回溯算法:递增子序列
491. 递增子序列
给定一个整型数组, 你的任务是找到所有该数组的递增子序列,递增子序列的长度至少是 2 。
输入:[4, 6, 7, 7]
输出:[[4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 6, 7], [4, 6, 7, 7], [6, 7], [6, 7, 7], [7,7], [4,7,7]]
思路
在 90. 子集 II 是通过排序,再加一个标记数组来达到去重的目的。而本题求自增子序列,是不能对原数组进行排序的,排完序的数组都是自增子序列了。
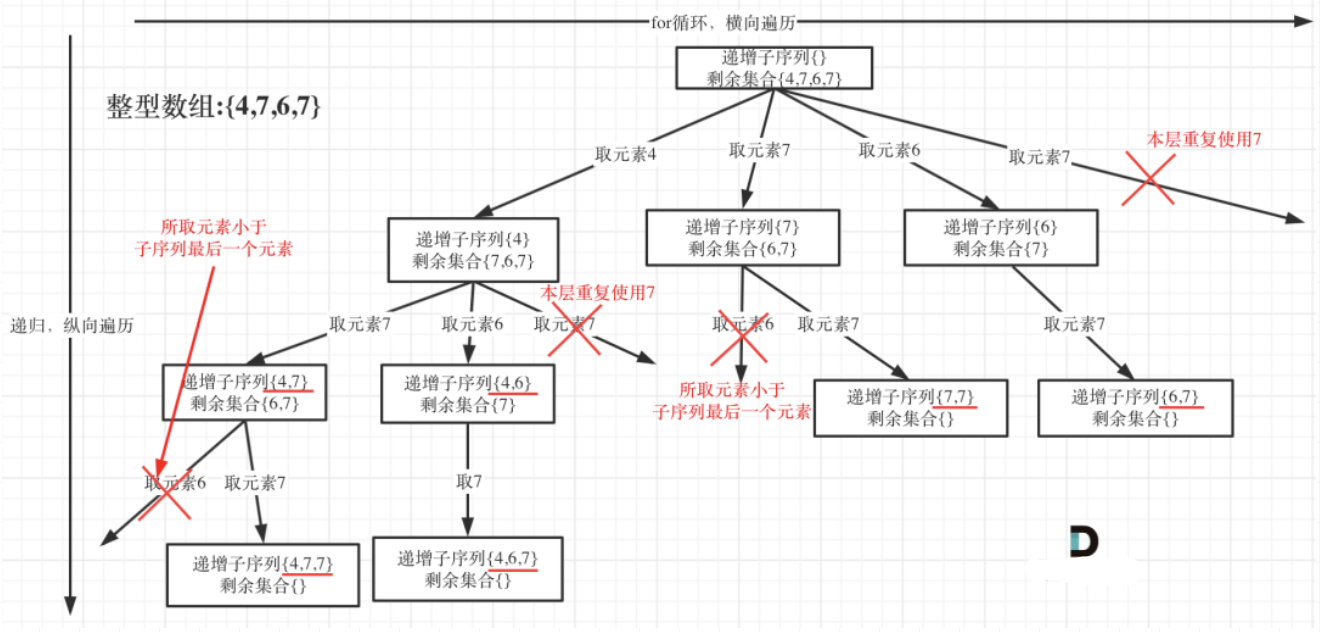
回溯三部曲
1.递归函数参数
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
private void backtracking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {}
2.终止条件
- 可以不加终止条件,startIndex每次都会加1,并不会无限递归
- 题目要求递增子序列大小至少为2
3.单层搜索逻辑
- 本题只要同层重复使用元素,递增子序列就会重复
- 如果选取的元素小于子序列最后一个元素,那么就不是递增的,需要去掉
去重的逻辑代码:
if ((!temp.isEmpty() && nums[i] < temp.get(temp.size()-1))
|| uset.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
代码
class Solution {
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
backtracking(nums,0);
return ans;
}
private void backtracking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {
if(temp.size() >=2) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(temp)); // 收集子集
// 注意这里不要加return,因为要取树上的所有节点
}
HashSet<Integer> uset = new HashSet<>(); // 使用set对本层元素进行去重
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
if ((!temp.isEmpty() && nums[i] < temp.get(temp.size()-1))
|| uset.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
uset.add(nums[i]); // 记录这个元素在本层用过了,本层后面不能再用了
temp.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
temp.remove(temp.size()-1);
}
}
}





