Shell阶段02 shell变量运算(整数运算/小数运算), 条件表达式(文件比较), 调用函数库, 数字的比较, 逻辑运算, 短路运算
加减乘除 求余 num1 + num2 num1 - num2 num1 * num2 num1 / num2 num1 % num2 求余
expr $(()) #运算效率最高 $[] let 只支持整数运算,不支持小数运算 expr 数值之间必须要有空格进行分开,当使用*乘的时候,需要对其进行转义使用,不能进行次方运算 [root@shell01 scripts]# expr 1 + 1 2 [root@shell01 scripts]# num1=10 [root@shell01 scripts]# num2=5 [root@shell01 scripts]# expr $num1 + $num2 15 [root@shell01 scripts]# expr $num1 \* $num2 #这里\取消*的特殊含义 50 [root@shell01 scripts]# expr $num1 / $num2 2 [root@shell01 scripts]# expr $num1 % $num2 0 $(()) 没有严格的格式要求,不能进行次方运算 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $(($num1+$num2)) #$(())没有严格的格式要求,当中不用有空格 15 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $(( $num1 - $num2 )) 5 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $(( $num1 * $num2 )) 50 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $(( $num1 / $num2 )) 2 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $(( $num1 % $num2 )) 0 $[] 没有严格的格式要求,不能进行次方运算 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $[$num1+$num2] 15 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $[$num1 - $num2] 5 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $[$num1 * $num2] 50 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $[$num1 / $num2] 2 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $[$num1 % $num2] 0
#内建的随机数生成器变量
$RANDOM #取值范围:0-32767
生成 0 - 49 之间随机数
[root@ubuntu2204 ~]# echo $[$RANDOM%50]
6
let 计数 [root@shell01 scripts]# a=10 [root@shell01 scripts]# let a++ [root@shell01 scripts]# let a++ [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $a 12 [root@shell01 scripts]# let a-- [root@shell01 scripts]# let a-- [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $a 10
[root@shell01 ~]# let sum=10+10 #或者 let sum=$num1+$num2
[root@shell01 ~]# echo $sum
20
例:i++与++i
[root@ubuntu2204 ~]# i=1;let j=i++;echo $i $j
#i=1; j=i; let i=i+1;echo $i $
2 1
[root@ubuntu2204 ~]# i=1;let j=++i;echo $i $j
#i=1;let i=i+1;j=i;echo $i $j
2 2
bc awk python bc默认是没有的,需要下载 [root@shell01 scripts]# yum install -y bc [root@shell01 scripts]# bc #交互式运算一般不用,除法值也有问题 bc 1.06.95 Copyright 1991-1994, 1997, 1998, 2000, 2004, 2006 Free Software Foundation, Inc. ... 1+1 2 3/2 1 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo 10 + 20 |bc 30 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $num1 10 [root@shell01 scripts]# $num3=3 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $num1 + $num3 |bc 13 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $num1 / $num3|bc #计算值有问题,没有小数位 3 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo "scale=2;$num1 / $num3"|bc #scale设定小数位为2位 3.33 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo $num1 ^ $num3 |bc #次方运算 1000 awk 默认对文件进行操作,加入行处理前BEGIN就不会报错,直接进行计算 BEGIN 行处理前 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{print 10 + 5}' 15 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{print 10 - 5}' 5 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{print 10 * 5}' 50 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{print 10 / 5}' 2 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{print 10 % 5}' 0 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{print 10 ^ 5}' #支持次方运算 100000 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{print 10 / 3}' #除法小数位是随机的,最大5位 3.33333 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{printf "%.3f\n",10/3}' #自定义小数位,采用python写法,\n进行换行 3.333 #注意awk用外部变量,要用双引号 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk "BEGIN{print $num1/$num2}" 2 #awk可以用内部变量 -v #自定义内部变量 [root@shell01 scripts]# awk -vnum1=10 -vnum2=5 'BEGIN{print num1/num2}' #这里变量前不要加$,不然变列行 2 python [root@shell01 scripts]# python #交互式 Python 2.7.5 (default, Oct 30 2018, 23:45:53) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-36)] on linux2 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> 10/3 3 >>> 10.0/3 #要得到小数,首先把数字变为浮点型 3.3333333333333335 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo "print $num1 + $num2" | python #这里采用python的写法 15 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo "print $num1 - $num3" | python 7 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo "print $num1 / $num3" | python 3 [root@shell01 scripts]# echo "print ${num1}.0 / $num3" | python 3.33333333333
1.ps aux命令下,求VSZ列的和 (VSZ虚拟内存集,RSS物理内存集) #第一种 [root@shell01 ~]# ps aux | awk 'NR>1{print $5}'|xargs #xargs分组作用,把一列分成一行 125884 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 37116 45744 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 62052 0 0 228320 26380 58236 73656 201724 612240 99576 300828 473820 225828 126388 110192 573932 112764 220792 89556 89728 161372 116332 89660 0 0 0 0 155464 113640 116332 [root@shell01 ~]# ps aux | awk 'NR>1{print $5}'|xargs |tr ' ' '+' 125884+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+37116+45744+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+0+62052+0+0+228320+26380+58236+73656+201724+612240+99576+300828+473820+225828+126388+110192+573932+112764+220792+89556+89728+161372+116332+89660+0+0+0+155464+113640+108352+108076 [root@shell01 ~]# ps aux | awk 'NR>1{print $5}'|xargs |tr ' ' '+'|bc 4863984 #第二种 [root@shell01 ~]# ps aux | awk 'NR>1{i+=$5}END{print i}' #第五列相加,END等前面计算结束 4531224 #第三种 [root@shell01 scripts]# vim for_vsz.sh #!/bin/bash he=0 for i in $(ps aux| awk 'NR>1{print $5}') do he=$(expr $he + $i) done echo $he [root@shell01 scripts]# sh -x for_vsz.sh #-x显示脚本执行过程 2.写个脚本,实现一个简单的计算器,实现加减乘除 [root@shell01 scripts]# vim jsq.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "请输入你要计算的第一个数字:" num1 read -p "请输入你要计算的第二个数字:" num2 echo "$num1 + $num2 = $[ $num1 + $num2 ]" echo "$num1 - $num2 = $[ $num1 - $num2 ]" echo "$num1 * $num2 = $[ $num1 * $num2 ]" echo "$num1 / $num2 = $(awk "BEGIN{print $num1 / $num2}")"
1.使用Shell脚本打印,系统版本、内核版本平台、虚拟平台、静态主机名、eth0网卡IP地址、lo网卡IP地址、当前主机的外网IP地址
curl icanhazip.com 或者 curl ifconfig.me #当前主机的外网IP地址 awk '{print$1,$4}' /etc/redhat-release #系统版本信息 hostnamectl | awk '/Kernel/{print $3}' #Kernel内核版本信息 hostnamectl | awk '/Virtua/{print $2}' #虚拟平台 hostnamectl | awk '/hostname/{print $3}' #静态主机名 ifconfig eth0|awk 'NR==2{print $2}' #eth0网卡IP地址 ifconfig lo|awk 'NR==2{print $2}' #lo网卡IP地址 [root@shell01 scripts]# vim var.sh #!/bin/bash Version=$(awk '{print$1,$4}' /etc/redhat-release) Kernel=$(hostnamectl | awk '/Kernel/{print $3}') Vm=$(hostnamectl | awk '/Virtua/{print $2}') Static_Hostname=$(hostnamectl | awk '/hostname/{print $3}') Eth0=$(ifconfig eth0|awk 'NR==2{print $2}') Lo=$(ifconfig lo|awk 'NR==2{print $2}') Wan=$(curl -s ifconfig.me) #-s:不输出错误和进度信息 echo "当前系统版本号为: $Version" echo "当前系统内核版本号为: ${Kernel%.e*}" echo "当前系统虚拟化平台为: $Vm" echo "当前系统静态主机名为: $Static_Hostname" echo "当前系统的Eth0网卡IP地址为: $Eth0" echo "当前系统的Lo网卡IP地址为: $Lo" echo "当前系统的外网IP地址为: $Wan" ---------------------------------------------------- 2.需求描述:变量string="Bigdata process is Hadoop, Hadoop is open source project",执行脚本后,打印输出string变量,并给出用户以下选项: #需求 1)打印string长度 2)删除字符串中的所有Hadoop 3)替换第一个Hadoop为Linux 4)替换全部Hadoop为Linux 用户请输入数字1|2|3|4,可以执行对应项的功能。 [root@shell01 scripts]# vim var-1.sh #!/bin/bash #1.定义变量 String='Bigdata process is Hadoop, Hadoop is open source project' #2.打印变量 echo $String #3.输出菜单 cat<<EOF 1)打印string长度 2)删除字符串中的所有Hadoop 3)替换第一个Hadoop为Linux 4)替换全部Hadoop为Linux EOF #4.提示用户输入对应的数字,执行对应的功能 read -p "请输入上方菜单对应的数字,执行对应的功能[1|2|3|4]: " Num #5.根据用户输入的数字进行执行对应的功能 if [ $Num -eq 1 ];then echo "打印string长度" echo ${#String} fi if [ $Num -eq 2 ];then echo "删除字符串中的所有Hadoop" echo ${#String//Hadoop/} fi if [ $Num -eq 3 ];then echo "替换变量中第一个Hadoop为Linux" echo ${#String/Hadoop/Linux} fi if [ $Num -eq 4 ];then echo "替换变量中全部Hadoop为Linux" echo ${#String//Hadoop/Linux} fi
[]======test #中括号相当于test命令, []比较常用 [ -f file ] 文件是否存在 且为普通文件 重点 # [后 和 ]前 必须有空格 [ -e file ] 文件/目录存在则为真 [ -e file/dir]
[ -s file ] 如果文件存在且至少有一个字符则为真(判断一个文件是否是空文件) [ -d file ] 目录存在则为真(判断为文件时则为假) 重点 [ -x file ] 文件有执行权限则为真 [ -w file ] 文件可写则为真 [ -r file ] 文件可读则为真 #示例 [root@shell01 ~]# [ -f /etc/hosts ] [root@shell01 ~]# echo $? 0 [root@shell01 ~]# [ ! -d /etc/hosts ] #!取反 [root@shell01 ~]# echo $? 0 [root@shell01 scripts]# test -f /etc/hosts && echo ok || echo error -f 判断文件是否存在
#测试URL地址是否能够访问(调用函数库) [root@shell01 scripts]# vim ping.sh #!/bin/bash [ -f /etc/init.d/functions ] && . /etc/init.d/functions #加载函数库,service启动用的也是该函数库 read -p "请输入一个网址: " url ping -c 1 -W 1 $url >/dev/null 2>&1 #-c次数 -W超时时间(s) [ $? -eq 0 ] && action "ping $url is" /bin/true || action "ping $url is" /bin/false #函数库使用action -d 判断是否为目录 目录是否存在 [root@shell01 scripts]# [ -d /alex ] || mkdir /alex
[ 数值1 比较符 数值2 ] -eq 相等 -ne 不等于 -gt 大于 -ge 大于等于 -lt 小于 -le 小于等于 [root@shell01 scripts]# [ 10 -eq 10 ] && echo ok || echo error ok #案例: 统计当前磁盘的使用率 如果大于5% 则把内容写入到以日期为名称的文本中 2019-08-01.txt 如果小了 则把当前的使用率 写入 2019-08-01.txt 1.如何取出当前的使用率 2.条件表达式 整数的比较 3.输出结果到文本 [root@shell01 ~]# [ `df -h|grep /$|awk -F "[ %]+" '{print $(NF-1)}'` -gt 5 ] && echo error || echo ok error #案例: 统计系统内存的使用率 如果大于10则 echo 使用率到 以时间命名的文件中 [root@shell01 ~]# free=`free|awk 'NR==2{print $3/$2*100}'` [root@shell01 ~]# [ ${free%.*} -gt 10 ] && echo error || echo ok
#注意也可以用 [[]] #如果用 [[]], 里面的比较符为 = != >= < <=
逻辑运算
与:& 和0相与结果为0,和1相与结果保留原值, 一假则假,全真才真
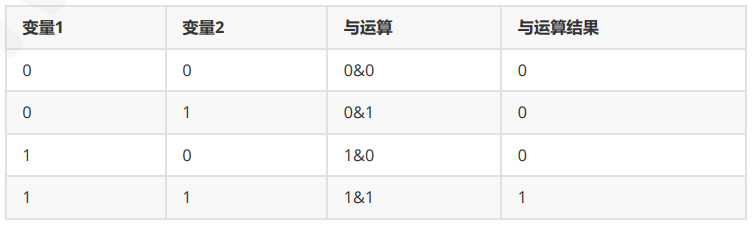
[root@ubuntu2204 ~]# x=$[2&6] [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# echo $x 2 [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# x=$[7&3] [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# echo $x 3
或:| 和1相或结果为1,和0相或结果保留原值,一真则真,全假才假
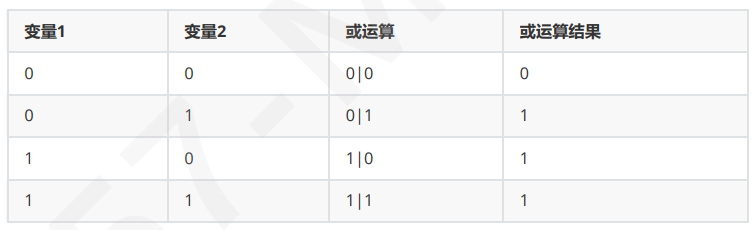
root@ubuntu2204 ~]# x=$[7|3] [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# echo $x 7
非:!
[root@ubuntu2204 ~]# ! true [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# echo $? 1
异或:^
异或的两个值,相同为假,不同为真。两个数字X,Y异或得到结果Z,Z再和任意两者之一X异或,将得 出另一个值Y

#变量互换(不通过中间值实现变量值互换) [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# x=10;y=20;temp=$x;x=$y;y=$temp;echo x=$x,y=$y x=20,y=10 [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# x=10;y=20;x=$[x^y];y=$[x^y];x=$[x^y];echo x=$x,y=$y x=20,y=10
短路运算
短路与 &&
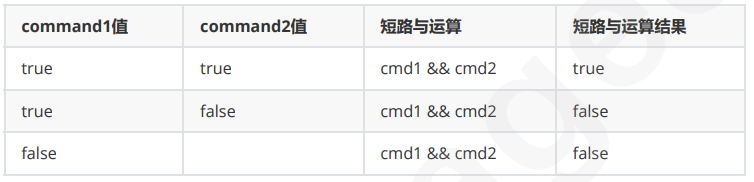
当 cmd1 的结果为 false 时,整个表达式就是 false, cmd2 不参与运算,这就是所谓的短路
短路或 ||
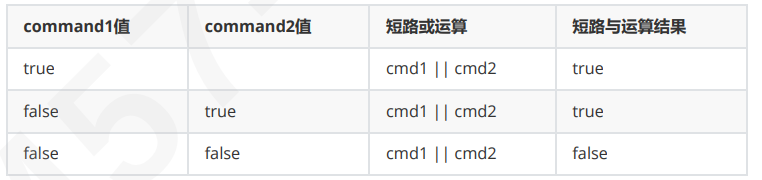
当 cmd1 的结果为 true 时,整个表达式就是 true, cmd2 不参与运算,这就是所谓的短路
短路与和或组合
cmd1 || cmd2 && cmd3 这种语法是错误的,不使用;
[root@ubuntu ~]# id tom &>/dev/null && echo "yes" || echo "no" yes [root@ubuntu ~]# id tom123 &>/dev/null && echo "yes" || echo "no" no #错误写法 [root@ubuntu ~]# id tom &>/dev/null || echo "yes" && echo "no" no [root@ubuntu ~]# id tom123 &>/dev/null || echo "yes" && echo "no" yes no
关于 () 和 {}
( cmd1;cmd2;... ) 和 { cmd1;cmd2;...; } 都可以将多个命令组合在一起,批量执行
( list ) 会开启子shell,并且list中变量赋值及内部命令执行后,将不再影响后续的环境
{ list; } 不会开启子shell, 在当前shell中运行,会影响当前shell环境,左侧要有空格,右侧要有;
结束
[root@ubuntu2204 ~]# name=mage;(echo $name;name=wang;echo $name );echo $name mage wang mage [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# name=mage;{ echo $name;name=wang;echo $name; } ;echo $name mage wang wang
#()会开启子shell [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# echo $BASHPID 1920 [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# ( echo $BASHPID;sleep 100) 1979 [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# pstree -p ├─sshd(719)───sshd(1906)───sshd(1919)─┬─bash(1920)───bash(1979)───sleep(1980) #{ } 不会开启子shell [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# echo $BASHPID 1920 [root@ubuntu2204 ~]# { echo $BASHPID; } 1920

