NIO
概念(NIO vs BIO)
NIO, Non-blocking I/O, 非阻塞式 I/O 模型。也可以解释为 New I/O, 区别于旧的阻塞式 I/O 模型(BIO)。
BIO 与 NIO 的区别如下:
| 类别 | I/O 方式 | 最低可用的 JDK 版本 |
|---|---|---|
| BIO | 流式 | JDK 1.0 |
| NIO | 块式 | JDK 1.4 |
所谓流式处理,就是单个字节的数据移动,通过一个称为 Stream 的对象一次移动一个字节;而块式处理,就是单个字节数组的数据移动,通过一个叫 Buffer 的对象一次移动一个字节数组。JDK 中的 NIO 库已经集成了原来的标准 I/O 功能。
缓冲区和通道(Buffer & Channel)
NIO 中的缓冲区(Buffer)实质是一个数组,通常为字节数组(ByteBuffer),用作读写缓冲,以及对数据的结构化访问,还可以用来跟踪系统的读写进程。
Buffer 类型:
- ByteBuffer
- CharBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
NIO 中的通道(Channel)类似 BIO 中的流(Stream),但是是双向的,可以用来读、写或者同时读写。流之所以是单向的,是因为一个 Stream 要么是 InputStream,要么是 OutputStream,不能兼有。
缓冲区内部细节(Buffer Internals)
状态变量(State Variables)
- Position,表征读了或写了多少数据到数组中,指向下一个元素的位置;
- Limit,表征剩余可读或可写的的数据量,初始情况下 Limit = Capacity。
- Capacity,表征 Buffer 的最大容量。
三者关系:Position <= Limit <= Capacity
下面从微观角度观察各状态变量在读写操作中的变化:
(1) Init
初始状态下,Position 指向第一个元素的位置,Limit 和 Capacity 指向最后一个元素的下一个虚拟元素的位置。由于 Capacity 保持不变,下面的讨论中予以略过。

(2)Channel.read
读取 5 个元素到缓冲区后,Position 指向第六个元素的位置,Limit 不变。

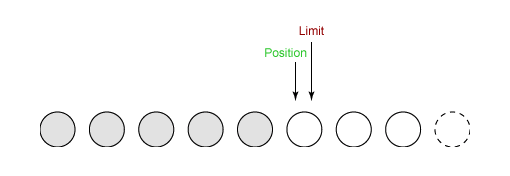
(3)Buffer.flip
进行 Flip 操作后,Limit 指向当前的 Position 的位置,Position 指回第一个元素的位置,
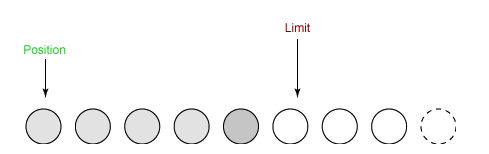
(4)Channel.write
从缓冲区读取 5 个元素写入 Channel 后,Position 指向 Limit 所在的位置。
(5)Buffer.clear
clear 后缓冲区重置到初始状态。
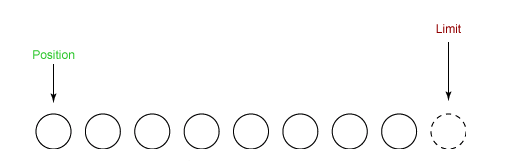
存取方法(Accessor )
存取方法分为:
- 相对方法(Relative Method):在当前 position 进行读写操作,随后 position 自增1。
- 绝对方法(Absolute Method):在某个索引位置进行读写操作,不影响 position 和 limit。
(1)get 系列方法(包括 array() ),用于读取缓冲区的数据,其中 byte get(int index) 为绝对方法。
(2)put 系列方法,用于写入数据到缓冲区,其中 ByteBuffer put(int index, byte b) 为绝对方法。
使用(Show U the Code)
读取文件
- 从 FileInputStream 中获取 Channel;
- 创建 Buffer;
- 将数据从 Channel 读到 Buffer 中。
示例如下:
// 将 a_file 读到 StringBuilder 中
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("/path/to/a_file");
FileChannel fc = fin.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (fc.read(buffer) != -1) {
sb.append(new String(buffer.array(), 0, buffer.position()));
}
写入文件
- 从 FileOutputStream 中获取 Channel;
- 创建 Buffer;
- 写入数据到 Buffer;
- 将数据从 Buffer 写入 Channel 中。
示例如下:
// 将 "Something" 写入 a_file 中
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/path/to/a_file");
FileChannel fc = fos.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byte[] content = "Something".getBytes();
for (byte aContent : content) {
buffer.put(aContent);
}
buffer.flip();
fc.write(buffer);
边读边写
- 清除 Buffer;
- 从输入流的 Channel 读数据到 Buffer;
- 写入 Buffer 中的数据到输出流的 Channel;
- 循环直到输入流的 Channel 中没有数据。
示例如下:
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("path/to/in_file");
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("path/to/out_file");
FileChannel fcin = fin.getChannel();
FileChannel fcout = fout.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (true) {
buffer.clear();
int r = fcin.read(buffer);
if (r == -1) {
break;
}
buffer.flip();
fcout.write(buffer);
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号