CentOS centos7的目录结构, 文件系统常用命令(pwd,cd,mkdir,touch,ls,cat,echo,cp,mv,rm), vim编辑器
bin ---- 命令,二进制文件的存放目录 boot ----- 系统引导程序+系统的内核 dev ---- 设备 硬盘,光驱 etc ---- 存储系统或者服务的配置文件 home ---- 普通用的家目录,贫民窟 lib ----- 库文件存放目录 lib64 ---- 库文件的存放目录(64位系统) media ---- linux识别的设备,比如u盘等,挂这个目录 mnt ----- 临时的挂载点目录 opt ----- 第三方的软件安装在整理 proc ----- 虚拟目录,显示内存中的信息(进场,内核的信息) root ----- root的家目录 相当于皇宫 run ----- 放的启动的东西 sbin --- 超级命令,只用root用户才能用的命令 srv ----- service的缩写,存放的是一些启动后需要的数据 sys ------ 虚拟目录,内存信息 tmp ----- 临时文件的存放位置 usr ---- 存放用户的程序 var ----- 存放经常变化的文件,比如日志等
解释:pwd = print working directory 显示当前所在的目录 [root@localhost run] # pwd /run [root@localhost network-scripts]# pwd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts
解释: cd ---> change directory 改变目录信息 ##注意点 /目录 表示绝对路径 ; 目录 表示相对路径 #绝对路径的方式 [root@localhost run]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ [root@localhost network-scripts]# pwd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts [root@localhost network-scripts]# cd /etc [root@localhost etc]# cd /etc [root@localhost etc]# cd /home [root@localhost home]# pwd /home #相对路径的方式 [root@localhost home]# cd /etc [root@localhost etc]# cd sysconfig/ [root@localhost sysconfig]# pwd /etc/sysconfig # 快速回到进入自己的家目录 [root@localhost sysconfig]# cd ~ [root@localhost ~]# pwd /root [root@localhost ~]# cd /root [root@localhost ~]# pwd /root [root@localhost ~]# [root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ [root@localhost network-scripts]# cd # 回到家目录 [root@localhost ~]# # 快速回到自己进过的目录 [root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/ [root@localhost sysconfig]# cd /bin [root@localhost bin]# pwd /bin [root@localhost bin]# cd - /etc/sysconfig [root@localhost sysconfig]# pwd /etc/sysconfig [root@localhost sysconfig]# #返回当前路径的上一级目录 [root@localhost lib]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ [root@localhost network-scripts]# pwd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts [root@localhost network-scripts]# cd ../ [root@localhost sysconfig]# pwd /etc/sysconfig [root@localhost sysconfig]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ [root@localhost network-scripts]# cd ../../ [root@localhost etc]# pwd /etc [root@localhost etc]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ [root@localhost network-scripts]# cd ../../../../../../../../../ [root@localhost /]# pwd /
mkdir ---> make directory [root@localhost /]# cd /oldboy -bash: cd: /oldboy: No such file or directory [root@localhost /]# mkdir /oldboy [root@localhost /]# cd /oldboy/ [root@localhost oldboy]# pwd /oldboy #用-p参数创建多级目录 [root@localhost oldboy]# mkdir /oldboy/olddog/jason mkdir: cannot create directory ‘/oldboy/olddog/jason’: No such file or directory [root@localhost oldboy]# mkdir /oldboy/olddog [root@localhost oldboy]# mkdir /oldboy/olddog/jason [root@localhost oldboy]# cd /oldboy/olddog/jason/ [root@localhost jason]# pwd /oldboy/olddog/jason [root@localhost jason]# cd / [root@localhost /]# mkdir -p /oldboy/oldgirl/tank [root@localhost /]# cd /oldboy/oldgirl/tank/ [root@localhost tank]# pwd /oldboy/oldgirl/tank #我们在创建目录的时候最好是用绝对路径
[root@localhost tank]# cd /oldboy/ [root@localhost oldboy]# pwd /oldboy [root@localhost oldboy]# touch oldboy.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# ls oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl [root@localhost oldboy]# touch /oldboy/olddog/jj [root@localhost oldboy]# ls /oldboy/olddog/ jason jj #在linux里面不会通过后缀名来区分文件的类型,但是我们约定,你什么样的文件,就用什么后缀名,免得搞不清楚
ls ----> list [root@localhost /]# cd oldboy/ [root@localhost oldboy]# ls oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl [root@localhost oldboy]# ls ol # 判断有没有改文件或文件夹 ls: cannot access ol: No such file or directory [root@localhost oldboy]# ls -l total 0 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Mar 24 18:09 oldboy.txt drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 29 Mar 24 18:10 olddog drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Mar 24 18:06 oldgirl [root@localhost oldboy]# ls -ltr total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Mar 24 18:06 oldgirl -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Mar 24 18:09 oldboy.txt drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 29 Mar 24 18:10 olddog [root@localhost oldboy]# ls -lt total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 29 Mar 24 18:10 olddog -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Mar 24 18:09 oldboy.txt drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Mar 24 18:06 oldgirl # ls -l 默认是创建时间最新到最老排序(测试是按照文件名排序) # ls -lt 创建时间最新到最老排序 # ls -ltr 创建时间最老到最新排序 ls -a 表示查看当前文件夹底下的所有文件,包括隐藏文件
# cat 是查看文件信息 [root@localhost oldboy]# cat /oldboy/oldboy.txt 123 [root@localhost oldboy]# cat oldgirl.txt 456 #查看多个文件的文件信息 [root@localhost oldboy]# cat oldboy.txt oldgirl.txt 123 456 # 将文件中的内容读取出来,放入到另一个文件中 [root@localhost oldboy]# cat oldboy.txt oldgirl.txt > jason.txt # 创建并覆盖写入 >>为接着写入 [root@localhost oldboy]# cat jason.txt 123 456
# 直接输出信息 [root@localhost oldboy]# echo "hello world" hello world # 将echo的内容写入到文件 ,> 是覆盖写入,>> 是追加写入 [root@localhost oldboy]# echo "hello world" > lxx.txt # 创建并覆盖写入 [root@localhost oldboy]# ls jason.txt lxx.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# cat lxx.txt hello world [root@localhost oldboy]# echo "hello world" > lxx.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# cat lxx.txt hello world [root@localhost oldboy]# echo "hello world" >> lxx.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# cat lxx.txt hello world hello world
# cp --->copy 语法格式: cp 参数(可选) 要复制的信息 复制到什么位置 # 在复制文件。在复制文件的时候,要复制的文件不要加/,一般是只能复制目录的时候加/ [root@localhost oldboy]# cp /etc/hosts /oldboy/ [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt lxx.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# cat hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 [root@localhost oldboy]# cp /etc/hosts /oldboy/ # 复制文件夹已存在该文件 cp: overwrite ‘/oldboy/hosts’? y # 是否覆盖 # 复制文件夹 [root@localhost sysconfig]# cp /etc/sysconfig/ /oldboy/oldgirl cp: omitting directory ‘/etc/sysconfig/’ [root@localhost sysconfig]# cp -r /etc/sysconfig/ /oldboy/oldgirl #复制整个文件夹 -r递归里面所有 [root@localhost sysconfig]# cd /oldboy/oldgirl [root@localhost oldgirl]# ls sysconfig tank [root@localhost oldgirl]# cd /oldboy/oldgirl/sysconfig/ [root@localhost sysconfig]# pwd /oldboy/oldgirl/sysconfig cp :的参数 -r 进行递归复制 -p 拷贝是时候属性保存不变 -d 和链接相关的文件 -a == -drp # 全部 # 利用cp做备份 [root@localhost oldboy]# cat jason.txt 123 456 [root@localhost oldboy]# cp jason.txt jason.txt.bak # 一般备份文件以.bak命名 [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt jason.txt.bak lxx.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# rm -rf jason.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt.bak lxx.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# cp jason.txt.bak jason.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt jason.txt.bak lxx.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# cat jason.txt 123 456 # 如果cp的时候,多个文件覆盖,会出现多次确定,如何避免 [root@localhost oldboy]# cp -r /etc/sysconfig/ /oldboy/oldgirl cp: overwrite ‘/oldboy/oldgirl/sysconfig/ip6tables-config’? y cp: overwrite ‘/oldboy/oldgirl/sysconfig/iptables-config’? y cp: overwrite ‘/oldboy/oldgirl/sysconfig/cbq/avpkt’? ^C #解决办法 \cp 不重复提示 [root@localhost oldboy]# \cp -r /etc/sysconfig/ /oldboy/oldgirl
mv --move 对文件或者文件夹进行剪切(移动) 语法格式: mv 要移动的文件或者文件夹 移动要什么位置 #在根目录创建test文件夹,然后创建heihei.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# mkdir /test [root@localhost oldboy]# cd /test [root@localhost test]# touch heihei.txt # 将 /test/heihei.txt文件 剪切(移动)到/oldboy/shanghai/的文件夹, [root@localhost test]# mv /test/heihei.txt /oldboy/shanghai/ mv: cannot move ‘/test/heihei.txt’ to ‘/oldboy/shanghai/’: Not a directory #创建/oldboy/shanghai文件夹 [root@localhost test]# mkdir /oldboy/shanghai [root@localhost test]# mv /test/heihei.txt /oldboy/shanghai/ [root@localhost test]# cd /oldboy/shanghai [root@localhost shanghai]# ls heihei.txt #原来的/test/heihei.txt文件消失 [root@localhost shanghai]# cd /test [root@localhost test]# ls # 将 /test/heihei.txt文件 剪切(移动)到/oldboy/shanghai,如果不加/,表示将heihei.txt文件内容写入 shanghai,文件,并将名字改成shanghai # 在linux系统没有重命名这个东西,我们可以同mv 命令实现 [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt jason.txt.bak lxx.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt shanghai [root@localhost oldboy]# mv lxx.txt lxxsb.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt jason.txt.bak lxxsb.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt shanghai
rm --->remove 语法:rm 参数 要删除的数据信息 #删除文件 [root@localhost ~]# cd /oldboy/ [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt jason.txt.bak lxxsb.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt shanghai [root@localhost oldboy]# rm jason.txt.bak rm: remove regular file ‘jason.txt.bak’? y [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt lxxsb.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt shanghai # 删除文件夹 [root@localhost oldboy]# rm shanghai rm: cannot remove ‘shanghai’: Is a directory [root@localhost oldboy]# rm -r shanghai rm: descend into directory ‘shanghai’? y rm: remove regular empty file ‘shanghai/heihei.txt’? y rm: remove directory ‘shanghai’? y #强行删除 [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt lxxsb.txt oldboy.txt olddog oldgirl oldgirl.txt [root@localhost oldboy]# rm -f oldboy.txt # -f不提醒,保存删除文件不存在 [root@localhost oldboy]# rm -rf olddog [root@localhost oldboy]# ls hosts jason.txt lxxsb.txt oldgirl oldgirl.txt #centos7这个命令会保护 rm -rf / #rm -rf /* 不受保护
vim三种模式切换
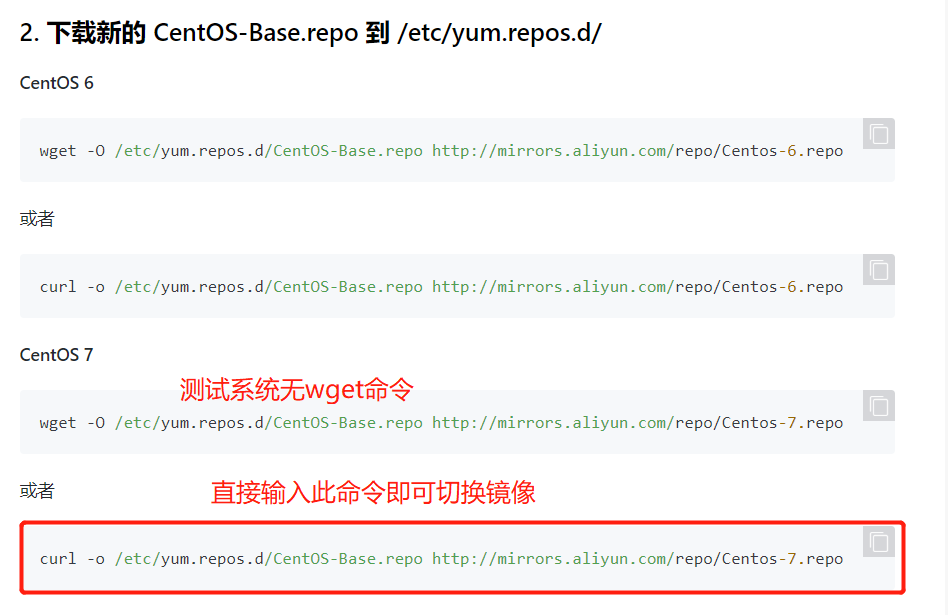
#安装之前先切换镜像源 https://developer.aliyun.com/mirror/centos?spm=a2c6h.13651102.0.0.3e221b11yCmuQx # 要用vim要安装 #命令:yum -y install vim 或者 yum install vim -y # -y表示确定 # vim 是编辑器,他有三种状态 1 正常模式 vim 文件 进入后就vim的正常模式,从正常如何进入编辑模式,输入 i,o,a,I,O,A,R,都可以,但是 我们只要记住一个i,因为方便记忆。 正常模式底下的命令: 拷贝: yy 粘贴:p # 光标所在行复制,并在光标下一行粘贴 拷贝当前行向下2行,并粘贴 拷贝2行:2yy 粘贴:p 删当前行: 删除:dd 删除当前的下两行: 删除:2dd
删除下方所有行:dG 光标移动到最后一行:G 光标移到首行:gg ggdG即全删 光标移到第二行:2gg 撤回:u 2 插入模式 进入编辑模式,就可以直接输入内容。 3 命令模式 1 查找内容: :/关键字 2 取消高亮: :nohl 3 显示行号: :set nu 4 取消行号 :set nonu 5 没有修改情况下退出 :q 6 如果修改了,但我们不想保存, :q! 7 如果修改,并且想保存, :wq # 如果发现vim 不能编辑这个文件 # 原因为linux非正常关机时产生的.swp文件 # 我在这个文件所在目录执行: ls -a # 你会发现有一个 .文件名.swp的隐藏文件 .开头为隐藏文件 #我们执行删除命令将其删除:rm -rf .文件名.swp


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号