Linux架构20 nginx优化: ab压测工具, 系统性能优化, 代理服务优化, 静态资源优化(缓存,读取,压缩), 防资源盗链, 允许跨域访问, CPU亲和
注:本文参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/wuqiuyin/p/15190616.html
一、性能优化概述
1.我们需要了解的
1、首先需要了解我们当前系统的结构和瓶颈,了解当前使用的是什么,运行的是什么业务,都有哪些服务,了解每个服务最大能支撑多少并发。
比如nginx作为静态资源服务并发是多少,最高瓶颈在哪里,能支持多少qps(每秒查询率)的访问请求,那我们怎么得出这组系统结构瓶颈呢,
比如top查看系统的CPU负载、内存使用率、总得运行进程等,也可以通过日志去分析请求的情况,当然也可以通过我们前面介绍到的stub_status模块查看当前的连接情况,
也可以对线上的业务进行压力测试(低峰期),去了解当前这套系统能承担多少的请求和并发,以做好响应的评估。这个是我们做性能优化最先考虑的地方。 2、其次我们需要了解业务模式,虽然我们是做性能优化,但每一个性能的优化都是为业务所提供的服务的,我们需要了解每个业务接口的类型,
比如:电商网站中的抢购模式,这种情况下,平时没什么流量,但到了抢购时间流量会突增。我们还需要了解系统层次化的结构,
比如:我们使用nginx做的是代理、还是动静分离、还是后端直接服务用户,那么这个就需要我们对每一层做好相应的梳理。以便更好的服务业务。 3、最后我们需要考虑性能与安全,往往注重了性能,但是忽略了安全。往往过于注重安全,对性能又会产生影响。比如:我们在设计防火墙功能时,
检测过于严密,这样就会给性能带来影响。那么如果对于性能完全追求,却不顾服务的安全,这个也会造成很大的隐患,所以需要评估好两者的关系,
把握好两者的孰重孰轻。以及整体的相关性,权衡好对应的点。 1.首先需要了解我们当前系统的结构和瓶颈 2.分析服务的限制和使用情况 3.了解业务模式 4.了解系统层次化的结构 5.考虑性能与安全
OSI 七层模型: 物理层,数据链路层,网络层,传输层,会话层,表示层,应用层 1.硬件 如果nginx做代理(CPU),静态资源(磁盘读写性能,磁盘大小),动态资源(CPU, 内存) 2.网络 带宽,丢包,延迟 3.系统 文件描述符(文件句柄数) 4.应用 服务与服务保持长连接 (结束时四次挥手,因为有等待中断,此时该随机端口处于time wait状态不可用,再连接要再开随机端口。
如果随机端口全部占用,要么超时返回要么直接访问失败。后面这一块可以优化) 5.服务 静态资源服务优化
# 查看命令所在的包 [root@web01 ~]# yum provides ab # 安装ab [root@web01 ~]# yum install -y httpd-tools
[root@web01 ~]# ab -n 10 -c 2 http://www.baidu.com/ -n 指定请求次数 -c 指定并发数 -k 开启长连接 [root@web01 ~]# ab Usage: ab [options] [http[s]://]hostname[:port]/path
#配置nginx [root@web01 conf.d]# vim ab.linux.com.conf server { listen 80; server_name ab.linux.com; location / { root /code/ab; try_files $uri $uri/ @java; } location @java { proxy_pass http://172.0.0.1:8080; } } # 配置nginx站点目录文件 [root@web01 conf.d]# echo linux_nginx > /code/ab/index.html
[root@web01 conf.d]# vim /etc/hosts #配置host 10.0.0.7 linux.ab.com [root@web01 conf.d]# ab -n 10000 -c 200 http://ab.linux.com/index.html Server Software: nginx/1.18.0 #被测试的服务器软件信息 Server Hostname: linux.ab.com #被测的主机名 Server Port: 80 Document Path: /index.html Document Length: 12 bytes #请求文件大小(上面index.html文件) Concurrency Level: 200 #并发 Time taken for tests: 4.195 seconds #一共消耗的时间 Complete requests: 10000 #总的请求数 Failed requests: 0 #错误的请求数 Write errors: 0 #写的错误(要进行写的操作) Total transferred: 2420000 bytes #所有请求一共返回了多少字节(包含请求头) HTML transferred: 120000 bytes #页面上展示一共多少字节 Requests per second: 2383.81 [#/sec] (mean) #请求速率,每秒2383.81个请求 Time per request: 83.899 [ms] (mean) #客户端请求服务器的速度 Time per request: 0.419 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)#请求处理的速度 Transfer rate: 563.36 [Kbytes/sec] received #网速
#1.下载或上传tomcat包 [root@web01 ~]# mkdir /service [root@web01 ~]# cd /service [root@web01 service]# rz apache-tomcat-8.5.51.tar.gz #2.解压代码包 [root@web01 service]# tar xf apache-tomcat-8.5.51.tar.gz #3.配置java环境 1.上传并解压至指定文件夹 [root@web01 service]# tar xf jdk-8u40-linux-x64.gz -C /service/ [root@web01 service]# mv jdk1.8.0_40 java1.8 2.修改添加环境变量 [root@web01 service]# vim /etc/profile.d/java.sh export JAVA_HOME=/service/java1.8 export JRE_HOME=/service/java1.8/jre export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib:$JRE_HOME/lib:$CLASSPATH export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin [root@web01 service]# source /etc/profile #4.配置tomcat页面 [root@web01 service]# echo "linux_tomcat" > apache-tomcat-8.5.51/webapps/ROOT/index.html #5.启动tomcat,启动的时候最好看着日志(tomcat启动很容易报错) [root@web01 service]# /service/apache-tomcat-8.5.96/bin/startup.sh && tail -f /service/apache-tomcat-8.5.96/logs/catalina.out
[root@web01 conf.d]# rm -rf /code/ab [root@web01 conf.d]# ab -n 10000 -c 200 http://linux.ab.com/ Server Software: nginx/1.18.0 Server Hostname: linux.ab.com Server Port: 80 Document Path: / Document Length: 13 bytes Concurrency Level: 200 Time taken for tests: 25.036 seconds Complete requests: 10000 Failed requests: 0 Write errors: 0 Total transferred: 2490000 bytes HTML transferred: 130000 bytes Requests per second: 399.42 [#/sec] (mean) Time per request: 500.727 [ms] (mean) Time per request: 2.504 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests) Transfer rate: 97.12 [Kbytes/sec] received
nginx处理静态资源速度比tomcat快很多
1、网络 (1) 网络的流量 (2) 网络是否丢包 (3) 这些会影响http的请求与调用 2、系统 (1) 硬件有没有磁盘损坏,磁盘速率 (2) 系统的负载、内存、系统稳定性 3、服务 (1) 连接优化。请求优化 (2) 根据业务形态做对应的服务设置 4、程序 (1) 接口性能 (2) 处理速度 (3) 程序执行效率 5、数据库
文件句柄,Linux一切皆文件,文件句柄可以理解为就是一个索引,文件句柄会随着我们进程的调用频繁增加,系统默认文件句柄是有限制的,
不能让一个进程无限的调用,所以我们需要限制每个进程和每个服务使用多大的文件句柄,文件句柄也是必须要调整的优化参数。 # 查看文件句柄数 ulimit -n # 查看一个服务打开多少文件句柄 lsof -p pid # 查看一共打开多少文件句柄 lsof -i | awk '{print $2}'|wc -l 做模板镜像时,配置过下方参数,ulimit -n命令查看最大文件描述符的数量就是65535 # 调整单个进程最大能打开文件的数量 echo '* - nofile 65535' >> /etc/security/limits.conf # 查看一个服务打开多少文件句柄 [root@web01 conf.d]# yum install -y lsof [root@web01 conf.d]# ps -ef| grep nginx root 6897 1 0 Nov21 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf www 6900 6897 0 Nov21 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 10425 9185 0 00:45 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx [root@web01 conf.d]# lsof -p 6897 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME nginx 6897 root cwd DIR 8,3 280 64 / nginx 6897 root rtd DIR 8,3 280 64 / nginx 6897 root txt REG 8,3 1399232 593974 /usr/sbin/nginx ... nginx 6897 root 11w REG 8,3 0 51426742 /var/log/nginx/error.log
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf 1.系统全局修改文件句柄 # 65535并不是最大值,还能配到100万... # * 代表所有用户,soft代表提醒,hard直接限制,nofile指定打开最大文件数量 * - nofile 65535 # -表示soft和hard同时设定 * soft nofile 65535 * hard nofile 65535 2.用户局部修改 root - nofile 65535 root soft nofile 65535 root hard nofile 65535 3.进程指定修改 # 例如nginx配置文件中可以修改,下方针对nginx进程,nginx自带配置nginx.conf [root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf worker_rlimit_nofile 65535; # 写在最外层
# 调整内核参数:让time_wait状态端口可以重新使用 (四次挥手下的time_wait状态,随机端口不可使用) [root@web01 ~]# sysctl -a # 查看所有内核参数 [root@web01 ~]# sysctl -p # 查看我们手动配置的内核参数 [root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf # 重用time_wait状态端口 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 #tw就是time_wait状态,reuse就是可以复用 # tcp_timestamps会导致网络是通的,但是tcp连接不上,时间戳不准会导致tcp连接不上 net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0 # 三次握手和四次挥手的时候,会带时间戳(其实不用给,默认为1开着这里不配也没事) [root@web01 ~]# sysctl -p # 设置完再查看,就能看到配置的参数 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
通常nginx作为代理服务,负责转发用户的请求,那么在转发的过程中建议开启HTTP长连接,用于减少握手次数,降低服务器损耗。
# nginx配置中参数 keepalive_timeout 65; 指连接到nginx最长连接为65秒。这里设置nginx到后端的长连接时间,也就是代理长连接时间 [root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/daili.conf upstream tomcat { server 127.0.0.1:8080; keepalive 16; # 写上数字就代表开启长连接,不写就是web1.0短连接。前16个连接都是长连接,这个值没有多大意义,写上就行给多少都行 } server { listen 80; server_name daili.linux.com; location /tomcat/ { proxy_pass http://tomcat; proxy_http_version 1.1; #指定http协议为1.1版本,否则wireshark抓包显示web1.0版本 proxy_set_header Connection ""; #清除“connection”头字段 include proxy_params; # 调用优化配置 proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;#平滑过渡到另一台机器 } } # 配置nginx代理,proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Connection ""; 这两条都是默认带上的
注: 上面可以代理nginx,tomcat。因为都是proxy_pass。下面换了fastcgi_pass协议
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/dailiphp.conf upstream php_conn { server 127.0.0.1:9000; keepalive 16; } server { listen 80; server_name php.linux.com; location /php/ { root /code; fastcgi_pass php_conn; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_keep_conn on; # 开启长连接 fastcgi_connect_timeout 60s; # 长连接超时时间,连接保持60s就断开 include proxy_params; } }
Nginx作为静态资源Web服务器,用于静态资源处理,传输非常的高效
静态资源指的是非WEB服务器端运行处理而生成的文件
| 种类 | |
|---|---|
| 浏览器渲染 | HTML、CSS、JS |
| 图片文件 | JEPG、GIF、PNG |
| 视频文件 | FLV、Mp4、AVI |
| 其他文件 | TXT、DOC、PDF、... |
1.静态资源缓存
浏览器缓存设置用于提高网站性能,尤其是新闻网站,图片一旦发布,改动的可能是非常小的,所以我们希望能否用户访问一次后,图片缓存在用户的浏览器长时间缓存。
浏览器是有自己的缓存机制,他是基于HTTP协议缓存机制来实现的,在HTTP协议中有很多头信息,那么实现浏览器的缓存就需要依赖特殊的头信息来与服务器进行特殊的验证,
如Expires(http/1.0); Cache-control(http/1.1)。
#响应头(这几个值存在服务器数据库里) ETag: "5e6864a0-c" #服务器改内容或名字,该值就会变化 Last-Modified: Wed, 11 Mar 2020 04:10:08 GMT Cache-Control: max-age=315360000 #后面值为秒,有值就代表没有过期 Expires: Wed, 02 Jan 2030 12:14:50 GMT #请求头(这两个值存在浏览器里) If-Modified-Since: Wed, 11 Mar 2020 04:10:08 GMT If-None-Match: "5e6864a0-c" #If-None-Match是文件的唯一标识符,请求的时候拿浏览器的这个标签和服务器上的ETag标签对比。如果对得上,说明文件没有改变。那就走缓存就行。 #如果没有If-None-Match,就去看If-Modified-Since,是浏览器保存的文件最后修改时间。把它和服务器上的Last-Modified最后修改时间对比,如果一样说明没修改过,走缓存
浏览器缓存过期校验机制
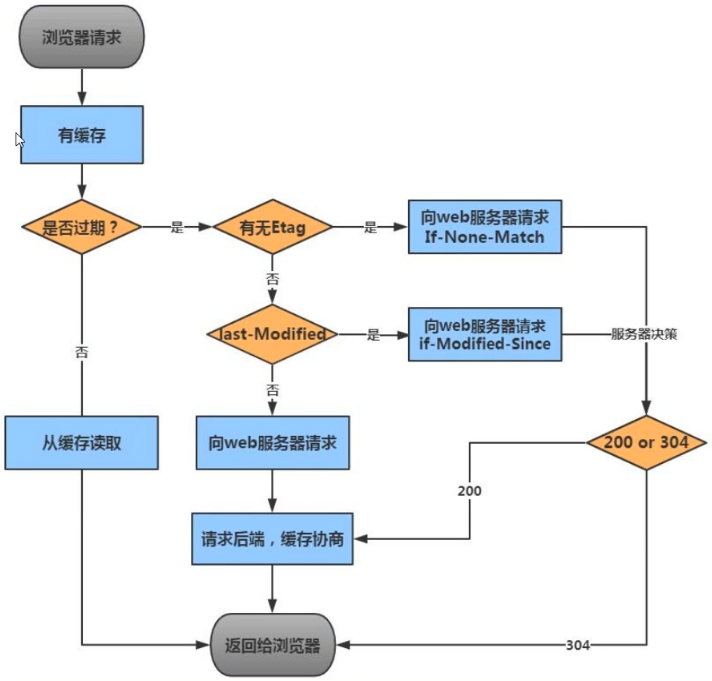
1.浏览器请求服务器会进行Expires、Cache-Control的检查,检查珲春是否过期,如果没有过期则直接从缓存文件中读取。(哪怕文件变了,也读缓存) 2.如果缓存过期首先检查是否存在etag,如果存在那么客户端会带着If-None-Match向web服务器请求,与etag值进行对比,如果值一致则走缓存,如果不一致则不走缓存。 3.如果etag不存在,则进行Last-Modified检查,客户端会带着If-Modified-Since向web服务器请求,与Last-Modified进行比对,如果值一致则走缓存,如果不一致则不走缓存。 Last-Modified:服务器上文件的最后修改时间 ETag:服务器上的文件标识
Expires:本地缓存目录中,文件过期的时间 Cache-Control:本地缓存目录中,文件过期的时间
#语法 #作用:添加Cache-Control Expires头 Syntax: expires [modified] time; epoch | max | off; Default: expires off; Context: http, server, location, if in location #配置静态资源缓存 [root@web01 conf.d]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/huancun.conf server { listen 80; server_name static.linux.com; root /code/static; location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif)$ { expires 7d; # 缓存过期时间,7天 } } [root@web01 conf.d]# mkdir /code/static [root@web01 conf.d]# cd /code/static [root@web01 static]# rz [root@web01 static]# systemctl restart nginx # 配host后,进行访问
#1.开启无痕模式 #2.勾上disable_cache #3.配置nginx [root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/huancun.conf server { listen 80; server_name static.linux.com; root /code/static; location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif)$ { expires 7d; } location ~* \.(css|js|html) { #访问css|js|html,不走缓存 add_header Cache-Control no-store; # 配上这两句话就不走缓存了 add_header Pragma no-cache; } } # 写一个html,访问查看响应头有下方内容 Cache-Control:no-store #表示不走缓存
Syntax: sendfile on | off; Default: sendfile off; #nginx的配置文件中默认配置开启 Context: http, server, location, if in location
#将多个数据打个包,一次推送,大文件的适合打开此配置,必须打开sendfile才能配置 Syntax: tcp_nopush on | off; Default: tcp_nopush off; Context: http, server, location
#来一个数据就推一个数据,需要开启keepalive Syntax: tcp_nodelay on | off; Default: tcpnodelay off; Context: http, server, location
#注:高效传输和长连接传输互相冲突,只能配其中一个。要么传输效率高,要么传输实时性高
CLIENT 请求头带 Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate #表示客户端支持压缩 SERVER gzip on #启用压缩功能 text/html #默认数据类型,进行压缩 如果文件没后缀名,系统无法识别,可以在配置中设定文件类型 如果有文件后缀名,没有压缩,可以把默认配置/etc/nginx/nginx.conf中 gzip_types text/plain...这行注释放开
1)静态资源压缩语法
注: 图片压缩比例较小, 保证展示效果。文档压缩比例会较大。
#gzip传输压缩,传输前压缩,传输后解压 Syntax: gzip on | off; Default: gzip off; Context: http, server, location, if in location #gzip压缩哪些文件 Syntax: gzip_types mime-type ...; #参考/etc/nginx/mime.types,下面填左侧那一列内容 Default: gzip_types text/html; # 可以写多个,用空格隔开 Context: http, server, location #gzip压缩比例,加快传输,但压缩本身比较耗费服务器性能 Syntax: gzip_comp_level level; Default: gzip_comp_level 1; #级别越高,压缩的越小,一般设3-5间 值范围:1-9 Context: http, server, location #gzip压缩协议版本,压缩使用在http哪个协议,主流选择1.1版本 Syntax: gzip_http_version 1.0 | 1.1; Default: gzip_http_version 1.1; Context: http, server, location
[root@web01 conf.d]# vim gzip.conf server { listen 80; server_name gzip.linux.com; root /code/static; location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif)$ { gzip on; gzip_types image/jpeg image/png image/gif; gzip_comp_level 5; gzip_http_version 1.1; } location ~* \.(css|js|txt) { gzip on; gzip_types text/css application/javascript text/plain; gzip_comp_level 5; gzip_http_version 1.1; } } [root@web01 static]# ll total 728 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 740265 Dec 24 2021 1.png -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 790265 Nov 29 02:25 1.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5 Nov 28 06:53 index.html #访问网站: http://gzip.linux.com/1.png # f12查看浏览器返回文件大小,和服务器文件大小对比。经测试,txt压缩比png压缩比例大很多
防盗链,就是指资源被其他网站恶意盗用 基础防盗链设置思路:主要针对客户端请求过程中所携带的一些Header信息来验证请求的合法性,比如客户端在请求的过程中都会携带referer信息。
优点是规则简单,配置和使用都很方便,缺点是防盗链所依赖的Referer验证信息是可以伪造的。所以通过referer信息防盗链并非100%可靠,
但是他能够限制大部分的盗链情况。
Syntax: valid_referers none | blocked | server_name |string ...; #可以写多个,空格分割 Default: -; Context: server, location #none: referer来源头部为空的情况,则$invalid_referer 变量为空 #blocked: referer来源头部不为空,这些都不以http://或者https://开头,则$invalid_referer 变量为空 #server_name: 来源头部信息包含当前域名,可以正则匹配,如果匹配则$invalid_referer 变量为空
(也可用server_names正则匹配,可以写一个或多个.但前面不能加完全匹配的域名。server_name可以,更好用,建议使用这个) #官方案例,server_names后面一定跟正则匹配的内容(注:用server_name,前面可加完全匹配地址,server_names不行) valid_referers none blocked www.linux.com server_name *.example.com example.* www.example.org/galleries/ ~\.google\.; if ($invalid_referer) { # 判断是否为空,if指令后面要有空格 return 403; #如果不是上述referer,就返回403 }
#1.配置nginx [root@web02 conf]# vim beidl.conf server { listen 80; server_name beidl.linux.com; location / { root /code; index index.html; } } #2.上传2张图片 [root@web02 conf.d]# cd /code [root@web02 conf.d]# rz # 传2张图片 [root@web02 code]# chown www.www * #3.重启nginx
#1.配置nginx [root@web01 conf.d]# vim dl.conf server { listen 80; server_name dl.linux.com; location / { root /code/dl; index index.html; } } #配置盗链的页面 [root@web01 conf.d]# vim /code/dl/dl.html <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>dl.com</title> </head> <body style="background-color:pink;"> <img src="http://beidl.linux.com/1.jpg"/> </body> </html> #盗链的机器配hosts(因为测试环境不认识域名地址) [root@web01 dl]# vim /etc/hosts 10.0.0.8 beidl.linux.com # 配置windows的host,后访问http://dl.linux.com/dl.html测试。图片背景是粉色
[root@web02 conf]# vim beidl.conf server { listen 80; server_name beidl.linux.com; root /code; location / { index index.html; } location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif)$ {#设置允许的域名访问规则 #none表示没有域名"-",这种是直接访问图片地址;blocked接受没有http/https头。一般都写none,blocked valid_referers none blocked beidl.linux.com; #完全匹配,如果后面有正则匹配内容,用server_names if ($invalid_referer) {#0:等于上面的值,1:表示不等于上面的值。这里1表示true return 403; # 直接返回错误 # rewrite (.*) /2.jpg break; # 跳转到另一张图片 } } } # 测试 curl -e "www.baidu.com" -I beidl.linux.com/1.jpg #curl -e指定域名 200 curl -e "https://www.baidu.com" -I beidl.linux.com/1.jpg #curl -e指定域名 403
[root@web02 conf]# vim beidl.conf server { listen 80; server_name beidl.linux.com; root /code; location / { index index.html; } location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif)$ { #如果使用server_name其前面可以加匹配的域名,如果使用server_names则前面不能加匹配域名 #valid_referers none blocked server_names *.example.com *.linux.com; valid_referers none blocked beidl.linux.com server_name *.example.com; #用server_name也可以,并且server_name前面可以加完全匹配的域名 if ($invalid_referer) {# 不匹配的话 return 403; # 直接返回错误 # rewrite (.*) /2.jpg break; # 跳转到另一张图片 } } }
[root@web01 conf.d]# curl -e "www.baidu.com" -I beidl.linux.com/1.jpg #curl -e指定域名 200 [root@web01 conf.d]# curl -e "https://www.baidu.com" -I beidl.linux.com/1.jpg #curl -e指定域名 403
什么是跨域访问,当我们通过浏览器访问a网站时,同时会利用到ajax或其他方式,同时也请求b网站,这样的话就会出现请求一个页面,
使用了两个域名,这种方式对浏览器来说默认是禁止的。 #注跨域和盗链的区别在于,跨域是http请求去访问,对方网页可能会修改自己的内容。
而盗链只是get请求获取静态资源,对方网页不会修改自己的内容
#1.配置nginx [root@web02 conf.d]# vim beikuayu.conf server { listen 80; server_name beikuayu.linux.com; location / { root /code; index index.html; } } #2.重启nginx #3.配置页面 [root@web02 conf.d]# echo "beikuayuwangzhan" > /code/index.html
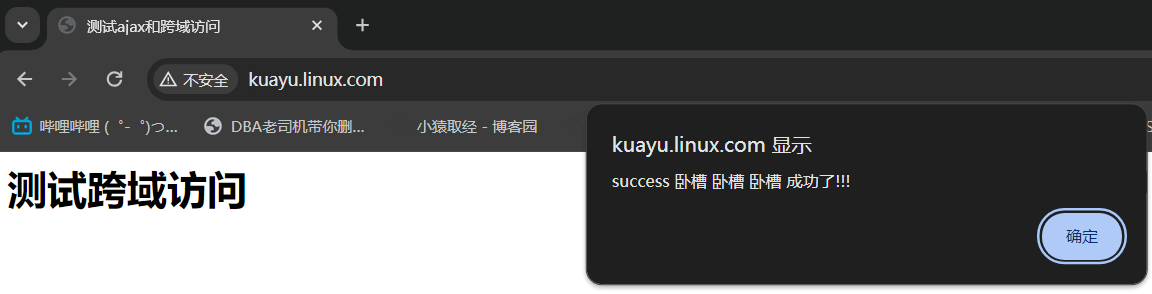
#1.配置nginx [root@web01 conf.d]# vim kuayu.conf server { listen 80; server_name kuayu.linux.com; location / { root /code/kuayu; index index.html; } } #2.配置页面 [root@web01 conf.d]# mkdir /code/kuayu [root@web01 conf.d]# vim /code/kuayu/index.html <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>测试ajax和跨域访问</title> <script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.min.js"></script> </head> <script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function(){ $.ajax({ type:"GET", url:"http://beikuayu.linux.com", success: function(data) { alert("success 卧槽 卧槽 卧槽 成功了!!!"); }, error: function() { alert("fail!!,跨不过去啊,不让进去啊,只能蹭蹭!") } }); }); </script> <body> <h1>测试跨域访问</h1> </body> </html> #3.配置hosts [root@web01 conf.d]# vim /etc/hosts 10.0.0.8 beikuayu.linux.com #4.重启nginx
[root@web02 conf.d]# vim beikuayu.conf server { listen 80; server_name beikuayu.linux.com; root /code; index index.html; location ~* \.html$ { add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *; #add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin http://kuayu.linux.com;#只允许这一个域名 add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS; } }
CPU亲和(affinity)减少进程之间不断频繁切换,减少性能损耗,其实现原理是建CPU核心和Nginx工作进程绑定方式,
把每个worker进程固定到对应的cpu上执行,减少切换CPU的cache miss,获得更好的性能。 #就是CPU有几个核,就配几个worker,每个核处理一个worker,cpu的核不会为了worker去切换。worker不会抢占,工作效率提高
[root@web02 ~]# lscpu Architecture: x86_64 CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit CPU(s): 4 On-line CPU(s) list: 0-3 # cpu列表,0代表第一个 Thread(s) per core: 1 # 1块物理cpu Core(s) per socket: 4 # 4个核心 NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-3 # 一个物理CPU上面有四个内核,分别是 0 1 2 3
# nginx worker进程数量,一定要与核心数保持一致 # 下面是手动修改核心数,但不能保证绑定在不同核心上 [root@web02 nginx]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf worker_processes 4; [root@web02 conf]# systemctl restart nginx [root@web02 conf]# ps -ef|grep nginx # 查看worker数量 root 7361 1 0 23:21 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf www 7362 7361 0 23:21 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process www 7363 7361 0 23:21 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process www 7364 7361 0 23:21 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process www 7365 7361 0 23:21 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process # 查看worker起在哪个核心上(这个是随机的,不确定) [root@web02 conf]# ps -eo pid,args,psr|grep [n]ginx 7361 nginx: master process /usr/ 1 7362 nginx: worker process 3 7363 nginx: worker process 1 7364 nginx: worker process 0 7365 nginx: worker process 2 # 下面是保证cpu亲和的三种方式 # 第一种绑定组合方式(不推荐) worker_processes 12; worker_cpu_affinity 000000000001 000000000010 000000000100 000000001000 000000010000 000000100000
000001000000 000010000000 000100000000 001000000000 010000000000 100000000000; # 第二种方式(使用较少) worker_processes 2; worker_cpu_affinity 101010101010 010101010101; # 第三种最佳绑定方式,修改nginx启动的work进程为自动。 worker_processes auto; # 自动配成内核数量 worker_cpu_affinity auto;
[root@web02 nginx]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf user www; worker_processes auto; # nginx配置的时候就加上这2条,肯定不会有问题 worker_cpu_affinity auto; # 配完后重启查看worker在哪个核心上 [root@web02 conf]# ps -eo pid,args,psr|grep [n]ginx 7430 nginx: master process /usr/ 1 #master不用管,只做管理,不工作 7431 nginx: worker process 0 7432 nginx: worker process 1 7433 nginx: worker process 2 7434 nginx: worker process 3





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
2019-11-28 python基础语法17 面向对象4 多态,抽象类,鸭子类型,绑定方法classmethod与staticmethod,isinstance与issubclass,反射**