32位程序中获取64位函数地址
总结一下之前学习过的在blackbone中的一个x86程序中获取x64位进程函数地址的方法,之前就已经系统地梳理了一遍,今天贴出来分享一下。
这个程序的目的说白了就是要让让运行在Wow64环境中的x86应用程序可以获取到x64下ntdll.dll中的Native API的地址,从而能够直接调用x64下ntdll.dll中的Native API。
0x01 理论基础:
在分析源码之前,先讲几个相关的知识点:
1.64位计算机系统下的进程,无论是是32 位或者是 64 位,都映射了两个地址空间,一个 是 32 位,一个是 64 位。所以 32 位和 64 位,可以理解为一个进程的两种工作模式,并且这 两种工作模式可以切换。
2.64位计算机系统下的进程,每个32位进程都会加重ntdll32.dll和ntdll.dll模块。其中ntdll.dll是64位模块。我们可以将进程的32位模式切换到64位,获取64位的ntdll中的导出函数来使用,这样就能够操作64位的进程。
功能实现的逻辑:
1. 进程由 32 位变成 64 位 CS: 0x23 -- > 0x32 具体代码如下:利用 retf,把堆栈上的值写进 cs 寄存器,同时保证 ip 的正确性。
2. 获取 64 位模式下的 TEB (r12寄存器指向64位的TEB结构(TEB64))
3. 从 64 位 TEB 获取到 64 位 Ntdll.dll 的地址 TEB->PEB->LDR LDR 匹配的 Ntdll.dll,找到基址
4. 找到需要调用的 Ntdll.dll 的函数 找到 Ntdll.dll 地址,分析 PE 结构,可以找到函数的入口地址。
5. 调用函数 x64 的调用规则,前 4 个参数依次是 rcx, rdx, r8, r9,更多的参数由堆栈传递。 X64Call 这个函数封了 32 位模式下对 64 位函数的调用。
0x02 源码分析
1.32位程序切换到64位模式实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | #define X64_Start() X64_Start_with_CS(0x33)//switch(x64)//通过retf将0x33赋值给cs寄存器#define X64_Start_with_CS(_cs) \ { \ EMIT(0x6A) EMIT(_cs) /* push _cs */ \ EMIT(0xE8) EMIT(0) EMIT(0) EMIT(0) EMIT(0) /* call $+5 */ \ EMIT(0x83) EMIT(4) EMIT(0x24) EMIT(5) /* add dword [esp], 5 */ \ EMIT(0xCB) /* retf */ \ } |
windbg中对应的反汇编代码:
1 2 3 4 | 00ad2461 6a33 push 33h00ad2463 e800000000 call Demo+0x12468 (00ad2468)00ad2468 83042405 add dword ptr [esp],500ad246c cb retf |
通过windbg中对应的反汇编代码可以看出操作就是将0x33压栈 原地call将下一条指令地址压栈,再将esp中保存的地址的值加5,那么此时在esp栈顶的地址值将成为retf指令之后的地址值,从而确保了retf之后指令指针寄存器ip的正确性,再retf会pop eip,再pop cs,修改段选择子,这样CS寄存器中原本的值0x23就变成了0x33,同时保证了指令指针寄存器中的eip的正确性。
话不多说,直接看windbg中esp栈顶地址最直白:
1 | push 33h 之后的栈顶地址内容:(0x33被压入栈顶) |
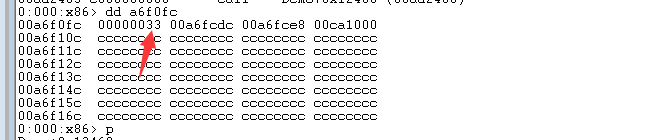
1 | 00ad2463 e800000000 call Demo+0x12468 (00ad2468) 之后的栈顶内容(call指令的下一跳指令的地址00ad2468被压入栈顶) |

1 | 00ad2468 83042405 add dword ptr [esp],5 之后的栈顶内容(栈顶保存的地址加了5个字节大小,其实也就是到了retf指令之后的地址,这里的00ad246d将成为rip寄存器中的值) |

最终retf指令执行过后,将pop eip,再pop cs,即将ad246d的值赋给eip寄存器,将0x33赋值给cs寄存器。
如图,retf前的cs寄存器中的内容为0x23:

retf后~化腐朽为神奇了!

当前rip寄存器中的ad246d正是之前esp栈顶中的值,cs寄存器中的值被修改为0x33了,顿时windbg的整个画风都变了。此时就成功切换到了64位模式下啦。
2.获取32位进程64位模式下的TEB地址
union Register64
{
DWORD64 dw64;
DWORD dw[2];
};
//定义一个寄存器
Register64 v1;
v1.dw64 = 0;
1 2 3 4 5 6 | X64_Push(_R12); // below pop will pop QWORD from stack, as we're in x64 mode now //将R12pop给v1 TEB在其中 __asm pop v1.dw[0] #define X64_Push(Value) EMIT(0x48 | ((Value) >> 3)) EMIT(0x50 | ((Value) & 7)) |
直接上windbg中对应的汇编指令:
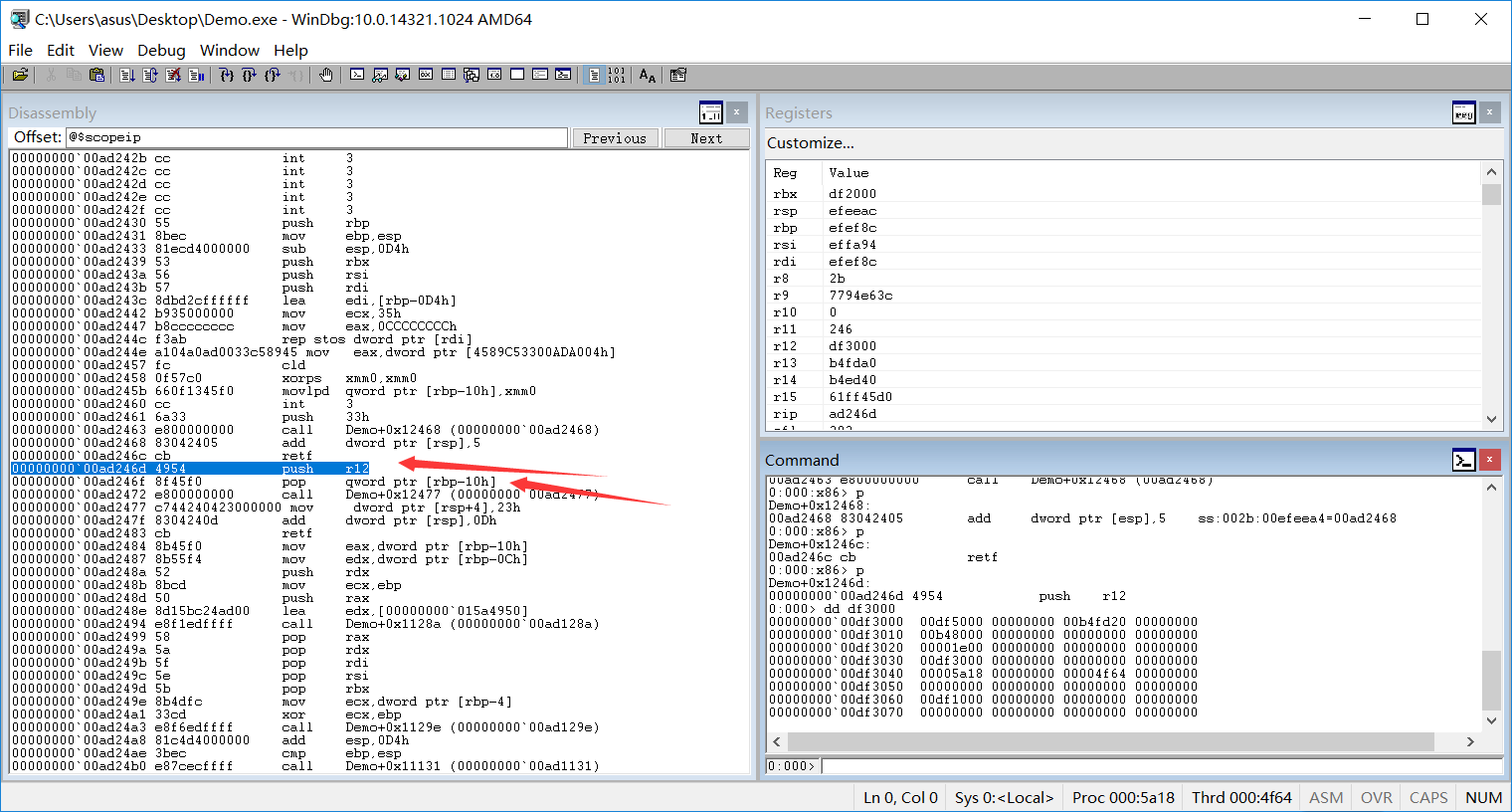
push r12这条指令,因为不能使用嵌入式汇编表示64寄存器,所以采用机器码书写,随后再将r12寄存器中的值保存到我们的局部变量中,成功取得了TEB的地址(r12寄存器指向64位的TEB结构(TEB64)),这时候再切换回32位模式,将TEB中的内容赋值给我们自定义的结构体:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | template <class T>struct _TEB_T_{ _NT_TIB_T<T> NtTib; T EnvironmentPointer; _CLIENT_ID<T> ClientID; T ActiveRpcHandle; T ThreadLocalStoragePointer; T ProcessEnvironmentBlock; DWORD LastErrorValue; DWORD CountOfOwnedCriticalSections; T CsrClientThread; T Win32ThreadInfo; DWORD User32Reserved[26];};typedef _TEB_T_<DWORD> TEB32;typedef _TEB_T_<DWORD64> TEB64; |
3.获取PEB地址
这里我们通过自定义的TEB结构体和之前获取的TEB结构体来得到PEB的基地址
在/32位下切入64位模式执行64位汇编实现字符串copy:

1 PEB64 Peb; 2 GetMemoy64(&Peb, Teb.ProcessEnvironmentBlock, sizeof(PEB64)); 3 4 //32位下执行64位汇编实现字符串copy 5 void GetMemoy64(void* DestinationMemory, DWORD64 SourceMemory, size_t SourceMemoryLength) 6 { 7 if ((NULL == DestinationMemory) || (0 == SourceMemory) || (0 == SourceMemoryLength)) 8 return; 9 10 Register64 v1 = { SourceMemory }; 11 #ifdef _M_IX86 12 __asm 13 { 14 X64_Start(); 15 16 ;// below code is compiled as x86 inline asm, but it is executed as x64 code 17 ;// that's why it need sometimes REX_W() macro, right column contains detailed 18 ;// transcription how it will be interpreted by CPU 19 20 push edi;// push rdi 21 push esi;// push rsi 22 mov edi, DestinationMemory; // mov edi, dword ptr [dstMem] ; high part of RDI is zeroed 23 REX_W mov esi, v1.dw[0]; // mov rsi, qword ptr [_src] REX_W 自减 24 mov ecx, SourceMemoryLength; // mov ecx, dword ptr [sz] ; high part of RCX is zeroed 25 26 mov eax, ecx; // mov eax, ecx 27 and eax, 3; // and eax, 3 28 shr ecx, 2; // shr ecx, 2 29 30 rep movsd; // rep movs dword ptr [rdi], dword ptr [rsi] 31 32 test eax, eax; // test eax, eax 33 je _move_0; // je _move_0 34 cmp eax,1; // cmp eax, 1 35 je _move_1; // je _move_1 36 movsw // movs word ptr [rdi], word ptr [rsi] 37 cmp eax, 2; // cmp eax, 2 38 je _move_0; // je _move_0 39 _move_1: 40 movsb // movs byte ptr [rdi], byte ptr [rsi] 41 42 _move_0: 43 pop esi;// pop rsi 44 pop edi;// pop rdi 45 46 X64_End(); 47 } 48 #endif 49 }
4.通过PEB得到PEB_LDR_DATA64的地址,在通过遍历PEB_LDR_DATA64结构中的链表,找到ntdll.dll的基地址。回忆一下这经常用到的LDR结构和它令人心动的三条LIST_ENTRY链表~~~
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | typedef struct _PEB_LDR_DATA { ULONG Length; BOOLEAN Initialized; PVOID SsHandle; LIST_ENTRY InLoadOrderModuleList; LIST_ENTRY InMemoryOrderModuleList; LIST_ENTRY InInitializationOrderModuleList;} PEB_LDR_DATA,*PPEB_LDR_DATA;<br><br><br><br> PEB_LDR_DATA64 PebLdrData; GetMemoy64(&PebLdrData, Peb.Ldr, sizeof(PEB_LDR_DATA64));<br><br> |
DWORD64 LastEntry = Peb.Ldr + offsetof(PEB_LDR_DATA64, InLoadOrderModuleList);
LDR_DATA_TABLE_ENTRY64 LdrDataTableEntry;
LdrDataTableEntry.InLoadOrderLinks.Flink = PebLdrData.InLoadOrderModuleList.Flink;
do
{
//遍历链表
GetMemoy64(&LdrDataTableEntry, LdrDataTableEntry.InLoadOrderLinks.Flink, sizeof(LDR_DATA_TABLE_ENTRY64));
wchar_t BaseDllName[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
//得到模块名
GetMemoy64(BaseDllName, LdrDataTableEntry.BaseDllName.Buffer, LdrDataTableEntry.BaseDllName.MaximumLength);
if (0 == _wcsicmp(ModuleName, BaseDllName))
return LdrDataTableEntry.DllBase;
} while (LdrDataTableEntry.InLoadOrderLinks.Flink != LastEntry);
到目前为止,我们已经成功get了64位模式下的ntdll.dll的基地址了。
5.解析PE结构导出表,得到对应的函数地址。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 | DWORD64 GetFunctionAddressFromExportTable64(WCHAR* ModuleName,char* FunctionName){ DWORD* AddressOfFunctions = 0; WORD* AddressOfNameOrdinals = 0; DWORD* AddressOfNames = 0; DWORD64 ModuleBase = GetModuleHandle64(ModuleName); if (0 == ModuleBase) return 0; __try { IMAGE_DOS_HEADER ImageDosHeader; GetMemoy64(&ImageDosHeader, ModuleBase, sizeof(IMAGE_DOS_HEADER)); IMAGE_NT_HEADERS64 ImageNtHeaders; GetMemoy64(&ImageNtHeaders, ModuleBase + ImageDosHeader.e_lfanew, sizeof(IMAGE_NT_HEADERS64)); IMAGE_DATA_DIRECTORY& ImageDataDirectory = ImageNtHeaders.OptionalHeader.DataDirectory[IMAGE_DIRECTORY_ENTRY_EXPORT]; if (0 == ImageDataDirectory.VirtualAddress) return 0; IMAGE_EXPORT_DIRECTORY ImageExportDirectory; GetMemoy64(&ImageExportDirectory, ModuleBase + ImageDataDirectory.VirtualAddress, sizeof(IMAGE_EXPORT_DIRECTORY)); AddressOfFunctions = (DWORD*)malloc(sizeof(DWORD)*ImageExportDirectory.NumberOfFunctions); if (NULL == AddressOfFunctions) { return 0; } //得到函数地址数组 GetMemoy64(AddressOfFunctions, ModuleBase + ImageExportDirectory.AddressOfFunctions, sizeof(DWORD)*ImageExportDirectory.NumberOfFunctions); AddressOfNameOrdinals = (WORD*)malloc(sizeof(WORD)*ImageExportDirectory.NumberOfFunctions); if (NULL == AddressOfNameOrdinals) { return 0; } //得到索引数组 GetMemoy64(AddressOfNameOrdinals, ModuleBase + ImageExportDirectory.AddressOfNameOrdinals, sizeof(WORD)*ImageExportDirectory.NumberOfFunctions); AddressOfNames = (DWORD*)malloc(sizeof(DWORD)*ImageExportDirectory.NumberOfNames); if (nullptr == AddressOfNames) { return 0; } //根据函数名得到函数索引 GetMemoy64(AddressOfNames, ModuleBase + ImageExportDirectory.AddressOfNames, sizeof(DWORD)*ImageExportDirectory.NumberOfNames); for (DWORD i = 0; i < ImageExportDirectory.NumberOfFunctions; i++) { if (!CompareMemory64(FunctionName, ModuleBase + AddressOfNames[i], strlen(FunctionName) + 1)) continue; else //根据索引得到函数相对地址 基地址+相对地址=函数绝对地址 return ModuleBase + AddressOfFunctions[AddressOfNameOrdinals[i]]; } } __finally { if (AddressOfFunctions != NULL) { free(AddressOfFunctions); AddressOfFunctions = NULL; } if (AddressOfNameOrdinals != NULL) { free(AddressOfNameOrdinals); AddressOfNameOrdinals = NULL; } if (AddressOfNames != NULL) { free(AddressOfNames); AddressOfNames = NULL; } } return 0;} |







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
· AI Agent开发,如何调用三方的API Function,是通过提示词来发起调用的吗