内置函数
内置函数: input()用户交互 len ()可迭代对象的长度。 sum()求和 open()打开文件 print()打印结果 id()查看内存地址。 forzenset()冻结。 int() range()自定制一个数字范围列表。 str() dict() enumerate() dir()查看对象所有的方法 list() type()查看类型 globals()将全局所有的变量放在一个字典中。 locals()当前位置的局部变量 bool() tuple() set() next() isinstance() iter()
1.1作用域相关: ***globals()以字典的形式返回全部全局变量。 ***locals()以字典的形式返回当前位置的全部局部变量

q = 666 def wrapper(args): a = 3 print(locals()) #1{a:3,argv:2} def inner (argv1): b = 4 c = 5 print(locals()) #2{b:4 c:5,argv1:6} inner(6) wrapper(2) print(globals()) #3 a = 1 b = 2 print(locals()) print(globals())

a = 1 b = 2 print(locals()) print(globals()) # 这两个一样,因为是在全局执行的。

a = 333 b = 222 def func1(): a1 = 2 b1 = 3 # print(globals()) def func2(): c = 666 print('*****',locals()) func2() print(locals()) func1() # print(locals()) # print(globals())
1.2其他相关: 1.2.1字符串类型代码的执行eval,exec,complie ***eval 执行字符串类型的代码,并返回最终结果

s = '{"a":1,"b":3}' dic = eval(s) print(dic,type(dic))#{'a': 1, 'b': 3} print(eval('2+2')) #4 print(eval('print(666)')) # 666 None print('1 + 3') # 1+3 print(eval('1+3')) # 4 print(eval('3 * 3')) # 9 dic = eval("{'name': 'alex'}") print(dic,type(dic)) #{'name': 'alex'} <class 'dict'>
***exec:执行字符串类型的代码

print(exec('1+1')) #-7914447530519101743 ret = ''' name = input('请输入名字:').strip() if name == 'alex': print(666) ''' exec(ret) print(exec(ret)) code = ''' for i in range(1, 11): print(i) ''' exec(code) # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
compile:将字符串类型的代码编译。代码对象能够通过exec语句来执行或者eval()进行求值。
有返回值的字符串形式的代码用eval,没有返回值的字符串形式的代码用exec,一般不用compile。
1.2.2输入输出相关:input print
input:函数接受一个标准输入数据,返回为string类型。
print:打印输出

name = input('请%s输入名字:'%'alex') print(name) print(1,2,3,sep'|') print(1,2,3,sep='*') #sep设定每个元素的链接方式 print('alex') print('老男孩') print('alex',end='')#end控制的是换行 end='\n' 换行 print('老男孩')
1.2.3内存相关: **hash:获取一个对象(可哈希对象:int,str,Bool,tuple)的哈希值。 ** id:用于获取对象的内存地址。

print(hash('name')) print(hash('age')) #-3222027233094400776 print(hash(1,2,3,)) print(hash(1)) print(id('name')) #1502096
1.2.4文件操作相关: ***open:函数用于打开一个文件,创建一个file对象,相关的方法才可以调用它进行读写。

f1 = open('log',encoding='utf-8',mode='w') print('666',file=f1) # file 操作文件句柄,写入文件 f1.close() f1 = open('log', encoding='utf-8', mode='w') print('随便写的内容',file=f1) f1.close()
1.2.5模块相关: __import__:函数用于动态加载类和函数。 1.2.6帮助: *help:函数用于查看函数或模块用途的详细说明。 print(help(str))
1.2.7调用相关: **callable:函数用于检查一个对象是否是可调用的。 如果返回Ture,object仍然可能调用失败;但如果返回False,调用对象ojbect绝对不会成功。

def func1(): print(666) print(callable(func1)) ##True age = 16 print(callable('name')) #False print(callable(age)) #False
1.2.8查看内置属性: dir:函数不带参数时,返回当前范围内的变量,方法和定义的类型列表: 带参数时,返回参数的属性,方法列表。如果参数包含方法__dir__(),该方法将被调用。如果参数不包含__dir__, 该方法将最大限度的收集参数信息。 print(dir(str)) 查看内部含什么方法
1.3迭代器生成器相关: ***range:函数可创建一个整数对象,一般用在 for 循环中。 iter():函数用来生成迭代器(讲一个可迭代对象,生成迭代器)。 next():内部实际使用了__next__方法,返回迭代器的下一个项目。

print(len(range(100))) #100 l= [1,2,3,4,5] l_obj = l.__iter__() l_obj = iter(l) print(l_obj) #<list_iterator object at 0x0000000001E98208> print(l_obj.__next__()) #1 print(next(l_obj)) #2
1.4基础数据类型相关: 1.4.1数字相关(14): 数据类型(4): bool:用于将给定参数转换为布尔类型,如果没有参数,if 返回False: int:函数用于将一个字符串 或数字转换为整型。

print(int('123')) #123 print(int(1.234))# 1 print(int(1.768)) #1
float:函数用于将整数和字符串转换成浮点数。

i = 3.1415 print(i,type(i)) s = '1.234' print(int(1.234)) print(float(s))
complex:函数用于创建一个值为real+imag*j的复数或者转化一个字符串或数为复数。 如果第一个参数为字符串,则不需要指定第二个参数。 compilex(1,2) (1 + 2j) 进制转换(3): bin:将十进制转化成二进制并返回。 print(bin(100)) oct;将十进制转化成八进制字符串并返回。 print(oct(10)) hex:将十进制转化成十六进制字符串并返回。 print(hex(13)) 数学运算:(7) ***abs:函数返回数字的绝对值。 print(abs(-5)) #5 ***divmod:计算除数与被除数的结果,返回一个包含商和余数的元组(a//b , a % b) print(divmod(7,3)) #(2, 1) ***round:保留浮点数的小数位数,默认保留整数。 print(round(1.234,2))#1.23(保留两位小数) ***pow:求x**y次幂。(三个参数为x**y的结果对z取余) print(pow(2,3)) #2的三次幂 # 8 print(pow(2,3,3)) #2的三次幂对3取余数 #2 ***sum:对可迭代对象进行求和计算(可设置初始值) print(sum([1,2,3,4])) #10 print(sum([1,2,3,4],100)) #110 #(10 初始值) ***min:返回可迭代对象的最小值(可加key,key为函数名,通过函数的规则,返回最小值) print(min([1,2,3,5,7,-4])) # 4 print(min([1,2,3,4,-4],key=abs)) #-1 ***max:返回可迭代对象的最大值(可加key,key为函数名,通过函数的规则,返回最大值) print(max([1,3,5,7,-4])) #7 print(max([1,3,5,7,-9],key=abs)) #-9

l1 = [[1,3],[4,2],[5,8],[9,3]] def func(x): return x[1] print(max(l1,key=func)) l2 = [[1517991992.94, 100], [1517992000.94, 200], [1517992014.94, 300]] def func(x): return x[1] print(max(l2,key=func))

dic = {'a':1,'b':44,'c':34}
def func(x):
return dic[x]
print(dic[max(dic,key=func)])

dic = {'a':3,'b':2,'c':1}
def func(x): return dic[x]
print(max(dic,key=func))
1.4.2和数据结构相关(24): 列表和元组(2): list:将一个可迭代对象转化成列表(如果是字典,默认将key作为列表的元素)。

l1 = list({'name':'alex','age':100})
tu = (1,2,3)
print(list(1,2,3))
tuple:将一个可迭代对象转化成元组(如果是字典,默认将key作为元组的元素)。 相关内置函数(2): ***reversed:将一个序列翻转,并返回此翻转序列的迭代器。

l1 = [11,22,33,44,77,66] l_obj = reversed(11) # print(l_obj) #<list_reverseiterator object at 0x00000000021D8048> for i in l_obj: print(i) #66 77 44 33 22 11
slice:构造一个切片,用于列表的切片。

l1 = [2,3,5,7,8] l2 = [3,6,8,2,56] rule = slice(0,3) print(l1[rule]) print(l2[rule])

l1 = [11,22,33,44,77,66] print(l1[1::2]) l2 = [111,222,333,444,777,666] rule = slice(1,len(l2),2) print(l2[rule])
字符串相关(9): str:将数据转化成字符串。 format:与具体数据相关,用于计算各种小数,精算等。

print(format('test','<20'))#左对齐 print(format('test','>20'))#右对齐 print(format('test','^20'))#居中
***bytes:用于不同编码之间的转化。

bytes:str--->bytes s1 = 'alex' b1 = s1.encode('utf-8') print(b1) #b'alex' print(b2) #b'alex'
bytearry:返回一个新字节数组。这个数组里的元素是可变的,并且每个元素的值范围:0<=x<256.

ret = bytearray('alex',encoding='utf-8') print(id(ret)) print(ret) print([0]) ret[0] = 65 print(ret) print(id(ret))
memoryview:

b1 = bytes('你好',encoding='utf-8') print(b1) ret = memoryview(b1) print(len(ret)) print(ret) print(bytes(ret[:3]).decode('utf-8')) print(bytes(ret[3:]).decode('utf-8'))
ord:输入字符串找改字符编码的位置

print(ord('a')) print(ord('中')) #unicode
chr:输入位置数字找出其对应的字符

print(chr(65)) print(chr(20013)) #unicode
asscii:是ascii码中的返回该值,不是就返回/u。

print(asscii('a')) print(asscii('1')) print(asscii('中'))
***repr:返回一个对象的string形式(原形毕露)

msg = '小数%f'%(1.234) print(msg) #小数1.234000 msg = '姓名:%r'%('alex') print(msg) #姓名:'alex'
数据集合(3): dict:创建一个字典。 set:创建一个集合。 frozenset:返回一个冻结的集合,冻结后集合不能再添加或删除任何元素。 相关内置函数(8): ***len:返回一个对象中元素的个数。 ***sorted:对所有可迭代的对象进行排序操作。返回的是列表

print(sorted([1,2,3,4,5,-6])) #[-6, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(sorted([1,2,3,4,5,-6],key=abs)) #[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, -6]

l = [('a',1),('c',3),('d',4),('b',2),] print(sorted(l)) #[('a', 1), ('b', 3), ('c', 2), ('d', 4)] def func1(x): return x[1] l = [('a',1),('c',2),('d',4),('b',3),] print(sorted(l,key=func1)) #[('a', 1), ('c', 2), ('b', 3), ('d', 4)]
enumerate:枚举,返回一个枚举对象。

print(enumerate([1,2,3])) for i in enumerate([1,2,3]): print(i) for i in enumerate([1,2,3],100): print(i)
*all:可迭代对象中。全部都是Ture才是Ture
*any:可迭代对象中。有一个Ture就是Ture

print(all([1,'alex',True,(1,2,3)])) #True print(all([0,'',True,(1,2,3)])) #False print(any([0,'alex',False,(1,2,3)])) ##True print(any([0,'',False,()])) #False
***zip:拉链方法 返回的是一个迭代器
(函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。如果各个迭代器的元素个数不一致,则返回列表长度与最短的对象相同。)

l1 = [1,2,3,4] tu1 = ('老男孩','alex','wusir') l2 = ['*','**','***','****'] obj=zip(l1,tu1,l2) for i in obj: print(i) ###(1, '老男孩', '*') (2, 'alex', '**') (3, 'wusir', '***')
***map:循环模式,返回的是迭代器 可加key(key,可迭代对象)

def func2(x): return x**2 obj = map(func2,[1,2,3,4]) for i in obj: print(i) #1 4 9 16 print([i**2 for i in [1,2,3,4]]) #[1, 4, 9, 16]
提供了两个列表,对相同位置的列表数据进行相加

def func2(x,y): return x + y obj1 = map(func2,[1,2,3,4,6],(2,3,4,5)) for i in obj1: print(i) # 3 5 7 9
***filter:(过滤) 筛选模式 返回的是迭代器 可加key(key,可迭代对象)

def func(x): return x % 2 == 0 ret = filter(func,[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]) print(ret) for i in ret: print(i) # 2 4 6 print([i for i in [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] if i % 2 == 0]) # 2 4 6
匿名函数:为了解决那些功能很简单的需求而设计的一句话函数。
***lambda 匿名函数 一句话函数

#这段代码 def calc(n): return n**n print(calc(10)) #换成匿名函数 calc = lambda n:n**n print(calc(10))

def func1(x,y): return x + y ret = lambda x, y:x+y print(ret(2,3)) # 5 def func1(x, y): return x if x > y else y ret = lambda x, y: x if x > y else y print(ret(2,3)) # 3 def func(x):return x % 2 == 0 ret = filter(lambda x:x % 2 == 0, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) print(ret) for i in ret: print(i) # 2 4 6 def func1(x): return x[1] L = [('a', 1), ('c', 2), ('d', 4),('b', 3), ] print(sorted(L, key=func1)) #[('a', 1), ('c', 2), ('b', 3), ('d', 4)]
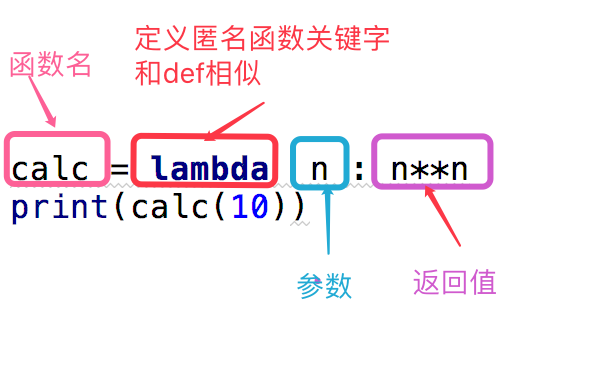
函数名 = lambda 参数 :返回值 #参数可以有多个,用逗号隔开 #匿名函数不管逻辑多复杂,只能写一行,且逻辑执行结束后的内容就是返回值 #返回值和正常的函数一样可以是任意数据类型

1,[1,2,3,4,5,6,7][1,4,9,16...]用map转化成lambda形式 ret2 = map(lambda x:x**2,[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]) for i in ret2: print(i)

2,students=[('john','A',15),('jane','B',12),('dave','B',10)] l = sorted(students,key=lambda x:x[2]) print(l)

取51的索引: l1 = [i for i in range(100) if i % 2 == 1] print(l1) count = 0 for i in l1: if i == 51: print(count) count += 1
posted on 2018-06-20 14:04 liangliang123456 阅读(149) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报


