CICD05 Jenkins流水线, 代码质量检查sonarqube ubuntu使用
3.2.3.5 Pipeline 简单案例
#范例: 脚本式 node { stage('Get code') { echo '获取代码' //git clone } stage('Build') { echo '构建项目代码' } stage('Test') { echo '测试项目功能' } stage('Deploy') { echo '部署项目' } } #范例: 声明式 pipeline { agent any stages { stage('获取代码') { steps { echo '获取代码' } } stage('构建代码') { steps { echo '构建项目代码' } } stage('代码测试') { steps { echo '测试项目功能' } } stage('项目部署') { steps { echo '部署项目' } } } }
安装 Pipeline 插件 (不装也能创流水线任务, 执行任务时可能会报错 )
Pipeline Stage View 插件 (执行任务,右侧直接显示执行过程,阶段视图)
#jenkins创建流水线任务 #流水线下有流水线语法,点进去,可以自动生成语句,左侧可调出环境变量 #流水线输入代码 pipeline { agent any #应用在任意主机上 stages { stage('获取代码') { #构建任务阶段 steps { echo '获取代码' } } stage('构建代码') { steps { echo '构建项目代码' } } stage('代码测试') { steps { echo '测试项目功能' } } stage('项目部署') { steps { echo '部署项目' } } } } #点保存,构建任务 #可以点击左侧 从指定阶段重新运行,可以选择阶段开始,不用从头开始执行,方便调试 #左侧 打开Blue Ocean,可以看到每个阶段状态,也可选阶段执行,如果没有先点上方整体重新运行 #某个构建任务下,左侧回放,相当于临时修改代码调试,代码不保存
3.2.7.1 案例:基本语法
steps 内部的命令,每一条单独的命令都在当前任务的工作目录下执行。
pipeline { environment { APP = "testapp" } agent any stages { stage ('cmd test') { steps { echo '命令测试' sh 'pwd' sh 'rm -rf *' sh 'mkdir testdir1' sh 'cd testdir1 && pwd && mkdir testdir2 && cd testdir2 && pwd' sh 'pwd && tree' #pwd还是在初始目录下,上面的命令不影响这行 sh 'echo $WORKSPACE' sh 'echo $JOB_NAME' sh 'mkdir $WORKSPACE/$JOB_NAME' sh 'touch $WORKSPACE/$JOB_NAME/${APP}.log' sh 'pwd && tree' } } } }
Jenkins环境变量可分为内置变量和用户自定义变量两类
引用全局环境变量格式有三种:
#注:sh里不属于pipeline语法,不支持这些变量定义 ${env.<ENV_VAR_NAME>} $env.<ENV_VAR_NAME> $<ENV_VAR_NAME> ${ENV_VAR_NAME} #注意:变量引用有时要加双引号引起来,如:"${env.<ENV_VAR_NAME>}"
范例:声明和使用变量
pipeline { agent any environment { NAME = "wangxiaochun" } stages { stage('declare var') { steps { script { #把who|wc -l 赋值给LOGIN变量 env.LOGIN=sh(returnStdout: true, script: "who|wc -l") } } } stage('get var') { steps { echo "NAME=${NAME}" echo "LOGIN=${LOGIN}" } } } }
范例:spring-boot-helloworld 完整案例(推荐)
#说明:环境准备 #提前在部署目标服务器上创建目录 mkdir -p /data/appdir #提前在Manage Jenkins-tools-Maven安装中创建maven-3.6.3 pipeline { agent any //修改git地址和jenkins用的凭据,APP_PATH部署的路径(目标机器建目录) environment { REPO="git@gitlab.wang.org:example1/spring-boot-helloworld.git" CREDENTIAL="gitlab-root-private-key" APP="spring-boot-helloworld" APP_PATH="/data/appdir" } tools { //jenkins系统管理/全局工具配置的Maven(可jenkins安装,也可配自己安装的) maven 'maven-3.6.3' } stages { stage('code clone') { steps { git branch: 'main', credentialsId: "${CREDENTIAL}" ,url: "${REPO}" } } stage('Build') { steps { //sh 'mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true' sh 'mvn -B -DskipTests clean package' } } stage('Test') { steps { sh 'mvn test' } } stage("停止spring boot服务"){ steps { sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.153 "killall -0 java && killall -9 java|| true"' sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.154 "killall -0 java && killall -9 java || true"' } } stage("代码复制"){ steps { sh "scp target/${APP}-*-SNAPSHOT.jar root@10.0.0.153:${APP_PATH}" sh "scp target/${APP}-*-SNAPSHOT.jar root@10.0.0.154:${APP_PATH}" } } stage("启动spring boot服务"){ steps { sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.153 "nohup java -jar ${APP_PATH}/${APP}-*.jar --server.port=8888 &>/dev/null & "' sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.154 "nohup java -jar ${APP_PATH}/${APP}-*.jar --server.port=8888 &>/dev/null & "' } } } }
3.2.7.3 案例:使用凭据 Credential
1.Username with password #用户名和密码使用变量名可自行指定,Jenkins都会通过credentialsID从指定的凭证提取出来用户名和密码并赋值给指定对应的变量 withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsID: '<ID>', usernameVariable: '<variable to hold username>', passwordVariable: '<variable to hold password>')]) 2.SSH密钥 withCredentials(sshUserPrivateKey(credentialsId: '<credentials-id>’, keyFileVariable: 'MYKEYFILE' passphraseVariable: 'PASSPHRASE’, usernameVariable: USERNAME')]) { // some block }
范例:构建和推送Docker镜像
#确保docker信任harbor,docker info查看Insecure Registries是否信任harbor网址 pipeline { agent any tools { maven 'maven-3.6.3' } environment { codeRepo="http://gitlab.wang.org/example1/spring-boot-helloworld.git" credential="gitlab-root-password" harborServer='harbor.wang.org' projectName='spring-boot-helloworld' imageUrl="${harborServer}/example/${projectName}" imageTag="${BUILD_ID}" harborUserName="admin" harborPassword="123456" } stages { stage('Source') { steps { git branch: 'main', credentialsId: "${credential}", url: "${codeRepo}" } } stage('Build') { steps { sh 'mvn -B -DskipTests clean package' } } stage('Test') { steps { //注意:不要修改hello()函数,否则会导致下面失败 sh 'mvn test' } } stage('Build Docker Image') { steps { sh 'docker build . -t "${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' } } stage('Push Docker Image') { steps { sh "echo ${harborPassword} | docker login -u ${harborUserName} --password-stdin ${harborServer}" //sh "docker login -u ${harborUserName} -p ${harborPassword} ${harborServer}" sh "docker push ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" } } stage('Run Docker ') { steps { //sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.153 "docker rm -f ${projectName} ; docker run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' //sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.154 "docker rm -f ${projectName} ; docker run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' sh "docker -H 10.0.0.153 rm -f ${projectName} ; docker -H 10.0.0.153 run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" sh "docker -H 10.0.0.154 rm -f ${projectName} ; docker -H 10.0.0.154 run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" } } } }
范例:基于凭据实现构建和推送Docker镜像
pipeline { agent any tools { maven 'maven-3.6.3' } environment { codeRepo="http://gitlab.wang.org/example1/spring-boot-helloworld.git" credential="gitlab-root-password" harborServer='harbor.wang.org' projectName='spring-boot-helloworld' imageUrl="${harborServer}/example/${projectName}" imageTag="${BUILD_ID}" //harborUserName="admin" //harborPassword="123456" } stages { stage('Source') { steps { git branch: 'main', credentialsId: "${credential}", url: "${codeRepo}" } } stage('Build') { steps { sh 'mvn -B -DskipTests clean package' } } stage('Test') { steps { //注意:不要修改hello()函数,否则会导致下面失败 sh 'mvn test' } } stage('Build Docker Image') { steps { sh 'docker build . -t "${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' } } stage('Push Docker Image') { steps { withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'harbor-xiaoming-password', \ passwordVariable: 'harborPassword', usernameVariable: 'harborUserName')]) { sh "echo ${harborPassword} | docker login -u ${env.harborUserName} --password-stdin ${harborServer}" //sh "docker login -u ${env.harborUserName} -p ${harborPassword} ${harborServer}" sh "docker push ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" echo "username=${env.harborUserName}" echo "password=${harborPassword}" //打印不出密码 } } } stage('Run Docker ') { steps { //sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.153 "docker rm -f ${projectName} ; docker run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' //sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.154 "docker rm -f ${projectName} ; docker run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' sh "docker -H 10.0.0.153 rm -f ${projectName} ; docker -H 10.0.0.153 run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" sh "docker -H 10.0.0.154 rm -f ${projectName} ; docker -H 10.0.0.154 run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" } } } }
Jenkinsfile放在gitlab项目中, 优点: 可以跟着版本走, 有些公司是开发写的
#把pipeline代码写入Jenkinsfile文件中,把该文件放入gitlab项目中 #jenkins流水线项目,流水线定义选pipeline script from SCM #SCM选git,输入仓库,凭据,分支 #脚本路径 Jenkinsfile (这里没写路径代表项目根目录下)
相当于自由风格中的参数化构建
注意:第一个执行PipleLine没有Build with Parameters的提示,会用默认值, 第二次执行才会出现
pipeline { agent any parameters { string(name: 'PERSON', defaultValue: 'Mr Jenkins', description: 'Who should I say hello to?') text(name: 'BIOGRAPHY', defaultValue: '', description: 'Enter some information about the person') booleanParam(name: 'TOGGLE', defaultValue: true, description: 'Toggle this value') choice(name: 'CHOICE', choices: ['One', 'Two', 'Three'], description: 'Pick something') password(name: 'PASSWORD', defaultValue: 'SECRET', description: 'Enter a password') } stages { stage('Example') { steps { echo "Hello ${params.PERSON}" echo "Biography: ${params.BIOGRAPHY}" echo "Toggle: ${params.TOGGLE}" echo "Choice: ${params.CHOICE}" echo "Password: ${params.PASSWORD}" } } } }
input 指令支持中断当前任务,以待确认和取消
pipeline { agent any stages { stage('Example') { steps { script { def userInput = input(submitterParameter: "approver", id: "approve", message: "Provide your approval to proceed", parameters: [string(defaultValue: "approved", description: 'Please provide the message why you are approving', name: 'remarks')]) echo "Remarks:${userInput['remarks']}" echo "It was ${userInput.approver} who approved this job" } } } } }
对于pipeline来说,使用if语句或者try语句,或者when来进行条件的流程控制,这两种方式效果相似
when是用在stage段中的指令,用于限定当前stage的运行条件
pipeline { agent any parameters { booleanParam(name:'pushImage', defaultValue: 'true', description: 'Push Image to Harbor?') } tools { maven 'maven-3.8.6' } environment { codeRepo="http://gitlab.wang.org/root/spring-boot-helloWorld.git" harborServer='harbor.wang.org' projectName='spring-boot-helloworld' imageUrl="${harborServer}/example/${projectName}" imageTag='latest' } stages { stage('Source') { steps { git branch: 'main', credentialsId: 'gitlab-root-credential', url: "${codeRepo}" } } stage('Build') { steps { sh 'mvn -B -DskipTests clean package' } } stage('Test') { steps { sh 'mvn test' } } stage('Build Docker Image') { steps { sh 'docker image build . -t "${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' } } stage('Push Docker Image') { agent any when { expression { params.pushImage } // expression { "${params.pushImage}" == 'true' } //beforeAgent: true } steps { // input(message: 'continue?') withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'harbor-user-credential', passwordVariable: 'harborPassword', usernameVariable: 'harborUserName')]) { sh "echo ${harborPassword} | docker login -u ${env.harborUserName} --password-stdin ${harborServer}" sh "docker image push ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" } } } } }
声明性Parallel的代码块中的可以嵌套多个stage,从而让多个stage任务并行执行。
jenkins左侧 打开blue ocean才能看到效果
pipeline { agent any stages { stage( 'Deploy') { parallel { stage('deploy_proxy'){ steps { echo "部署反向代理服务" } } stage('deploy app1') { steps { echo "部署deploy_app1应用" } } stage ('deploy app2'){ stages { stage ('delete container') { steps { echo "删除旧容器" } } stage('start container') { steps { echo "启动新容器" } } } } } } } }
3.2.7.8 案例:触发器
#注意:第一次需要手动执行,后续才能生效 pipeline { agent any tools { maven 'maven-3.8.6' } triggers { gitlab(triggerOnPush: true, acceptMergeRequestOnSuccess: true, //合并请求 //triggerOnMergeRequest: true, branchFilterType: 'All', //所有分支 secretToken: '62dad2cd1d9ae62686ada8dc4cdOae66') } parameters { booleanParam(name: "PUSH", defaultValue: true) environment { GitRepo="http://gitlab.wang.org/ops/spring-boot-helloWorld.git HarborServer='harbor.wang.org' ImageUrl="example/spring-boot-helloworld ImageTag="latest" stages { stage('Source'){ steps { git branch: 'main', url: "${GitRepo}" } } ....... } }
范例:通过 Gitlab 插件实现
#第一次构建后,再次进入会显示对应的配置 pipeline { agent any parameters { booleanParam(name:'pushImage', defaultValue: 'true', description: 'Push Image to Harbor?') } tools { maven 'maven-3.8.6' } triggers { gitlab(triggerOnPush: true, acceptMergeRequestOnSuccess: true, triggerOnMergeRequest: true, branchFilterType: 'All', addVoteOnMergeRequest: true, secretToken: '62dad2cd1d9ae62686ada8dc4cdOae66') } environment { codeRepo="http://gitlab.wang.org/devops/spring-boot-helloWorld.git" harborServer='harbor.wang.org' projectName='spring-boot-helloworld' imageUrl="${harborServer}/example/${projectName}" imageTag="${BUILD_ID}" } stages { stage('Source') { steps { git branch: 'main', credentialsId: 'gitlab-root-credential', url: "${codeRepo}" } } stage('Build') { steps { sh 'mvn -B -DskipTests clean package' } } stage('Test') { steps { sh 'mvn test' } } stage('Build Docker Image') { steps { sh 'docker image build . -t "${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' } } stage('Push Docker Image') { agent any when { expression { params.pushImage == 'true' } beforeAgent: true } steps { // input(message: 'continue?') withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'harbor-user-credential', passwordVariable: 'harborUserPassword', usernameVariable: 'harborUserName')]) { sh "echo ${harborUserPassword} | docker login -u ${env.harborUserName} --password-stdin ${harborServer}" sh "docker image push ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" } } } } }
流水线也提供了构建后的动作,常可用于消息通知
#在stages同级别的位置,添加一个post配置段 post { always { echo '任执行结束后执行此操作' } } #例如 ... post { always { //成功失败都执行 mail to: 'root@wangxiaochun.com', subject: "Status of pipeline: ${currentBuild.fullDisplayName}", body: "${env.BUILD_URL} has result ${currentBuild.result}" } } } #范例:综合案例,成功发邮件,失败发企业微信 pipeline { agent any parameters { booleanParam(name:'pushImage', defaultValue: 'true', description: 'Push Image to Harbor?') } tools { maven 'maven-3.6.3' } stages { stage('Source') { steps { echo "source" } } stage('Build') { steps { echo "Build" } } stage('Build Docker Image') { steps { echo "Build Docker image" } } stage('Push Docker Image') { agent any when { expression { "${params.pushImage}" == 'true' } } steps { echo "Push" } } stage('Run Docker ') { steps { echo "run docker" } } } post { success { mail to: 'root@wangxiaochun.com', subject: "Status of pipeline: ${currentBuild.fullDisplayName}", body: "${env.BUILD_URL} has result ${currentBuild.result}" } failure{ qyWechatNotification failNotify: true, webhookUrl: 'https://qyapi.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/webhook/send?key=1a4e1e74-e7d6-4376-99f6-048b01a7b7fc' } } }
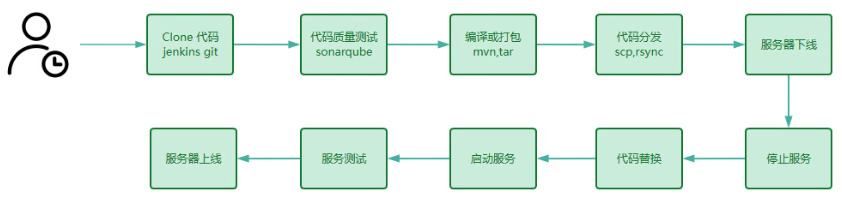
4.1.3 架构和集成
4.1.3.1 SonarQube 架构
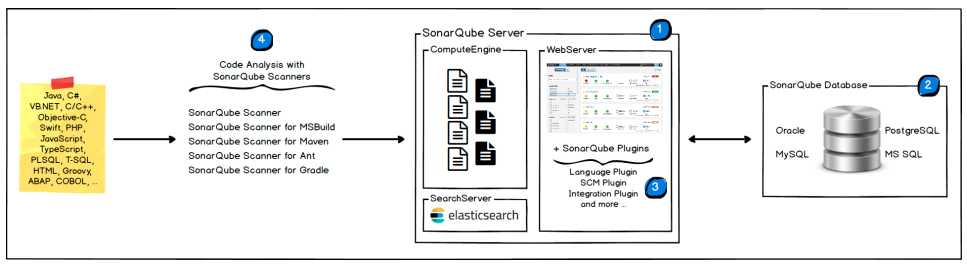
1.SonarQube Server 包括三个主要部分 Web Server: UI 界面 Search Server :为UI提供搜索功能,基于 ElasticSearch 实现 Compute Engine Server:处理代码分析报告,并将之存储到 SonarQube Database 2.SonarQube Database: 负责存储 SonarQube 的配置,以及项目的质量快照等 #下面2个属于客户端 3.SonarQube Plugin: 开发语言工具idea上可以安装该插件,发送数据给 SonarQube Server 4.Code analysis Scanners: 代码扫描器,是SonarQube Server的客户端, 将代码扫描后得出报告提交给 SonarQube Server
SonarQube 分为: 社区版,开发版,企业版和数据中心版
其中只有社区版是开源免费的
#SonarQube 分两种版本: LTS 和非 LTS 版 #官方LTS版本说明 https://www.sonarqube.org/downloads/lts/ #各种版本下载 https://www.sonarsource.com/products/sonarqube/downloads/historical-downloads/ https://www.sonarqube.org/downloads/ #LTS 版有如下版本 9.9 8.9 7.9 6.7 5.6 4.5 3.7
4.2.1 硬件要求
#硬件需求 1.小型应用至少需要2GB的RAM (最好起步4个G) 2.磁盘空间取决于SonarQube分析的代码量 3.必须安装在读写性能较好的磁盘, 存储数据的目录中包含ElasticSearch的索引,服务器启动并运行时,将会在该索引上进行大是I/O操作 4.不支持32位操作系统
[root@SonarQube-Server ~]#vim /etc/sysctl.conf vm.max_map_count=262144 #此项必须修改,否则无法启动 fs.file-max=65536 #此项可不改,默认值满足要求 #此文件可不改,可选 [root@SonarQube-Server ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf sonarqube - nofile 65536 sonarqube - nproc 4096 #如果以systemd 运行SonarQube,需要在service文件配置 [servcie] ..... LimitNOFILE=65536 LimitNPROC=4096 ......
注意:SonarQube 7.9 不再支持MySQL,可以选择安装 PostgreSQL
4.2.4 Java 环境依赖说明
SonarQube 7.9 以上版本不再支持 java 11, 客户端还支持java 11
#使用普通账户启动sonarqube,因为sonarqube内置了ES,所以不允许能root启动 #Ubuntu使用useradd创建用户时默认使用/bin/sh,并且不创建家目录 [root@SonarQube-Server ~]#useradd -s /bin/bash -m sonarqube
4.3.1.1 安装和配置 PostgreSQL 数据库
4.3.2 下载 SonarQube 和修改配置文件
4.3.3 启动 SonarQube
4.3.4 创建 service 文件
范例: 创建 service 文件
#先停止sonarqube [root@SonarQube-Server ~]#su - sonarqube sonarqube@SonarQube-Server:~$ /usr/local/sonarqube/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh stop sonarqube@SonarQube-Server:~$ /usr/local/sonarqube/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh status SonarQube is not running. sonarqube@SonarQube-Server:~$exit #创建service文件 [root@SonarQube-Server ~]#vim /etc/systemd/system/sonarqube.service [Unit] Description=SonarQube service After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=simple User=sonarqube Group=sonarqube PermissionsStartOnly=true ExecStart=/usr/bin/nohup /usr/bin/java -Xms32m -Xmx32m -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -jar /usr/local/sonarqube/lib/sonar-application-8.9.2.46101.jar #ExecStart=/usr/bin/nohup /usr/bin/java -Xms32m -Xmx32m -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -jar /usr/local/sonarqube/lib/sonar-application-7.9.6.jar StandardOutput=syslog LimitNOFILE=65536 LimitNPROC=4096 TimeoutStartSec=5 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target [root@SonarQube-Server ~]#systemctl daemon-reload [root@SonarQube-Server ~]#systemctl enable --now sonarqube.service [root@SonarQube-Server ~]#systemctl status sonarqube.service
下面为脚本实现整个安装过程
#!/bin/bash #SONARQUBE从9.9版本以后要求安装JDK17 #支持在线和离线安装,在线下载可能很慢,建议离线安装 SONARQUBE_VER="9.9.4.87374" #SONARQUBE_VER="9.9.3.79811" #SONARQUBE_VER="9.9.2.77730" #SONARQUBE_VER="9.9.1.69595" #SONARQUBE_VER="9.9.0.65466" #SONARQUBE_VER="8.9.10.61524" #SONARQUBE_VER="8.9.9.56886" #SONARQUBE_VER="8.9.2.46101" #SONARQUBE_VER="7.9.2" SONARQUBE_URL="https://binaries.sonarsource.com/Distribution/sonarqube/sonarqube-${SONARQUBE_VER}.zip" SONAR_USER=sonarqube SONAR_USER_PASSWORD=123456 WORK_DIR=`pwd` HOST=`hostname -I|awk '{print $1}'` GREEN="echo -e \E[32;1m" END="\E[0m" . /etc/os-release color () { RES_COL=60 MOVE_TO_COL="echo -en \\033[${RES_COL}G" SETCOLOR_SUCCESS="echo -en \\033[1;32m" SETCOLOR_FAILURE="echo -en \\033[1;31m" SETCOLOR_WARNING="echo -en \\033[1;33m" SETCOLOR_NORMAL="echo -en \E[0m" echo -n "$1" && $MOVE_TO_COL echo -n "[" if [ $2 = "success" -o $2 = "0" ] ;then ${SETCOLOR_SUCCESS} echo -n $" OK " elif [ $2 = "failure" -o $2 = "1" ] ;then ${SETCOLOR_FAILURE} echo -n $"FAILED" else ${SETCOLOR_WARNING} echo -n $"WARNING" fi ${SETCOLOR_NORMAL} echo -n "]" echo } install_jdk() { java -version &>/dev/null && { color "JDK 已安装!" 1 ; return; } if command -v yum &>/dev/null ; then yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel || { color "安装JDK失败!" 1; exit 1; } elif command -v apt &>/dev/null ; then apt update apt install openjdk-17-jdk -y || { color "安装JDK失败!" 1; exit 1; } #apt install openjdk-11-jdk -y || { color "安装JDK失败!" 1; exit 1; } #apt install openjdk-8-jdk -y || { color "安装JDK失败!" 1; exit 1; } else color "不支持当前操作系统!" 1 exit 1 fi java -version && { color "安装 JDK 完成!" 0 ; } || { color "安装JDK失败!" 1; exit 1; } } system_prepare () { useradd -s /bin/bash -m sonarqube cat >> /etc/sysctl.conf <<EOF vm.max_map_count=524288 fs.file-max=131072 EOF sysctl -p cat >> /etc/security/limits.conf <<EOF sonarqube - nofile 131072 sonarqube - nproc 8192 EOF } install_postgresql(){ if [ $ID = "centos" -o $ID = "rocky" ];then if [ $VERSION_ID -eq 7 ];then rpm -i http://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm yum -y install postgresql12-server postgresql12 postgresql12-libs postgresql-12-setup --initdb else #rpm -i http://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-8-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm color "不支持此操作系统!" 1 exit fi systemctl enable postgresql.service systemctl start postgresql.service else apt update apt -y install postgresql fi if [ $? -eq 0 ];then color "安装postgresql完成!" 0 else color "安装postgresql失败!" 1 exit fi } config_postgresql () { if [ $ID = "centos" -o $ID = "rocky" ];then sed -i.bak "/listen_addresses/a listen_addresses = '*'" /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf cat >> /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf <<EOF host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 EOF else sed -i.bak "/listen_addresses/c listen_addresses = '*'" /etc/postgresql/1*/main/postgresql.conf cat >> /etc/postgresql/*/main/pg_hba.conf <<EOF host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 EOF fi systemctl restart postgresql su - postgres -c "psql -U postgres <<EOF CREATE USER $SONAR_USER WITH ENCRYPTED PASSWORD '$SONAR_USER_PASSWORD'; CREATE DATABASE sonarqube ; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE sonarqube TO $SONAR_USER; EOF" } install_sonarqube() { cd $WORK_DIR if [ -f sonarqube-${SONARQUBE_VER}.zip ] ;then mv sonarqube-${SONARQUBE_VER}.zip /usr/local/src else wget -P /usr/local/src ${SONARQUBE_URL} || { color "下载失败!" 1 ;exit ; } fi cd /usr/local/src unzip ${SONARQUBE_URL##*/} ln -s /usr/local/src/sonarqube-${SONARQUBE_VER} /usr/local/sonarqube chown -R sonarqube.sonarqube /usr/local/sonarqube/ cat > /lib/systemd/system/sonarqube.service <<EOF [Unit] Description=SonarQube service After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=simple User=sonarqube Group=sonarqube PermissionsStartOnly=true ExecStart=/usr/bin/nohup /usr/bin/java -Xms32m -Xmx32m -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -jar /usr/local/sonarqube/lib/sonar-application-${SONARQUBE_VER}.jar StandardOutput=syslog LimitNOFILE=65536 LimitNPROC=8192 TimeoutStartSec=5 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF cat >> /usr/local/sonarqube/conf/sonar.properties <<EOF sonar.jdbc.username=$SONAR_USER sonar.jdbc.password=$SONAR_USER_PASSWORD sonar.jdbc.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost/sonarqube EOF } start_sonarqube() { systemctl enable --now sonarqube.service systemctl is-active sonarqube if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo color "sonarqube 安装完成!" 0 echo "-------------------------------------------------------------------" echo -e "访问链接: \c" ${GREEN}"http://$HOST:9000/"${END} echo -e "用户和密码: \c" ${GREEN}"admin/admin"${END} else color "sonarqube 安装失败!" 1 exit fi } install_jdk system_prepare install_postgresql config_postgresql install_sonarqube start_sonarqube
用浏览器访问地址: http:10.0.0.155:9000 新版默认必须登录,不支持匿名访问 默认用户名和密码都是 admin #第一次要修改密码 改成 123456
4.4 管理 SonarQube 服务器
4.4.1 安装中文支持
#上方Administration下Marketplace可以安装插件,需要先同意风险才能安装 #汉化插件,搜chinese,安装Chinese Pack #安装完后,点 Restart Server #插件在这个路径下(可以拷贝给其他机器) [root@SonarQube-Server ~]#ll /usr/local/sonarqube/extensions/plugins/
#上方权限下用户(全局权限可以看到对应权限) #创建用户 xiaoming/123456 #创建完,右侧点击令牌,输入名称,过期时间,生成,获得令牌(自己保存下来,窗口一次性的) squ_8f7075d74b1f707610bc935a4b9cbf9884af769e
8.9.X 新版默认取消了匿名用户访问,可以在上方配置下权限 关闭Force user authentication
4.5 部署代码扫描器 sonar-scanner
下载地址: https://docs.sonarqube.org/latest/analyzing-source-code/scanners/sonarscanner/ #在jenkins机器上安装 sonar-scanner [root@jenkins-ubuntu ~]#cd /usr/local/src #新版 [root@jenkins-ubuntu src]#wget https://binaries.sonarsource.com/Distribution/sonar-scanner-cli/sonar-scanner-cli-4.6.2.2472-linux.zip [root@jenkins-ubuntu src]#unzip sonar-scanner-cli-4.6.2.2472-linux.zip [root@jenkins-ubuntu src]#ln -s /usr/local/src/sonar-scanner-4.6.2.2472-linux/ /usr/local/sonar-scanner #创建软链接方便运行 [root@jenkins-ubuntu ~]#ln -s /usr/local/sonar-scanner/bin/sonar-scanner /usr/local/bin/ [root@jenkins-ubuntu ~]#ldd /usr/local/sonar-scanner/bin/sonar-scanner 不是动态可执行文件 #配置sonar-scanner连接sonarqube服务器 [root@jenkins-ubuntu ~]#vim /usr/local/sonar-scanner/conf/sonar-scanner.properties #指向sonarqube服务器的地址和端口 sonar.host.url=http://sonarqube.wang.org:9000 sonar.sourceEncoding=UTF-8 #如果登录sonarqube server需要验证,还要加下面两行sonarqube的预先创建的用户信息 #sonar.login=admin #sonar.password=123456 #sonar.login=xiaoming #密码方式未来会淘汰 #sonar.password=123456 #建议使用Token方式 sonar.login=squ_8f7075d74b1f707610bc935a4b9cbf9884af769e
#项目目录下要有 sonar-project.properties文件 [root@jenkins python-sonar-runner]#ls README.md sonar-project.properties src validation.txt #sonar-project.properties下要有这两项,projectKey是id,projectName是sonar出报告的项目名 [root@jenkins python-sonar-runner]#cat sonar-project.properties sonar.projectKey=org.sonarqube:python-simple-sonar-scanner sonar.projectName=Python :: Simple Project : SonarQube Scanner #项目源码编译生成的二进制文件路径,从sonar-scanner-4.1.2起,仅java项目要求sonar.java.binaries参数 sonar.java.binaries=. #路径写.可以在子目录下,如写./target编译前没该文件扫描会报错 ... #把代码提交给SonarQube服务器,自动寻找sonar-project.properties文件 [root@jenkins python-sonar-runner]#sonar-scanner #范例:无需配置文件sonar-project.properties,扫描项目 [root@jenkins spring-boot-helloWorld]#sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=myapp -Dsonar.projectKey=myapp -Dsonar.java.binaries=./ #无需配置sonar-scanner.properties中的token,扫描项目 [root@jenkins spring-boot-helloWorld]#sonar-scanner -Dsonar.login=<token> #SonarQube网站项目能看到提交的结果
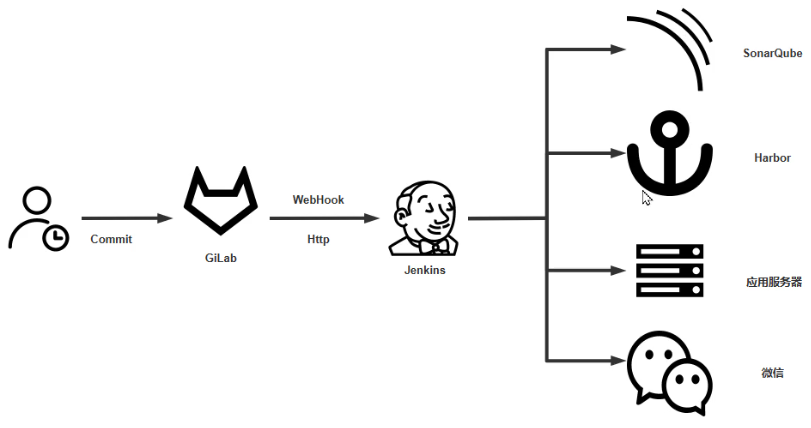
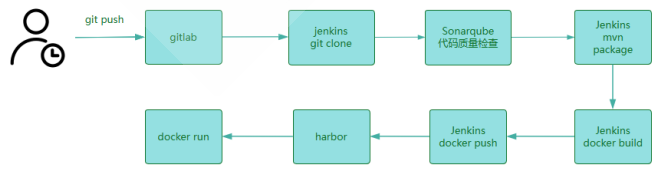
4.8.1 安装 GitLab 和准备项目
4.8.2 安装 Harbor 并配置 Jenkins 连接 Harbor
4.8.3 安装 Jenkins 并安装相关插件
4.8.4 在 Jenkins 创建凭据连接 Harbor
4.8.5 在 Jenkins 安装 Maven 工具
4.8.6 在 Jenkins 上配置 Maven 环境
4.8.7 在 Jenkins 创建连接 GitLab 的凭据
4.8.8 在 Jenkins 上修改 Docker 的 socket 文件权限
4.8.9 安装 SonarQube 并创建用户和令牌
4.8.10 在 SonarQube 添加 Jenkins 的回调接口
jenkins需要知道SonarQube的报告质量如何
#sonarqube上方配置下,左侧配置下webhook,点击创建 #名称随便起,这里写 jenkins #URL(jenkins固定地址,保证后面域名可以解析) http://jenkins.wang.org:8080/sonarqube-webhook #密码防止攻击使用,随意输入,下面通过命令生成密码 [root@ubuntu2204 ~]#openssl rand -base64 21 PiTVO6epEqIUlvU1DBoK1bVS3bkh #点击创建
4.8.12 在 Jenkins 创建访问 Sonarqube的令牌凭据
用前面小节生成的Sonarqube中用户令牌,在Jenkins 创建凭据
#jenkins左侧系统管理,凭据管理,创建一个凭据 #类型(光一个key) Secret text #Secret输入上面生成的用户令牌 squ_8f7075d74b1f707610bc935a4b9cbf9884af769e #ID/描述写 sonarqube-xiaoming-secret
#jenkins左侧系统管理,系统配置 #SonarQube servers下,点击Add SonarQube #Name(未来调用的就是这个名字)写 sonarqube #Server URL 写 http://10.0.0.155:9000 #Server authentication token 选上面的凭据 sonarqube-xiaoming-secret #保存
上面已经手动安装了, 这里不再进行安装
如果未安装,也可以在jenkins系统管理/全局工具配置中SonarQube Scanner安装
4.8.15 准备微信机器人
4.8.16 创建任务使用 Pipeline Script
#jenkins新建pipeline任务 pipeline { agent any tools { maven 'maven-3.6.3' } environment { codeRepo="http://gitlab.wang.org/example1/spring-boot-helloworld.git" harborServer='harbor.wang.org' credential='gitlab-root-password' projectName='spring-boot-helloworld' imageUrl="${harborServer}/example/${projectName}" imageTag="${BUILD_ID}" } stages { stage('Source') { steps { git branch: 'main', credentialsId: "${credential}", url: "${codeRepo}" } } stage("SonarQube Analysis") { steps { //这个名字要写在jenkins上配SonarQube 服务器名字 withSonarQubeEnv('sonarqube') { //java这个写法也支持向sonar服务器发送代码扫描 sh 'mvn sonar:sonar -Dsonar.java.binaries=target/' } } } stage("Quality Gate") { steps { timeout(time: 30, unit: 'MINUTES') { //质量阈通过往下执行,失败就不往下执行 waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: true } } } stage('Build') { steps { sh 'mvn -B -DskipTests clean package' } } stage('Test') { steps { sh 'mvn test' } } stage('Build Docker Image') { steps { sh 'docker image build . -t "${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' // input(message: '镜像已经构建完成,是否要推送?') } } stage('Push Docker Image') { steps { withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'harbor-xiaoming-password', passwordVariable: 'harborPassword', usernameVariable: 'harborUserName')]) { sh "docker login -u ${env.harborUserName} -p ${env.harborPassword} ${harborServer}" sh "docker image push ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" } } } stage('Run Docker') { steps { //sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.202 "docker rm -f ${projectName} && docker run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' //sh 'ssh root@10.0.0.203 "docker rm -f ${projectName} && docker run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}"' sh "docker -H 10.0.0.153:2375 rm -f ${projectName} && docker -H 10.0.0.153:2375 run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" sh "docker -H 10.0.0.154:2375 rm -f ${projectName} && docker -H 10.0.0.154:2375 run --name ${projectName} -p 80:8888 -d ${imageUrl}:${imageTag}" } } } post { success { mail to: 'root@wangxiaochun.com', subject: "Status of pipeline: ${currentBuild.fullDisplayName}", body: "${env.BUILD_URL} has result ${currentBuild.result}" } failure{ qyWechatNotification failNotify: true, webhookUrl: 'https://qyapi.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/webhook/send?key=938039da-1123-4862-b47b-f0396020f45b' } } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号