2020.10.20收获(动手动脑四续)
二、多态
简单来说,多态就是相同一条语句,在不同的运行环境中可以产生不同的运行结果
关键点:多态的最本质特征就是父类(或接口)变量可以引用子类(或实现了接口的类)的对象,换句话说:子类对象可以被当成基类对象使用
Parent p= new Child() ;
IMyClass obj = new MyClass();
总是可以让更一般的对象容纳更具体化的对象
特别的,Java类库的最顶层类是 Object ,因此每个对象都可以赋值给 Object变量
java中子类与基类变量间的赋值:
怎么判断对象是否可以转换: instanceof
Object obj="Hello";
if( obj instanceof String) { ... }
TestInstanceof.java
public class TestInstanceof
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//声明hello时使用Object类,则hello的编译类型是Object,Object是所有类的父类
//但hello变量的实际类型是String
Object hello = "Hello";
//String是Object类的子类,所以返回true。
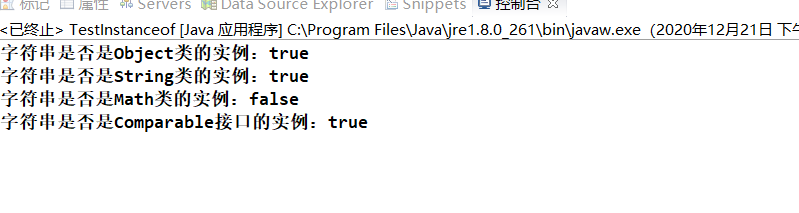
System.out.println("字符串是否是Object类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Object));
//返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是String类的实例:" + (hello instanceof String));
//返回false。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Math));
//String实现了Comparable接口,所以返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Comparable接口的实例:" + (hello instanceof Comparable));
String a = "Hello";
//String类既不是Math类,也不是Math类的父类,所以下面代码编译无法通过
//System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (a instanceof Math));
}
}
运行结果:
TestCast.java
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;
//d=m;
d=(Dog)m;
//d=c;
//c=(Cat)m;
}
}
注:编译器在编译上述代码时,采用的方法是“滞后绑定(late bind) ”,因为它在编译时无法知道到底调用哪个方法。
ParentChildTest.java
public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); parent.myValue++; parent.printValue(); ((Child)parent).myValue++; parent.printValue(); } } class Parent{ public int myValue=100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
- 左边的程序运行结果是什么?
- 你如何解释会得到这样的输出?
- 计算机是不会出错的,之所以得到这样的运行结果也是有原因的,那么从这些运行结果中,你能总 结出Java的哪些语法特性?
结果:
Parent.printValue(),myValue=100 Child.printValue(),myValue=200 Child.printValue(),myValue=200 Child.printValue(),myValue=200 Child.printValue(),myValue=201
总结:
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
这个特性实际上就是面向对象“多态”特性的具体表现。
如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。
如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的
请使用javap查看编译器为TestPolymorphism.java生成的字节码指令,然后通过互联网搜索资料,尝试从底层开始理解Java编译器是如何为多态代码生成字节码指令,在程序运行过程中,多态特性又是如何实现的。
class Parent { public int value=100; public void Introduce() { System.out.println("I'm father"); } } class Son extends Parent { public int value=101; public void Introduce() { System.out.println("I'm son"); } } class Daughter extends Parent { public int value=102; public void Introduce() { System.out.println("I'm daughter"); } } public class TestPolymorphism { public static void main(String args[]) { Parent p=new Parent(); p.Introduce(); System.out.println(p.value); p=new Son(); p.Introduce(); System.out.println(p.value); p=new Daughter(); p.Introduce(); System.out.println(p.value); } }
运行结果:
I'm father
100
I'm son
100
I'm daughter
100
- 强制的:一种隐式做类型转换的方法。
- 重载的:将一个标志符用作多个意义。
- 参数的:为不同类型的参数提供相同的操作。
- 包含的:类包含关系的抽象操作。
多态依赖于类型和实现的分离,多用来把接口和实现分离。
这种编程方式有什么不合理的地方吗?

结果:
我不吃肉谁敢吃肉!
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。
我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。
我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。
我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。
我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。
我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。
为什么要用多态?它有什么好处?
使用多态最大的好处是:当你要修改程序并扩充系统时,你需要修改的地方较少,对其它部分代码的影响较小!千万不要小看这两个“较”字!程序规模越大,其优势就越突出。


