获取,修改进程命令行
在XDebug的源码学习中看到的命令行操作,将主要源码摘录出来做了个获取和更改进程命令行的Demo.
0x01 获取命令行
这里获取命令行的方式并不是通过调用GetCommandLine函数。
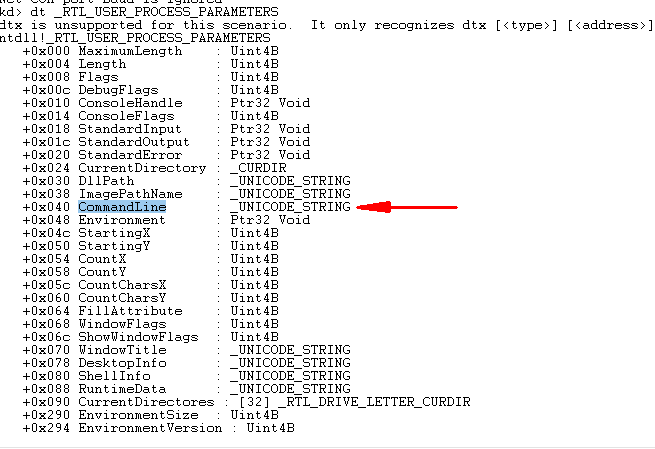
而是借由ntdll中的NtQueryInformationProcess函数查询ProcessBasicInformation,得到ProcessBasicInformation中的PebBaseAddress字段。得到进程PEB地址后,再通过PEB地址的获取ProcessParameter字段地址,
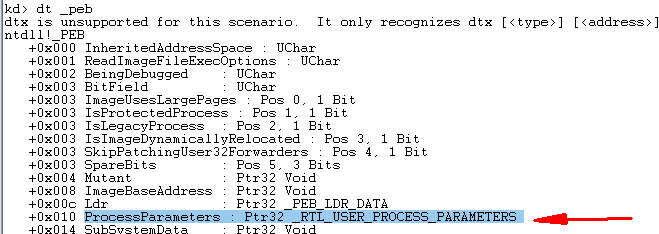
最后通过ProcessParameter字段获取到ProcessParameter的 CommandLine 字段,得到了命令行的存储地址。
主要源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | void* GetPEBLocation(HANDLE hProcess){ ULONG RequiredLen = 0; void* PebAddress = 0; PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION myProcessBasicInformation[5] = { 0 }; if (NtQueryInformationProcess(hProcess, ProcessBasicInformation, myProcessBasicInformation, sizeof(PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION), &RequiredLen) == STATUS_SUCCESS) { PebAddress = (void*)myProcessBasicInformation->PebBaseAddress; } else { if (NtQueryInformationProcess(hProcess, ProcessBasicInformation, myProcessBasicInformation, RequiredLen, &RequiredLen) == STATUS_SUCCESS) { PebAddress = (void*)myProcessBasicInformation->PebBaseAddress; } } return PebAddress;}BOOL Getcommandlineaddr(duint *CommandLineAddressdr){ duint PEBAddress; duint pprocess_parameters; duint ProcessParametersAddress; duint ReturnLength; PEBAddress = (duint)GetPEBLocation(__ProcessHandle); ProcessParametersAddress = (duint) & (((PPEB)PEBAddress)->ProcessParameters); ReadProcessMemory(__ProcessHandle, reinterpret_cast<LPVOID>(ProcessParametersAddress), &pprocess_parameters, sizeof(pprocess_parameters), reinterpret_cast<SIZE_T*>(&ReturnLength)); *CommandLineAddressdr = (duint) & (((RTL_USER_PROCESS_PARAMETERS*)pprocess_parameters)->CommandLine); return TRUE;} |
0x02 修改命令行
修改命令行的关键就是操作内存。
XDebug首先获取GetCommandLineA或GetCommandLineW函数的地址。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 | if (!valfromstring("kernelBase:GetCommandLineA", &getcommandline)) { if (!valfromstring("kernel32:GetCommandLineA", &getcommandline)) { return FALSE; } }bool valfromstring(const char* string, duint* value, bool silent, bool baseonly, int* value_size, bool* isvar, bool* hexonly, bool allowassign){ duint result; if (!Calculate(string, result, false /*valuesignedcalc()*/, allowassign, silent, baseonly, value_size, isvar, hexonly)) return false; *value = result; return true;}bool Calculate(const char* string, duint & value, bool signedcalc, bool allowassign, bool silent, bool baseonly, int* value_size, bool* isvar, bool* hexonly){ return DoEvaluate(string, value, silent, baseonly, value_size, isvar, hexonly);}bool DoEvaluate(const char* string, duint & result, bool silent, bool baseonly, int* value_size, bool* isvar, bool* hexonly){ return valfromstring_noexpr(string, (duint*)&result, silent, baseonly, value_size, isvar, hexonly);}bool valfromstring_noexpr(const char* string, duint* value, bool silent, bool baseonly, int* value_size, bool* isvar, bool* hexonly){ if (!value || !string || !*string) return false; if (valapifromstring(string, value, value_size, true, silent, hexonly)) //then come APIs return true; return false;}bool valapifromstring(const char* name, duint* value, int* value_size, bool printall, bool silent, bool* hexonly){ //explicit API handling const char* apiname = strchr(name, ':'); //the ':' character cannot be in a path: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa365247(v=vs.85).aspx#naming_conventions bool noexports = false; if (!apiname) //not found { apiname = strstr(name, "..") ? strchr(name, '.') : strrchr(name, '.'); //kernel32.GetProcAddress support if (!apiname) //not found { apiname = strchr(name, '?'); //the '?' character cannot be in a path either noexports = true; } } if (apiname) { char modname[MAX_MODULE_SIZE] = ""; strncpy_s(modname, name, _TRUNCATE); modname[apiname - name] = 0; apiname++; if (!strlen(apiname)) return false; duint modbase = 0;//ModBaseFromName(modname);从MAP表里查基地址 char szModPath[MAX_PATH] = "kernel32.dll"; if (!1/*ModPathFromAddr(modbase, szModPath, _countof(szModPath))*/)//查表得到完整路径 { //if (!silent) //dprintf(QT_TRANSLATE_NOOP("DBG", "Could not get filename of module %p\n"), modbase); } else { HMODULE mod = LoadLibraryExW(Utf8ToUtf16(szModPath).c_str(), 0, DONT_RESOLVE_DLL_REFERENCES); if (!mod) { //if (!silent) // dprintf(QT_TRANSLATE_NOOP("DBG", "Unable to load library %s\n"), szModPath); } else { duint addr = noexports ? 0 : SafeGetProcAddress(mod, apiname); //if (addr) //found exported function // addr = modbase + (addr - (duint)mod); //correct for loaded base //else //not found { } FreeLibrary(mod); if (addr) //found! { if (value_size) *value_size = sizeof(duint); if (hexonly) *hexonly = true; *value = addr; return true; } } } return false; } return true;} |
获取到这个所谓的“函数地址后并没有结束,这里需要设计到重定向表的重定向问题,在这个地址的基础上还需要两次跳转才能得到真正的功能函数地址。这个地址上的第一次跳转,是跳向重定向表,然后重定向表再给出地址,跳向库中真正的功能函数地址。
对应的源码操作(图中getcommandline即为前文valfromstring函数获取的GetCommandLineA或GetCommandLineW函数的地址。)

调试反汇编查看获取到的getcommandline地址:
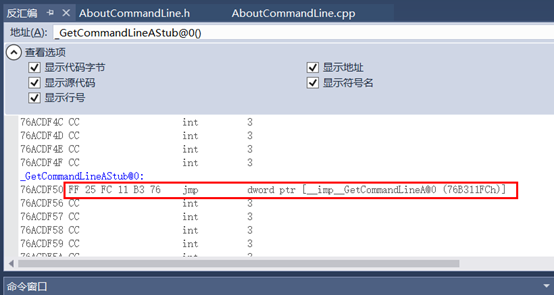
越过FF 25两字节,获取到跳转地址76b311fch:
1 | ReadProcessMemory(__ProcessHandle, reinterpret_cast<LPVOID>(getcommandline + 2), data, 100, reinterpret_cast<SIZE_T*>(&ReturnLength)); |
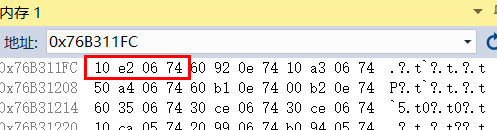
内存窗口查看76b311fch:处内容,得到重定向表给出的功能函数地址:0x7406e210
1 | ReadProcessMemory(__ProcessHandle, reinterpret_cast<LPVOID>(*(int*)data), data, 100, reinterpret_cast<SIZE_T*>(&ReturnLength)); |
反汇编窗口中查看0x7406e210中的内容:

现在就可以通过字符串匹配来得到命令行的存储地址:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | /* 750FE9CA | A1 CC DB 1A 75 | mov eax,dword ptr ds:[751ADBCC] | 750FE9CF | C3 | ret | */ if (data[0] != 0xA1 || data[5] != 0xC3) { return FALSE; } command_line_stored = *((duint*)& data[1]); |
找到地址后最后一步写入地址:
1 2 3 | WriteProcessMemory(__ProcessHandle, reinterpret_cast<LPVOID>(command_line_stored), &new_command_line, sizeof(new_command_line), reinterpret_cast<SIZE_T*>(&ReturnLength)); //update the pointer in the debuggee |





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
· AI Agent开发,如何调用三方的API Function,是通过提示词来发起调用的吗