数据结构——树
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3576328.html
概要
本章先对二叉树的相关理论知识进行介绍,然后给出C语言的详细实现。关于二叉树的学习,需要说明的是:它并不难,不仅不难,而且它非常简单。初次接触树的时候,我也觉得它似乎很难;而之所产生这种感觉主要是由于二叉树有一大堆陌生的概念、性质等内容。而当我真正的实现了二叉树再回过头来看它的相关概念和性质的时候,觉得原来它是如此的简单!因此,建议在学习二叉树的时候:先对二叉树基本的概念、性质有个基本了解,遇到难懂的知识点,可以画图来帮助理解;在有个基本的概念之后,再亲自动手实现二叉查找树(这一点至关重要!);最后再回过头来总结一下二叉树的理论知识时,你会发现——它的确很简单!在代码实践中,我以"二叉查找树,而不是单纯的二叉树"为例子进行说明,单纯的二叉树非常简单,实际使用很少。况且掌握了二叉查找树,二叉树也就自然掌握了。
请务必深刻理解、实践并掌握"二叉查找树"!它是后面学习AVL树、伸展树、红黑树等相关树结构的基石!
树的介绍
1. 树的定义
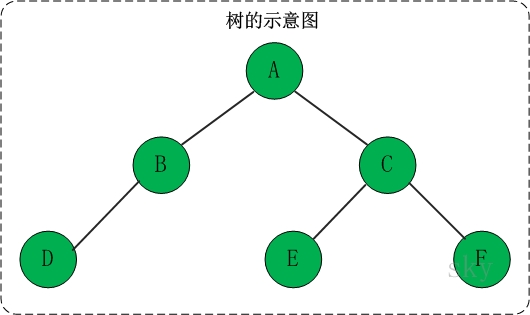
树是一种数据结构,它是由n(n>=1)个有限节点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。
把它叫做“树”是因为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。它具有以下的特点:
(01) 每个节点有零个或多个子节点;
(02) 没有父节点的节点称为根节点;
(03) 每一个非根节点有且只有一个父节点;
(04) 除了根节点外,每个子节点可以分为多个不相交的子树。
2. 树的基本术语
若一个结点有子树,那么该结点称为子树根的"双亲",子树的根是该结点的"孩子"。有相同双亲的结点互为"兄弟"。一个结点的所有子树上的任何结点都是该结点的后裔。从根结点到某个结点的路径上的所有结点都是该结点的祖先。
结点的度:结点拥有的子树的数目。
叶子:度为零的结点。
分支结点:度不为零的结点。
树的度:树中结点的最大的度。
层次:根结点的层次为1,其余结点的层次等于该结点的双亲结点的层次加1。
树的高度:树中结点的最大层次。
无序树:如果树中结点的各子树之间的次序是不重要的,可以交换位置。
有序树:如果树中结点的各子树之间的次序是重要的, 不可以交换位置。
森林:0个或多个不相交的树组成。对森林加上一个根,森林即成为树;删去根,树即成为森林。
二叉树的介绍
1. 二叉树的定义
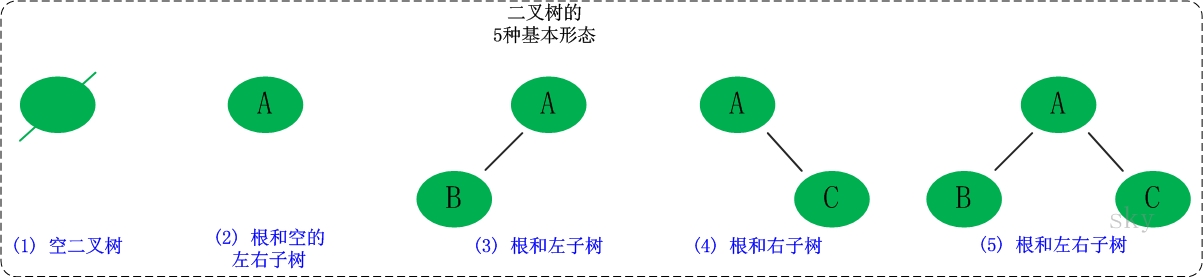
二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构。它有五种基本形态:二叉树可以是空集;根可以有空的左子树或右子树;或者左、右子树皆为空。
2. 二叉树的性质
二叉树有以下几个性质:TODO(上标和下标)
性质1:二叉树第i层上的结点数目最多为 2{i-1} (i≥1)。
性质2:深度为k的二叉树至多有2{k}-1个结点(k≥1)。
性质3:包含n个结点的二叉树的高度至少为log2 (n+1)。
性质4:在任意一棵二叉树中,若终端结点的个数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0=n2+1。
2.1 性质1:二叉树第i层上的结点数目最多为 2{i-1} (i≥1)
证明:下面用"数学归纳法"进行证明。
(01) 当i=1时,第i层的节点数目为2{i-1}=2{0}=1。因为第1层上只有一个根结点,所以命题成立。
(02) 假设当i>1,第i层的节点数目为2{i-1}。这个是根据(01)推断出来的!
下面根据这个假设,推断出"第(i+1)层的节点数目为2{i}"即可。
由于二叉树的每个结点至多有两个孩子,故"第(i+1)层上的结点数目" 最多是 "第i层的结点数目的2倍"。即,第(i+1)层上的结点数目最大值=2×2{i-1}=2{i}。
故假设成立,原命题得证!
2.2 性质2:深度为k的二叉树至多有2{k}-1个结点(k≥1)
证明:在具有相同深度的二叉树中,当每一层都含有最大结点数时,其树中结点数最多。利用"性质1"可知,深度为k的二叉树的结点数至多为:
20+21+…+2k-1=2k-1(等比数列1+2+4+…+2^(k-1) = 2^k-1)。
故原命题得证!
2.3 性质3:包含n个结点的二叉树的高度至少为log2 (n+1)
证明:根据"性质2"可知,高度为h的二叉树最多有2{h}–1个结点。反之,对于包含n个节点的二叉树的高度至少为log2(n+1)。
2.4 性质4:在任意一棵二叉树中,若终端结点的个数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0=n2+1
证明:因为二叉树中所有结点的度数均不大于2,所以结点总数(记为n)="0度结点数(n0)" + "1度结点数(n1)" + "2度结点数(n2)"。由此,得到等式一。
(等式一) n=n0+n1+n2
另一方面,0度结点没有孩子,1度结点有一个孩子,2度结点有两个孩子,故二叉树中孩子结点总数是:n1+2n2。此外,只有根不是任何结点的孩子。故二叉树中的结点总数又可表示为等式二。
(等式二) n=n1+2n2+1
由(等式一)和(等式二)计算得到:n0=n2+1。原命题得证!
3. 满二叉树,完全二叉树和二叉查找树
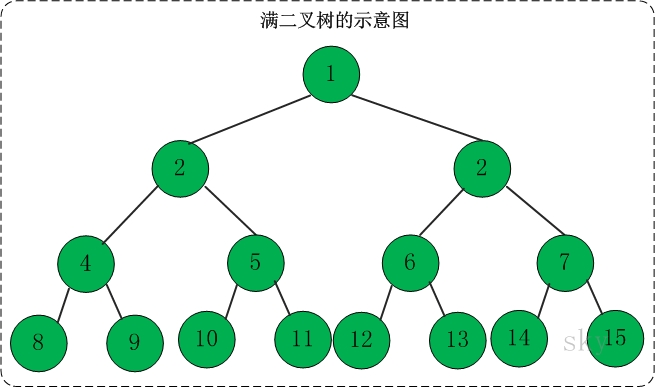
3.1 满二叉树
定义:高度为h,并且由2{h} –1个结点的二叉树,被称为满二叉树。
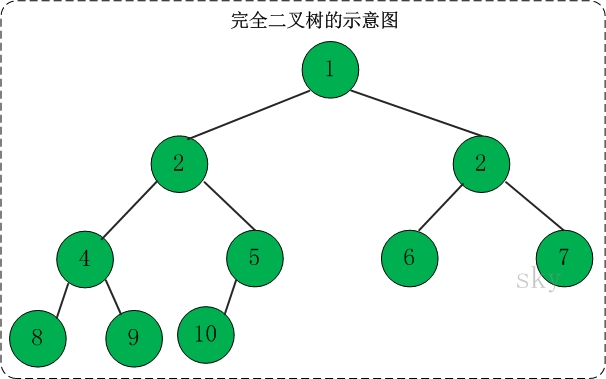
3.2 完全二叉树
定义:一棵二叉树中,只有最下面两层结点的度可以小于2,并且最下一层的叶结点集中在靠左的若干位置上。这样的二叉树称为完全二叉树。
特点:叶子结点只能出现在最下层和次下层,且最下层的叶子结点集中在树的左部。显然,一棵满二叉树必定是一棵完全二叉树,而完全二叉树未必是满二叉树。
3.3 二叉查找树
定义:二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),又被称为二叉搜索树。设x为二叉查找树中的一个结点,x节点包含关键字key,节点x的key值记为key[x]。如果y是x的左子树中的一个结点,则key[y] <= key[x];如果y是x的右子树的一个结点,则key[y] >= key[x]。
在二叉查找树中:
(01) 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
(02) 任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
(03) 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
(04) 没有键值相等的节点(no duplicate nodes)。
二叉查找树的实现
1. 二叉查找树节点的定义
public class BSTNode<T> where T : IComparable<T> // extends Comparable<T> { public T key; // 关键字(键值) public BSTNode<T> left; // 左孩子 public BSTNode<T> right; // 右孩子 public BSTNode<T> parent; // 父结点 public BSTNode(T key, BSTNode<T> parent, BSTNode<T> left, BSTNode<T> right) { this.key = key; this.parent = parent; this.left = left; this.right = right; } public int CompareTo(T other, T other1) { return other.CompareTo(other1); } public T getKey() { return key; } public String toString() { return "key:" + key; } }
BSTree是二叉树,它保护了二叉树的根节点mRoot;mRoot是BSTNode类型,而BSTNode是二叉查找树的节点,它是BSTree的内部类。BSTNode包含二叉查找树的几个基本信息:
(01) key -- 它是关键字,是用来对二叉查找树的节点进行排序的。
(02) left -- 它指向当前节点的左孩子。
(03) right -- 它指向当前节点的右孩子。
(04) parent -- 它指向当前节点的父结点。
2 遍历
这里讲解前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历3种方式。
2.1 前序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(01) 访问根结点;
(02) 先序遍历左子树;
(03) 先序遍历右子树。
前序遍历代码
/* * 前序遍历"二叉树" 顺序:根左右 */ private void preOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree != null) { Console.Write(tree.key + " "); preOrder(tree.left); preOrder(tree.right); } } public void preOrder() { preOrder(mRoot); }
2.2 中序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(01) 中序遍历左子树;
(02) 访问根结点;
(03) 中序遍历右子树。
中序遍历代码
/* * 中序遍历"二叉树" 顺序:左根右 */ private void inOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree != null) { inOrder(tree.left); Console.Write(tree.key + " "); inOrder(tree.right); } } public void inOrder() { inOrder(mRoot); }
2.3 后序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(01) 后序遍历左子树;
(02) 后序遍历右子树;
(03) 访问根结点。
后序遍历代码
/// <summary> /// 后序遍历"二叉树" 顺序:左右根 /// </summary> /// <param name="tree"></param> private void postOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree != null) { postOrder(tree.left); postOrder(tree.right); Console.Write(tree.key + " "); } } public void postOrder() { postOrder(mRoot); }
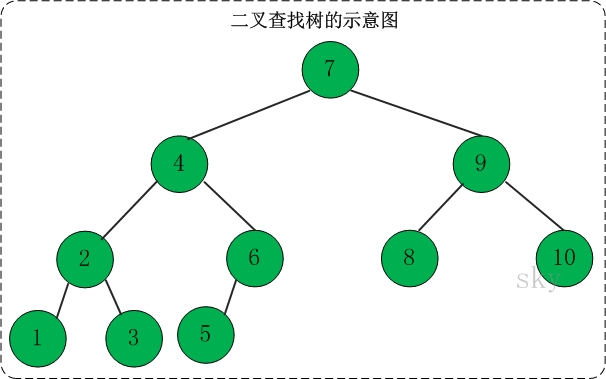
看看下面这颗树的各种遍历方式:
对于上面的二叉树而言,
(01) 前序遍历结果: 3 1 2 5 4 6
(02) 中序遍历结果: 1 2 3 4 5 6
(03) 后序遍历结果: 2 1 4 6 5 3
3. 查找
递归版本的代码
/// <summary> /// (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 /// </summary> /// <param name="x"></param> /// <param name="key"></param> /// <returns></returns> private BSTNode<T> search(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { if (x == null) return x; int cmp = key.CompareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) return search(x.left, key); else if (cmp > 0) return search(x.right, key); else return x; } public BSTNode<T> search(T key) { return search(mRoot, key); }
非递归版本的代码
/* * (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 */ private BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { while (x != null) { int cmp = key.CompareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else if (cmp > 0) x = x.right; else return x; } return x; } public BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) { return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key); }
4. 最大值和最小值
查找最大值的代码
/* * 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最大结点。 */ private BSTNode<T> maximum(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return null; while (tree.right != null) tree = tree.right; return tree; } public T maximum() { BSTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot); if (p != null) return p.key; return default(T); }
查找最小值的代码
/* * 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最小结点。 */ private BSTNode<T> minimum(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return null; while (tree.left != null) tree = tree.left; return tree; } public T minimum() { BSTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot); if (p != null) return p.key; return default(T); }
5. 前驱和后继
节点的前驱:是该节点的左子树中的最大节点。
节点的后继:是该节点的右子树中的最小节点。
查找前驱节点的代码
/* * 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。 */ public BSTNode<T> predecessor(BSTNode<T> x) { // 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。 if (x.left != null) return maximum(x.left); // 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y != null) && (x == y.left)) { x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; }
查找后继节点的代码
/* * 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。 */ public BSTNode<T> successor(BSTNode<T> x) { // 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。 if (x.right != null) return minimum(x.right); // 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y != null) && (x == y.right)) { x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; }
6. 插入
插入节点的代码
/* * 将结点插入到二叉树中 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的 * z 插入的结点 */ private void insert(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) { int cmp; BSTNode<T> y = null; BSTNode<T> x = bst.mRoot; // 查找z的插入位置 while (x != null) { y = x; cmp = z.key.CompareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else x = x.right; } z.parent = y; if (y == null) bst.mRoot = z; else { cmp = z.key.CompareTo(y.key); if (cmp < 0) y.left = z; else y.right = z; } } /* * 新建结点(key),并将其插入到二叉树中 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的根结点 * key 插入结点的键值 */ public void insert(T key) { BSTNode<T> z = new BSTNode<T>(key, null, null, null); // 如果新建结点失败,则返回。 if (z != null) insert(this, z); }
注:本文实现的二叉查找树是允许插入相同键值的节点的。若想禁止二叉查找树中插入相同键值的节点,可以参考"二叉查找树(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现"中的插入函数进行修改。
7. 删除
删除节点的代码
/* * 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点 * * 参数说明: * bst 二叉树 * z 删除的结点 */ private BSTNode<T> remove(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) { BSTNode<T> x = null; BSTNode<T> y = null; if ((z.left == null) || (z.right == null)) y = z; else y = successor(z); if (y.left != null) x = y.left; else x = y.right; if (x != null) x.parent = y.parent; if (y.parent == null) bst.mRoot = x; else if (y == y.parent.left) y.parent.left = x; else y.parent.right = x; if (y != z) z.key = y.key; return y; } /* * 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的根结点 * z 删除的结点 */ public void remove(T key) { BSTNode<T> z, node; if ((z = search(mRoot, key)) != null) if ((node = remove(this, z)) != null) node = null; }
8. 打印
打印二叉查找树的代码
/* * 打印"二叉查找树" * * key -- 节点的键值 * direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点; * -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子; * 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。 */ private void print(BSTNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) { if (tree != null) { if (direction == 0) // tree是根节点 Console.WriteLine("{0} is root\n", tree.key); else // tree是分支节点 Console.WriteLine("{0} is {1}'s {2} child\n", tree.key, key, direction == 1 ? "right" : "left"); print(tree.left, tree.key, -1); print(tree.right, tree.key, 1); } } public void print() { if (mRoot != null) print(mRoot, mRoot.key, 0); }
9. 销毁
销毁二叉查找树的代码
/* * 销毁二叉树 */ private void destroy(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return; if (tree.left != null) destroy(tree.left); if (tree.right != null) destroy(tree.right); tree = null; } public void clear() { destroy(mRoot); mRoot = null; }
完整的实现代码
public class BSTNode<T> where T : IComparable<T> // extends Comparable<T> { public T key; // 关键字(键值) public BSTNode<T> left; // 左孩子 public BSTNode<T> right; // 右孩子 public BSTNode<T> parent; // 父结点 public BSTNode(T key, BSTNode<T> parent, BSTNode<T> left, BSTNode<T> right) { this.key = key; this.parent = parent; this.left = left; this.right = right; } public int CompareTo(T other, T other1) { return other.CompareTo(other1); } public T getKey() { return key; } public String toString() { return "key:" + key; } } public class BSTree<T> where T : IComparable<T>// extends Comparable<T> { private BSTNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点 public BSTree() { mRoot = null; } /* * 前序遍历"二叉树" 顺序:根左右 */ private void preOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree != null) { Console.Write(tree.key + " "); preOrder(tree.left); preOrder(tree.right); } } public void preOrder() { preOrder(mRoot); } /* * 中序遍历"二叉树" 顺序:左根右 */ private void inOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree != null) { inOrder(tree.left); Console.Write(tree.key + " "); inOrder(tree.right); } } public void inOrder() { inOrder(mRoot); } /// <summary> /// 后序遍历"二叉树" 顺序:左右根 /// </summary> /// <param name="tree"></param> private void postOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree != null) { postOrder(tree.left); postOrder(tree.right); Console.Write(tree.key + " "); } } public void postOrder() { postOrder(mRoot); } /// <summary> /// (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 /// </summary> /// <param name="x"></param> /// <param name="key"></param> /// <returns></returns> private BSTNode<T> search(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { if (x == null) return x; int cmp = key.CompareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) return search(x.left, key); else if (cmp > 0) return search(x.right, key); else return x; } public BSTNode<T> search(T key) { return search(mRoot, key); } /* * (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 */ private BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { while (x != null) { int cmp = key.CompareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else if (cmp > 0) x = x.right; else return x; } return x; } public BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) { return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key); } /* * 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最小结点。 */ private BSTNode<T> minimum(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return null; while (tree.left != null) tree = tree.left; return tree; } public T minimum() { BSTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot); if (p != null) return p.key; return default(T); } /* * 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最大结点。 */ private BSTNode<T> maximum(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return null; while (tree.right != null) tree = tree.right; return tree; } public T maximum() { BSTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot); if (p != null) return p.key; return default(T); } /* * 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。 */ public BSTNode<T> successor(BSTNode<T> x) { // 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。 if (x.right != null) return minimum(x.right); // 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y != null) && (x == y.right)) { x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; } /* * 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。 */ public BSTNode<T> predecessor(BSTNode<T> x) { // 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。 if (x.left != null) return maximum(x.left); // 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y != null) && (x == y.left)) { x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; } /* * 将结点插入到二叉树中 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的 * z 插入的结点 */ private void insert(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) { int cmp; BSTNode<T> y = null; BSTNode<T> x = bst.mRoot; // 查找z的插入位置 while (x != null) { y = x; cmp = z.key.CompareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else x = x.right; } z.parent = y; if (y == null) bst.mRoot = z; else { cmp = z.key.CompareTo(y.key); if (cmp < 0) y.left = z; else y.right = z; } } /* * 新建结点(key),并将其插入到二叉树中 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的根结点 * key 插入结点的键值 */ public void insert(T key) { BSTNode<T> z = new BSTNode<T>(key, null, null, null); // 如果新建结点失败,则返回。 if (z != null) insert(this, z); } /* * 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点 * * 参数说明: * bst 二叉树 * z 删除的结点 */ private BSTNode<T> remove(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) { BSTNode<T> x = null; BSTNode<T> y = null; if ((z.left == null) || (z.right == null)) y = z; else y = successor(z); if (y.left != null) x = y.left; else x = y.right; if (x != null) x.parent = y.parent; if (y.parent == null) bst.mRoot = x; else if (y == y.parent.left) y.parent.left = x; else y.parent.right = x; if (y != z) z.key = y.key; return y; } /* * 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的根结点 * z 删除的结点 */ public void remove(T key) { BSTNode<T> z, node; if ((z = search(mRoot, key)) != null) if ((node = remove(this, z)) != null) node = null; } /* * 销毁二叉树 */ private void destroy(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return; if (tree.left != null) destroy(tree.left); if (tree.right != null) destroy(tree.right); tree = null; } public void clear() { destroy(mRoot); mRoot = null; } /* * 打印"二叉查找树" * * key -- 节点的键值 * direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点; * -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子; * 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。 */ private void print(BSTNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) { if (tree != null) { if (direction == 0) // tree是根节点 Console.WriteLine("{0} is root\n", tree.key); else // tree是分支节点 Console.WriteLine("{0} is {1}'s {2} child\n", tree.key, key, direction == 1 ? "right" : "left"); print(tree.left, tree.key, -1); print(tree.right, tree.key, 1); } } public void print() { if (mRoot != null) print(mRoot, mRoot.key, 0); } public int CompareTo(T other,T other1) { return other.CompareTo(other1); } }
测试代码
public class BSTreeTest { private int[] arr = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6 }; public void test() { int i, ilen; BSTree<int> tree = new BSTree<int>(); Console.WriteLine("== 依次添加: "); ilen = arr.Length; for (i = 0; i < ilen; i++) { Console.Write(arr[i] + " "); tree.insert(arr[i]); } Console.WriteLine("\n== 前序遍历: "); tree.preOrder(); Console.WriteLine("\n== 中序遍历: "); tree.inOrder(); Console.WriteLine("\n== 后序遍历: "); tree.postOrder(); Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("== 最小值: " + tree.minimum()); Console.WriteLine("== 最大值: " + tree.maximum()); Console.WriteLine("== 树的详细信息: "); tree.print(); Console.WriteLine("\n== 删除根节点: " + arr[3]); tree.remove(arr[3]); Console.WriteLine("\n== 中序遍历: "); tree.inOrder(); Console.WriteLine(); // 销毁二叉树 tree.clear(); } }
在二叉查找树的实现中,使用了泛型,也就意味着支持任意类型; 但是该类型必须要实现Comparable接口。
二叉查找树的测试程序
运行结果如下:
== 依次添加: 1 5 4 3 2 6 == 前序遍历: 1 5 4 3 2 6 == 中序遍历: 1 2 3 4 5 6 == 后序遍历: 2 3 4 6 5 1 == 最小值: 1 == 最大值: 6 == 树的详细信息: 1 is root 5 is 1's right child 4 is 5's left child 3 is 4's left child 2 is 3's left child 6 is 5's right child == 删除根节点: 3 == 中序遍历: 1 2 4 5 6
下面对测试程序的流程进行分析!
(01) 新建"二叉查找树"root。
(02) 向二叉查找树中依次插入1,5,4,3,2,6 。如下图所示:
(03) 遍历和查找
插入1,5,4,3,2,6之后,得到的二叉查找树如下:
前序遍历结果: 1 5 4 3 2 6
中序遍历结果: 1 2 3 4 5 6
后序遍历结果: 2 3 4 6 5 1
最小值是1,而最大值是6。
(04) 删除节点4。如下图所示:
(05) 重新遍历该二叉查找树。
中序遍历结果: 1 2 4 5 6