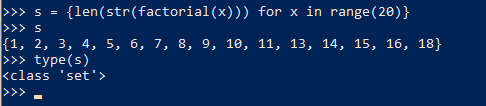
3. Dictionary Comprehensions
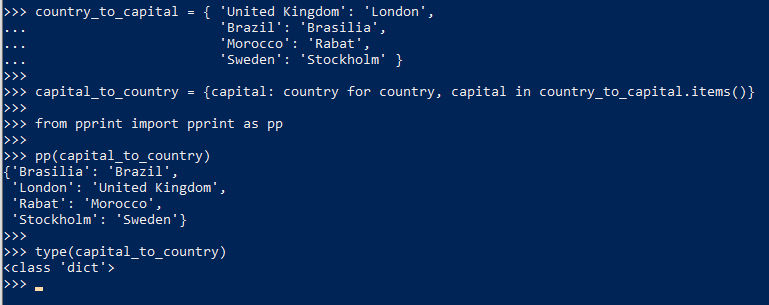
下面的例子里,去每个item的第一个字母作为key,只有最后一组被保留了,因为key必须唯一
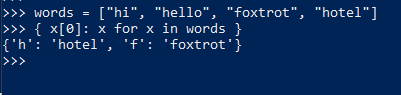
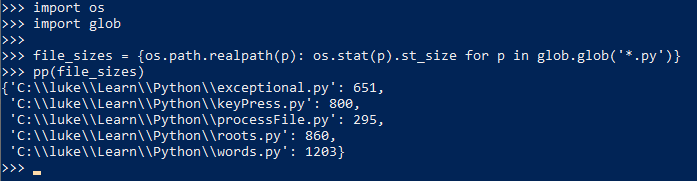
4. 不要把comprehension写的太复杂,比如下面的例子,列出目录中的python文件及其大小
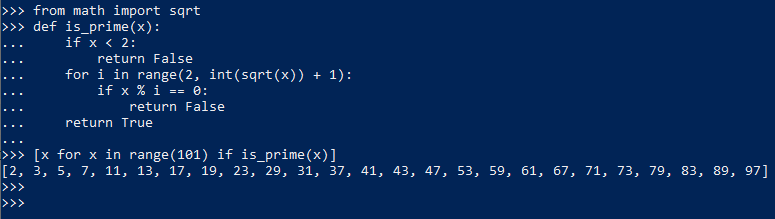
5. 给comprehension加上过滤filter以得到101内的质数
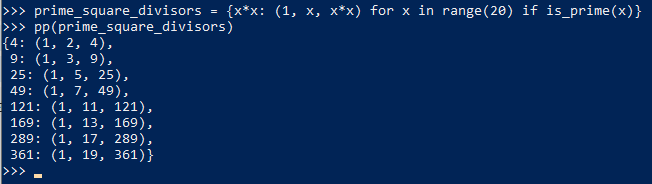
6.
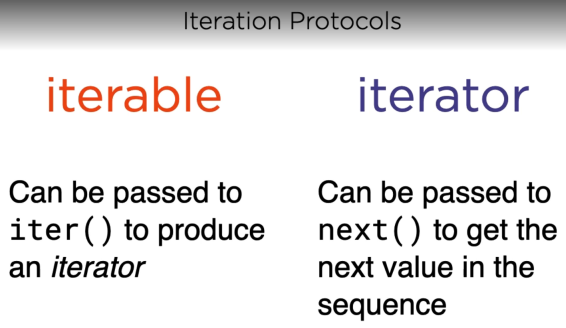
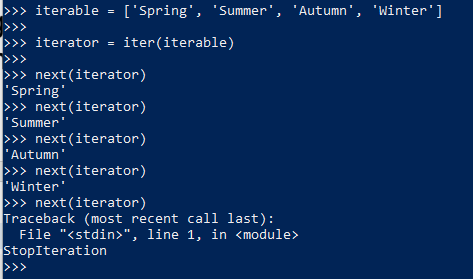
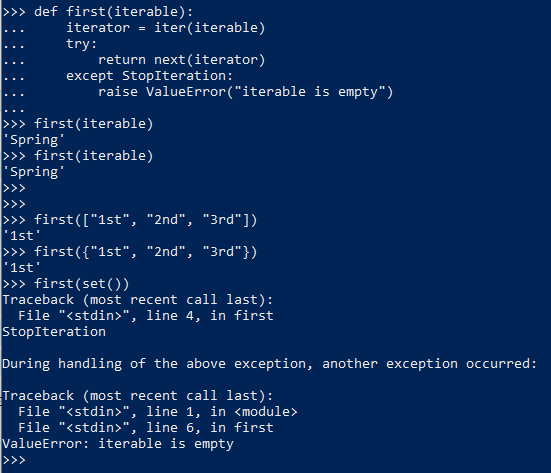
7. Generator functions
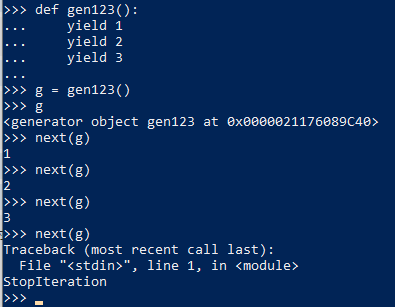
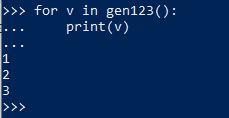
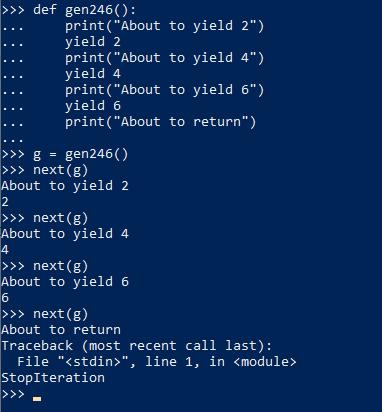
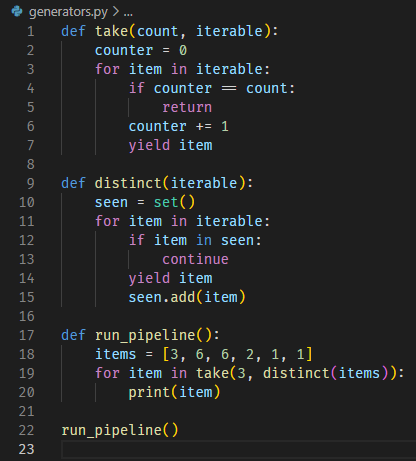
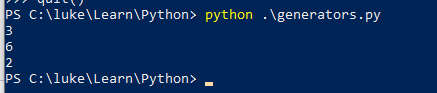
8. Laziness, 只有执行到才会求解

9. Generator Expression
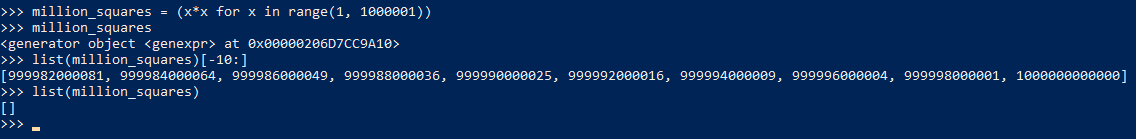
节省内存占用
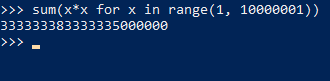
带过滤条件

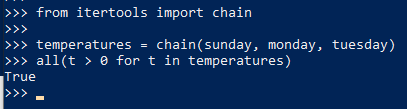
10. Iteration Tools
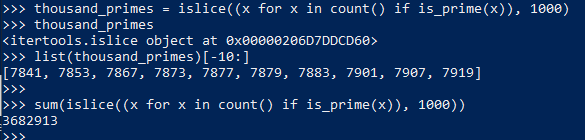
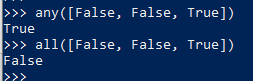
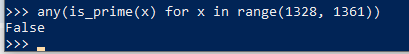
11. any and all
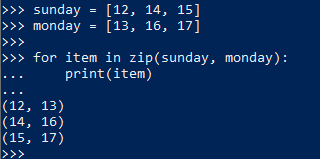
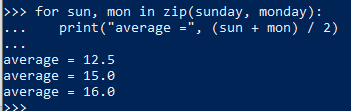
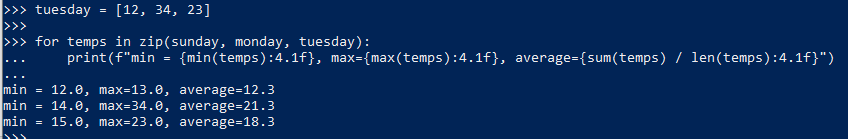
12. zip()
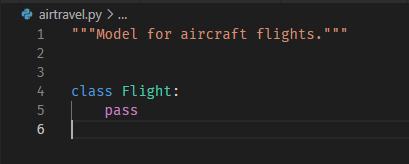
13. Class
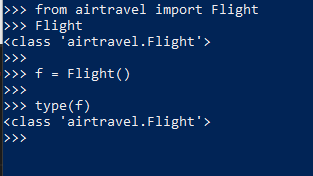
14. self, Instance methods must accept a reference to the actual instance on which the method was called as the first argument.
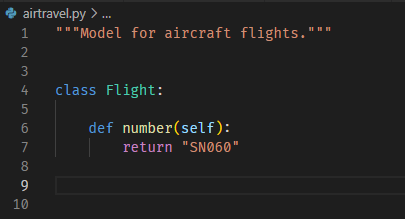
f.number()只是Flight.number(f)的语法糖

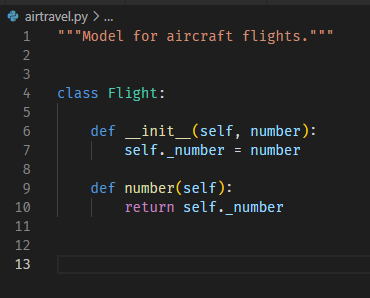
__init__并不是constractor, 只是初始化变量
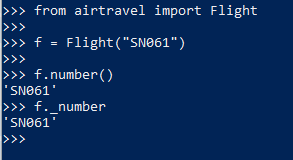
class的所有成员都是public的
15. Class invariants: truths about an object that endure for its lifetime.
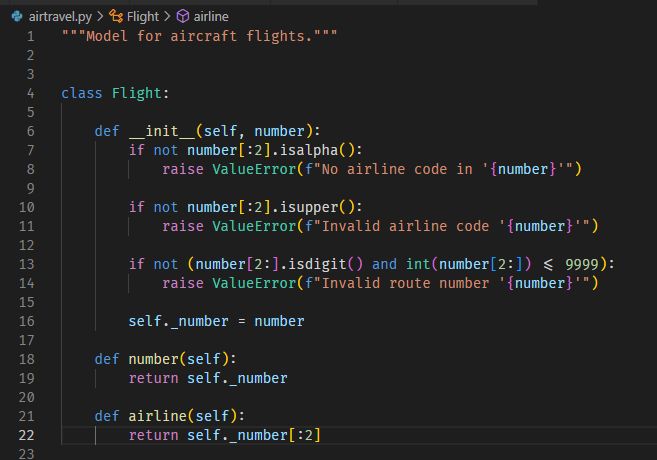
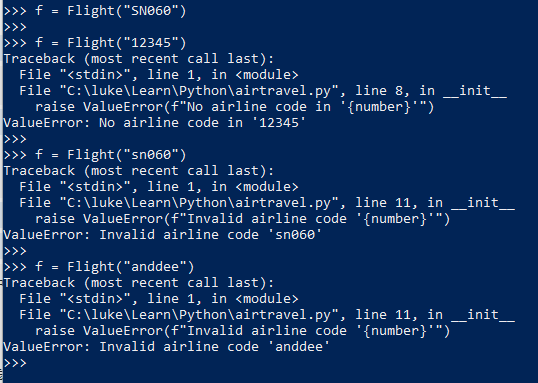
16. another class example:
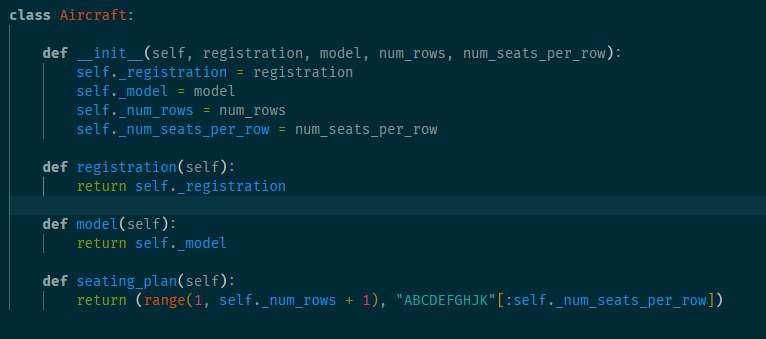
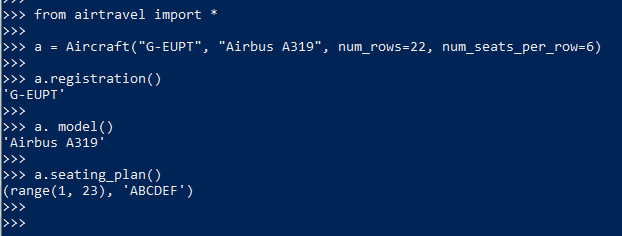
17. Class reference to another class
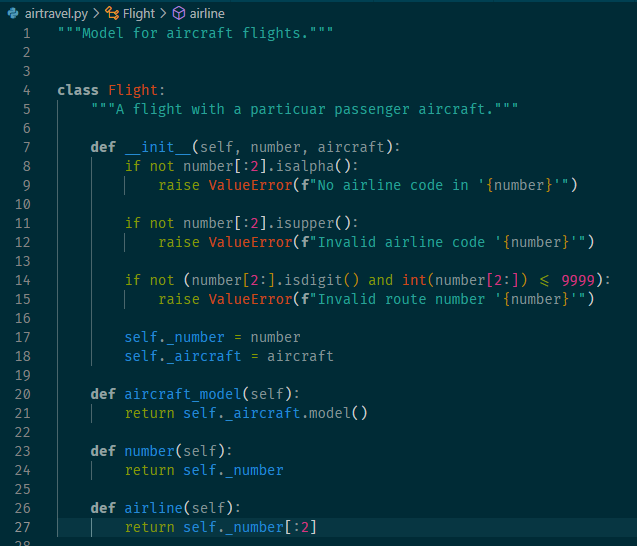
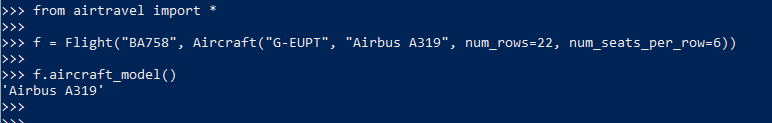
18. seating definition
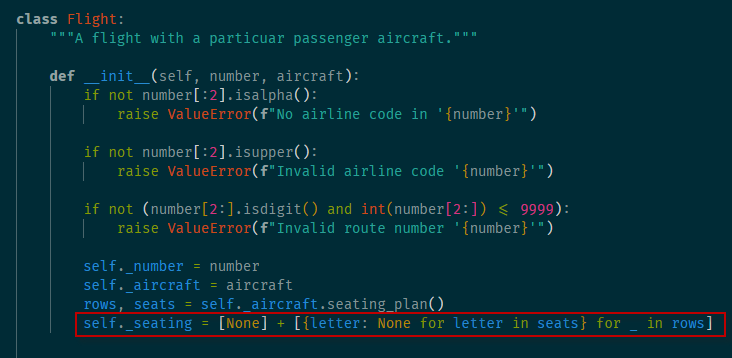

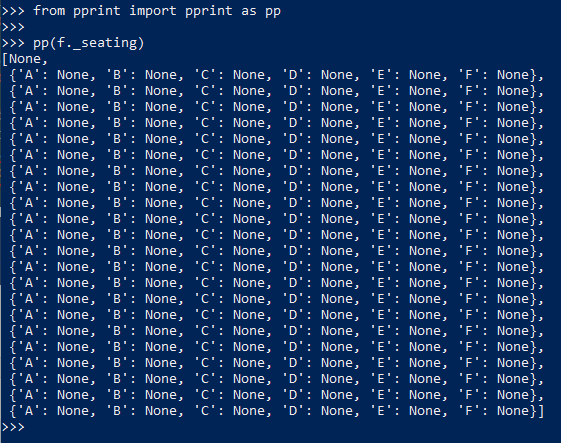
allocate set method
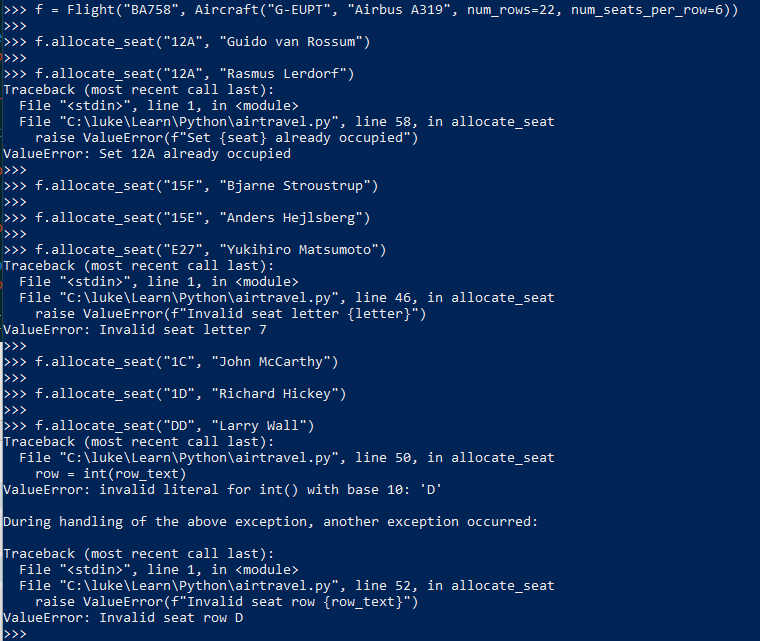
testing allocate seat method
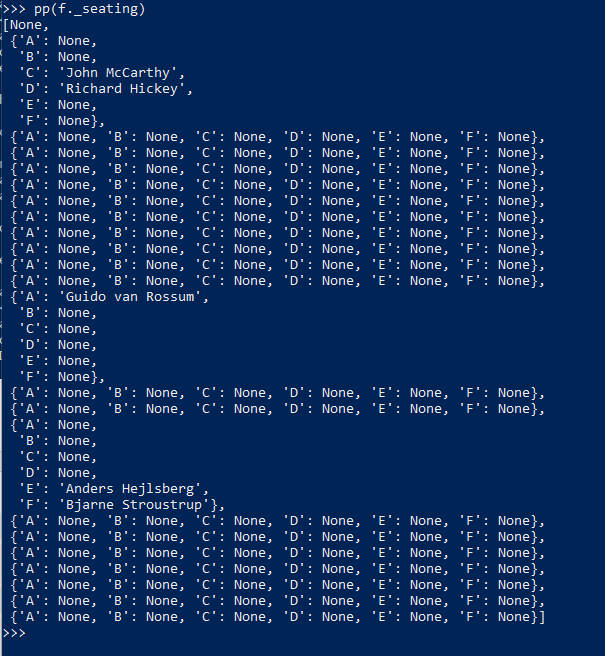
show the result of setting
19. 将函数作为参数传递
类成员
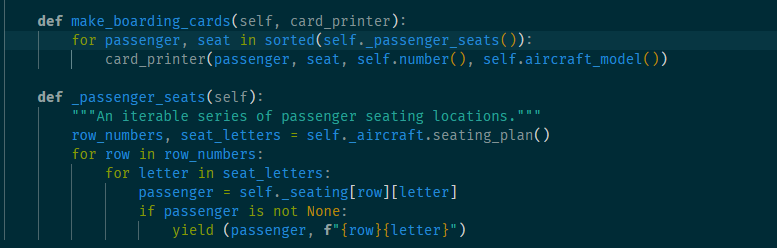
非类成员
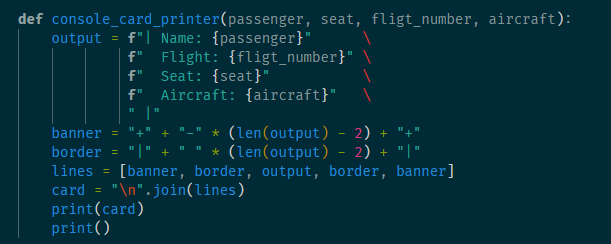
调用过程,非类成员函数console_card_printer被当作参数传递
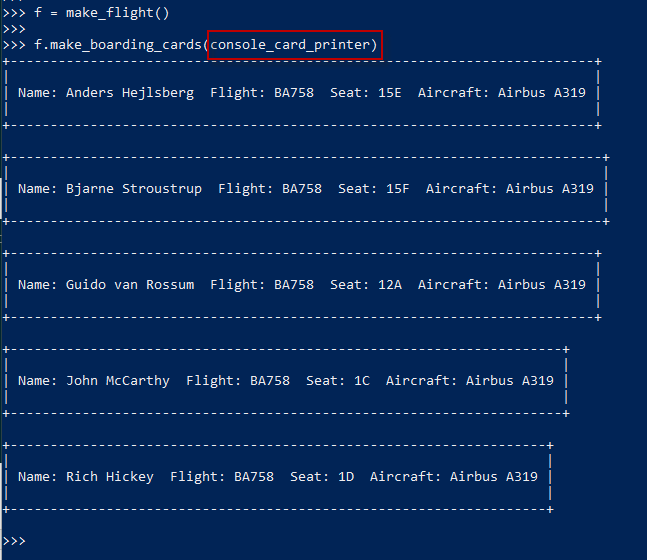
示例完整代码
1 """Model for aircraft flights.""" 2 3 4 class Flight: 5 """A flight with a particuar passenger aircraft.""" 6 7 def __init__(self, number, aircraft): 8 if not number[:2].isalpha(): 9 raise ValueError(f"No airline code in '{number}'") 10 11 if not number[:2].isupper(): 12 raise ValueError(f"Invalid airline code '{number}'") 13 14 if not (number[2:].isdigit() and int(number[2:]) <= 9999): 15 raise ValueError(f"Invalid route number '{number}'") 16 17 self._number = number 18 self._aircraft = aircraft 19 rows, seats = self._aircraft.seating_plan() 20 self._seating = [None] + \ 21 [{letter: None for letter in seats} for _ in rows] 22 23 def aircraft_model(self): 24 return self._aircraft.model() 25 26 def number(self): 27 return self._number 28 29 def airline(self): 30 return self._number[:2] 31 32 def allocate_seat(self, seat, passenger): 33 """Allocate a seat to a passenger. 34 35 Args: 36 seat: A seat designator such as '12C' or '21F'. 37 passenger: The passenger name. 38 39 Raises: 40 ValueError: If the seat is unavailable. 41 """ 42 row, letter = self._parse_seat(seat) 43 44 if self._seating[row][letter] is not None: 45 raise ValueError(f"Set {seat} already occupied") 46 47 self._seating[row][letter] = passenger 48 49 def _parse_seat(self, seat): 50 rows, seat_letters = self._aircraft.seating_plan() 51 52 letter = seat[-1] 53 if letter not in seat_letters: 54 raise ValueError(f"Invalid seat letter {letter}") 55 56 row_text = seat[:-1] 57 try: 58 row = int(row_text) 59 except ValueError: 60 raise ValueError(f"Invalid seat row {row_text}") 61 62 if row not in rows: 63 raise ValueError(f"Invalid row number {row}") 64 65 return row, letter 66 67 def relocate_passenger(self, from_seat, to_seat): 68 """Relocate a passenger to a different seat. 69 70 Args: 71 from_seat: The existing seat designator for the 72 passenger to be moved. 73 74 to_set: The new seat designator. 75 """ 76 from_row, from_letter = self._parse_seat(from_seat) 77 if self._seating[from_row][from_letter] is None: 78 raise ValueError(f"No passenger to relocate in seat {from_seat}") 79 80 to_row, to_letter = self._parse_seat(to_seat) 81 if self._seating[to_row][to_letter] is not None: 82 raise ValueError(f"Seat {to_seat} already occupied") 83 84 self._seating[to_row][to_letter] = self._seating[from_row][from_letter] 85 self._seating[from_row][from_letter] = None 86 87 def num_available_seats(self): 88 return sum(sum(1 for s in row.values() if s is None) for row in self._seating if row is not None) 89 90 def make_boarding_cards(self, card_printer): 91 for passenger, seat in sorted(self._passenger_seats()): 92 card_printer(passenger, seat, self.number(), self.aircraft_model()) 93 94 def _passenger_seats(self): 95 """An iterable series of passenger seating locations.""" 96 row_numbers, seat_letters = self._aircraft.seating_plan() 97 for row in row_numbers: 98 for letter in seat_letters: 99 passenger = self._seating[row][letter] 100 if passenger is not None: 101 yield (passenger, f"{row}{letter}") 102 103 104 def console_card_printer(passenger, seat, fligt_number, aircraft): 105 output = f"| Name: {passenger}" \ 106 f" Flight: {fligt_number}" \ 107 f" Seat: {seat}" \ 108 f" Aircraft: {aircraft}" \ 109 " |" 110 banner = "+" + "-" * (len(output) - 2) + "+" 111 border = "|" + " " * (len(output) - 2) + "|" 112 lines = [banner, border, output, border, banner] 113 card = "\n".join(lines) 114 print(card) 115 print() 116 117 118 class Aircraft: 119 120 def __init__(self, registration, model, num_rows, num_seats_per_row): 121 self._registration = registration 122 self._model = model 123 self._num_rows = num_rows 124 self._num_seats_per_row = num_seats_per_row 125 126 def registration(self): 127 return self._registration 128 129 def model(self): 130 return self._model 131 132 def seating_plan(self): 133 return (range(1, self._num_rows + 1), "ABCDEFGHJK"[:self._num_seats_per_row]) 134 135 136 def make_flight(): 137 f = Flight("BA758", Aircraft("G-EUPT", "Airbus A319", 138 num_rows=22, num_seats_per_row=6)) 139 f.allocate_seat("12A", "Guido van Rossum") 140 f.allocate_seat("15F", "Bjarne Stroustrup") 141 f.allocate_seat("15E", "Anders Hejlsberg") 142 f.allocate_seat("1C", "John McCarthy") 143 f.allocate_seat("1D", "Rich Hickey") 144 return f
20. polymorphism



增加的代码
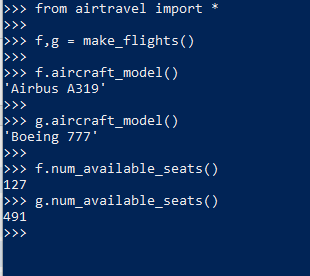
1 def make_flights(): 2 f = Flight("BA758", AirbusA319("G-EUPT")) 3 f.allocate_seat("12A", "Guido van Rossum") 4 f.allocate_seat("15F", "Bjarne Stroustrup") 5 f.allocate_seat("15E", "Anders Hejlsberg") 6 f.allocate_seat("1C", "John McCarthy") 7 f.allocate_seat("1D", "Rich Hickey") 8 9 g = Flight("AF72", Boeing777("F-GSPS")) 10 g.allocate_seat("55K", "Larry Wall") 11 g.allocate_seat("33G", "Yukihiro Matsumoto") 12 g.allocate_seat("4B", "Brian Kernighan") 13 g.allocate_seat("4A", "Dennis Richie") 14 15 return f, g 16 17 18 class AirbusA319: 19 20 def __init__(self, registration): 21 self._registration = registration 22 23 def registration(self): 24 return self._registration 25 26 def model(self): 27 return "Airbus A319" 28 29 def seating_plan(self): 30 return range(1, 23), "ABCDEF" 31 32 class Boeing777: 33 34 def __init__(self, registration): 35 self._registration = registration 36 37 def registration(self): 38 return self._registration 39 40 def model(self): 41 return "Boeing 777" 42 43 def seating_plan(self): 44 # For simplicity's sake, we ignore complex 45 # seating arrangement for first-class 46 return range(1, 56), "ABCDEGHJK"
运行示例:
21.


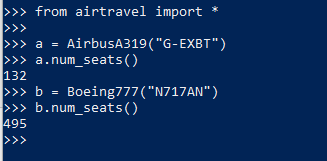
1 class AircraftBase: 2 3 def __init__(self, registration): 4 self._registration = registration 5 6 def registration(self): 7 return self._registration 8 9 def num_seats(self): 10 rows, row_seats = self.seating_plan() 11 return len(rows) * len(row_seats) 12 13 class AirbusA319(AircraftBase): 14 15 def model(self): 16 return "Airbus A319" 17 18 def seating_plan(self): 19 return range(1, 23), "ABCDEF" 20 21 class Boeing777(AircraftBase): 22 23 def model(self): 24 return "Boeing 777" 25 26 def seating_plan(self): 27 # For simplicity's sake, we ignore complex 28 # seating arrangement for first-class 29 return range(1, 56), "ABCDEGHJK"
运行:
22. open file

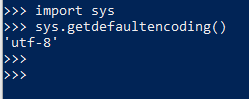
23. mode
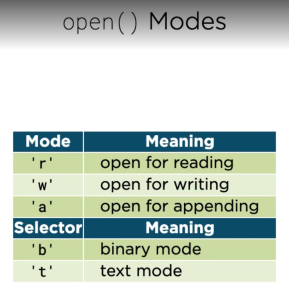
24. example of write
\n是python使用的换行符,在保存时会自动转换为系统的换行符,所以同样是本例,linux的文件会比windows的少一个字节
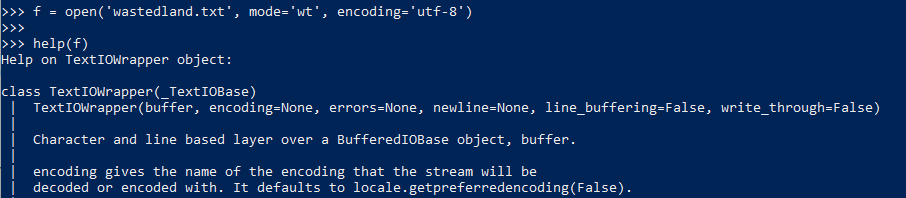
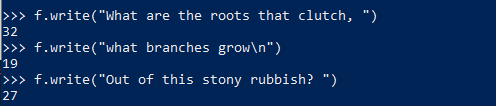
只有在执行了close()之后,文件才会保存
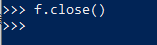

25. read from file
seek只能赋值为0,对于文本文件来说
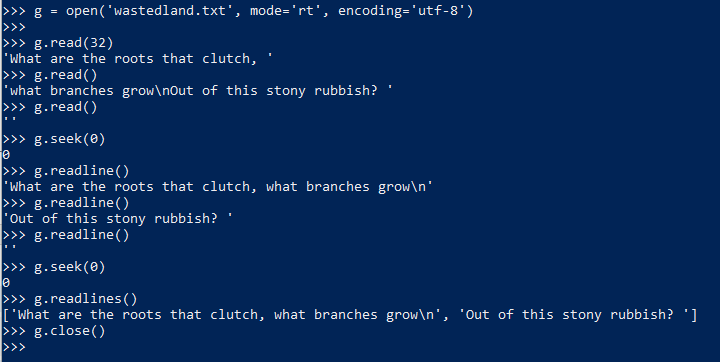
26. append to file

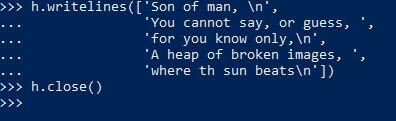

27. Iterating over files
1 import sys 2 3 f = open(sys.argv[1], mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') 4 for line in f: 5 print(line) 6 f.close()
output:
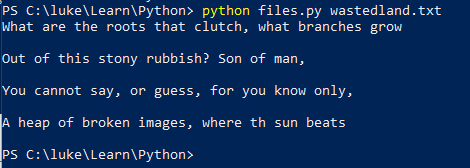
避免多一个换行
1 import sys 2 3 f = open(sys.argv[1], mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') 4 for line in f: 5 sys.stdout.write(line) 6 f.close()
output:
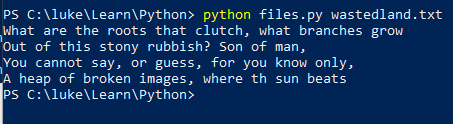
28. write Recaman data
1 from re import A 2 import sys 3 from itertools import count, islice 4 5 6 def sequence(): 7 """Generate Recaman's sequence.""" 8 seen = set() 9 a = 0 10 for n in count(1): 11 yield a 12 seen.add(a) 13 c = a - n 14 if c < 0 or c in seen: 15 c = a + n 16 a = c 17 18 19 def write_sequence(filename, num): 20 """Write Recaman's sequence to a text file.""" 21 f = open(filename, mode='wt', encoding='utf-8') 22 f.writelines(f"{r}\n" for r in islice(sequence(), num + 1)) 23 f.close() 24 25 26 if __name__ == '__main__': 27 write_sequence(filename=sys.argv[1], num=int(sys.argv[2]))
运行:

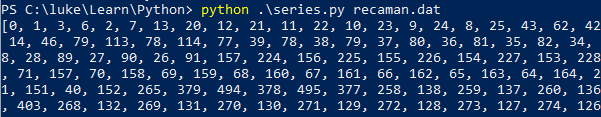
29. read file
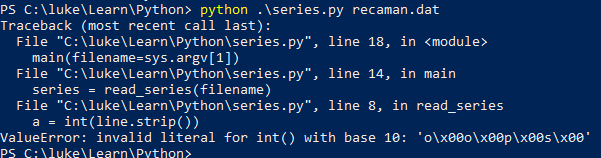
1 """Read and print an integer series.""" 2 import sys 3 4 def read_series(filename): 5 f = open(filename, mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') 6 series = [] 7 for line in f: 8 a = int(line.strip()) 9 series.append(a) 10 f.close() 11 return series 12 13 def main(filename): 14 series = read_series(filename) 15 print(series) 16 17 if __name__ == "__main__": 18 main(filename=sys.argv[1])
运行:
故意制造一个类型错误

运行出错
出错后,file没有close,优化程序:
1 """Read and print an integer series.""" 2 import sys 3 4 def read_series(filename): 5 try: 6 f = open(filename, mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') 7 return [int(line.strip()) for line in f] 8 # series = [] 9 # for line in f: 10 # a = int(line.strip()) 11 # series.append(a) 12 finally: 13 f.close() 14 return series 15 16 def main(filename): 17 series = read_series(filename) 18 print(series) 19 20 if __name__ == "__main__": 21 main(filename=sys.argv[1])
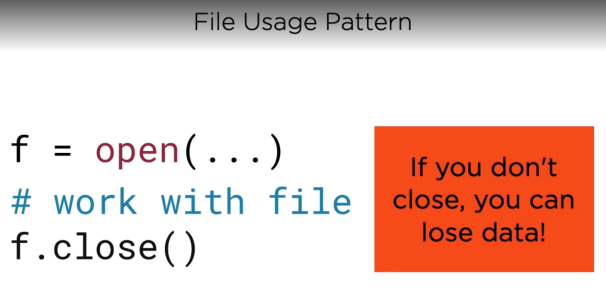
30. File usage pattern
31.

用with重写的函数
1 from re import A 2 import sys 3 from itertools import count, islice 4 5 6 def sequence(): 7 """Generate Recaman's sequence.""" 8 seen = set() 9 a = 0 10 for n in count(1): 11 yield a 12 seen.add(a) 13 c = a - n 14 if c < 0 or c in seen: 15 c = a + n 16 a = c 17 18 19 def write_sequence(filename, num): 20 """Write Recaman's sequence to a text file.""" 21 f = open(filename, mode='wt', encoding='utf-8') 22 f.writelines(f"{r}\n" for r in islice(sequence(), num + 1)) 23 f.close() 24 25 26 def write_sequence_with(filename, num): 27 """Write Recaman's sequence to a text file.""" 28 with open(filename, mode='wt', encoding='utf-8') as f: 29 f.writelines(f"{r}\n" for r in islice(sequence(), num + 1)) 30 31 32 if __name__ == '__main__': 33 write_sequence_with(filename=sys.argv[1], num=int(sys.argv[2]))
1 """Read and print an integer series.""" 2 import sys 3 4 def read_series(filename): 5 try: 6 f = open(filename, mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') 7 return [int(line.strip()) for line in f] 8 # series = [] 9 # for line in f: 10 # a = int(line.strip()) 11 # series.append(a) 12 finally: 13 f.close() 14 return series 15 16 def read_series_with(filename): 17 with open(filename, mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') as f: 18 return [int(line.strip()) for line in f] 19 20 21 def main(filename): 22 series = read_series_with(filename) 23 print(series) 24 25 if __name__ == "__main__": 26 main(filename=sys.argv[1])
32. bmp.py
1 """A module for dealing with BMP bitmap image files.""" 2 3 def write_grayscale(filename, pixels): 4 """Creates and writes a grayscale BMP file. 5 6 Args: 7 filename: The name of the BMP file to me created. 8 9 pixels: A rectangular image stored as a sequence of rows. 10 Each row must be an iterable series of integers in the 11 range 0-255. 12 13 Raises: 14 ValueError: If any of the integer values are out of range. 15 OSError: If the file couldn't be written. 16 """ 17 height = len(pixels) 18 width = len(pixels[0]) 19 20 with open(filename, 'wb') as bmp: 21 #BMP Header 22 bmp.write(b'BM') 23 24 size_bookmark = bmp.tell() # The next four bytes hold the filesize as a 32-bit 25 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00') # little-endian integer. Zero placeholder for now. 26 27 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00') # Unused 16-bit integer - should be zero 28 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00') # Unused 16-bit integer - should be zero 29 30 pixel_offset_bookmark = bmp.tell() # The next four bytes hold the integer offset to the 31 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00') # pixel data. Zero placeholder for now. 32 33 # Image Header 34 bmp.write(b'\x28\x00\x00\x00') # Image header size in bytes - 40 decimal 35 bmp.write(_int32_to_bytes(width)) # Image width in pixels 36 bmp.write(_int32_to_bytes(height)) # Image height in pixels 37 bmp.write(b'\x01\x00') # Number of image planes 38 bmp.write(b'\x08\x00') # Bits per pixel 8 for grayscale 39 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00') # No compression 40 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00') # Zero for uncompressed images 41 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00') # Unused pixels per meter 42 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00') # Unused pixels per meter 43 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00') # Use whole color table 44 bmp.write(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00') # All colors are important 45 46 # Color palette - a linear grayscale 47 for c in range(256): 48 bmp.write(bytes((c,c,c,0))) # Blue, Green, Red, Zero 49 50 # Pixel data 51 pixel_data_bookmark = bmp.tell() 52 for row in reversed(pixels): # BMP files are bottom to top 53 row_data = bytes(row) 54 bmp.write(row_data) 55 padding = b'\x00' * ((4 - (len(row) % 4)) % 4) # Pad row to multiple of four bytes 56 bmp.write(padding) 57 58 # End of file 59 eof_bookmark = bmp.tell() 60 61 # Fill in file size placeholder 62 bmp.seek(size_bookmark) 63 bmp.write(_int32_to_bytes(eof_bookmark)) 64 65 # Fill in pixel offset placeholder 66 bmp.seek(pixel_offset_bookmark) 67 bmp.write(_int32_to_bytes(pixel_data_bookmark)) 68 69 def _int32_to_bytes(i): 70 """Convert an integer to four bytes in little-endian format.""" 71 72 # &: Bitwise-and 73 # >>: Right-shift 74 75 return bytes((i & 0xff, i >> 8 & 0xff, i >> 16 & 0xff, i >> 24 & 0xff))
fractal.py
1 """Gomputing Mandelbrot sets.""" 2 3 import math 4 5 def mandel(real, imag): 6 """The logarithm of number of iterations needed to 7 determine whether a complex point is in the 8 Mandelbrot set. 9 10 Args: 11 real: The real coordinate 12 imag: The imaginary coordinate 13 14 Returns: 15 An integer in the range 1-255. 16 """ 17 x = 0 18 y = 0 19 for i in range(1, 257): 20 if x*x + y*y > 4.0: 21 break 22 xt = real + x*x - y*y 23 y = imag + 2.0 * x * y 24 x = xt 25 return int(math.log(i) * 256 / math.log(256)) - 1 26 27 def mandelbrot(size_x, size_y): 28 """Make an Mandelbrot set image. 29 30 Args: 31 size_x: Image width 32 sixe_y: Image height 33 34 Returns: 35 A list of lists of integers in the range 0-255. 36 """ 37 return [[mandel((3.5 * x / size_x) - 2.5, (2.0 * y / size_y) -1.0) for x in range(size_x)] for y in range(size_y)]
执行:
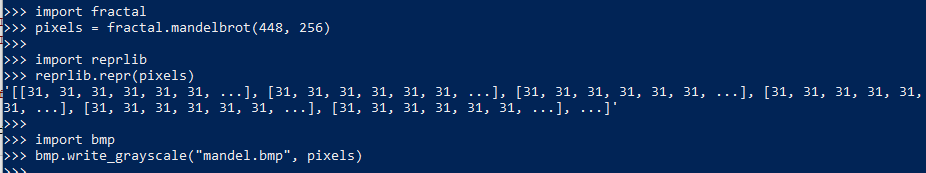
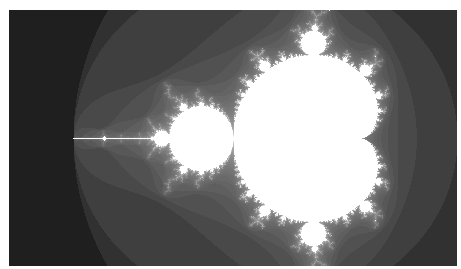
生成的bmp
add function in bmp.py to read from bmp file
1 def dimensions(filename): 2 """Determine the dimensions in pixels of a BMP image. 3 4 Args: 5 filename: The filename of a BMP file. 6 7 Returns: 8 A tuple containing two integers with the width 9 and height in pixels. 10 11 Raises: 12 ValueError: If the file was not a BMP file. 13 OSError: If there was a problem reading the file. 14 """ 15 with open(filename, 'rb') as f: 16 magic = f.read(2) 17 if magic != b'BM': 18 raise ValueError(f"{filename} is not a BMP file") 19 20 f.seek(18) 21 width_bytes = f.read(4) 22 height_bytes = f.read(4) 23 24 return (_bytes_to_int32(width_bytes), _bytes_to_int32(height_bytes)) 25 26 def _bytes_to_int32(b): 27 """Convert a bytes object containing four bytes into an integer.""" 28 return b[0] | (b[1] << 8) | (b[2] << 16) | (b[3] << 24)
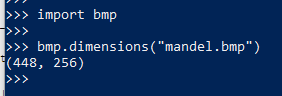
33.

1 >>> def words_per_line(flo): 2 ... return [len(line.split()) for line in flo.readlines()] 3 ... 4 >>> with open("wastedland.txt", mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') as real_file: 5 ... wpl = words_per_line(real_file) 6 ... 7 >>> wpl 8 [9, 8, 9, 9] 9 >>> 10 >>> type(real_file) 11 <class '_io.TextIOWrapper'> 12 >>> 13 >>> from urllib.request import urlopen 14 >>> with urlopen("http://sixty-north.com/c/t.txt") as web_file: 15 ... wpl = words_per_line(web_file) 16 ... 17 >>> wpl 18 [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 5, 5, 7, 8, 14, 12, 8] 19 >>> 20 >>> type(web_file) 21 <class 'http.client.HTTPResponse'> 22 >>>
34. Context Manager
1 """Demonstrate raiding a refrigerator.""" 2 3 from contextlib import closing 4 5 class RefrigeratorRaider: 6 """Raid a refrigerator""" 7 8 def open(self): 9 print("Open fridge door.") 10 11 def take(self, food): 12 print(f"Finding {food}...") 13 if food == 'deep fried pizza': 14 raise RuntimeError("Health warning!") 15 print(f"Taking {food}") 16 17 def close(self): 18 print("Close fridge door.") 19 20 def raid(food): 21 #r = RefrigeratorRaider() 22 with closing(RefrigeratorRaider()) as r: 23 r.open() 24 r.take(food) 25 #r.close()
保证冰箱总能被关闭
1 >>> from fridge import raid 2 >>> 3 >>> raid('bacon') 4 Open fridge door. 5 Finding bacon... 6 Taking bacon 7 Close fridge door. 8 >>> 9 >>> raid('deep fried pizza') 10 Open fridge door. 11 Finding deep fried pizza... 12 Close fridge door. 13 Traceback (most recent call last): 14 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 15 File "C:\luke\Learn\Python\fridge.py", line 24, in raid 16 r.take(food) 17 File "C:\luke\Learn\Python\fridge.py", line 14, in take 18 raise RuntimeError("Health warning!") 19 RuntimeError: Health warning! 20 >>>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号