知识点:
bootmem分配器
memblock分配器
一、bootmem分配器--临时引导内存分配器
在内核初始化的过程中需要分配内存,内核提供临时的引导内存分配器,在页分配器和块分配器初始化完成之后,把空闲的物理页交给页分配器管理,丢弃引导内存分配器bootmem分配器定义的数据结构,内核源码如下:
D:\linux-4.1.2\Linux-4.12\include\linux\bootmem.h
用来描述节点的结构体 typedef struct pglist_data { //该节点所在管理区为ZONE_HIGHMEM ZONE_NORMAL ZONE_DMA 包含了结点中各内存域的数据结构 struct zone node_zones[MAX_NR_ZONES]; /*备用结点及其内存域的列表,以便在当前结点没有可用空间时,在备用结点分配内存*/ struct zonelist node_zonelists[MAX_ZONELISTS]; /*表示该节点管理区的数目,1-3之间,并不是所有的节点都有三个管理区*/ int nr_zones; #ifdef CONFIG_FLAT_NODE_MEM_MAP /* means !SPARSEMEM */ struct page *node_mem_map; #ifdef CONFIG_PAGE_EXTENSION struct page_ext *node_page_ext; #endif #endif #ifndef CONFIG_NO_BOOTMEM struct bootmem_data *bdata;//引导内存bootmem分配器, 每个内存节点都应该有一个该分配器

bootmem分配器提供分配内存/释放内存(alloc_bootmem/free_bootmem)。ARM64架构的内核已不使用bootmem分配器,但其它处理器架构还在使用 bootmem分配器。

二、memblock分配器--代替bootmem
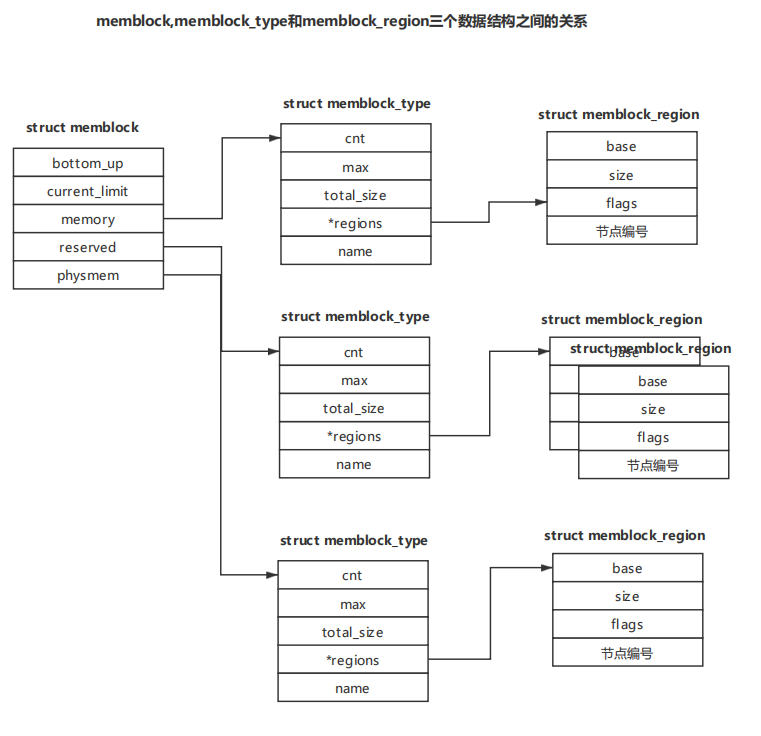
1、memblock数据结构
MEMBLOCK 内存分配器作为 arm32 早期的内存管理器,用于维护系统可用的物理内存。 系统启动过程中,可以使用 MEMBLOCK 内存分配器获得所需的物理内存,也可以将特定物理内存预留给特殊功能使用。MEMBLOCK 内存分配器逻辑框架简单易用,框架中将物理内存和已分配的物理内存维护在不同的数据结构中,以此实现 MEMBLOCK 分配器对物理 内存的分配和回收等操作。
MEMBLOCK 分配器使用一个 struct memblock 结构维护着两种内存, 其中成员 memory 维护着可用物理内存区域;成员 reserved 维护着操作系统预留的内存区域。 每个区域使用数据结构 struct memblock_type 进行管理,其成员 regions 负责维护该类型内存的所有内存区,每个内存区使用数据结构 struct memblock_region 进行维护。
struct memblock_type { unsigned long cnt; /* number of regions */ unsigned long max; /* size of the allocated array */ phys_addr_t total_size; /* size of all regions */ struct memblock_region *regions; char *name; };
struct memblock { bool bottom_up; /* 表示分配内存的方式 is bottom up direction? */ phys_addr_t current_limit; struct memblock_type memory; memory 维护着可用物理内存区域 struct memblock_type reserved; reserved 维护着操作系统预留的内存区域 #ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_MEMBLOCK_PHYS_MAP struct memblock_type physmem; #endif };
/* Definition of memblock flags. */ enum { //表示没有特殊要求的区域 MEMBLOCK_NONE = 0x0, /* No special request */ //表示可以热插拔的区域,即在系统运行过程中可以拔出或者插入物理内存 MEMBLOCK_HOTPLUG = 0x1, /* hotpluggable region */ //表示镜像的区域,将内存数据做两个复制,分配放在在内存和镜像内存中 MEMBLOCK_MIRROR = 0x2, /* mirrored region */ //表示不添加到内存直接映射区域,即线性映射区域 MEMBLOCK_NOMAP = 0x4, /* don't add to kernel direct mapping */ }; 内存块区域的数据结构 struct memblock_region { phys_addr_t base; phys_addr_t size; unsigned long flags; #ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_MEMBLOCK_NODE_MAP int nid; #endif };
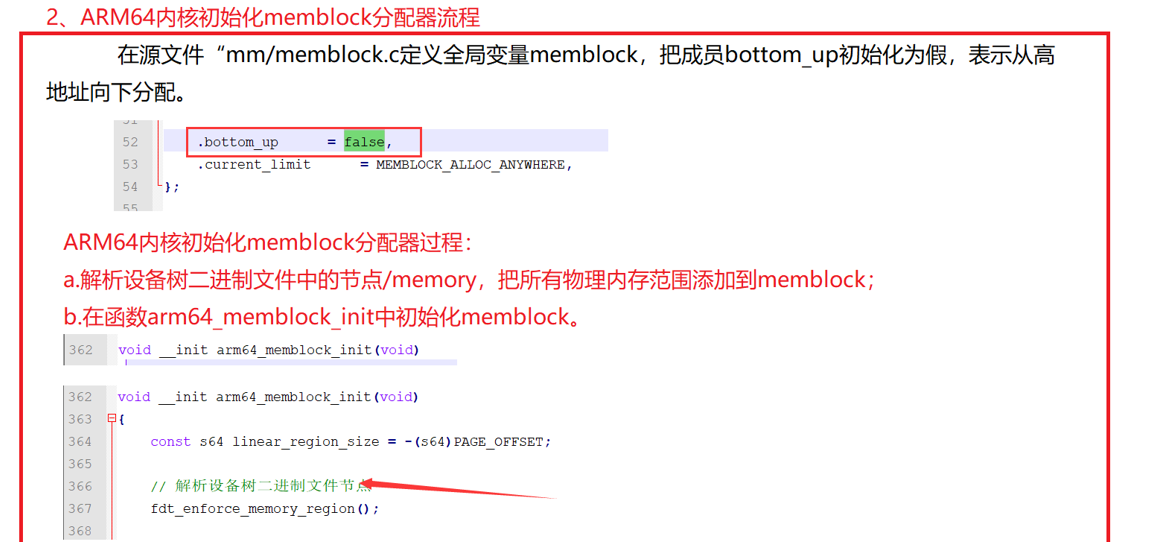
2、arm64内核初始化memblock分配器流程
1、memblock数据结构

2、arm64内核初始化memblock分配器
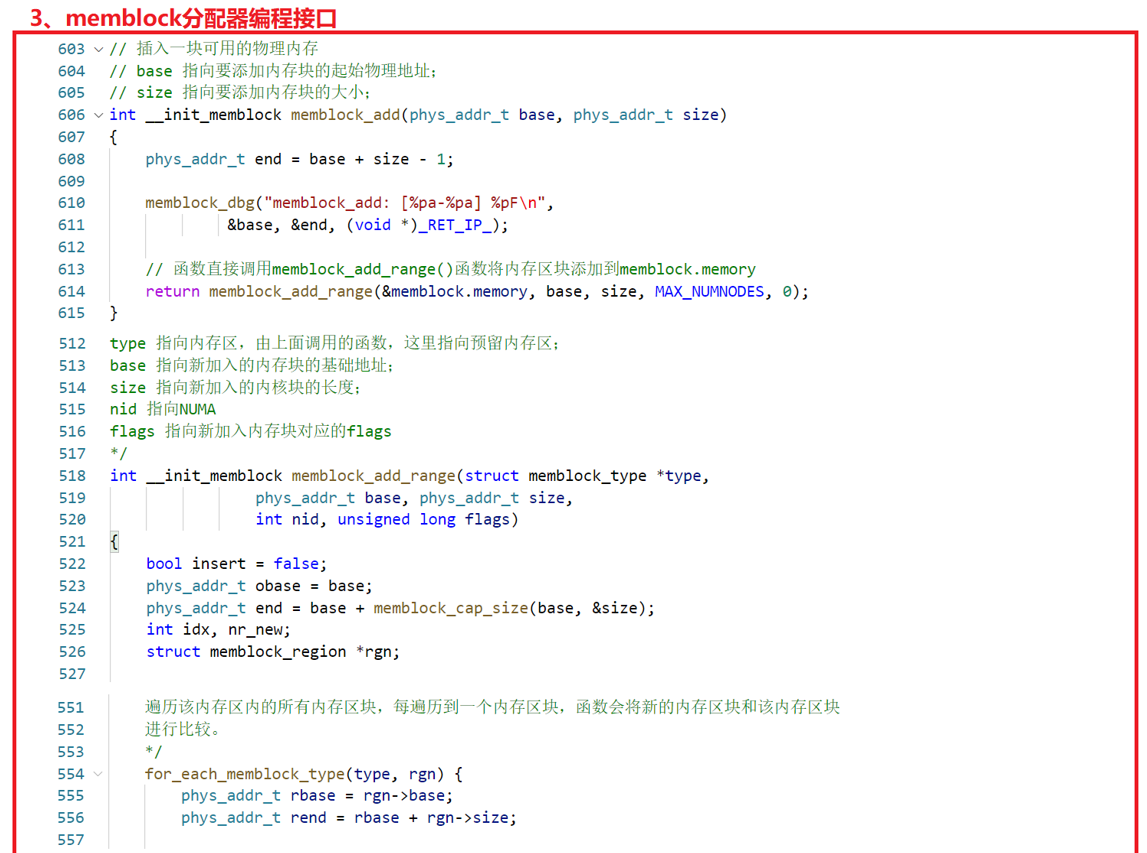
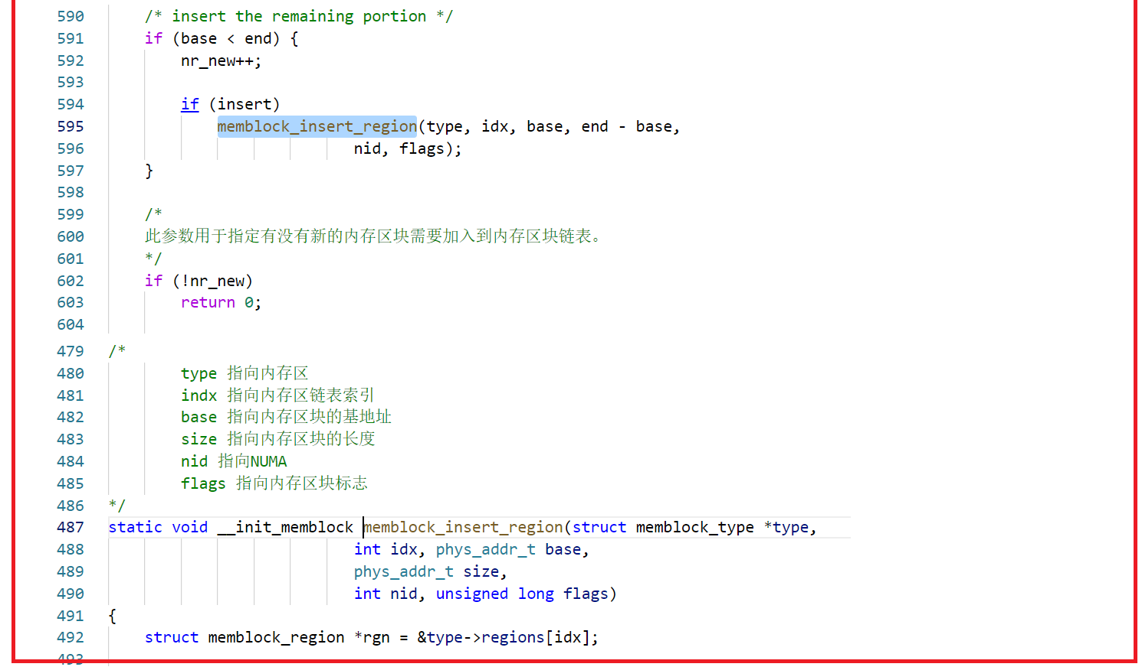
memblock_add:添加新的内存块区域到memblock.memory中;
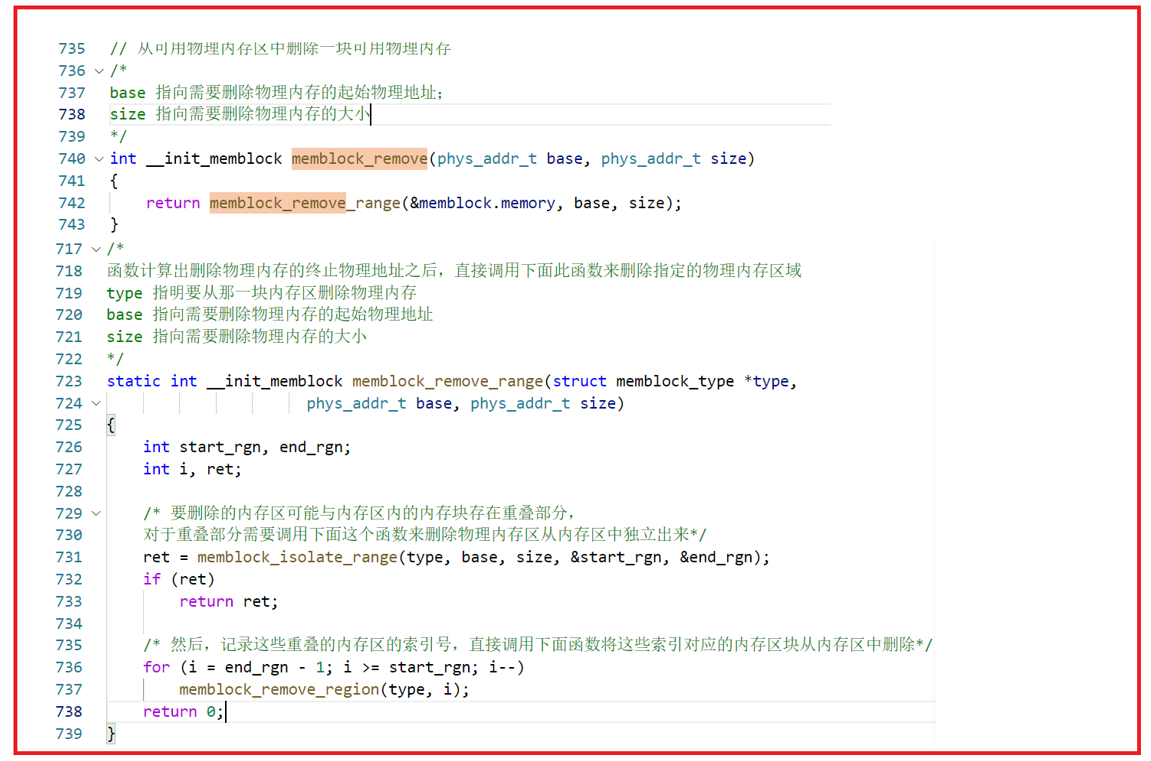
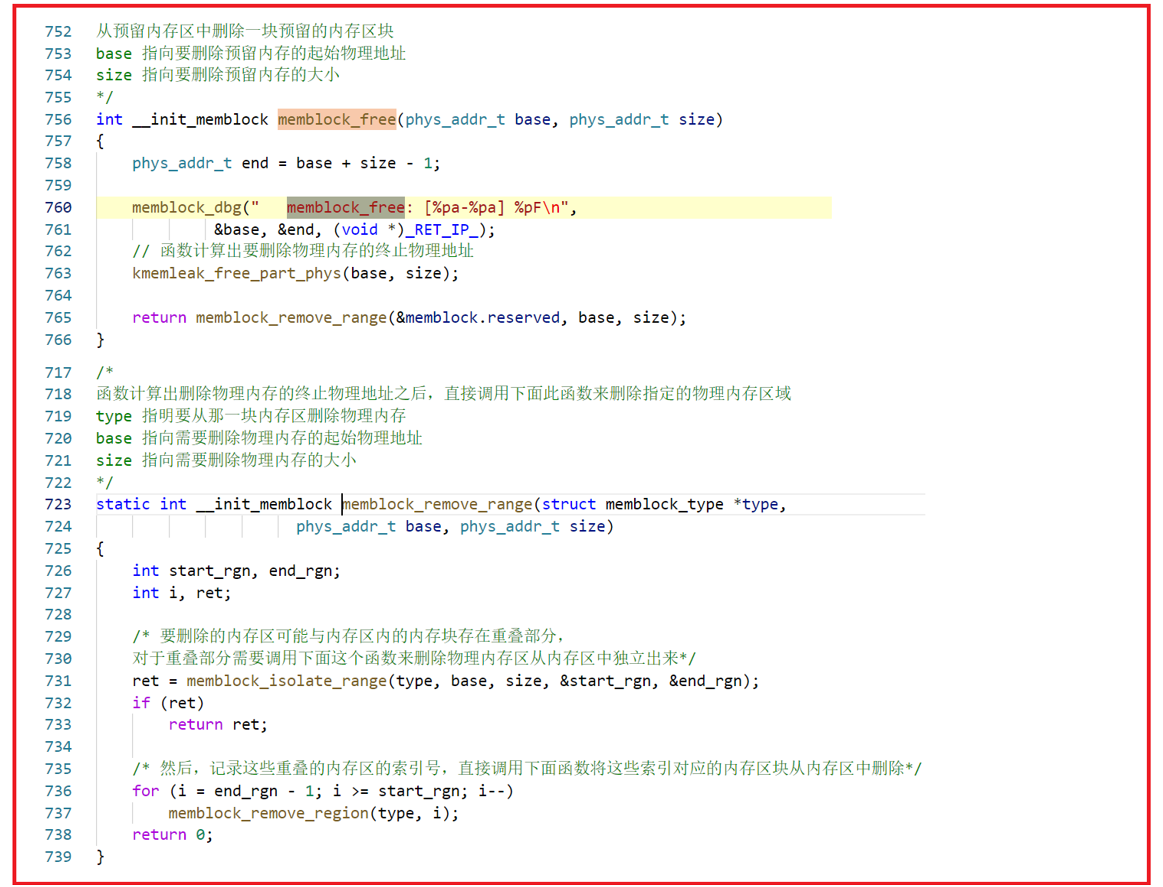
memblock_remove:删除内存块区域;
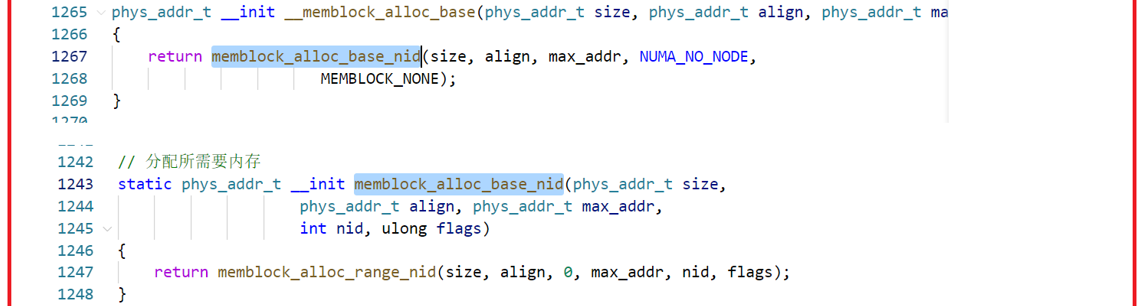
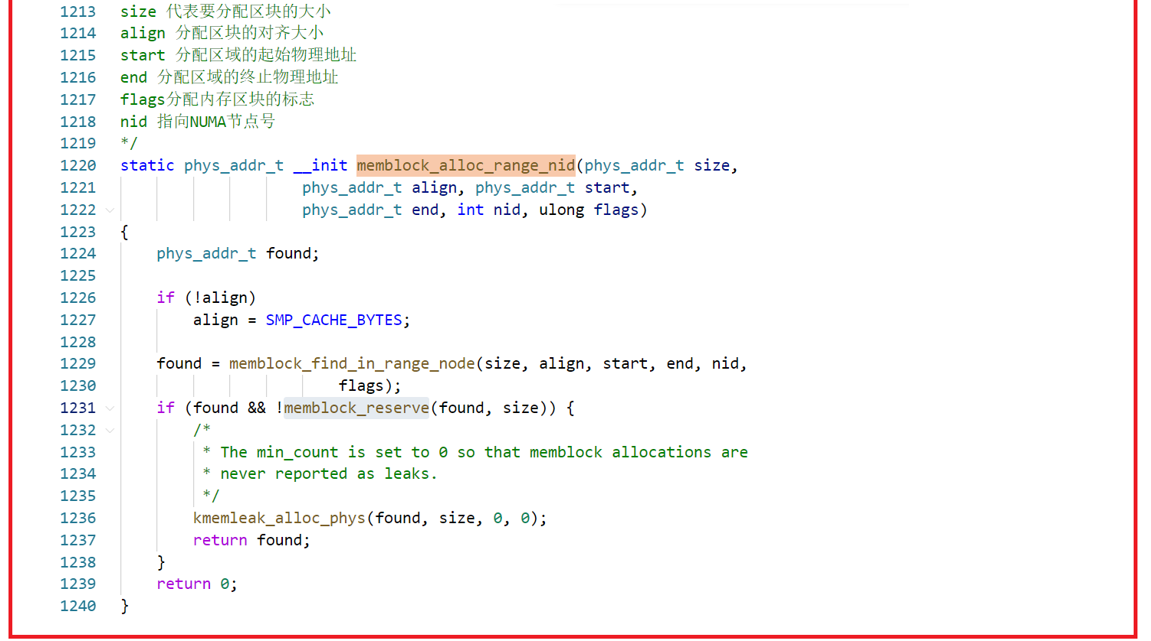
memblock_alloc:分配内存;
memblock_free:释放内存。

初始化过程:
void __init setup_arch(char **cmdline_p) { pr_info("Boot CPU: AArch64 Processor [%08x]\n", read_cpuid_id()); sprintf(init_utsname()->machine, UTS_MACHINE); init_mm.start_code = (unsigned long) _text; init_mm.end_code = (unsigned long) _etext; init_mm.end_data = (unsigned long) _edata; init_mm.brk = (unsigned long) _end; *cmdline_p = boot_command_line; early_fixmap_init(); early_ioremap_init(); setup_machine_fdt(__fdt_pointer); parse_early_param(); /* * Unmask asynchronous aborts after bringing up possible earlycon. * (Report possible System Errors once we can report this occurred) */ local_async_enable(); /* * TTBR0 is only used for the identity mapping at this stage. Make it * point to zero page to avoid speculatively fetching new entries. */ cpu_uninstall_idmap(); xen_early_init(); efi_init(); arm64_memblock_init();
.......
void __init arm64_memblock_init(void) { const s64 linear_region_size = -(s64)PAGE_OFFSET; /* 解析设备数二进制文件 Handle linux,usable-memory-range property */ fdt_enforce_memory_region(); /* * Ensure that the linear region takes up exactly half of the kernel * virtual address space. This way, we can distinguish a linear address * from a kernel/module/vmalloc address by testing a single bit. */ BUILD_BUG_ON(linear_region_size != BIT(VA_BITS - 1)); /* * 全局变量memstart_addr 记录为内存的起始物理地址Select a suitable value for the base of physical memory. */ memstart_addr = round_down(memblock_start_of_DRAM(), ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN); /* * Remove the memory that we will not be able to cover with the * linear mapping. Take care not to clip the kernel which may be * high in memory. *把线性映射区不能覆盖的物理内存范围从memblock删除 ,为什么??*/ memblock_remove(max_t(u64, memstart_addr + linear_region_size, __pa_symbol(_end)), ULLONG_MAX); if (memstart_addr + linear_region_size < memblock_end_of_DRAM()) { /* ensure that memstart_addr remains sufficiently aligned */ memstart_addr = round_up(memblock_end_of_DRAM() - linear_region_size, ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN); memblock_remove(0, memstart_addr); } /* * Apply the memory limit if it was set. Since the kernel may be loaded * high up in memory, add back the kernel region that must be accessible * via the linear mapping. */ if (memory_limit != (phys_addr_t)ULLONG_MAX) { memblock_mem_limit_remove_map(memory_limit); memblock_add(__pa_symbol(_text), (u64)(_end - _text)); } if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD) && initrd_start) { /* * Add back the memory we just removed if it results in the * initrd to become inaccessible via the linear mapping. * Otherwise, this is a no-op */ u64 base = initrd_start & PAGE_MASK; u64 size = PAGE_ALIGN(initrd_end) - base; /* * We can only add back the initrd memory if we don't end up * with more memory than we can address via the linear mapping. * It is up to the bootloader to position the kernel and the * initrd reasonably close to each other (i.e., within 32 GB of * each other) so that all granule/#levels combinations can * always access both. */ if (WARN(base < memblock_start_of_DRAM() || base + size > memblock_start_of_DRAM() + linear_region_size, "initrd not fully accessible via the linear mapping -- please check your bootloader ...\n")) { initrd_start = 0; } else { memblock_remove(base, size); /* clear MEMBLOCK_ flags */ memblock_add(base, size); memblock_reserve(base, size); } } if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_RANDOMIZE_BASE)) { extern u16 memstart_offset_seed; u64 range = linear_region_size - (memblock_end_of_DRAM() - memblock_start_of_DRAM()); /* * If the size of the linear region exceeds, by a sufficient * margin, the size of the region that the available physical * memory spans, randomize the linear region as well. */ if (memstart_offset_seed > 0 && range >= ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN) { range = range / ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN + 1; memstart_addr -= ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN * ((range * memstart_offset_seed) >> 16); } } /* * Register the kernel text, kernel data, initrd, and initial * pagetables with memblock. *把内核镜像占用物理内存范围添加到menblock中*/ memblock_reserve(__pa_symbol(_text), _end - _text); #ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD if (initrd_start) { memblock_reserve(initrd_start, initrd_end - initrd_start); /* the generic initrd code expects virtual addresses */ initrd_start = __phys_to_virt(initrd_start); initrd_end = __phys_to_virt(initrd_end); } #endif //从设备树二进制文件中的内存保留区域,对应设备源文件字段和机电 early_init_fdt_scan_reserved_mem(); /* 4GB maximum for 32-bit only capable devices */ if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ZONE_DMA)) arm64_dma_phys_limit = max_zone_dma_phys(); else arm64_dma_phys_limit = PHYS_MASK + 1; reserve_crashkernel(); reserve_elfcorehdr(); dma_contiguous_reserve(arm64_dma_phys_limit); memblock_allow_resize(); }
3、memblock编程入口