Direct Approach (No Receivers)
简化的并行性:不需要创建多个输入Kafka流并将其合并。 使用directStream,Spark Streaming将创建 与使用Kafka分区一样多的RDD分区,这些分区将全部从Kafka并行读取数据。 所以在Kafka和RDD分 区之间有一对一的映射关系。 效率:在第一种方法中实现零数据丢失需要将数据存储在预写日志中,这会进一步复制数据。 这实际 上是效率低下的,因为数据被有效地复制了两次 - 一次是Kafka,另一次是由预先写入日志(Write Ahead Log)复制。 这个第二种方法消除了这个问题,因为没有接收器,因此不需要预先写入日志。 只要Kafka数据保留时间足够长。 正好一次(Exactly-once)的语义:第一种方法使用Kafka的高级API来在Zookeeper中存储消耗的偏移 量。传统上这是从Kafka消费数据的方式。虽然这种方法(结合预写日志)可以确保零数据丢失 (即至少一次语义),但是在某些失败情况下,有一些记录可能会消费两次。发生这种情况是因为 Spark Streaming可靠接收到的数据与Zookeeper跟踪的偏移之间的不一致。因此,在第二种方法中, 我们可以不使用Zookeeper的简单Kafka API。在其检查点内,Spark Streaming跟踪偏移量。这消除了 Spark Streaming和Zookeeper / Kafka之间的不一致,因此Spark Streaming每次记录都会在发生故障的 情况下有效地收到一次。为了实现输出结果的一次语义,将数据保存到外部数据存储区的输出操作必须 是幂等的,或者是保存结果和偏移量的原子事务。
模拟一个消费者--Direct
/**
* Consumes messages from one or more topics in Kafka and does wordcount.
* Usage: DirectKafkaWordCount <brokers> <topics>
* <brokers> is a list of one or more Kafka brokers
* <topics> is a list of one or more kafka topics to consume from
*
* Example:
* $ bin/run-example streaming.DirectKafkaWordCount broker1-host:port,broker2-host:port \
* topic1,topic2
*/
object DirectKafkaWordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
if (args.length < 2) {
System.err.println(s"""
|Usage: DirectKafkaWordCount <brokers> <topics>
| <brokers> is a list of one or more Kafka brokers
| <topics> is a list of one or more kafka topics to consume from
|
""".stripMargin)
System.exit(1)
}
val Array(brokers, topics) = args
// Create context with 2 second batch interval
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("DirectKafkaWordCount").setMaster("local[2]")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(2))
// Create direct kafka stream with brokers and topics
val topicsSet = topics.split(",").toSet
val kafkaParams = Map[String, String]("metadata.broker.list" -> brokers)
val messages = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String, StringDecoder, StringDecoder](
ssc, kafkaParams, topicsSet)
// Get the lines, split them into words, count the words and print
val lines = messages.map(_._2)
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordCounts = words.map(x => (x, 1L)).reduceByKey(_ + _)
wordCounts.print()
// Start the computation
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}
Kafka Offset 管理
使用外部存储保存offset
Checkpoints HBase ZooKeeper Kafka ...
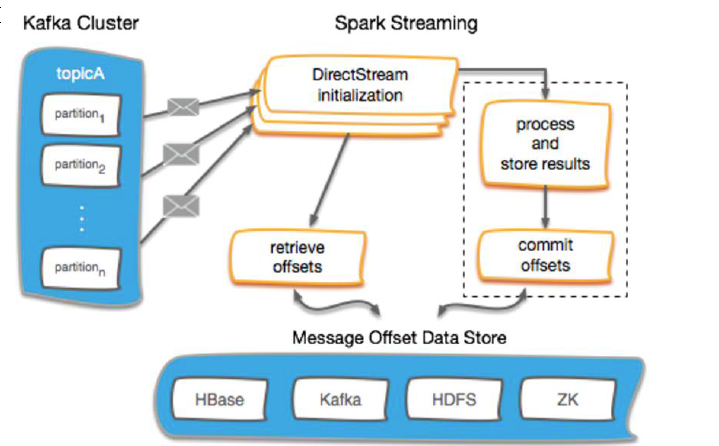
不保存offset
Kafka Offset 管理--Checkpoint
-
启用Spark Streaming的checkpoint是存储偏移量最简单的方法。
-
流式checkpoint专门用于保存应用程序的状态, 比如保存在HDFS上, 在故障时能恢复。
-
Spark Streaming的checkpoint无法跨越应用程序进行恢复。
-
Spark 升级也将导致无法恢复。
-
在关键生产应用, 不建议使用spark检查点的管理offset方式。
/**
* 用checkpoint记录offset
* 优点:实现过程简单
* 缺点:如果streaming的业务更改,或别的作业也需要获取该offset,是获取不到的
*/
import kafka.serializer.StringDecoder
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka.KafkaUtils
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Duration, Seconds, StreamingContext}
object StreamingWithCheckpoint {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
//val Array(brokers, topics) = args
val processingInterval = 2
val brokers = "node01:9092,node02:9092,node03:9092"
val topics = "mytest1"
// Create context with 2 second batch interval
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("ConsumerWithCheckPoint").setMaster("local[2]")
// Create direct kafka stream with brokers and topics
val topicsSet = topics.split(",").toSet
val kafkaParams = Map[String, String]("metadata.broker.list" -> brokers, "auto.offset.reset" -> "smallest")
val checkpointPath = "hdfs://node01:9000/spark_checkpoint1"
def functionToCreateContext(): StreamingContext = {
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(processingInterval))
val messages = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String, StringDecoder, StringDecoder](ssc, kafkaParams, topicsSet)
ssc.checkpoint(checkpointPath)
messages.checkpoint(Duration(8 * processingInterval.toInt * 1000))
messages.foreachRDD(rdd => {
if (!rdd.isEmpty()) {
println("################################" + rdd.count())
}
})
ssc
}
// 如果没有checkpoint信息,则新建一个StreamingContext
// 如果有checkpoint信息,则从checkpoint中记录的信息恢复StreamingContext
// createOnError参数:如果在读取检查点数据时出错,是否创建新的流上下文。
// 默认情况下,将在错误上引发异常。
val context = StreamingContext.getOrCreate(checkpointPath, functionToCreateContext _)
context.start()
context.awaitTermination()
}
}
// 以上案例测试过程:
// 模拟消费者向mytest1插入10条数据,
// 强制停止streaming,
// 再插入20条数据并启动streaming查看读取的条数为20条
Kafka Offset 管理--Zookeeper(常用)
1. 路径:
val zkPath = s"${kakfaOffsetRootPath}/${groupName}/${o.topic}/${o.partition}"
2. 如果Zookeeper中未保存offset,根据kafkaParam的配置使用最新或者最旧的offset
3. 如果 zookeeper中有保存offset,我们会利用这个offset作为kafkaStream的起始位置
import kafka.common.TopicAndPartition
import kafka.message.MessageAndMetadata
import kafka.serializer.StringDecoder
import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFrameworkFactory
import org.apache.curator.retry.ExponentialBackoffRetry
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.streaming.dstream.InputDStream
import org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka.{HasOffsetRanges, KafkaUtils, OffsetRange}
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import scala.collection.JavaConversions._
object KafkaZKManager extends Serializable{
/**
* 创建rookeeper客户端
*/
val client = {
val client = CuratorFrameworkFactory
.builder
.connectString("node01:2181/kafka0.9") // zk中kafka的路径
.retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3)) // 重试指定的次数, 且每一次重试之间停顿的时间逐渐增加
.namespace("mykafka") // 命名空间:mykafka
.build()
client.start()
client
}
val kafkaOffsetRootPath = "/consumers/offsets"
/**
* 确保zookeeper中的路径是存在的
* @param path
*/
def ensureZKPathExists(path: String): Unit = {
if (client.checkExists().forPath(path) == null) {
client.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().forPath(path)
}
}
// 保存offset
def storeOffsets(offsetsRanges:Array[OffsetRange], groupName:String) = {
for (o <- offsetsRanges) {
val zkPath = s"${kafkaOffsetRootPath}/${groupName}/${o.topic}/${o.partition}"
ensureZKPathExists(zkPath)
// 保存offset到zk
client.setData().forPath(zkPath, o.untilOffset.toString.getBytes())
}
}
/**
* 用于获取offset
* @param topic
* @param groupName
* @return
*/
def getFromOffsets(topic : String,groupName : String): (Map[TopicAndPartition, Long], Int) = {
// 如果 zookeeper中有保存offset,我们会利用这个offset作为kafkaStream 的起始位置
var fromOffsets: Map[TopicAndPartition, Long] = Map()
val zkTopicPath = s"${kafkaOffsetRootPath}/${groupName}/${topic}"
// 确保zookeeper中的路径是否存在
ensureZKPathExists(zkTopicPath)
// 获取topic中,各分区对应的offset
val offsets: mutable.Buffer[(