PyTorch中LSTM实现与SpikingJelly中SpikingLSTM实现的对比
LSTM:

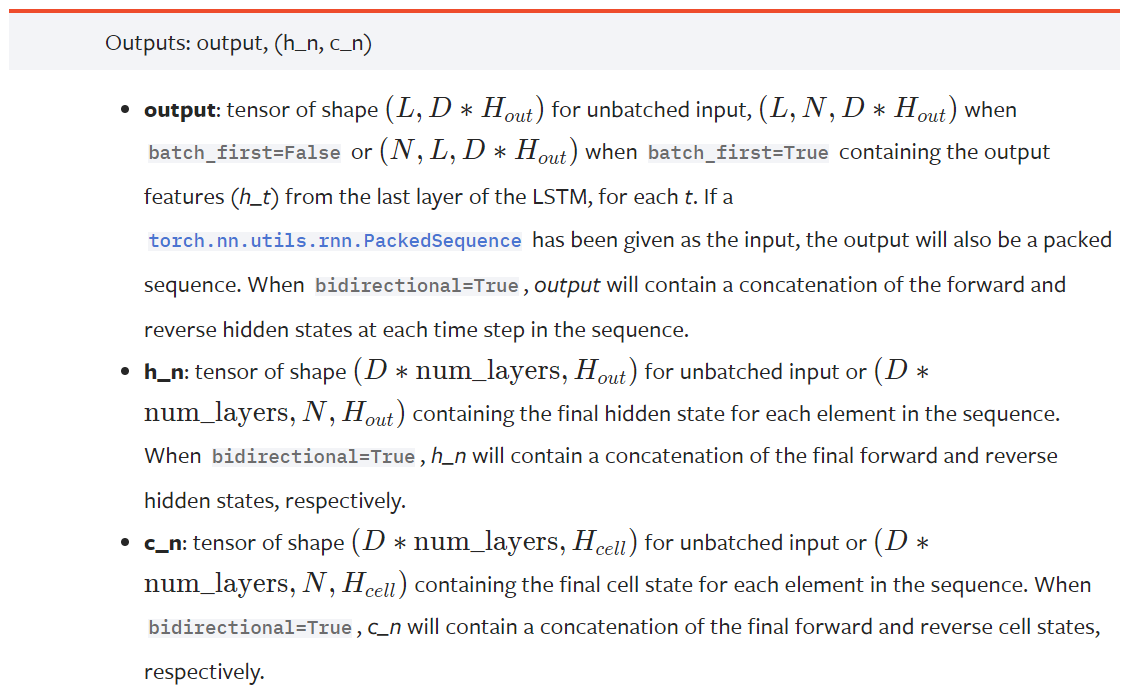
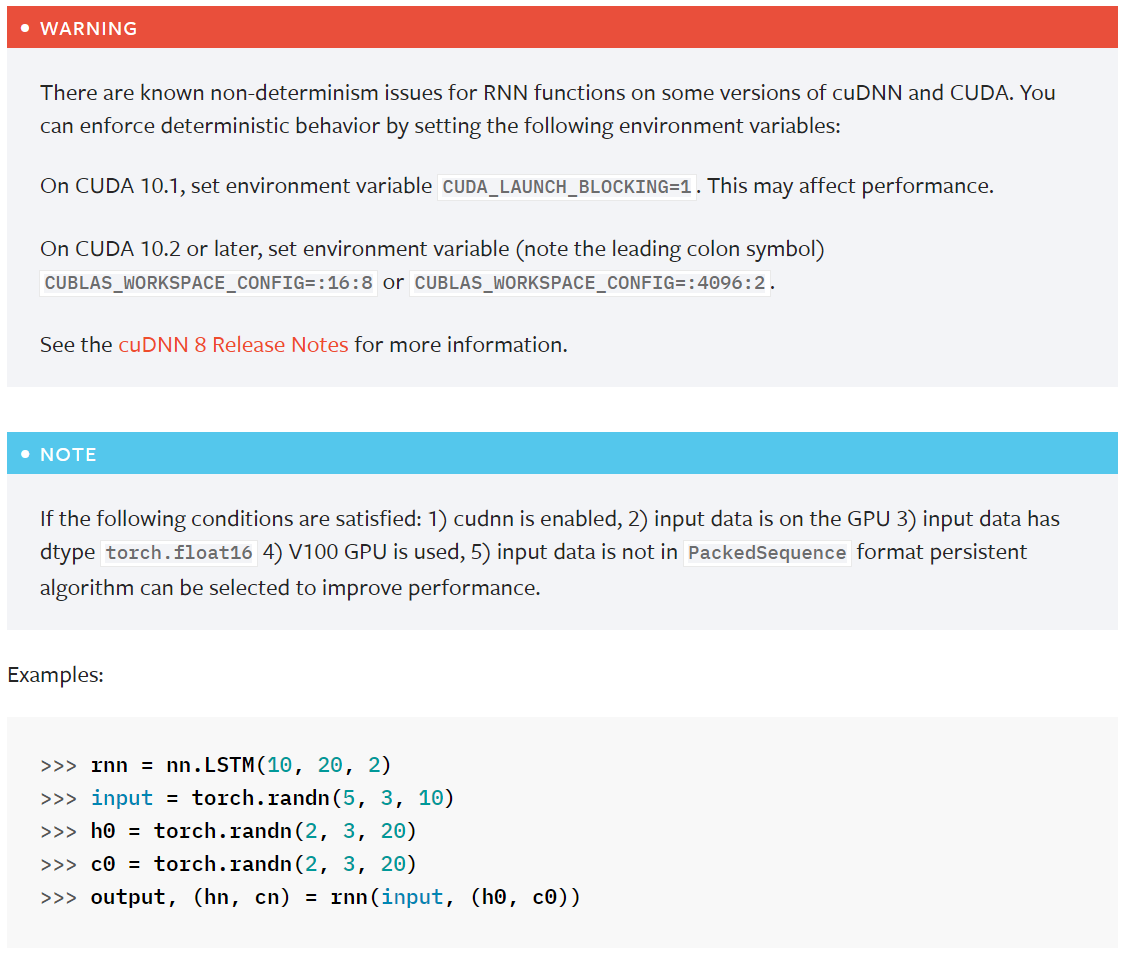
class LSTM(RNNBase): r"""Applies a multi-layer long short-term memory (LSTM) RNN to an input sequence. For each element in the input sequence, each layer computes the following function: .. math:: \begin{array}{ll} \\ i_t = \sigma(W_{ii} x_t + b_{ii} + W_{hi} h_{t-1} + b_{hi}) \\ f_t = \sigma(W_{if} x_t + b_{if} + W_{hf} h_{t-1} + b_{hf}) \\ g_t = \tanh(W_{ig} x_t + b_{ig} + W_{hg} h_{t-1} + b_{hg}) \\ o_t = \sigma(W_{io} x_t + b_{io} + W_{ho} h_{t-1} + b_{ho}) \\ c_t = f_t \odot c_{t-1} + i_t \odot g_t \\ h_t = o_t \odot \tanh(c_t) \\ \end{array} where :math:`h_t` is the hidden state at time `t`, :math:`c_t` is the cell state at time `t`, :math:`x_t` is the input at time `t`, :math:`h_{t-1}` is the hidden state of the layer at time `t-1` or the initial hidden state at time `0`, and :math:`i_t`, :math:`f_t`, :math:`g_t`, :math:`o_t` are the input, forget, cell, and output gates, respectively. :math:`\sigma` is the sigmoid function, and :math:`\odot` is the Hadamard product. In a multilayer LSTM, the input :math:`x^{(l)}_t` of the :math:`l` -th layer (:math:`l >= 2`) is the hidden state :math:`h^{(l-1)}_t` of the previous layer multiplied by dropout :math:`\delta^{(l-1)}_t` where each :math:`\delta^{(l-1)}_t` is a Bernoulli random variable which is :math:`0` with probability :attr:`dropout`. If ``proj_size > 0`` is specified, LSTM with projections will be used. This changes the LSTM cell in the following way. First, the dimension of :math:`h_t` will be changed from ``hidden_size`` to ``proj_size`` (dimensions of :math:`W_{hi}` will be changed accordingly). Second, the output hidden state of each layer will be multiplied by a learnable projection matrix: :math:`h_t = W_{hr}h_t`. Note that as a consequence of this, the output of LSTM network will be of different shape as well. See Inputs/Outputs sections below for exact dimensions of all variables. You can find more details in https://arxiv.org/abs/1402.1128. Args: input_size: The number of expected features in the input `x` hidden_size: The number of features in the hidden state `h` num_layers: Number of recurrent layers. E.g., setting ``num_layers=2`` would mean stacking two LSTMs together to form a `stacked LSTM`, with the second LSTM taking in outputs of the first LSTM and computing the final results. Default: 1 bias: If ``False``, then the layer does not use bias weights `b_ih` and `b_hh`. Default: ``True`` batch_first: If ``True``, then the input and output tensors are provided as `(batch, seq, feature)` instead of `(seq, batch, feature)`. Note that this does not apply to hidden or cell states. See the Inputs/Outputs sections below for details. Default: ``False`` dropout: If non-zero, introduces a `Dropout` layer on the outputs of each LSTM layer except the last layer, with dropout probability equal to :attr:`dropout`. Default: 0 bidirectional: If ``True``, becomes a bidirectional LSTM. Default: ``False`` proj_size: If ``> 0``, will use LSTM with projections of corresponding size. Default: 0 Inputs: input, (h_0, c_0) * **input**: tensor of shape :math:`(L, H_{in})` for unbatched input, :math:`(L, N, H_{in})` when ``batch_first=False`` or :math:`(N, L, H_{in})` when ``batch_first=True`` containing the features of the input sequence. The input can also be a packed variable length sequence. See :func:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence` or :func:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_sequence` for details. * **h_0**: tensor of shape :math:`(D * \text{num\_layers}, H_{out})` for unbatched input or :math:`(D * \text{num\_layers}, N, H_{out})` containing the initial hidden state for each element in the input sequence. Defaults to zeros if (h_0, c_0) is not provided. * **c_0**: tensor of shape :math:`(D * \text{num\_layers}, H_{cell})` for unbatched input or :math:`(D * \text{num\_layers}, N, H_{cell})` containing the initial cell state for each element in the input sequence. Defaults to zeros if (h_0, c_0) is not provided. where: .. math:: \begin{aligned} N ={} & \text{batch size} \\ L ={} & \text{sequence length} \\ D ={} & 2 \text{ if bidirectional=True otherwise } 1 \\ H_{in} ={} & \text{input\_size} \\ H_{cell} ={} & \text{hidden\_size} \\ H_{out} ={} & \text{proj\_size if } \text{proj\_size}>0 \text{ otherwise hidden\_size} \\ \end{aligned} Outputs: output, (h_n, c_n) * **output**: tensor of shape :math:`(L, D * H_{out})` for unbatched input, :math:`(L, N, D * H_{out})` when ``batch_first=False`` or :math:`(N, L, D * H_{out})` when ``batch_first=True`` containing the output features `(h_t)` from the last layer of the LSTM, for each `t`. If a :class:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequence` has been given as the input, the output will also be a packed sequence. When ``bidirectional=True``, `output` will contain a concatenation of the forward and reverse hidden states at each time step in the sequence. * **h_n**: tensor of shape :math:`(D * \text{num\_layers}, H_{out})` for unbatched input or :math:`(D * \text{num\_layers}, N, H_{out})` containing the final hidden state for each element in the sequence. When ``bidirectional=True``, `h_n` will contain a concatenation of the final forward and reverse hidden states, respectively. * **c_n**: tensor of shape :math:`(D * \text{num\_layers}, H_{cell})` for unbatched input or :math:`(D * \text{num\_layers}, N, H_{cell})` containing the final cell state for each element in the sequence. When ``bidirectional=True``, `c_n` will contain a concatenation of the final forward and reverse cell states, respectively. Attributes: weight_ih_l[k] : the learnable input-hidden weights of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer `(W_ii|W_if|W_ig|W_io)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size, input_size)` for `k = 0`. Otherwise, the shape is `(4*hidden_size, num_directions * hidden_size)`. If ``proj_size > 0`` was specified, the shape will be `(4*hidden_size, num_directions * proj_size)` for `k > 0` weight_hh_l[k] : the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer `(W_hi|W_hf|W_hg|W_ho)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size, hidden_size)`. If ``proj_size > 0`` was specified, the shape will be `(4*hidden_size, proj_size)`. bias_ih_l[k] : the learnable input-hidden bias of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer `(b_ii|b_if|b_ig|b_io)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size)` bias_hh_l[k] : the learnable hidden-hidden bias of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer `(b_hi|b_hf|b_hg|b_ho)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size)` weight_hr_l[k] : the learnable projection weights of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer of shape `(proj_size, hidden_size)`. Only present when ``proj_size > 0`` was specified. weight_ih_l[k]_reverse: Analogous to `weight_ih_l[k]` for the reverse direction. Only present when ``bidirectional=True``. weight_hh_l[k]_reverse: Analogous to `weight_hh_l[k]` for the reverse direction. Only present when ``bidirectional=True``. bias_ih_l[k]_reverse: Analogous to `bias_ih_l[k]` for the reverse direction. Only present when ``bidirectional=True``. bias_hh_l[k]_reverse: Analogous to `bias_hh_l[k]` for the reverse direction. Only present when ``bidirectional=True``. weight_hr_l[k]_reverse: Analogous to `weight_hr_l[k]` for the reverse direction. Only present when ``bidirectional=True`` and ``proj_size > 0`` was specified. .. note:: All the weights and biases are initialized from :math:`\mathcal{U}(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k})` where :math:`k = \frac{1}{\text{hidden\_size}}` .. note:: For bidirectional LSTMs, forward and backward are directions 0 and 1 respectively. Example of splitting the output layers when ``batch_first=False``: ``output.view(seq_len, batch, num_directions, hidden_size)``. .. note:: For bidirectional LSTMs, `h_n` is not equivalent to the last element of `output`; the former contains the final forward and reverse hidden states, while the latter contains the final forward hidden state and the initial reverse hidden state. .. note:: ``batch_first`` argument is ignored for unbatched inputs. .. include:: ../cudnn_rnn_determinism.rst .. include:: ../cudnn_persistent_rnn.rst Examples:: >>> rnn = nn.LSTM(10, 20, 2) >>> input = torch.randn(5, 3, 10) >>> h0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20) >>> c0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20) >>> output, (hn, cn) = rnn(input, (h0, c0)) """ def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super(LSTM, self).__init__('LSTM', *args, **kwargs) def get_expected_cell_size(self, input: Tensor, batch_sizes: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tuple[int, int, int]: if batch_sizes is not None: mini_batch = int(batch_sizes[0]) else: mini_batch = input.size(0) if self.batch_first else input.size(1) num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1 expected_hidden_size = (self.num_layers * num_directions, mini_batch, self.hidden_size) return expected_hidden_size # In the future, we should prevent mypy from applying contravariance rules here. # See torch/nn/modules/module.py::_forward_unimplemented def check_forward_args(self, # type: ignore[override] input: Tensor, hidden: Tuple[Tensor, Tensor], batch_sizes: Optional[Tensor], ): self.check_input(input, batch_sizes) self.check_hidden_size(hidden[0], self.get_expected_hidden_size(input, batch_sizes), 'Expected hidden[0] size {}, got {}') self.check_hidden_size(hidden[1], self.get_expected_cell_size(input, batch_sizes), 'Expected hidden[1] size {}, got {}') # Same as above, see torch/nn/modules/module.py::_forward_unimplemented def permute_hidden(self, # type: ignore[override] hx: Tuple[Tensor, Tensor], permutation: Optional[Tensor] ) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]: if permutation is None: return hx return apply_permutation(hx[0], permutation), apply_permutation(hx[1], permutation) # Same as above, see torch/nn/modules/module.py::_forward_unimplemented @overload # type: ignore[override] @torch._jit_internal._overload_method # noqa: F811 def forward(self, input: Tensor, hx: Optional[Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]] = None ) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]]: # noqa: F811 pass # Same as above, see torch/nn/modules/module.py::_forward_unimplemented @overload @torch._jit_internal._overload_method # noqa: F811 def forward(self, input: PackedSequence, hx: Optional[Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]] = None ) -> Tuple[PackedSequence, Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]]: # noqa: F811 pass def forward(self, input, hx=None): # noqa: F811 orig_input = input # xxx: isinstance check needs to be in conditional for TorchScript to compile batch_sizes = None if isinstance(orig_input, PackedSequence): input, batch_sizes, sorted_indices, unsorted_indices = input max_batch_size = batch_sizes[0] max_batch_size = int(max_batch_size) else: batch_sizes = None is_batched = input.dim() == 3 batch_dim = 0 if self.batch_first else 1 if not is_batched: input = input.unsqueeze(batch_dim) max_batch_size = input.size(0) if self.batch_first else input.size(1) sorted_indices = None unsorted_indices = None if hx is None: num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1 real_hidden_size = self.proj_size if self.proj_size > 0 else self.hidden_size h_zeros = torch.zeros(self.num_layers * num_directions, max_batch_size, real_hidden_size, dtype=input.dtype, device=input.device) c_zeros = torch.zeros(self.num_layers * num_directions, max_batch_size, self.hidden_size, dtype=input.dtype, device=input.device) hx = (h_zeros, c_zeros) else: if batch_sizes is None: # If not PackedSequence input. if is_batched: if (hx[0].dim() != 3 or hx[1].dim() != 3): msg = ("For batched 3-D input, hx and cx should " f"also be 3-D but got ({hx[0].dim()}-D, {hx[1].dim()}-D) tensors") raise RuntimeError(msg) else: if hx[0].dim() != 2 or hx[1].dim() != 2: msg = ("For unbatched 2-D input, hx and cx should " f"also be 2-D but got ({hx[0].dim()}-D, {hx[1].dim()}-D) tensors") raise RuntimeError(msg) hx = (hx[0].unsqueeze(1), hx[1].unsqueeze(1)) # Each batch of the hidden state should match the input sequence that # the user believes he/she is passing in. hx = self.permute_hidden(hx, sorted_indices) self.check_forward_args(input, hx, batch_sizes) if batch_sizes is None: result = _VF.lstm(input, hx, self._flat_weights, self.bias, self.num_layers, self.dropout, self.training, self.bidirectional, self.batch_first) else: result = _VF.lstm(input, batch_sizes, hx, self._flat_weights, self.bias, self.num_layers, self.dropout, self.training, self.bidirectional) output = result[0] hidden = result[1:] # xxx: isinstance check needs to be in conditional for TorchScript to compile if isinstance(orig_input, PackedSequence): output_packed = PackedSequence(output, batch_sizes, sorted_indices, unsorted_indices) return output_packed, self.permute_hidden(hidden, unsorted_indices) else: if not is_batched: output = output.squeeze(batch_dim) hidden = (hidden[0].squeeze(1), hidden[1].squeeze(1)) return output, self.permute_hidden(hidden, unsorted_indices)





SpikingLSTM:

class SpikingLSTM(SpikingRNNBase): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, bias=True, dropout_p=0, invariant_dropout_mask=False, bidirectional=False, surrogate_function1=surrogate.Erf(), surrogate_function2=None): ''' * :ref:`API in English <SpikingLSTM.__init__-en>` .. _SpikingLSTM.__init__-cn: 多层`脉冲` 长短时记忆LSTM, 最先由 `Long Short-Term Memory Spiking Networks and Their Applications <https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.04779>`_ 一文提出。 每一层的计算按照 .. math:: i_{t} &= \\Theta(W_{ii} x_{t} + b_{ii} + W_{hi} h_{t-1} + b_{hi}) \\\\ f_{t} &= \\Theta(W_{if} x_{t} + b_{if} + W_{hf} h_{t-1} + b_{hf}) \\\\ g_{t} &= \\Theta(W_{ig} x_{t} + b_{ig} + W_{hg} h_{t-1} + b_{hg}) \\\\ o_{t} &= \\Theta(W_{io} x_{t} + b_{io} + W_{ho} h_{t-1} + b_{ho}) \\\\ c_{t} &= f_{t} * c_{t-1} + i_{t} * g_{t} \\\\ h_{t} &= o_{t} * c_{t-1}' 其中 :math:`h_{t}` 是 :math:`t` 时刻的隐藏状态,:math:`c_{t}` 是 :math:`t` 时刻的细胞状态,:math:`h_{t-1}` 是该层 :math:`t-1` 时刻的隐藏状态或起始状态,:math:`i_{t}`,:math:`f_{t}`,:math:`g_{t}`,:math:`o_{t}` 分别是输入,遗忘,细胞,输出门, :math:`\\Theta` 是heaviside阶跃函数(脉冲函数), and :math:`*` 是Hadamard点积,即逐元素相乘。 :param input_size: 输入 ``x`` 的特征数 :type input_size: int :param hidden_size: 隐藏状态 ``h`` 的特征数 :type hidden_size: int :param num_layers: 内部RNN的层数,例如 ``num_layers = 2`` 将会创建堆栈式的两层RNN,第1层接收第0层的输出作为输入, 并计算最终输出 :type num_layers: int :param bias: 若为 ``False``, 则内部的隐藏层不会带有偏置项 ``b_ih`` 和 ``b_hh``。 默认为 ``True`` :type bias: bool :param dropout_p: 若非 ``0``,则除了最后一层,每个RNN层后会增加一个丢弃概率为 ``dropout_p`` 的 `Dropout` 层。 默认为 ``0`` :type dropout_p: float :param invariant_dropout_mask: 若为 ``False``,则使用普通的 `Dropout`;若为 ``True``,则使用SNN中特有的,`mask` 不 随着时间变化的 `Dropout``,参见 :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.layer.Dropout`。默认为 ``False`` :type invariant_dropout_mask: bool :param bidirectional: 若为 ``True``,则使用双向RNN。默认为 ``False`` :type bidirectional: bool :param surrogate_function1: 反向传播时用来计算脉冲函数梯度的替代函数, 计算 ``i``, ``f``, ``o`` 反向传播时使用 :type surrogate_function1: spikingjelly.clock_driven.surrogate.SurrogateFunctionBase :param surrogate_function2: 反向传播时用来计算脉冲函数梯度的替代函数, 计算 ``g`` 反向传播时使用。 若为 ``None``, 则设置成 ``surrogate_function1``。默认为 ``None`` :type surrogate_function2: None or spikingjelly.clock_driven.surrogate.SurrogateFunctionBase * :ref:`中文API <SpikingLSTM.__init__-cn>` .. _SpikingLSTM.__init__-en: The `spiking` multi-layer long short-term memory (LSTM), which is firstly proposed in `Long Short-Term Memory Spiking Networks and Their Applications <https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.04779>`_. For each element in the input sequence, each layer computes the following function: .. math:: i_{t} &= \\Theta(W_{ii} x_{t} + b_{ii} + W_{hi} h_{t-1} + b_{hi}) \\\\ f_{t} &= \\Theta(W_{if} x_{t} + b_{if} + W_{hf} h_{t-1} + b_{hf}) \\\\ g_{t} &= \\Theta(W_{ig} x_{t} + b_{ig} + W_{hg} h_{t-1} + b_{hg}) \\\\ o_{t} &= \\Theta(W_{io} x_{t} + b_{io} + W_{ho} h_{t-1} + b_{ho}) \\\\ c_{t} &= f_{t} * c_{t-1} + i_{t} * g_{t} \\\\ h_{t} &= o_{t} * c_{t-1}' where :math:`h_t` is the hidden state at time `t`, :math:`c_t` is the cell state at time `t`, :math:`x_t` is the input at time `t`, :math:`h_{t-1}` is the hidden state of the layer at time `t-1` or the initial hidden state at time `0`, and :math:`i_t`, :math:`f_t`, :math:`g_t`, :math:`o_t` are the input, forget, cell, and output gates, respectively. :math:`\\Theta` is the heaviside function, and :math:`*` is the Hadamard product. :param input_size: The number of expected features in the input ``x`` :type input_size: int :param hidden_size: The number of features in the hidden state ``h`` :type hidden_size: int :param num_layers: Number of recurrent layers. E.g., setting ``num_layers=2`` would mean stacking two LSTMs together to form a `stacked RNN`, with the second RNN taking in outputs of the first RNN and computing the final results :type num_layers: int :param bias: If ``False``, then the layer does not use bias weights `b_ih` and `b_hh`. Default: ``True`` :type bias: bool :param dropout_p: If non-zero, introduces a `Dropout` layer on the outputs of each RNN layer except the last layer, with dropout probability equal to :attr:`dropout`. Default: 0 :type dropout_p: float :param invariant_dropout_mask: If ``False``,use the naive `Dropout`;If ``True``,use the dropout in SNN that `mask` doesn't change in different time steps, see :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.layer.Dropout` for more information. Defaule: ``False`` :type invariant_dropout_mask: bool :param bidirectional: If ``True``, becomes a bidirectional LSTM. Default: ``False`` :type bidirectional: bool :param surrogate_function1: surrogate function for replacing gradient of spiking functions during back-propagation, which is used for generating ``i``, ``f``, ``o`` :type surrogate_function1: spikingjelly.clock_driven.surrogate.SurrogateFunctionBase :param surrogate_function2: surrogate function for replacing gradient of spiking functions during back-propagation, which is used for generating ``g``. If ``None``, the surrogate function for generating ``g`` will be set as ``surrogate_function1``. Default: ``None`` :type surrogate_function2: None or spikingjelly.clock_driven.surrogate.SurrogateFunctionBase ''' super().__init__(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, bias, dropout_p, invariant_dropout_mask, bidirectional, surrogate_function1, surrogate_function2) @staticmethod def base_cell(): return SpikingLSTMCell @staticmethod def states_num(): return 2
SpikingRNNBase:

class SpikingRNNBase(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, bias=True, dropout_p=0, invariant_dropout_mask=False, bidirectional=False, *args, **kwargs): ''' * :ref:`API in English <SpikingRNNBase.__init__-en>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.__init__-cn: 多层 `脉冲` RNN的基类。 :param input_size: 输入 ``x`` 的特征数 :type input_size: int :param hidden_size: 隐藏状态 ``h`` 的特征数 :type hidden_size: int :param num_layers: 内部RNN的层数,例如 ``num_layers = 2`` 将会创建堆栈式的两层RNN,第1层接收第0层的输出作为输入, 并计算最终输出 :type num_layers: int :param bias: 若为 ``False``, 则内部的隐藏层不会带有偏置项 ``b_ih`` 和 ``b_hh``。 默认为 ``True`` :type bias: bool :param dropout_p: 若非 ``0``,则除了最后一层,每个RNN层后会增加一个丢弃概率为 ``dropout_p`` 的 `Dropout` 层。 默认为 ``0`` :type dropout_p: float :param invariant_dropout_mask: 若为 ``False``,则使用普通的 `Dropout`;若为 ``True``,则使用SNN中特有的,`mask` 不 随着时间变化的 `Dropout``,参见 :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.layer.Dropout`。默认为 ``False`` :type invariant_dropout_mask: bool :param bidirectional: 若为 ``True``,则使用双向RNN。默认为 ``False`` :type bidirectional: bool :param args: 子类使用的额外参数 :param kwargs: 子类使用的额外参数 * :ref:`中文API <SpikingRNNBase.__init__-cn>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.__init__-en: The base-class of a multi-layer `spiking` RNN. :param input_size: The number of expected features in the input ``x`` :type input_size: int :param hidden_size: The number of features in the hidden state ``h`` :type hidden_size: int :param num_layers: Number of recurrent layers. E.g., setting ``num_layers=2`` would mean stacking two LSTMs together to form a `stacked RNN`, with the second RNN taking in outputs of the first RNN and computing the final results :type num_layers: int :param bias: If ``False``, then the layer does not use bias weights `b_ih` and `b_hh`. Default: ``True`` :type bias: bool :param dropout_p: If non-zero, introduces a `Dropout` layer on the outputs of each RNN layer except the last layer, with dropout probability equal to :attr:`dropout`. Default: 0 :type dropout_p: float :param invariant_dropout_mask: If ``False``,use the naive `Dropout`;If ``True``,use the dropout in SNN that `mask` doesn't change in different time steps, see :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.layer.Dropout` for more information. Defaule: ``False`` :type invariant_dropout_mask: bool :param bidirectional: If ``True``, becomes a bidirectional LSTM. Default: ``False`` :type bidirectional: bool :param args: additional arguments for sub-class :param kwargs: additional arguments for sub-class ''' super().__init__() self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.num_layers = num_layers self.bias = bias self.dropout_p = dropout_p self.invariant_dropout_mask = invariant_dropout_mask self.bidirectional = bidirectional if self.bidirectional: # 双向LSTM的结构可以参考 https://cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/CSE676/10.3%20BidirectionalRNN.pdf # https://cs224d.stanford.edu/lecture_notes/LectureNotes4.pdf self.cells, self.cells_reverse = self.create_cells(*args, **kwargs) else: self.cells = self.create_cells(*args, **kwargs) def create_cells(self, *args, **kwargs): ''' * :ref:`API in English <SpikingRNNBase.create_cells-en>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.create_cells-cn: :param args: 子类使用的额外参数 :param kwargs: 子类使用的额外参数 :return: 若 ``self.bidirectional == True`` 则会返回正反两个堆栈式RNN;否则返回单个堆栈式RNN :rtype: nn.Sequential * :ref:`中文API <SpikingRNNBase.create_cells-cn>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.create_cells-en: :param args: additional arguments for sub-class :param kwargs: additional arguments for sub-class :return: If ``self.bidirectional == True``, return a RNN for forward direction and a RNN for reverse direction; else, return a single stacking RNN :rtype: nn.Sequential ''' if self.bidirectional: cells = [] cells_reverse = [] cells.append(self.base_cell()(self.input_size, self.hidden_size, self.bias, *args, **kwargs)) cells_reverse.append(self.base_cell()(self.input_size, self.hidden_size, self.bias, *args, **kwargs)) for i in range(self.num_layers - 1): cells.append(self.base_cell()(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size, self.bias, *args, **kwargs)) cells_reverse.append(self.base_cell()(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size, self.bias, *args, **kwargs)) return nn.Sequential(*cells), nn.Sequential(*cells_reverse) else: cells = [] cells.append(self.base_cell()(self.input_size, self.hidden_size, self.bias, *args, **kwargs)) for i in range(self.num_layers - 1): cells.append(self.base_cell()(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size, self.bias, *args, **kwargs)) return nn.Sequential(*cells) @staticmethod def base_cell(): ''' * :ref:`API in English <SpikingRNNBase.base_cell-en>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.base_cell-cn: :return: 构成该RNN的基本RNN Cell。例如对于 :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.rnn.SpikingLSTM`, 返回的是 :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.rnn.SpikingLSTMCell` :rtype: nn.Module * :ref:`中文API <SpikingRNNBase.base_cell-cn>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.base_cell-en: :return: The base cell of this RNN. E.g., in :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.rnn.SpikingLSTM` this function will return :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.rnn.SpikingLSTMCell` :rtype: nn.Module ''' raise NotImplementedError @staticmethod def states_num(): ''' * :ref:`API in English <SpikingRNNBase.states_num-en>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.states_num-cn: :return: 状态变量的数量。例如对于 :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.rnn.SpikingLSTM`,由于其输出是 ``h`` 和 ``c``, 因此返回 ``2``;而对于 :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.rnn.SpikingGRU`,由于其输出是 ``h``,因此返回 ``1`` :rtype: int * :ref:`中文API <SpikingRNNBase.states_num-cn>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.states_num-en: :return: The states number. E.g., for :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.rnn.SpikingLSTM` the output are ``h`` and ``c``, this function will return ``2``; for :class:`~spikingjelly.clock_driven.rnn.SpikingGRU` the output is ``h``, this function will return ``1`` :rtype: int ''' # LSTM: 2 # GRU: 1 # RNN: 1 raise NotImplementedError def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, states=None): ''' * :ref:`API in English <SpikingRNNBase.forward-en>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.forward-cn: :param x: ``shape = [T, batch_size, input_size]``,输入序列 :type x: torch.Tensor :param states: ``self.states_num()`` 为 ``1`` 时是单个tensor, 否则是一个tuple,包含 ``self.states_num()`` 个tensors。 所有的tensor的尺寸均为 ``shape = [num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size]``, 包含 ``self.states_num()`` 个初始状态 如果RNN是双向的, ``num_directions`` 为 ``2``, 否则为 ``1`` :type states: torch.Tensor or tuple :return: output, output_states output: torch.Tensor ``shape = [T, batch, num_directions * hidden_size]``,最后一层在所有时刻的输出 output_states: torch.Tensor or tuple ``self.states_num()`` 为 ``1`` 时是单个tensor, 否则是一个tuple,包含 ``self.states_num()`` 个tensors。 所有的tensor的尺寸均为 ``shape = [num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size]``, 包含 ``self.states_num()`` 个最后时刻的状态 * :ref:`中文API <SpikingRNNBase.forward-cn>` .. _SpikingRNNBase.forward-en: :param x: ``shape = [T, batch_size, input_size]``, tensor containing the features of the input sequence :type x: torch.Tensor :param states: a single tensor when ``self.states_num()`` is ``1``, otherwise a tuple with ``self.states_num()`` tensors. ``shape = [num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size]`` for all tensors, containing the ``self.states_num()`` initial states for each element in the batch. If the RNN is bidirectional, ``num_directions`` should be ``2``, else it should be ``1`` :type states: torch.Tensor or tuple :return: output, output_states output: torch.Tensor ``shape = [T, batch, num_directions * hidden_size]``, tensor containing the output features from the last layer of the RNN, for each ``t`` output_states: torch.Tensor or tuple a single tensor when ``self.states_num()`` is ``1``, otherwise a tuple with ``self.states_num()`` tensors. ``shape = [num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size]`` for all tensors, containing the ``self.states_num()`` states for ``t = T - 1`` ''' # x.shape=[T, batch_size, input_size] # states states_num 个 [num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size] T = x.shape[0] batch_size = x.shape[1] if isinstance(states, tuple): # states非None且为tuple,则合并成tensor states_list = torch.stack(states) # shape = [self.states_num(), self.num_layers * 2, batch_size, self.hidden_size] elif isinstance(states, torch.Tensor): # states非None且不为tuple时,它本身就是一个tensor,例如普通RNN的状态 states_list = states elif states is None: # squeeze(0)的作用是,若states_num() == 1则去掉多余的维度 if self.bidirectional: states_list = torch.zeros( size=[self.states_num(), self.num_layers * 2, batch_size, self.hidden_size]).to(x).squeeze(0) else: states_list = torch.zeros(size=[self.states_num(), self.num_layers, batch_size, self.hidden_size]).to( x).squeeze(0) else: raise TypeError if self.bidirectional: # y 表示第i层的输出。初始化时,y即为输入 y = x.clone() if self.training and self.dropout_p > 0 and self.invariant_dropout_mask: mask = F.dropout(torch.ones(size=[self.num_layers - 1, batch_size, self.hidden_size * 2]), p=self.dropout_p, training=True, inplace=True).to(x) for i in range(self.num_layers): # 第i层神经元的起始状态从输入states_list获取 new_states_list = torch.zeros_like(states_list.data) if self.states_num() == 1: cell_init_states = states_list[i] cell_init_states_reverse = states_list[i + self.num_layers] else: cell_init_states = states_list[:, i] cell_init_states_reverse = states_list[:, i + self.num_layers] if self.training and self.dropout_p > 0: if i > 1: if self.invariant_dropout_mask: y = y * mask[i - 1] else: y = F.dropout(y, p=self.dropout_p, training=True) y, ss, ss_r = bidirectional_rnn_cell_forward( self.cells[i], self.cells_reverse[i], y, cell_init_states, cell_init_states_reverse) # 更新states_list[i] if self.states_num() == 1: new_states_list[i] = ss new_states_list[i + self.num_layers] = ss_r else: new_states_list[:, i] = torch.stack(ss) new_states_list[:, i + self.num_layers] = torch.stack(ss_r) states_list = new_states_list.clone() if self.states_num() == 1: return y, new_states_list else: # split使得返回值是tuple return y, torch.split(new_states_list, 1, dim=0) else: if self.training and self.dropout_p > 0 and self.invariant_dropout_mask: mask = F.dropout(torch.ones(size=[self.num_layers - 1, batch_size, self.hidden_size]), p=self.dropout_p, training=True, inplace=True).to(x) output = [] for t in range(T): new_states_list = torch.zeros_like(states_list.data) if self.states_num() == 1: new_states_list[0] = self.cells[0](x[t], states_list[0]) else: new_states_list[:, 0] = torch.stack(self.cells[0](x[t], states_list[:, 0])) for i in range(1, self.num_layers): y = states_list[0, i - 1] if self.training and self.dropout_p > 0: if self.invariant_dropout_mask: y = y * mask[i - 1] else: y = F.dropout(y, p=self.dropout_p, training=True) if self.states_num() == 1: new_states_list[i] = self.cells[i](y, states_list[i]) else: new_states_list[:, i] = torch.stack(self.cells[i](y, states_list[:, i])) if self.states_num() == 1: output.append(new_states_list[-1].clone().unsqueeze(0)) else: output.append(new_states_list[0, -1].clone().unsqueeze(0)) states_list = new_states_list.clone() if self.states_num() == 1: return torch.cat(output, dim=0), new_states_list else: # split使得返回值是tuple return torch.cat(output, dim=0), torch.split(new_states_list, 1, dim=0)






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 2025年我用 Compose 写了一个 Todo App
· 张高兴的大模型开发实战:(一)使用 Selenium 进行网页爬虫
2021-05-12 A Learning Theory for Reward-Modulated Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity with Application to Biofeedback
2021-05-12 Functional Requirements for Reward-Modulated Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity