python3+pyshark读取wireshark数据包并追踪telnet数据流
一、程序说明
本程序有两个要点,第一个要点是读取wireshark数据包(当然也可以从网卡直接捕获改个函数就行),这个使用pyshark实现。pyshark是tshark的一个python封装,至于tshark可以认为是命令行版的wireshark,随wireshark一起安装。
第二个要点是追踪流,追踪流在wireshark中是“tcp.stream eq 70”之类的形式,但是70这类值暂是不知道具体怎么计算出来的,但从网上资料看,是依据[IP address A, TCP port A, IP address B, TCP port B]四元组计算出来的,只要这四个值一样那么计算出来的tcp.stream也就一样,就认为是同一个流。那么,反过来也就是说“tcp.stream eq 70”这种形式,其实等价于"ip.addr == ip_a and tcp.port == port_a and ip.addr == ip_b and tcp.port == port_b"的形式,我们这里就是用这种形式来追踪telnet流。
至于为什么一再强调是追踪telnet流而不是追踪流,是因为感觉各应用层协议没有统一获取应用层协议内容的方法,比如这里通过tmp_packet[highest_layer_name].get_field('data')形式读取telnet数据的,但http则得用tmp_packet['http'].file_data读取,ftp等其他协议又要通过其他不同属性来获取。
另外还要说明的一点是,数据包的每次过滤主要是借助写display_filter重新读取数据包文件,而不是将所有数据包读入后自己写代码进行过滤(就实际来看这种方法比借助写display_filter重新读取数据包文件要复杂且运行速度要慢)或者写display_filter进行二次过滤(tshark本身就不支持二次过滤,就观察来看wireshark自己也没有二次过滤这种东西在执行过滤器表达式时都是重新读取数据包文件)
运行效果如下:
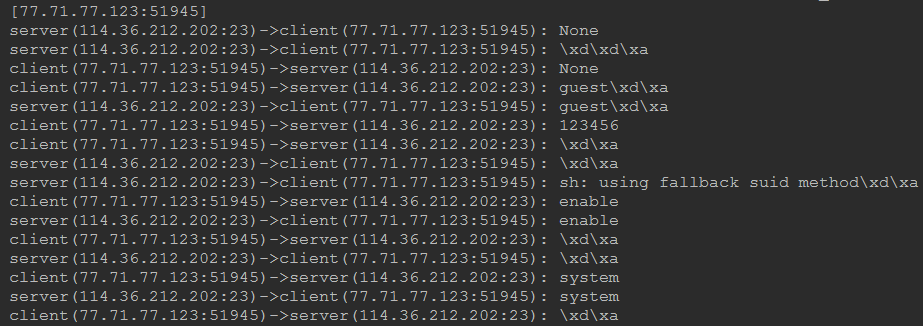
二、程序源代码
import pyshark class wireshark_analysis_script(): # 此函数的作用是封装一下pyshark.FileCapture def read_packets_from_file(self,packets_file_path,tshark_path,display_filter): packets_file_obj = pyshark.FileCapture(input_file=packets_file_path,tshark_path=tshark_path,display_filter=display_filter) return packets_file_obj # 此函数的作用是从传送过来的所有数据包中,抽取并返回{ip_server,ip_client,port_server,port_client}四元组 def get_target_client_ip_port(self,packets_file_obj): for tmp_packet in packets_file_obj: ip_server = tmp_packet.ip.src port_server = tmp_packet.tcp.srcport ip_client = tmp_packet.ip.dst port_client = tmp_packet.tcp.dstport yield {"ip_server":ip_server,"port_server":port_server,"ip_client":ip_client, "port_client":port_client} # 此函数的作用是读取传过来的所有数据包应用层的数据,并打印 def follow_tcp_stream(self,packets_file_obj,ip,port): for tmp_packet in packets_file_obj: highest_layer_name = tmp_packet.highest_layer if ((tmp_packet.ip.dst == ip) and (tmp_packet.tcp.dstport == port)): print("server(%s:%s)->client(%s:%s): %s" % (tmp_packet.ip.src, tmp_packet.tcp.srcport, tmp_packet.ip.dst, tmp_packet.tcp.dstport, tmp_packet[highest_layer_name].get_field('data'))) elif ((tmp_packet.ip.src == ip) and (tmp_packet.tcp.srcport == port)): print("client(%s:%s)->server(%s:%s): %s" % (tmp_packet.ip.src, tmp_packet.tcp.srcport, tmp_packet.ip.dst, tmp_packet.tcp.dstport, tmp_packet[highest_layer_name].get_field('data'))) if __name__ == '__main__': # 要读取的wireshark数据包的所在的路径 packets_file_path = 'F:\\PycharmProjects\\telnet\\pyshark_pack' # tshark程序所在的路径,tshark随wireshark安装 tshark_path = 'D:\\tools\\Wireshark\\tshark.exe' # 过滤器表达式,与在wireshark中使用时的写法完全相同 first_step_filter = 'telnet contains "HiLinux"' # 用于存放要追踪流的ip和端口 target_client_ip_port = [] # 实例化类 wireshark_analysis_script_instance = wireshark_analysis_script() # 使用first_step_filter过滤器表达式,过滤出要追踪流的数据包 first_step_obj = wireshark_analysis_script_instance.read_packets_from_file(packets_file_path, tshark_path, first_step_filter) # 从要追踪流的数据包中抽取出ip和端口 target_client_ip_port = wireshark_analysis_script_instance.get_target_client_ip_port(first_step_obj) first_step_obj.close() # 遍历要追踪流的ip+端口组合 for target_client_ip_port_temp in target_client_ip_port: ip_server = target_client_ip_port_temp['ip_server'] port_server = target_client_ip_port_temp['port_server'] ip_client = target_client_ip_port_temp['ip_client'] port_client = target_client_ip_port_temp['port_client'] # 这里是追踪流的关键,所有数据包中如果数据包中{ip_server,ip_client,port_server,port_client}四元组相同,那么就认为是同一个流 # 当然追踪流一般都是追踪应用层的数据流,所以加上应用层协议运行过滤去掉三次握手四次挥手等没有应用层数据的数据包;我这里要追踪telnet数据流,所以除四元组外还加了telnet做过滤 second_step_filter = 'telnet and ip.addr == %s and ip.addr == %s and tcp.port == %s and tcp.port == %s' % (ip_server,ip_client,port_server,port_client) second_step_obj = wireshark_analysis_script_instance.read_packets_from_file(packets_file_path, tshark_path, second_step_filter) print("[%s:%s]" % (ip_client, port_client)) # 调用follow_tcp_stream将认为是同一个流的所有数据包的应用层数据打印 wireshark_analysis_script_instance.follow_tcp_stream(second_step_obj, ip_client, port_client) second_step_obj.close()
三、使用与wireshark一致的形式【20180929更新】
在前边的解决方案中,我们使用"ip.addr == ip_a and tcp.port == port_a and ip.addr == ip_b and tcp.port == port_b"等价代替wireshark中“tcp.stream eq 70”的形式来实现追踪流,当时的想法是不知道某个流的70这种值如何计算。
现在发现这种值pyshark在tcp.stream属性直接给出了,所以我们完全可以使用和wireshark的“tcp.stream eq 70”一致的形式来追踪流。第二大节程序可等介修改如下。
(当然因为是等价形式所以输出结果还是一样的,都是要重新解析数据包文件所以效率也就差不多,主要是为了说追流可以使用和wireshark一样的形式)

import pyshark class wireshark_analysis_script(): # 此函数的作用是封装一下pyshark.FileCapture def read_packets_from_file(self, packets_file_path, tshark_path, display_filter): packets_file_obj = pyshark.FileCapture(input_file=packets_file_path, tshark_path=tshark_path, display_filter=display_filter) return packets_file_obj # 此函数的作用是从传送过来的所有数据包中,抽取并返回{ip_server,ip_client,port_server,port_client}四元组 def get_target_client_ip_port(self, packets_file_obj): for tmp_packet in packets_file_obj: ip_server = tmp_packet.ip.src port_server = tmp_packet.tcp.srcport ip_client = tmp_packet.ip.dst port_client = tmp_packet.tcp.dstport stream_value = tmp_packet.tcp.stream yield {"ip_server": ip_server, "port_server": port_server, "ip_client": ip_client, "port_client": port_client,"stream_value":stream_value} # 此函数的作用是读取传过来的所有数据包应用层的数据,并打印 def follow_tcp_stream(self, packets_file_obj, ip, port): for tmp_packet in packets_file_obj: highest_layer_name = tmp_packet.highest_layer #追踪流时会有握手挥手tcp将其排除 if highest_layer_name != "TCP": if ((tmp_packet.ip.dst == ip) and (tmp_packet.tcp.dstport == port)): print("server(%s:%s)->client(%s:%s): %s" % (tmp_packet.ip.src, tmp_packet.tcp.srcport, tmp_packet.ip.dst, tmp_packet.tcp.dstport, tmp_packet[highest_layer_name].get_field('data'))) elif ((tmp_packet.ip.src == ip) and (tmp_packet.tcp.srcport == port)): print("client(%s:%s)->server(%s:%s): %s" % (tmp_packet.ip.src, tmp_packet.tcp.srcport, tmp_packet.ip.dst, tmp_packet.tcp.dstport, tmp_packet[highest_layer_name].get_field('data'))) if __name__ == '__main__': # 要读取的wireshark数据包的所在的路径 packets_file_path = 'F:\\PycharmProjects\\telnet\\pyshark_pack' # tshark程序所在的路径,tshark随wireshark安装 tshark_path = 'D:\\tools\\Wireshark\\tshark.exe' # 过滤器表达式,与在wireshark中使用时的写法完全相同 first_step_filter = 'telnet contains "HiLinux"' # 用于存放要追踪流的ip和端口 target_client_ip_port = [] # 实例化类 wireshark_analysis_script_instance = wireshark_analysis_script() # 使用first_step_filter过滤器表达式,过滤出要追踪流的数据包 first_step_obj = wireshark_analysis_script_instance.read_packets_from_file(packets_file_path, tshark_path, first_step_filter) # 从要追踪流的数据包中抽取出ip和端口 target_client_ip_port = wireshark_analysis_script_instance.get_target_client_ip_port(first_step_obj) first_step_obj.close() # 遍历要追踪流的ip+端口组合 for target_client_ip_port_temp in target_client_ip_port: # stream的值 stream_value = target_client_ip_port_temp['stream_value'] ip_client = target_client_ip_port_temp['ip_client'] port_client = target_client_ip_port_temp['port_client'] # tcp.stream eq 70形式。为了排除tcp其实可以再直接加上and telnet second_step_filter = 'tcp.stream eq %s' % (stream_value) second_step_obj = wireshark_analysis_script_instance.read_packets_from_file(packets_file_path, tshark_path, second_step_filter) print("[%s:%s]" % (ip_client, port_client)) # 调用follow_tcp_stream将认为是同一个流的所有数据包的应用层数据打印 wireshark_analysis_script_instance.follow_tcp_stream(second_step_obj, ip_client, port_client) second_step_obj.close()
参考:
http://kiminewt.github.io/pyshark/
https://www.wireshark.org/docs/wsug_html_chunked/
https://medium.com/@asfandyar.khalil/tcp-stream-in-pcap-file-using-python-6991a8e7b524




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号