java 流程控制篇 2021/02/26
正文
1. 用户交互Scanner
1.1 简单的Scanner用法
- 首先,需要 import java.util.Scanner
- 其次,需要创建一个 Scanner 类的对象, Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
- 通过调用Scanner对象的方法来完成,
- 一定要注意有开有关,最后要调用方法 close()
| 方法名称 | 搭配方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| boolean hasNext() | String next() | 一个用于查看是否有下一个输入,一个用于接收,空格视为结束 |
| boolean hasNextLine() | String nextLine() | 一个用于查看是否有下一个输入,一个用于接收,换行视为结束 |
- haveNext(), next() 方法的尝试
package com.luckylight.package3; import java.util.Scanner; public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("使用next方式接收:"); // next 相当于 scanf if (scan.hasNext()) { String str = scan.next(); System.out.println(str); } // 注意有开有关 scan.close(); } }
- haveNextLine(), nextLine()方法的尝试
package com.luckylight.package3; import java.util.Scanner; public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("使用nextline方式接收:"); // nextLine 相当于 gets if (scan.hasNextLine()) { String str = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println(str); } // 注意有开有关 scan.close(); } }
- next()与nextLine()细节方面的介绍
- next() -- 类似于 c++中的scanf
- 必须要读到有效字符才算结束
- 有效字符前的空白,next()方法将其自动去除
- 得不到带有空格的字符串
- nextLine() 类似于 c++中的 getline(cin, str);(String str) || cin.getline(buf, sizeof (buf));-->(char buf[N])
- 以 Enter 作为结束符
- 可以获得空白
- next() -- 类似于 c++中的scanf
1.2 Scanner 的进一步
- 之前Scanner 的部分仅仅是返回了 字符串 String类型,也可以进行 int, float, double 的类型,使用方法如下所示:
- 注意这个 has___这个东西是可以进行隐式转换的,也就是说double 可以接受 int。
- 而且注意,has这个仅是判断,并不接受内容,只有next,他的光标才会往后移动
- 而且也不能超出范围,否则has__是会返回false 的
| 方法名称 | 配套方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| hasNextInt() | nextInt() | 整数int |
| hasNextLong() | nextLong() | 整数long |
| hasNextFloat() | nextFloat() | 浮点数float |
| hasNextDouble() | nextDouble() | 浮点数double |
package com.luckylight.package3; import java.util.Scanner; public class demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int i = 0; float x = 0.0f; // 整数 if (scanner.hasNextInt()) { i = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println("你输入的一个整数是:" + i); } else { System.out.println("你没有输入一个整数"); } // 浮点数,这个是可以接受整数的 if (scanner.hasNextFloat()) { x = scanner.nextFloat(); System.out.println("你输入的一个浮点数float=" + x); } else { System.out.println("你没有输入一个浮点数"); } scanner.close(); } }
求输入整数数字的和以及平均值
package com.luckylight.package3; import java.util.Scanner; public class demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int n = 0; double sum = 0.0; while (scanner.hasNextLong()) { long tmp; n ++; tmp = scanner.nextLong(); sum += tmp; System.out.println("当前你输入的数据是=" + tmp + ", 当前的tmp和为" + sum); } System.out.println("最终的总和为" + sum +", 平均值为 " + sum / n); scanner.close(); } }
1.3 print 与 printLine()
都是java 输出语句
System.out.print(), System.out.printLine()
一个是输出完不换行,print, 一个是输出完会换行, println
2. 顺序结构 & 选择结构 & 循环结构
2.1 顺序结构
直接就是顺序执行,没啥好说的,最基础的程序执行结构,在这里补充一个 小常识。
==与equals的区别
-
"=="操作符的作用
1、用于基本数据类型的比较
2、判断引用是否指向堆内存的同一块地址。
-
equals的作用:
-
用于判断两个变量是否是对同一个对象的引用,即堆中的内容是否相同,返回值为布尔类型
-
用法:boolean b = obj1.equals(obj2);
-
-
== 与 equals 的区别
String作为一个对象来使用,查看他们的区别。
eg1: 对象不同,内容相同
String s1 = new String("java"); String s2 = new String("java"); System.out.println(s1==s2); //false System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true eg2:同一对象,"=="和equals结果相同
String s1 = new String("java"); String s2 = s1; System.out.println(s1==s2); //true System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true String作为一个基本类型来使用
如果值不相同,对象就不相同,所以"==" 和equals结果一样
String s1 = "java"; String s2 = "java"; System.out.println(s1==s2); //true System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true
综上所述,还是使用equals判断稳妥!!!
2.2 选择结构
2.2.1 if 类型
-
if (condition) ---
-
if (condition) --- else ---
-
if (condition1) --- else if (conditon2) ------- else ---
-
if 还可以进行嵌套
2.2.2 switch 类型
- 具体的类型如下示例所示
switch (expression) { case value1 : sentence_1; break; case value2 : sentence_2; break; ... ... default : sentence_n; break; }
- 其中的 break, default 都是可选的,一定要注意 有无的区别
- expression 变量可以使 byte, short, int , 或者是char
- 从 Java SE 7 开始, switch 就可以支持 String 类型了。
- case 后面必须跟的是常量表达式,不可以是变量
下面我们写一个switch文件试一试 String 类型,然后介绍IDEA的反编译
- 首先我们查看IDEA经过 javac生成的文件放在文件哪个位置
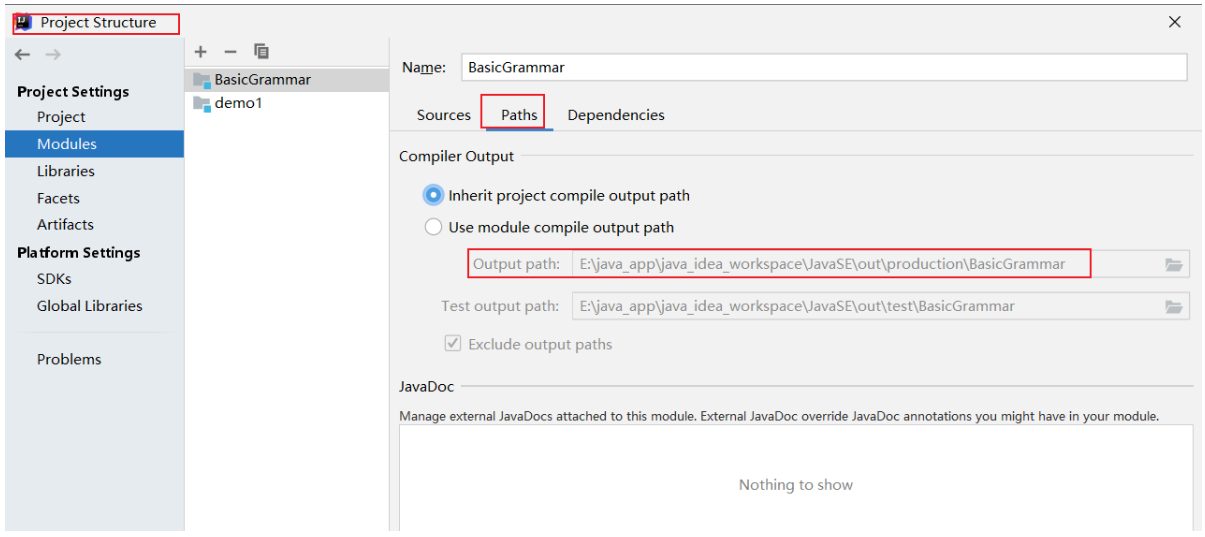
- 进入 class 文件路径,将其添加到 idea 的当前工作区域(不可以直接通过 IDEA 加入,但是可以通过文件夹手动加入)
加入后显示如下(倘若加入后还没有,直接 右键 reload from disk 该文件夹即可)

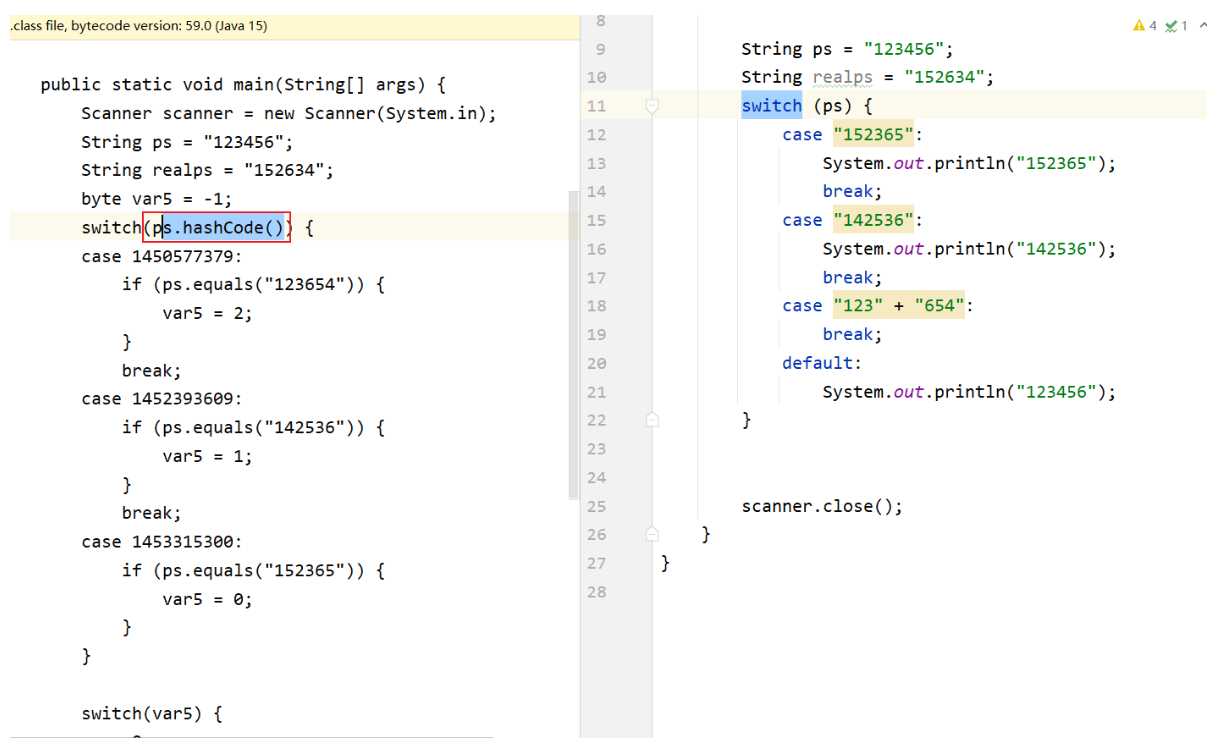
- 最后双击该文件打开即可,查看反编译后的文件,发现这个String的Switch原来是使用了 hash 操作。
2.3 循环结构
2.3.1 while, do~while, for
**while, do -- while, for **
while (booleanExpression) { // 循环体 } do { // 循环体 } while (booleanExpression); for (初始化; booleanExpression; 更新迭代) { // 循环体 }
练习一个打印九九乘法表格
注意这个是双引号,不是单引号
for 版本
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i ++ ) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ ) { System.out.printf("%-2d*%2d = %2d,\t", j, i, i * j); } System.out.println(); } // 这个是双引号 for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i ++ ) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ ) { System.out.print(j+"*"+i+"="+(i*j)+"\t"); } System.out.println(); }
while 版本
int i = 1, j = 1; while (i <= 9) { j = 1; while (j <= i) { System.out.printf("%d * %d = %2d,\t", j, i, i * j); j ++; } i ++; System.out.println(); }
2.3.2 增强的for循环
- Java5引入的一种用于数组或者是集合的增强型for循环, 这个东西好像和 c ++ 那个一样 for (auto x : v){} // 遍历vector数组
for (声明语句 : 表达式) { // 代码 }
测试样例
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 35}; for (int x : numbers) System.out.println(x);
3. Break & Continue
不带标签的 label 和 continue 是和 c ++ 一模一样的
带标签的 label 和 continue 奇奇怪怪,不建议使用。
public class MultTable { public static void main(String[] args) { label1 : for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i ++ ) { if ((i & 1) == 1) { // continue label1; break label1; } System.out.println(i); } } }
4. 练习&debug
打印一个三角形
package com.luckylight.package3; /** * @author LuckyLight * @since 8.0 * @ */ public class MultTable { public static void main(String[] args) { // 打印一个 n 行的三角形 int n = 5; int sumLine = n * 2 - 1; System.out.println(n); System.out.println(sumLine); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { int curCnt = i * 2 - 1; int left = (sumLine - curCnt) / 2; for (int j = 1; j <= sumLine; j ++ ) { if (j <= left || j >= sumLine - left + 1 ) { System.out.print(' '); } else { System.out.print('*'); } } System.out.println(); } } }
IDEA 的debug功能超级好用,建议多多尝试




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)