线程池是什么
线程池简介
线程过多会带来额外的开销,其中包括创建销毁线程的开销、调度线程的开销等等,同时也降低了计算机的整体性能。
线程池(Thread Pool)是一种基于池化思想管理线程的工具,它维护多个线程。在线程池中,总有几个活跃线程。当需要使用线程来执行任务时,可以从池子中随便拿一个空闲线程来用,当完成工作时,该线程并不会死亡,而是再次返回线程池中成为空闲状态,等待执行下一个任务。
这种做法,一方面避免了处理任务时创建销毁线程开销的代价,另一方面避免了线程数量膨胀导致的过分调度问题,保证了对内核的充分利用。
线程池创建核心参数
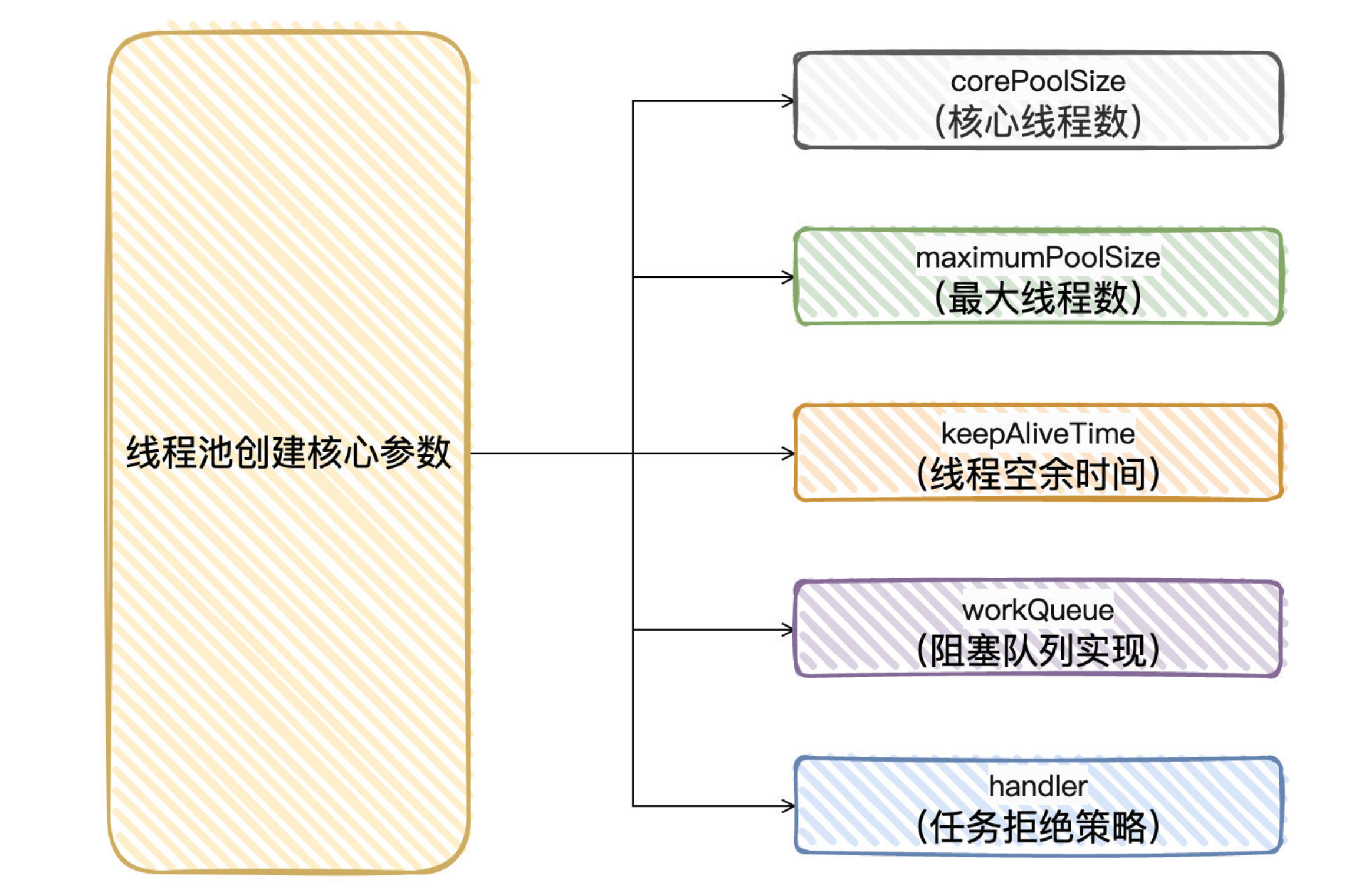
线程池的工作流程
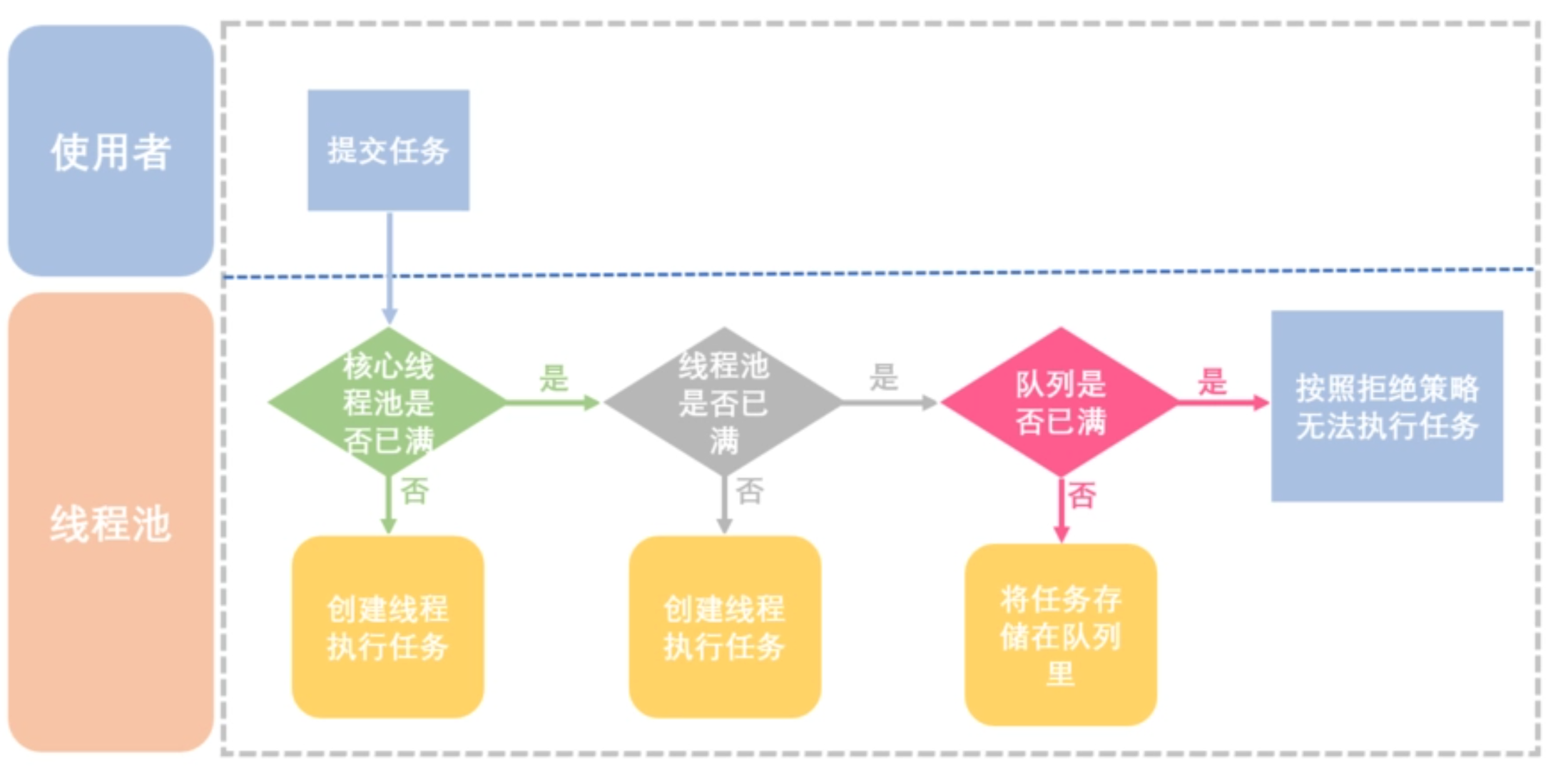
- 默认情况下,创建完线程池后并不会立即创建线程, 而是等到有任务提交时才会创建线程来进行处理。(除非调用prestartCoreThread或prestartAllCoreThreads方法)
- 当线程数小于核心线程数时,每提交一个任务就创建一个线程来执行,即使当前有线程处于空闲状态,直到当前线程数达到核心线程数。
- 当前线程数达到核心线程数时,如果这个时候还提交任务,这些任务会被放到工作队列里,等到线程处理完了手头的任务后,会来工作队列中取任务处理。
- 当前线程数达到核心线程数并且工作队列也满了,如果这个时候还提交任务,则会继续创建线程来处理,直到线程数达到最大线程数。
- 当前线程数达到最大线程数并且队列也满了,如果这个时候还提交任务,则会触发饱和策略。
- 如果某个线程的控线时间超过了keepAliveTime,那么将被标记为可回收的,并且当前线程池的当前大小超过了核心线程数时,这个线程将被终止。
饱和策略(拒绝策略)
当有界队列被填满后,饱和策略开始发挥作用。
- AbortPolicy:中止策略。默认的饱和策略,抛出未检查的RejectedExecutionException。调用者可以捕获这个异常,然后根据需求编写自己的处理代码。
- DiscardPolicy:抛弃策略。当新提交的任务无法保存到队列中等待执行时,该策略会悄悄抛弃该任务。
- DiscardOldestPolicy:抛弃最旧的策略。当新提交的任务无法保存到队列中等待执行时,则会抛弃下一个将被执行的任务,然后尝试重新提交新的任务。
- CallerRunsPolicy:调用者运行策略。该策略实现了一种调节机制,该策略既不会抛弃任务,也不会抛出异常,而是将某些任务回退到调用者(调用线程池执行任务的主线程)。它不会在线程池的某个线程中执行新提交的任务,而是在一个调用了execute的线程中执行该任务。当线程池的所有线程都被占用,并且工作队列被填满后,下一个任务会在调用execute时在主线程中执行(调用线程池执行任务的主线程)。
总体设计
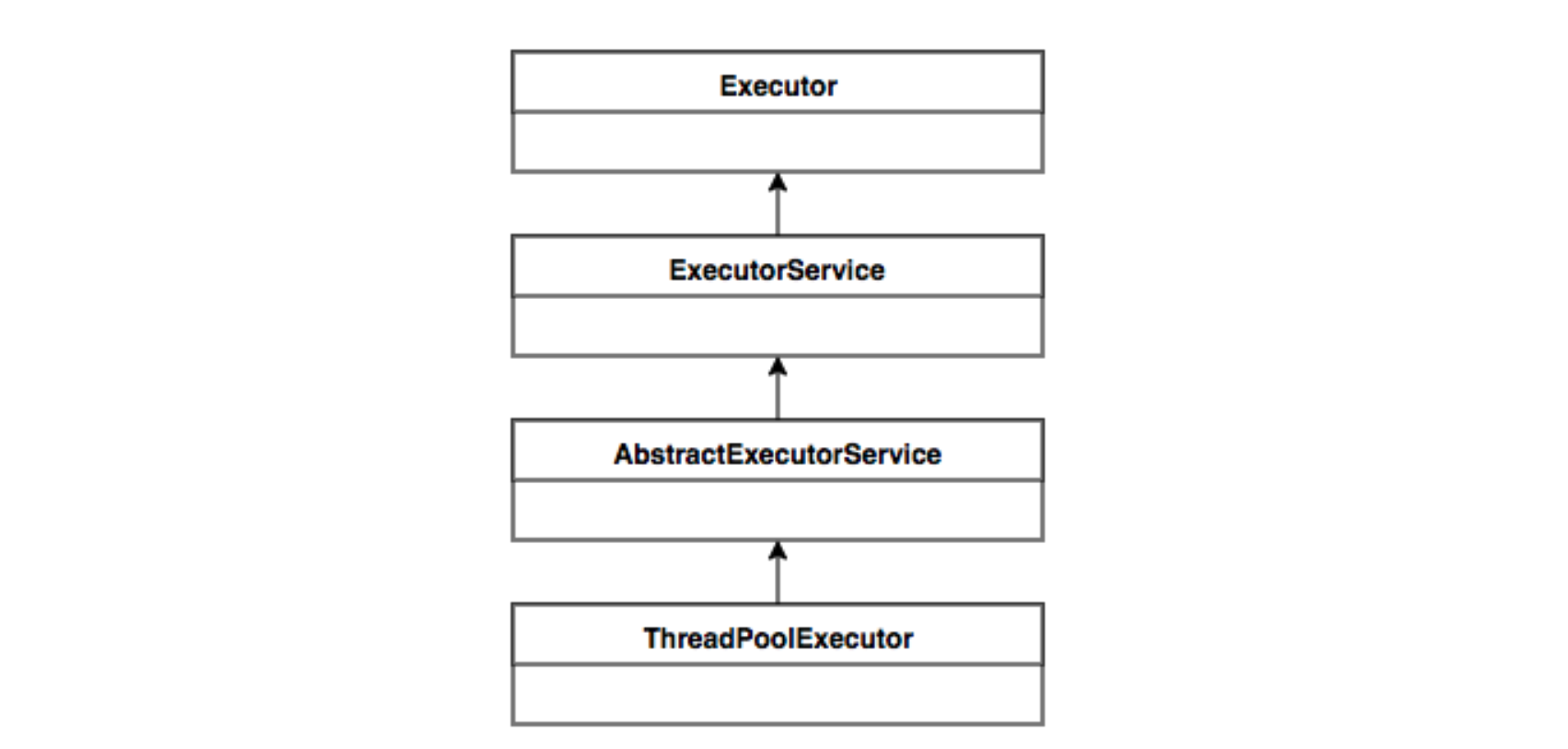
Java中的线程池核心实现类是ThreadPoolExecutor。
ThreadPoolExecutor的继承关系:
ThreadPoolExecutor运行机制:
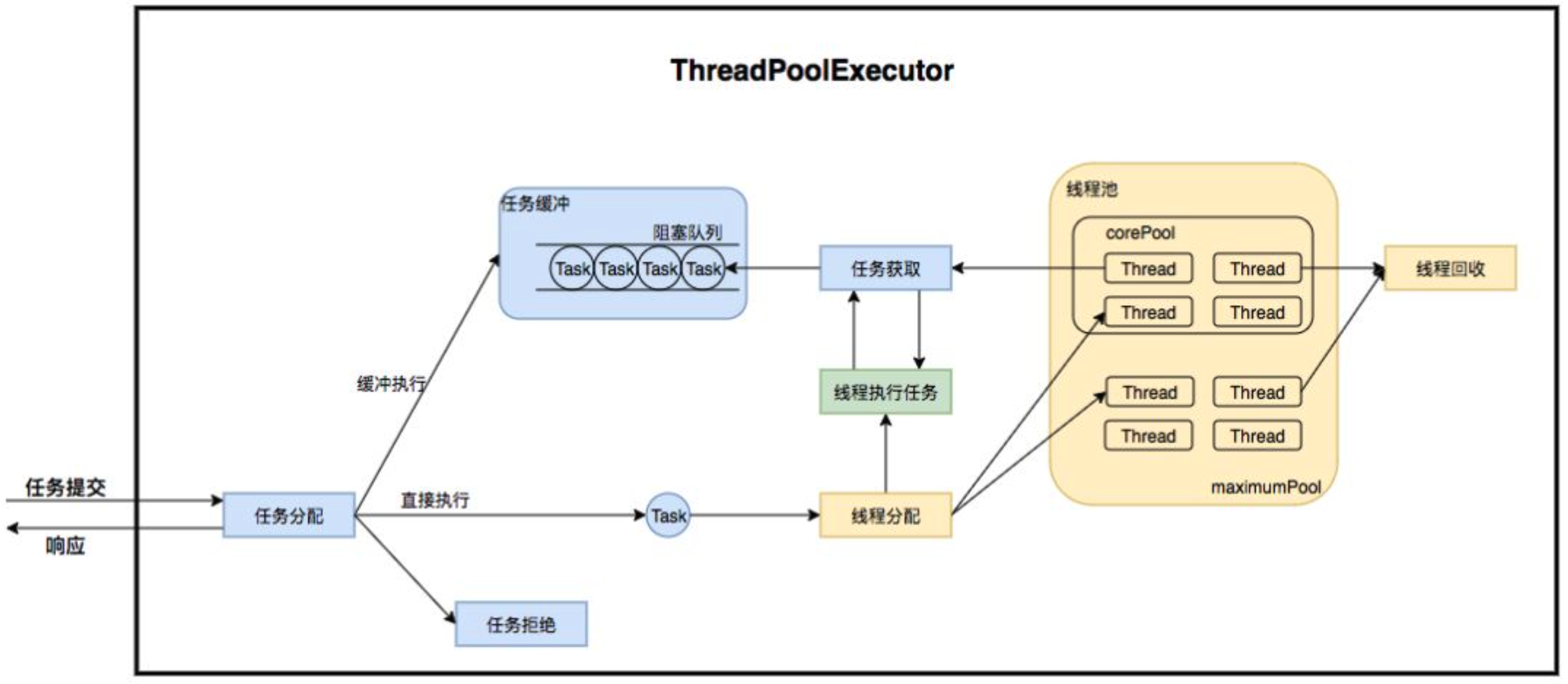
线程池在内部实际上构建了一个生产者消费者模型,将线程和任务两者解耦,并不直接关联,从而良好的缓冲任务,复用线程。
线程池的运行主要分成两部分:任务管理、线程管理。
- 任务管理部分充当生产者的角色,当任务提交后,线程池会判断该任务后续的流转:(1)直接申请线程执行该任务;(2)缓冲到队列中等待线程执行;(3)拒绝该任务。
- 线程管理部分是消费者,它们被统一维护在线程池内,根据任务请求进行线程的分配,当线程执行完任务后则会继续获取新的任务去执行,最终当线程获取不到任务的时候,线程就会被回收。
线程池实现例子
ThreadPool接口
public interface ThreadPool {
//提交任务到线程池
void execute(Runnable runnable);
//关闭线程池
void shutdown();
//获取线程池的初始化大小
int getInitSize();
//获取线程池的核心线程数量
int getCoreSize();
//获取线程池的最大线程数量
int getMaxSize();
//获取线程池中用于缓存任务队列的大小
int getQueueSize();
//获取线程池中活跃的线程的数量
int getActiveCount();
//查看线程池是否已经被shutdown
boolean isShutdown();
}
ThreadFactory接口
/**
* 创建个性化线程
*
* ThreadFactory提供创建线程的接口,以便个性化定制Thread,比如Thread应该被加入到哪个
* Thread Group中,优先级、线程名称,以及是否为守护线程等
**/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ThreadFactory {
Thread createThread(Runnable runnable);
}
RunnableQueue接口
/**
* 线程队列基本操作
*
* RunnableQueue主要用于存放提交的Runnable
* 该Runnable是一个BlockedQueue,并且有limit限制
**/
public interface RunnableQueue {
//当有新的任务进来时首先会offer到队列中
void offer(Runnable runnable);
//工作线程通过take方法获取Runnable
Runnable take() throws InterruptedException;
//获取任务队列中任务的数量
int size();
}
DenyPolicy接口
/**
* 线程池满时拒绝策略
**/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface DenyPolicy {
void reject(Runnable runnable,ThreadPool threadPool);
//该拒绝策略会直接将任务丢弃
class DiscardDenyPolicy implements DenyPolicy
{
@Override
public void reject(Runnable runnable,ThreadPool threadPool)
{
//do nothing
}
}
//该拒绝策略向任务提交者抛出异常
class AbortDenyPolicy implements DenyPolicy
{
@Override
public void reject(Runnable runnable,ThreadPool threadPool)
{
throw new RuntimeException("The runnable "+runnable+" will be abort.");
}
}
//该拒绝策略会使任务在提交者所在的线程中执行任务
class RunnerDenyPolicy implements DenyPolicy
{
@Override
public void reject(Runnable runnable,ThreadPool threadPool)
{
if(!threadPool.isShutdown())
{
runnable.run();
}
}
}
}
InternalTask
/**
* 不断从runnableQueue中取出Runnable并执行任务
**/
public class InternalTask implements Runnable{
private final RunnableQueue runnableQueue;
private volatile boolean running=true;
public InternalTask(RunnableQueue runnableQueue){
this.runnableQueue=runnableQueue;
}
@Override
public void run()
{
//如果当前任务为running且没有被中断,则将其不断地从queue中获取runnable,然后执行run
while(running && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted())
{
try
{
Runnable task=runnableQueue.take();
task.run();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
running=false;
break;
}
}
}
//停止当前任务,主要会在线程池的shutdown方法中使用
public void stop()
{
this.running=false;
}
}
LinkedRunnableQueue
/**
* 双向循环链表实现线程任务队列基本操作
**/
public class LinkedRunnableQueue implements RunnableQueue{
//任务队列的最大容量,在构造时传入
private final int limit;
//若任务队列中的任务已经满了,则需要执行拒绝策略
private final DenyPolicy denyPolicy;
//存放任务的队列
private final LinkedList<Runnable> runnableList = new LinkedList<>();
private final ThreadPool threadPool;
public LinkedRunnableQueue(int limit, DenyPolicy denyPolicy, ThreadPool threadPool) {
this.limit = limit;
this.denyPolicy = denyPolicy;
this.threadPool = threadPool;
}
@Override
public void offer(Runnable runnable) {
synchronized (runnableList){
if (runnableList.size()>=limit){
//无法容纳新的任务时执行拒绝策略
denyPolicy.reject(runnable,threadPool);
}else {
//将任务加入到队尾,并且唤醒阻塞中的线程
runnableList.addLast(runnable);
runnableList.notifyAll();
}
}
}
@Override
public Runnable take() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (runnableList){
while (runnableList.isEmpty()){
try {
//如果任务队列没有可执行任务,则当前线程会挂起,
//进入runnableList关联的monitor set中等待唤醒
runnableList.wait();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
//被中断时将异常抛出
throw e;
}
}
return runnableList.removeFirst();
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
synchronized (runnableList){
//返回当前任务队列的任务数
return runnableList.size();
}
}
}
RunnableDenyException
/**
* 错误抛出
*
* RunnableDenyException是RuntimeException的子类,主要通知人物提交者,任务队列
* 无法再接收新的任务
**/
public class RunnableDenyException extends RuntimeException{
public RunnableDenyException(String message)
{
super(message);
}
}
BasicThreadPool
/**
* 实现ThreadPool
*
* 线程池的初始化:数量控制属性、创建线程工厂、任务队列策略等功能
**/
public class BasicThreadPool extends Thread implements ThreadPool{
//初始化线程数量
private final int initSize;
//线程池最大线程数量
private final int maxSize;
//线程池核心线程数量
private final int coreSize;
//当前活跃的线程数量
private int activeCount;
//创建线程所需的工厂
private final ThreadFactory threadFactory;
//任务队列
private final RunnableQueue runnableQueue;
//线程池是否已经被shutdown
private volatile boolean isShutdown = false;
//工作线程队列
private final Queue<ThreadTask> threadQueue = new ArrayDeque<>();
private static final DenyPolicy DEFAULT_DENY_POLICY = new DenyPolicy.DiscardDenyPolicy();
private static final ThreadFactory DEFAULT_THREAD_FACTORY = new DefaultThreadFactory();
private final long keepAliveTime;
private final TimeUnit timeUnit;
//构造线程时传参
public BasicThreadPool(int initSize,int maxSize,int coreSize,int queueSize){
this(initSize,maxSize,coreSize,DEFAULT_THREAD_FACTORY,queueSize, DEFAULT_DENY_POLICY,10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
public BasicThreadPool(int initSize, int maxSize, int coreSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory,
int queueSize,DenyPolicy denyPolicy,
long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
this.initSize = initSize;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.runnableQueue = new LinkedRunnableQueue(queueSize,denyPolicy,this);
this.keepAliveTime = keepAliveTime;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.init();
}
//初始化时,先创建initSize个线程
private void init(){
start();
for (int i = 0; i < initSize; i++){
newThread();
}
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable runnable) {
if (this.isShutdown){
throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy");
}
//提交任务只是简单第往任务队列中插入Runnable
this.runnableQueue.offer(runnable);
}
private void newThread(){
//创建任务线程并且启动
InternalTask internalTask=new InternalTask(runnableQueue);
Thread thread=this.threadFactory.createThread(internalTask);
ThreadTask threadTask=new ThreadTask(thread,internalTask);
threadQueue.offer(threadTask);
this.activeCount++;
thread.start();
}
private void removeThread(){
//从线程池移除某个线程
ThreadTask threadTask=threadQueue.remove();
threadTask.internalTask.stop();
this.activeCount--;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//run方法继承自Thread,主要用于维护线程数量,比如扩容,回收
while (!isShutdown && !isInterrupted()){
try {
timeUnit.sleep(keepAliveTime);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
isShutdown=true;
break;
}
synchronized (this){
if (isShutdown){
break;
}
//当前队列中有任务尚未处理,并且activeCount<coreSize则继续扩容
if (runnableQueue.size()>0&&activeCount<coreSize){
for (int i=initSize;i<coreSize;i++){
newThread();
}
//continue的目的在于不想让线程的扩容直接达到maxSize
continue;
}
//当前队列中有任务尚未处理,并且activeCount<maxSize则继续扩容
if (runnableQueue.size()>0&&activeCount<maxSize){
for (int i=coreSize;i<maxSize;i++){
newThread();
}
}
//如果任务队列中没有任务,则需要回收,回收至coreSize即可
if (runnableQueue.size()==0&&activeCount>coreSize){
for (int i=coreSize;i<activeCount;i++){
removeThread();
}
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void shutdown() {
synchronized (this){
if (isShutdown)return;
isShutdown=true;
threadQueue.forEach(threadTask -> {
threadTask.internalTask.stop();
threadTask.thread.interrupt();
});
this.interrupt();
}
}
@Override
public int getInitSize() {
if (isShutdown)
throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy");
return this.initSize;
}
@Override
public int getCoreSize() {
if (isShutdown)
throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy");
return this.coreSize;
}
@Override
public int getQueueSize() {
if (isShutdown)
throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy");
return runnableQueue.size();
}
@Override
public int getMaxSize() {
if (isShutdown)
throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy");
return this.maxSize;
}
@Override
public int getActiveCount() {
if (isShutdown)
throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy");
return this.activeCount;
}
@Override
public boolean isShutdown() {
return this.isShutdown;
}
private static class ThreadTask{
Thread thread;
InternalTask internalTask;
public ThreadTask(Thread thread, InternalTask internalTask) {
this.thread = thread;
this.internalTask = internalTask;
}
}
private static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory{
private static final AtomicInteger group_counter=new AtomicInteger(1);
private static final ThreadGroup group =
new ThreadGroup("myGroup-"+group_counter.getAndDecrement());
public static final AtomicInteger COUNTER =new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread createThread(Runnable runnable) {
return new Thread(group,runnable,"thread-poll-"+COUNTER.getAndDecrement());
}
}
}
测试线程池
/**
* 一个简单的程序分别测试线程池的任务提交、线程池线程数量的动态扩展,以及线程池的销毁功能
*/
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//定义线程池,初始化程数为2,核心或程数为4,最大程数为6.任务队列最多允许1000个任务
final ThreadPool threadPool=new BasicThreadPool(2,6,4,1000);
//定义20个任务并且提交蛤线程池
for (int i=0;i<20;i++){
threadPool.execute(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" is" +
" running and done.");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
for (; ; ){
//不断输出线程池的信息
System.out.println("getActiveCount = "+threadPool.getActiveCount());
System.out.println("getQueueSize = "+threadPool.getQueueSize());
System.out.println("getCoreSize = "+threadPool.getCoreSize());
System.out.println("getMaxSize = "+threadPool.getMaxSize());
System.out.println("==========================================");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
}
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix