hibernate基于注解的维护权反转:@OneToMany(mappedBy=)
mappedBy 对应 XML中的inverse
先贴出最初的代码:一些基本的注解,在一对多的关系上没有使用JoinColumn和mappedBy属性
部门类:主要是第33、34行
1 package com.lizhou.entity.test;
2
3 import java.util.ArrayList;
4 import java.util.List;
5
6 import javax.persistence.Column;
7 import javax.persistence.Entity;
8 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
9 import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
10 import javax.persistence.Id;
11 import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
12 import javax.persistence.Table;
13
14 import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
15
16 /**
17 * 部门:与员工一对多关系
18 * @author bojiangzhou
19 *
20 */
21 @Entity
22 @Table(name="department")
23 public class Department {
24
25 @Id
26 @GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
27 @GenericGenerator(name="_native", strategy="native")
28 private int id; //ID
29
30 @Column(length=20)
31 private String dname; //部门名称
32
33 @OneToMany
34 private List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>(); //部门下的员工集合
35
36 // get/set方法59
60 }
员工类:主要是第32、33行
1 package com.lizhou.entity.test;
2
3 import javax.persistence.Column;
4 import javax.persistence.Entity;
5 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
6 import javax.persistence.Id;
7 import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
8 import javax.persistence.Table;
9
10 import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
11
12 /**
13 * 员工:与部门多对一关系
14 * @author bojiangzhou
15 *
16 */
17 @Entity
18 @Table(name="employee")
19 public class Employee {
20
21 @Id
22 @GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
23 @GenericGenerator(name="_native", strategy="native")
24 private int id; //ID
25
26 @Column(length=20)
27 private String ename; //员工姓名
28
29 @Column(length=20)
30 private String phone; //电话
31
32 @ManyToOne
33 private Department department; //所属部门
34
35
36 //get/set方法67
68 }
最初的注解配置里,在一对多的关系上,即employeeList和department没有使用JoinColumn。
看下图,employee表会自动添加一个外键列department_id,虽然关系映射上是正确了,但是有一个问题,数据库里多了一张表出来,这不是想要的结果。
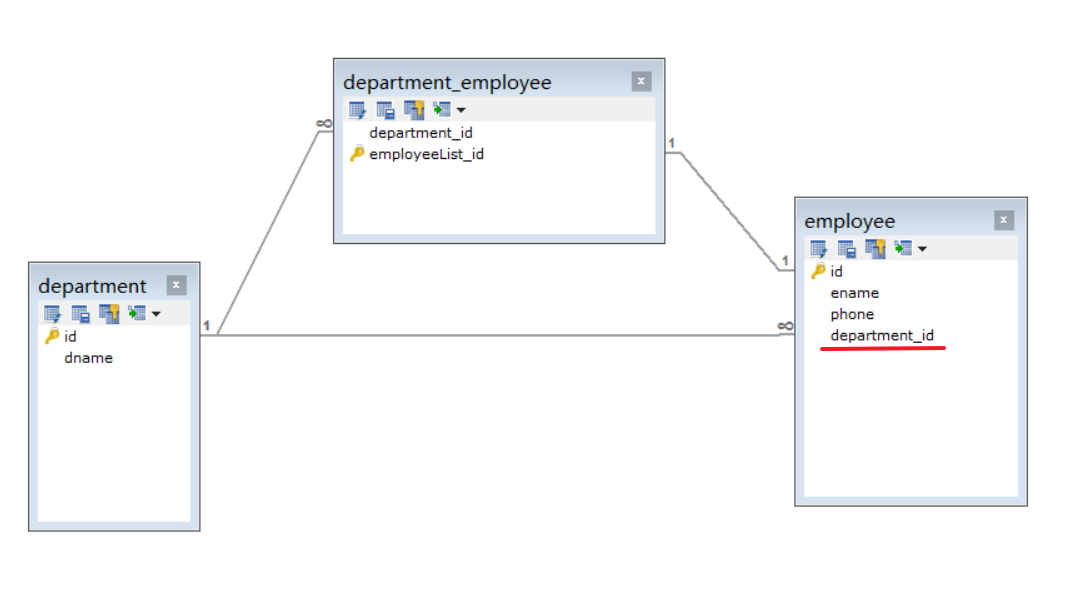
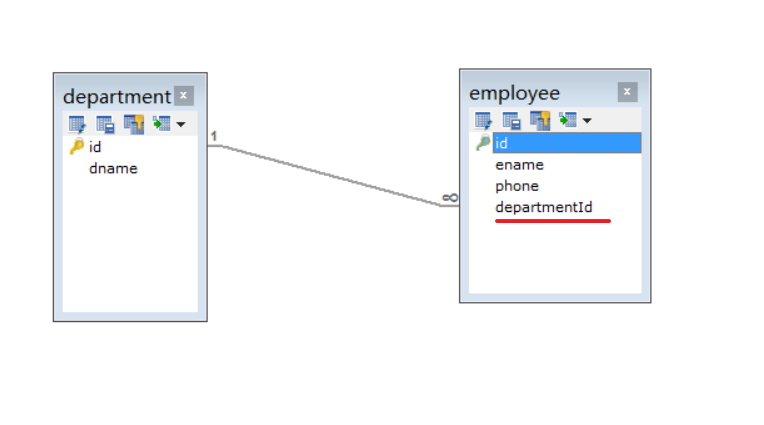
解决方法:在employeeList和department字段上加上@JoinColumn注解
1 @OneToMany 2 @JoinColumn(name="departmentId") 3 private List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>(); //部门下的员工集合
1 @ManyToOne// 2 @JoinColumn(name="departmentId")// 3 private Department department; //所属部门
这样一来的话就只有两张表了,所以在一对多或者一对一的关系下,需要加上@JoinColumn来指定外键列,避免生成一张中间表。
而且经试验,多的一方(Employee)里的department必须加上@JoinColumn,Department里不加不会影响表的结构,不知道会不会有其它影响;
但是如果Employee属于多的一方,如果没有指定外键列,还是会自动生成一个department_id外键列。
接下来讨论mappedBy属性:mappedBy属性主要是针对外键而言。与之相对应的是xml中的inverse属性。
如下是测试类代码:此时还没有设置mappedBy属性,映射时,默认是都由自身维护关联关系。
1 package com.lizhou.action.test;
2
3 import org.hibernate.Session;
4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
5 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
6 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
7 import org.junit.Test;
8 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
9 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
10
11 import com.lizhou.entity.test.Department;
12 import com.lizhou.entity.test.Employee;
13
14 /**
15 * 测试类
16 * @author bojiangzhou
17 *
18 */
19
20 public class TestAction {
21
22 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
23
24 static {
25 //读取classpath中applicationContext.xml配置文件
26 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
27 //获取session中配置的sessionFactory对象
28 sessionFactory = (SessionFactory) applicationContext.getBean("sessionFactory");
29 }
30
31 @Test
32 public void testSave(){
33 //创建一个部门对象
34 Department d1 = new Department();
35 d1.setDname("研发部");
36
37 //创建两个员工对象
38 Employee e1 = new Employee();
39 e1.setEname("张三");
40 e1.setPhone("13111111111");
41 Employee e2 = new Employee();
42 e2.setEname("李四");
43 e2.setPhone("18523222222");
44
45 //设置对象关联
46 d1.getEmployeeList().add(e1);
47 d1.getEmployeeList().add(e2);
48 e1.setDepartment(d1);
49 e2.setDepartment(d1);
50
51 //获取Session
52 Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
53 //开始事务
54 Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
55 try {
56 //添加数据
57 session.save(d1);
58 session.save(e1);
59 session.save(e2);
60 //提交事务
61 t.commit();
62 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
63 //有异常则回滚事务
64 t.rollback();
65 e.printStackTrace();
66 } finally {
67 //关闭session
68 session.close();
69 }
70 }
71
72
73 }
执行testSave后,控制台打印如下语句:
1 Hibernate: insert into department (dname) values (?) 2 Hibernate: insert into employee (departmentId, ename, phone) values (?, ?, ?) 3 Hibernate: insert into employee (departmentId, ename, phone) values (?, ?, ?) 4 Hibernate: update employee set departmentId=? where id=? 5 Hibernate: update employee set departmentId=? where id=?
可以看到多了两条update语句,这是因为两边都维护关系,先插入的部门,再插入员工,插入员工时,已经设置好外键了,但部门方也维护关系,会再执行一次更新操作,为员工设置外键,这样就导致多出了两条update语句,这里是有性能损耗的。
一种解决办法是:将第46、47行去掉,即对象上部门不关联员工
1 package com.lizhou.action.test;
2
3 import org.hibernate.Session;
4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
5 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
6 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
7 import org.junit.Test;
8 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
9 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
10
11 import com.lizhou.entity.test.Department;
12 import com.lizhou.entity.test.Employee;
13
14 /**
15 * 测试类
16 * @author bojiangzhou
17 *
18 */
19
20 public class TestAction {
21
22 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
23
24 static {
25 //读取classpath中applicationContext.xml配置文件
26 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
27 //获取session中配置的sessionFactory对象
28 sessionFactory = (SessionFactory) applicationContext.getBean("sessionFactory");
29 }
30
31 @Test
32 public void testSave(){
33 //创建一个部门对象
34 Department d1 = new Department();
35 d1.setDname("研发部");
36
37 //创建两个员工对象
38 Employee e1 = new Employee();
39 e1.setEname("张三");
40 e1.setPhone("13111111111");
41 Employee e2 = new Employee();
42 e2.setEname("李四");
43 e2.setPhone("18523222222");
44
45 //设置对象关联
46 // d1.getEmployeeList().add(e1);
47 // d1.getEmployeeList().add(e2);
48 e1.setDepartment(d1);
49 e2.setDepartment(d1);
50
51 //获取Session
52 Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
53 //开始事务
54 Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
55 try {
56 //添加数据
57 session.save(d1);
58 session.save(e1);
59 session.save(e2);
60 //提交事务
61 t.commit();
62 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
63 //有异常则回滚事务
64 t.rollback();
65 e.printStackTrace();
66 } finally {
67 //关闭session
68 session.close();
69 }
70 }
71
72
73 }
1 Hibernate: insert into department (dname) values (?) 2 Hibernate: insert into employee (departmentId, ename, phone) values (?, ?, ?) 3 Hibernate: insert into employee (departmentId, ename, phone) values (?, ?, ?)
这样部门方就不会去维护外键关系了。但是有一个问题,对象上就没有关联了,我们要做的是对象上要互相关联,数据库方面只让一方去维护关系即可。
对象上如果不关联,因为部门和员工添加到数据库后,是持久化状态,存在于session缓存中,那session操作缓存中这几个对象时,部门就没有关联员工了,那么就还得再查询一次数据库,这不是想要的结果。
这时就要用到mappedBy属性了。
在一的一方配置@OneToMany(mappedBy="department"),将维护权交由多的一方来维护;
那为什么不让多的一方交出维护权,让一的一方来维护呢?上面的实验也表明了如果让一的一方来维护,始终都会多出两条update语句,因为外键是在多的这一方的,所以维护权应该交由多的一方。
部门类的配置:第36行和第37行的配置,部门部门交出维护权利,让对方来维护
1 package com.lizhou.entity.test;
2
3 import java.util.ArrayList;
4 import java.util.List;
5
6 import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
7 import javax.persistence.Column;
8 import javax.persistence.Entity;
9 import javax.persistence.FetchType;
10 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
11 import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
12 import javax.persistence.Id;
13 import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
14 import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
15 import javax.persistence.Table;
16
17 import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
18
19 /**
20 * 部门:与员工一对多关系
21 * @author bojiangzhou
22 *
23 */
24 @Entity
25 @Table(name="department")
26 public class Department {
27
28 @Id
29 @GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
30 @GenericGenerator(name="_native", strategy="native")
31 private int id; //ID
32
33 @Column(length=20)
34 private String dname; //部门名称
35
36 @OneToMany(mappedBy="department")
37 private List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>(); //部门下的员工集合
38
39 // get/set方法62
63 }
员工类的配置不变。
调用testSave时,部门和员工再对象上依然是关联的:第46-49行
1 package com.lizhou.action.test;
2
3 import org.hibernate.Session;
4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
5 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
6 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
7 import org.junit.Test;
8 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
9 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
10
11 import com.lizhou.entity.test.Department;
12 import com.lizhou.entity.test.Employee;
13
14 /**
15 * 测试类
16 * @author bojiangzhou
17 *
18 */
19
20 public class TestAction {
21
22 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
23
24 static {
25 //读取classpath中applicationContext.xml配置文件
26 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
27 //获取session中配置的sessionFactory对象
28 sessionFactory = (SessionFactory) applicationContext.getBean("sessionFactory");
29 }
30
31 @Test
32 public void testSave(){
33 //创建一个部门对象
34 Department d1 = new Department();
35 d1.setDname("研发部");
36
37 //创建两个员工对象
38 Employee e1 = new Employee();
39 e1.setEname("张三");
40 e1.setPhone("13111111111");
41 Employee e2 = new Employee();
42 e2.setEname("李四");
43 e2.setPhone("18523222222");
44
45 //设置对象关联
46 d1.getEmployeeList().add(e1);
47 d1.getEmployeeList().add(e2);
48 e1.setDepartment(d1);
49 e2.setDepartment(d1);
50
51 //获取Session
52 Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
53 //开始事务
54 Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
55 try {
56 //添加数据
57 session.save(d1);
58 session.save(e1);
59 session.save(e2);
60 //提交事务
61 t.commit();
62 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
63 //有异常则回滚事务
64 t.rollback();
65 e.printStackTrace();
66 } finally {
67 //关闭session
68 session.close();
69 }
70 }
71
72
73 }
控制台打印的语句:只有三条插入语句,没有更新语句了
1 Hibernate: insert into department (dname) values (?) 2 Hibernate: insert into employee (departmentId, ename, phone) values (?, ?, ?) 3 Hibernate: insert into employee (departmentId, ename, phone) values (?, ?, ?)
这里遇到一个问题:如果配置mappedBy属性的同时加上@JoinColumn会抛出异常,所以不能同时使用@JoinColumn和mappedBy;因为@JoinColumn本身就是自己来维护外键,和mappedBy冲突了。--->>>不知道这样理解正确否!!^_^
1 package com.lizhou.entity.test;
2
3 import java.util.ArrayList;
4 import java.util.List;
5
6 import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
7 import javax.persistence.Column;
8 import javax.persistence.Entity;
9 import javax.persistence.FetchType;
10 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
11 import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
12 import javax.persistence.Id;
13 import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
14 import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
15 import javax.persistence.Table;
16
17 import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
18
19 /**
20 * 部门:与员工一对多关系
21 * @author bojiangzhou
22 *
23 */
24 @Entity
25 @Table(name="department")
26 public class Department {
27
28 @Id
29 @GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
30 @GenericGenerator(name="_native", strategy="native")
31 private int id; //ID
32
33 @Column(length=20)
34 private String dname; //部门名称
35
36 @OneToMany(mappedBy="department")
37 @JoinColumn(name="departmentId")
38 private List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>(); //部门下的员工集合
39
40 // set/get 方法63
64 }
抛出如下异常:
1 java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError 2 at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance0(Native Method) 3 at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(Unknown Source) 4 at sun.reflect.DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(Unknown Source) 5 at java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance(Unknown Source) 6 at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.createTest(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:217) 7 at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner$1.runReflectiveCall(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:266) 8 at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12) 9 at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.methodBlock(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:263) 10 at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:78) 11 at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:57) 12 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290) 13 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71) 14 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288) 15 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58) 16 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268) 17 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363) 18 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit4.runner.JUnit4TestReference.run(JUnit4TestReference.java:86) 19 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.TestExecution.run(TestExecution.java:38) 20 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:459) 21 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:675) 22 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.run(RemoteTestRunner.java:382) 23 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.main(RemoteTestRunner.java:192) 24 Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'sessionFactory' defined in class path resource [applicationContext.xml]: Invocation of init method failed; nested exception is org.hibernate.AnnotationException: Associations marked as mappedBy must not define database mappings like @JoinTable or @JoinColumn: com.lizhou.entity.test.Department.employeeList 25 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1553) 26 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:539) 27 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:475) 28 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory$1.getObject(AbstractBeanFactory.java:302) 29 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:228) 30 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:298) 31 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:193) 32 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:684) 33 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(AbstractApplicationContext.java:760) 34 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:482) 35 at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:139) 36 at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:83) 37 at com.lizhou.action.test.TestAction.<clinit>(TestAction.java:26) 38 ... 22 more 39 Caused by: org.hibernate.AnnotationException: Associations marked as mappedBy must not define database mappings like @JoinTable or @JoinColumn: com.lizhou.entity.test.Department.employeeList 40 at org.hibernate.cfg.annotations.CollectionBinder.bind(CollectionBinder.java:493) 41 at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationBinder.processElementAnnotations(AnnotationBinder.java:2156) 42 at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationBinder.processIdPropertiesIfNotAlready(AnnotationBinder.java:963) 43 at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationBinder.bindClass(AnnotationBinder.java:796) 44 at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration$MetadataSourceQueue.processAnnotatedClassesQueue(Configuration.java:3788) 45 at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration$MetadataSourceQueue.processMetadata(Configuration.java:3742) 46 at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.secondPassCompile(Configuration.java:1410) 47 at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.buildSessionFactory(Configuration.java:1844) 48 at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.buildSessionFactory(Configuration.java:1928) 49 at org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBuilder.buildSessionFactory(LocalSessionFactoryBuilder.java:343) 50 at org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean.buildSessionFactory(LocalSessionFactoryBean.java:431) 51 at org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean.afterPropertiesSet(LocalSessionFactoryBean.java:416) 52 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.invokeInitMethods(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1612) 53 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1549) 54 ... 34 more
还有一点说明下:
如果将第57行代码移到第59行后面,即先保存员工,再保存部门,会多出四条update语句
1 package com.lizhou.action.test;
2
3 import org.hibernate.Session;
4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
5 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
6 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
7 import org.junit.Test;
8 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
9 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
10
11 import com.lizhou.entity.test.Department;
12 import com.lizhou.entity.test.Employee;
13
14 /**
15 * 测试类
16 * @author bojiangzhou
17 *
18 */
19
20 public class TestAction {
21
22 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
23
24 static {
25 //读取classpath中applicationContext.xml配置文件
26 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
27 //获取session中配置的sessionFactory对象
28 sessionFactory = (SessionFactory) applicationContext.getBean("sessionFactory");
29 }
30
31 @Test
32 public void testSave(){
33 //创建一个部门对象
34 Department d1 = new Department();
35 d1.setDname("研发部");
36
37 //创建两个员工对象
38 Employee e1 = new Employee();
39 e1.setEname("张三");
40 e1.setPhone("13111111111");
41 Employee e2 = new Employee();
42 e2.setEname("李四");
43 e2.setPhone("18523222222");
44
45 //设置对象关联
46 d1.getEmployeeList().add(e1);
47 d1.getEmployeeList().add(e2);
48 e1.setDepartment(d1);
49 e2.setDepartment(d1);
50
51 //获取Session
52 Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
53 //开始事务
54 Transaction t = session.beginTransaction();
55 try {
56 //添加数据
57 session.save(e1);
58 session.save(e2);
59 session.save(d1);
60 //提交事务
61 t.commit();
62 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
63 //有异常则回滚事务
64 t.rollback();
65 e.printStackTrace();
66 } finally {
67 //关闭session
68 session.close();
69 }
70 }
71
72
73 }
1 Hibernate: insert into employee (departmentId, ename, phone) values (?, ?, ?) 2 Hibernate: insert into employee (departmentId, ename, phone) values (?, ?, ?) 3 Hibernate: insert into department (dname) values (?) 4 Hibernate: update employee set departmentId=?, ename=?, phone=? where id=? 5 Hibernate: update employee set departmentId=?, ename=?, phone=? where id=? 6 Hibernate: update employee set departmentId=? where id=? 7 Hibernate: update employee set departmentId=? where id=?
很明显,在插入员工时,还没有部门的信息,等插入部门的时候,员工方会维护外键关系,更新外键;而部门方也会维护一次,所以多了四条语句。所以在添加数据的时候先保存一的一方,再保存多的一方。
总结:mappedBy属性跟xml配置文件里的inverse一样。在一对多或一对一的关系映射中,如果不表明mappedBy属性,默认是由本方维护外键。但如果两方都由本方来维护的话,会多出一些update语句,性能有一定的损耗。
解决的办法就是在一的一方配置上mappedBy属性,将维护权交给多的一方来维护,就不会有update语句了。
至于为何要将维护权交给多的一方,可以这样考虑:要想一个国家的领导人记住所有人民的名字是不可能的,但可以让所有人民记住领导人的名字!
注意,配了mappedBy属性后,不要再有@JoinColumn,会冲突!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号