SpringBoot
SpringBoot
原理初探
自动配置:
pom.xml
- spring-boot-starter-parent:核心依赖在父工程中!
- 我们在写或者引入一些Springboot依赖的时候,不需要指定版本,就因为这些版本仓库
启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 启动器:说白了就是springboot的启动场景;
- 比如spring-boot-starter-web,他就会帮我们自动导入web环境所有的依赖!
- springboot会将所有的功能场景都变成一个个的启动器
- 如果我们要使用什么功能,就只需要找到对应的启动器就可以了
starter
主程序
//@SpringBootApplication:标注这个类是一个springboot的应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将springboot应用启动
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
-
@SpringBootConfiguration //springboot的配置 @Configuration //spring配置类 @Component //说明这也是一个spring的组件 @EnableAutoConfiguration //自动配置 @AutoConfigurationPackage //自动配置包 @Import({Registrar.class})//自动配置“包注册” @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})//自动导入选择 //获取所有的配置 List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
获取候选的配置
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
springboot的核心文件
META-INF/spring.factories

所有的资源加载到配置类中
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);


谈谈对Springboot的理解
- 自动装配
- run方法
- 推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是web项目
- web项目会一直启动 普通项目就会退了
- 查找并加载所有可用初始化器,设置到initializers属性中
- 找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
- 推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
- 推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是web项目
SpringbootBoot配置
yml
server:
port: 8081
#对空格的要求比较高 用空格分割
#普通的key
name: summer
#对象
student:
name: summer
age: ${random.int}
#对象行内写法
student1: {name: summer,age: 18}
#数组
pet:
-cat
-dog
-pig
#数组行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
注解
//yml拿对象 配置类赋值
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")//推荐
@Value("小哥哥")
ConfigurationProperties注解报红
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</dependency>
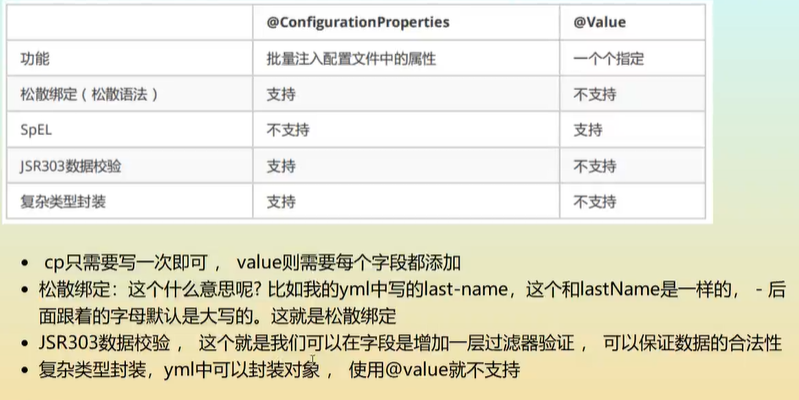
ConfigurationProperties注解支持对象赋值,松散绑定,JSR303数据校验,复杂类型封装
结论:
- 配置yml和配置properties都可以获取到值,强烈推荐yml
- 如果我们在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用一下@Value
- 如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来配合文件进行映射,就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties,不要犹豫!
JSR303数据校验
@Validated
@Email
@NotNull
@Max
@Pattern//正则
...
查看网站:https://blog.csdn.net/I_r_o_n_M_a_n/article/details/117257278
配置文件的优先级
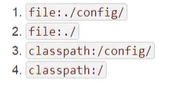
多环境配置:
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: test
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: test
自动配置原理

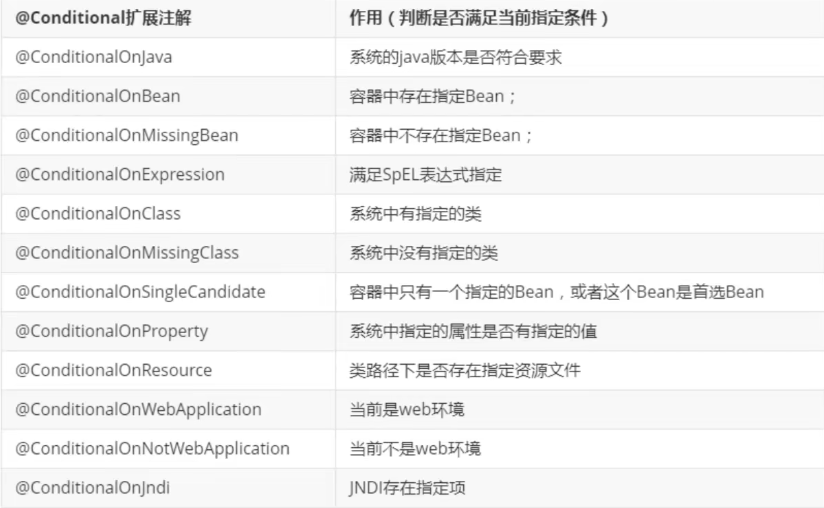
可以用过debug:true来查看,那些自动配置类生效,哪些没生效
