一、项目需求
1.该程序能够准确地读出.txt文件中的数据,文件格式简洁易懂、可灵活扩展
2.在某号线路上,能够查询各个站点的信息,输出该号线路上所有站点信息
3.在出发站与目的站之间输出一个最短路径
二、文件存储

三、文件位置
一共三个package:control、main、model
Dijkstra.java(此代码为最短路径算法,虽然叫Dijkstra,但其实并不是Dijkstra的算法;这是最核心的地方,该算法能很好地解决最短路径问题,这段代码是借鉴了网上的代码):
public void calculate(Beansubway s1, Beansubway s2){//计算从s1站到s2站的最短经过路径
String line="初始线";
if(outList.size() == station.totalStaion){
route.add("找到目标站点:"+s2.getStation()+",共经过"+(s1.getAllPassedStations(s2).size()-1)+"站\n");
int flag=0;
for(Beansubway station : s1.getAllPassedStations(s2)){
if(station.getLine()==null){//出发站
route.add(station.getStation()+"-->");
}
else if(station.getStation().equals(s2.getStation())){//最后1站
if(!station.getLine().equals(line)){
route.add("换乘"+station.getLine()+"\t\n"+"-->"+"到达 "+"-->"+station.getStation());
}
else {
route.add("到达 " +"-->"+ station.getStation());
}
}
else if(!station.getLine().equals(line)&&flag==1){//换乘后1站
line=station.getLine();
route.add("换乘"+station.getLine()+"\t\n"+"-->"+station.getStation()+"-->");
}
else if(!station.getLine().equals(line)&&flag==0){//第2站
line=station.getLine();
route.add("乘坐"+station.getLine()+"\t\n"+"-->"+station.getStation()+"-->");
flag=1;
}
else{//其余站
line=station.getLine();
route.add(station.getStation()+"-->");
}
}
return;
}
if(!outList.contains(s1)){
outList.add(s1);
}
//如果起点站的OrderSetMap为空,则第一次用起点站的前后站点初始化之
if(s1.getOrderSetMap().isEmpty()){
List<Beansubway> Linkedstations = getAllLinkedStations(s1);
for(Beansubway s : Linkedstations){
s1.getAllPassedStations(s).add(s);
}
}
Beansubway parent = getShortestPath(s1);//获取距离起点站s1最近的一个站(有多个的话,随意取一个)
if(parent == s2){
System.out.println("找到目标站点:"+s2+",共经过"+(s1.getAllPassedStations(s2).size()-1)+"站");
for(Beansubway station : s1.getAllPassedStations(s2)){
System.out.print(station.getStation()+"->");
}
return;
}
for(Beansubway child : getAllLinkedStations(parent)){
if(outList.contains(child)){
continue;
}
int shortestPath = (s1.getAllPassedStations(parent).size()-1) + 1;//前面这个1表示计算路径需要去除自身站点,后面这个1表示增加了1站距离
if(s1.getAllPassedStations(child).contains(child)){
//如果s1已经计算过到此child的经过距离,那么比较出最小的距离
if((s1.getAllPassedStations(child).size()-1) > shortestPath){
//重置S1到周围各站的最小路径
s1.getAllPassedStations(child).clear();
s1.getAllPassedStations(child).addAll(s1.getAllPassedStations(parent));
s1.getAllPassedStations(child).add(child);
}
} else {
//如果s1还没有计算过到此child的经过距离
s1.getAllPassedStations(child).addAll(s1.getAllPassedStations(parent));
s1.getAllPassedStations(child).add(child);
}
}
outList.add(parent);
calculate(s1,s2);//重复计算,往外面站点扩展
}
ui设计:
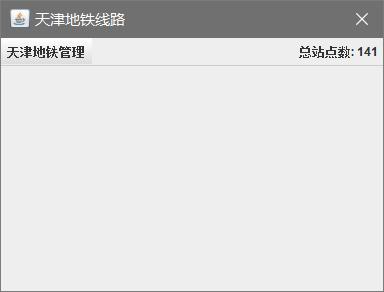
public FrmMain() {
this.setTitle("天津地铁线路");
this.setSize(400, 300);
workPane.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
label=new JLabel("总站点数: "+ station.totalStaion);
workPane.add(label);
menuSubway.add(menuitemLine);
menuitemLine.addActionListener(this);
menuSubway.add(menuitemStation);
menuitemStation.addActionListener(this);
menubar.add(menuSubway);
menubar.add(workPane);
this.setJMenuBar(menubar);
double width = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize().getWidth();
double height = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize().getHeight();
this.setLocation((int) (width - this.getWidth()) / 2,
(int) (height - this.getHeight()) / 2);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
this.setVisible(true);
}
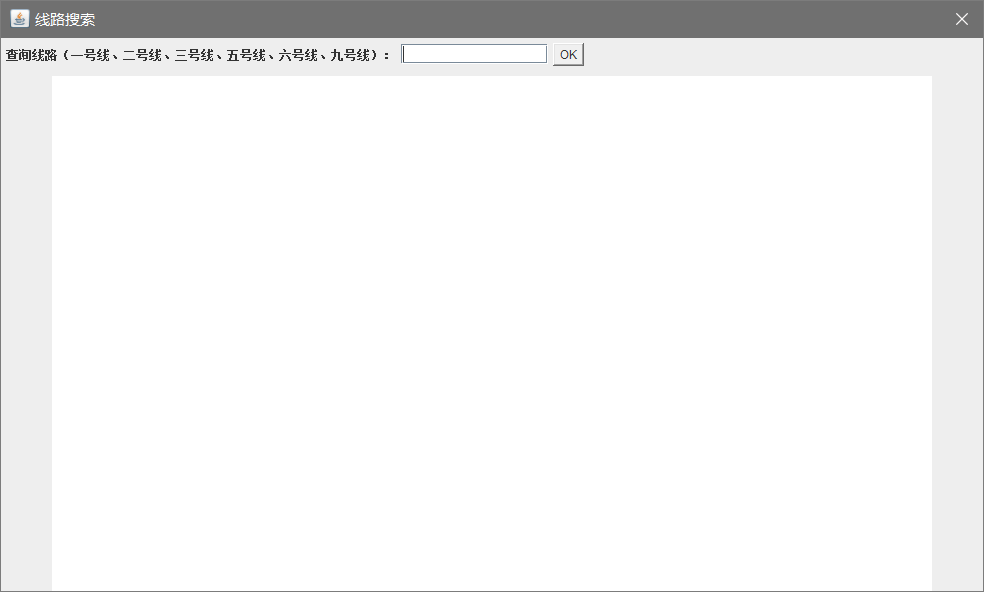
public class FrmSearchLine extends JDialog implements ActionListener{
private JPanel toolBar = new JPanel();
private JPanel workPane = new JPanel();
private Button btnOK = new Button("OK");
private JLabel labelline = new JLabel("查询线路(一号线、二号线、三号线、五号线、六号线、九号线):");
private JTextField edtline = new JTextField(13);
private JTextArea edtsubway = new JTextArea(60,110);
public FrmSearchLine(FrmMain f, String s, boolean b) {
super(f, s, b);
toolBar.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
toolBar.add(labelline);
toolBar.add(edtline);
toolBar.add(btnOK);
this.getContentPane().add(toolBar, BorderLayout.NORTH);
edtsubway.setFont(new Font("Monospaced", Font.BOLD, 14));
edtsubway.setLineWrap(true); //激活自动换行功能
edtsubway.setWrapStyleWord(false);
workPane.add(edtsubway);
this.getContentPane().add(workPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
this.setSize(1000, 600);
double width = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize().getWidth();
double height = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize().getHeight();
this.setLocation((int) (width - this.getWidth()) / 2,
(int) (height - this.getHeight()) / 2);
this.validate();
this.btnOK.addActionListener(this);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
}
});
}
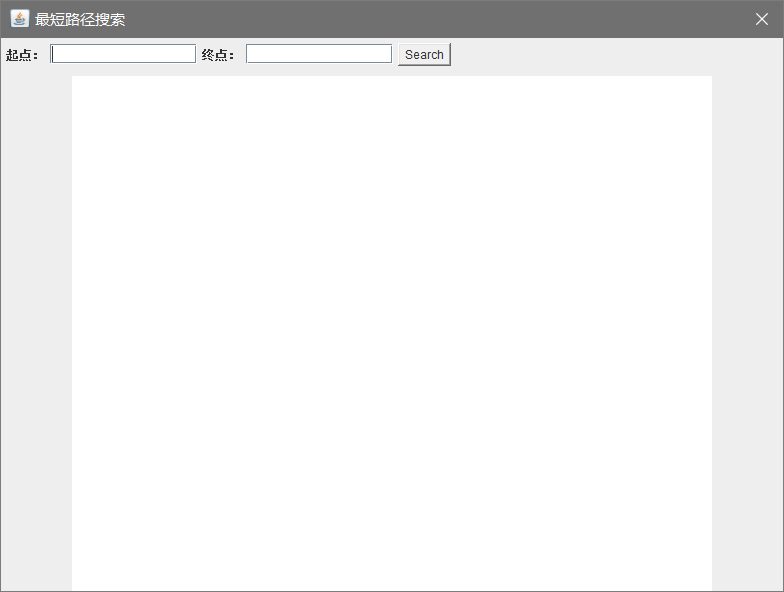
public class FrmSearchStation extends JDialog implements ActionListener{
private JPanel toolBar = new JPanel();
private JPanel workPane = new JPanel();
private Button btnSearch = new Button("Search");
private JLabel labelstart = new JLabel("起点:");
private JLabel labelend= new JLabel("终点:");
private JTextField edtstart = new JTextField(13);
private JTextField edtend = new JTextField(13);
private JTextArea edtsubway = new JTextArea(60,80);
public FrmSearchStation(FrmMain f, String s, boolean b) {
super(f, s, b);
toolBar.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
toolBar.add(labelstart);
toolBar.add(edtstart);
toolBar.add(labelend);
toolBar.add(edtend);
toolBar.add(btnSearch);
this.getContentPane().add(toolBar, BorderLayout.NORTH);
edtsubway.setFont(new Font("Monospaced", Font.BOLD, 14));
edtsubway.setLineWrap(true); //激活自动换行功能
edtsubway.setWrapStyleWord(false);
workPane.add(edtsubway);
this.getContentPane().add(workPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
this.setSize(800, 600);
double width = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize().getWidth();
double height = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize().getHeight();
this.setLocation((int) (width - this.getWidth()) / 2,
(int) (height - this.getHeight()) / 2);
this.validate();
this.btnSearch.addActionListener(this);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
}
});
}
Beansubway.java(是对于线路上变量函数的存储结构):
private String line;
private String station;
public Beansubway prev;
public Beansubway next;
private Map<Beansubway,LinkedHashSet<Beansubway>> orderSetMap = new HashMap<Beansubway,LinkedHashSet<Beansubway>>();
public String getLine() {
return line;
}
public void setLine(String line) {
this.line = line;
}
public String getStation() {
return station;
}
public void setStation(String station) {
this.station = station;
}
public Beansubway(String station) {
this.station = station;
}
public LinkedHashSet<Beansubway> getAllPassedStations(Beansubway station) {
if(orderSetMap.get(station) == null){
LinkedHashSet<Beansubway> set = new LinkedHashSet<Beansubway>();
set.add(this);
orderSetMap.put(station, set);
}
return orderSetMap.get(station);
}
public Map<Beansubway, LinkedHashSet<Beansubway>> getOrderSetMap() {
return orderSetMap;
}
Beanlujing.java(对于经过站点的存储)
private String name;
private List<Beansubway> passStations;//经过的站点
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<Beansubway> getPassStations() {
return passStations;
}
public void setPassStations(List<Beansubway> passStations) {
this.passStations = passStations;
}
public List<String> loadAllLineName(){//罗列所有线路名字
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<station.AllLine.size();i++){
list.add(station.AllLine.get(i).getName());
}
return list;
}
四、运行方法与测试
需求1:读取subway.txt文件的语句:
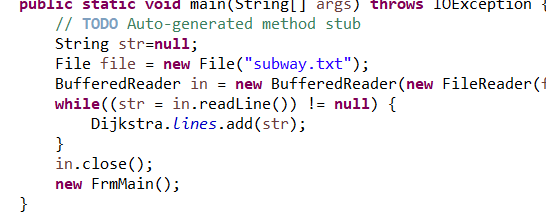
需求2:输出指定线路的所有站点
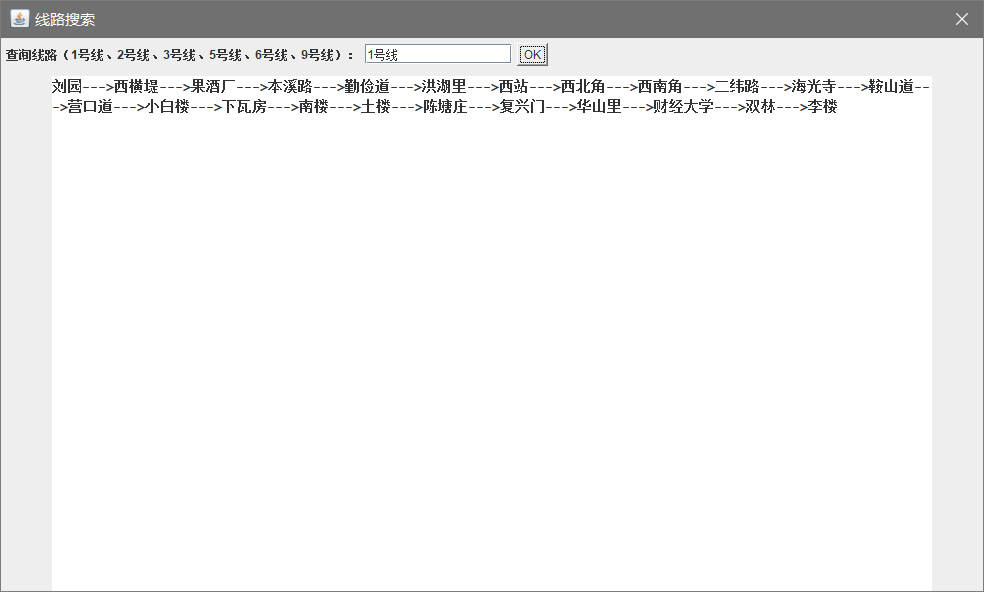
需求3:输出两站点之间的最短路径
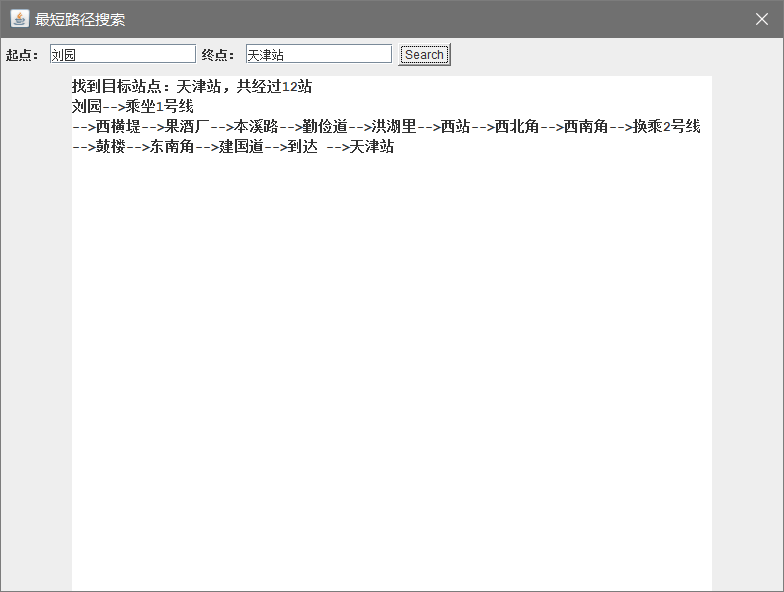
1.起点站不存在
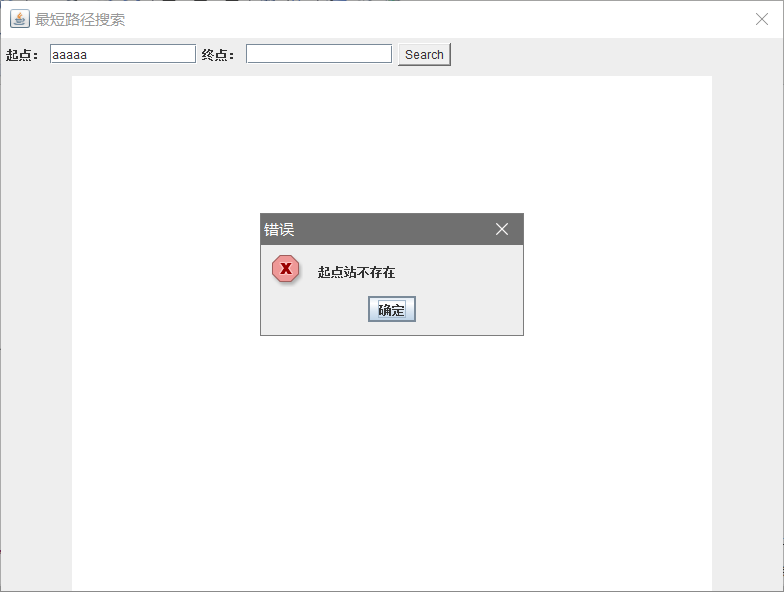
2.终点站不存在
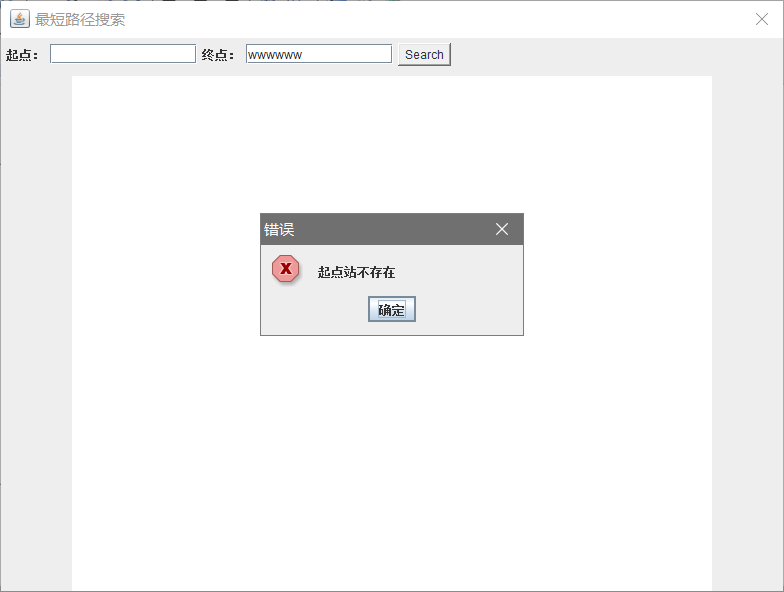
3.起点站与终点站相同

五、体会
由于是首次做一个感到如此艰难的个人项目,相比于暑期的短学期项目,这个明显难了很多,对于个人能力要求上了不止一个大档次。其次,刚开始写代码,一直卡在最短路径算法这个方向,后来想到了dijkstra算法,但是对这个算法又并没有那么熟悉,所以在这个个人项目中,借鉴了网上的其他算法代码,然后自己设计了一些UI元素,并且能够理解算法大致内容。



