数据存储--文件存储
数据存储--文件存储
考点:
输入输出流
FileOutputStream输出流写入文件
FileInputStream输入流从文件里写到系统里
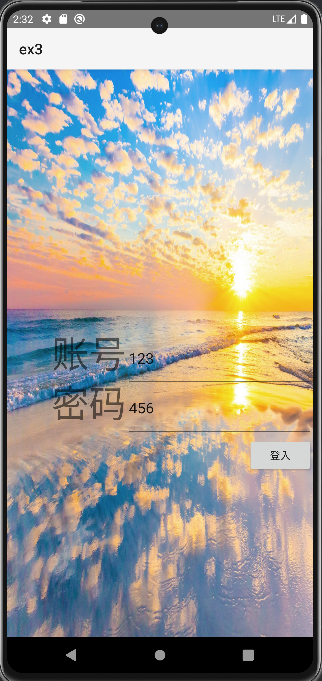
布局文件:
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/backgroundpic"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="账号"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="60dp"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et1"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv1"
android:text="请输入账号"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/tv1"
android:textSize="20dp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="密码"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="60dp"
android:layout_below="@id/tv1"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et2"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv2"
android:text="请输入密码"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/tv2"
android:textSize="20dp"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登入"
android:layout_below="@id/et2"
/>
</RelativeLayout>整体布局:
运用相对布局:
里面运用Imageview设置背景图片(用background属性)
两个文本框
账号
密码
两个输入文本框
账号输入框
密码输入框
Java文件
MainActivity.java
mainactivity.java
package com.example.ex3;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.Map;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private EditText et1;
private EditText et2;
private Button btn;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ini();//初始化
//获取当前密码账号
Map<String, String>userinformation=FileSaveLogin.getuserinfo(this);//调用获取信息函数,因为是静态函数所以可以用类名调用
if(userinformation!=null){//从文件中读出来,若文件不为空就取出来(读),作用是每次写完方便下次直接登入账号密码还在且显示。
//假如之前已经有写入账号密码,那么就不为空,就可以显示在文本框
et1.setText(userinformation.get("account"));
et2.setText(userinformation.get("password"));
}
}
public void ini(){//初始化获取各个控件以及设置按钮监听事件
et1=findViewById(R.id.et1);
et2=findViewById(R.id.et2);
btn=findViewById(R.id.btn);
btn.setOnClickListener(this);//为按钮设置点击监听器
}
//点击事件
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//获取输入的账号密码写入文件
//getText完一定要toString
String account=et1.getText().toString().trim();//trim移除字符串两侧空白字符
String password=et2.getText().toString();
//因为保存函数是静态函数可以直接用类调用
boolean issuccessful=FileSaveLogin.saveuserinfo(this,account,password);
if(issuccessful==true){
Toast.makeText(this,"保存成功",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
else{
Toast.makeText(this,"保存失败",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}工具类(FileSaveLogin.java)-->单独写与mainactivity分开
FilesaveLogin.java
package com.example.ex3;
import android.content.Context;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class FileSaveLogin {
//写(baocunxin
public static boolean saveuserinfo(Context context,String account,String password) {//三个参数:上下文,账号,密码(账号密码是本题要求填写。)
FileOutputStream a = null;//定义输出流
try {
a=context.openFileOutput("data.txt",Context.MODE_PRIVATE);//获取输出流,是将信息写入data.txt
a.write((account+":"+password).getBytes());//存入格式是账号:密码
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
finally {
try{
if(a!=null){//流不为空是正常的-->关流
a.close();
}
}
catch (IOException e){//有异常-->打印
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//读(从文件里读出保存的信息)
public static Map<String, String> getuserinfo(Context context){//读出的信息用Map存,前一个是账号,后一个是密码。函数参数上下文
String content="";//保存获取信息
FileInputStream fis=null;//定义输入流对象
try{
fis=context.openFileInput("data.txt");//获取输入流对象
byte[] buffer=new byte[fis.available()];//创建存放输入对象值的数组并分配空间(available可以获取输入流字节数)
fis.read(buffer);//将读的结果通过输入流对象放入buffer数组
content =new String(buffer);//字节数组转字符串String()
Map<String, String>m=new HashMap<String,String>();//创建Map<String,String>
String[] infos=content.split(":");//将字符串按照:前后划分存入字符串数组
m.put("account",infos[0]);//然后分别放入map。这个map有两个域,一个是账号域,一个是密码域。
m.put("password",infos[1]);
return m;
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
finally {
try{
if(fis!=null){//不为空是正常的-->关流
fis.close();
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();//不正常打印途径
}
}
}
}定义流
try{
获取流
}
catch(Exception e){
打印流途径
}
finally{
try{
if(流!=null){
流.close();//关流
}
catch(IOException e){
打印流途径
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步