Python模块 - re
Python 的 re 模块(Regular Expression 正则表达式)提供各种正则表达式的匹配操作,在文本解析、复杂字符串分析和信息提取时是一个非常有用的工具,下面我主要总结了re的常用方法。
1.re的简介
使用python的re模块,尽管不能满足所有复杂的匹配情况,但足够在绝大多数情况下能够有效地实现对复杂字符串的分析并提取出相关信息。python 会将正则表达式转化为字节码,利用 C 语言的匹配引擎进行深度优先的匹配。
import re print re.__doc__
可以查询re模块的功能信息,下面会结合几个例子说明。
2.re的正则表达式语法
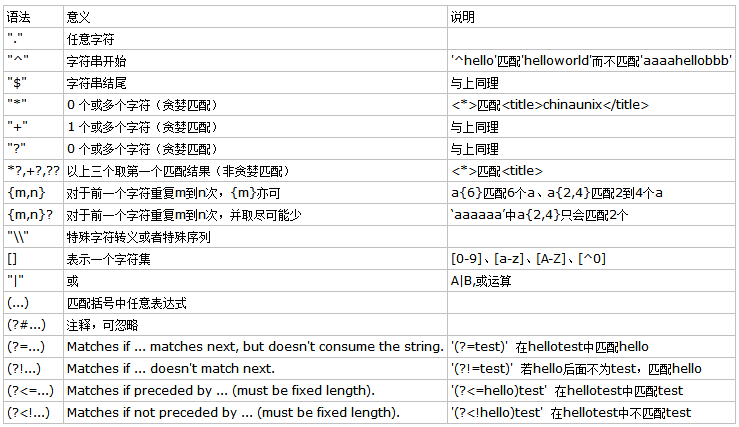
正则表达式语法表如下:
. 默认不匹配换行符
(?P<id>abc)
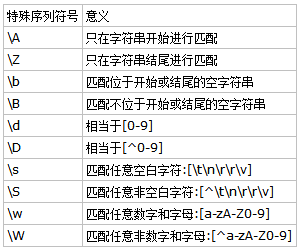
正则表达式特殊序列表如下:
3.re的主要功能函数
常用的功能函数包括:compile、search、match、split、findall(finditer)、sub(subn)
compile
re.compile(pattern[, flags])
作用:把正则表达式语法转化成正则表达式对象
print(re.fullmatch("\w+@\w+\.(com|cn|edu)", "alex@oldbodyedu.cn")) # -------------->相同 pattern = re.compile("\w+@\w+\.(com|cn|edu)") print(pattern.fullmatch("alex@oldbodyedu.cn"))
flags定义包括:
re.I:忽略大小写
re.L:表示特殊字符集 \w, \W, \b, \B, \s, \S 依赖于当前环境
re.M:多行模式,改变$,^的行为
re.S:’ . ’并且包括换行符在内的任意字符(注意:’ . ’不包括换行符)
re.U: 表示特殊字符集 \w, \W, \b, \B, \d, \D, \s, \S 依赖于 Unicode 字符属性数据库
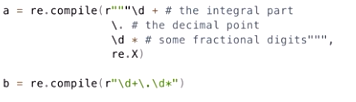
re.X :可以写注释
更多用法可以在http://www.devexception.com/sitemap_index.xml上查找
search
re.search(pattern, string[, flags])
search (string[, pos[, endpos]])
作用:在字符串中查找匹配正则表达式模式的位置,返回 MatchObject 的实例,如果没有找到匹配的位置,则返回 None。
match
re.match(pattern, string[, flags])
match(string[, pos[, endpos]])
作用:match() 函数只在字符串的开始位置尝试匹配正则表达式,也就是只报告从位置 0 开始的匹配情况
search() 函数是扫描整个字符串来查找匹配。
s = "asdqw1214" print(re.match("[0-9]", s)) # 从开始匹配,匹配一次 match_res = re.search("[0-9]", s) # 全局匹配,匹配一次 print(match_res) # <_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(5, 6), match='1'> if match_res: print(match_res.group()) # 拿到match的值 print(re.findall("[0-9]", s)) # 匹配所有
一旦match search 匹配成功返回match object对象
此对象有以下方法:
- group() # 返回匹配的字符串,可以输入组号,返回特定()匹配到的内容
- start()
- end()
- span()
- groups() # 返回正则表达式中定义的组
下面是几个例子:
例:最基本的用法,通过re.RegexObject对象调用
#!/usr/bin/env python import re r1 = re.compile(r'world') if r1.match('helloworld'): print 'match succeeds' else: print 'match fails' if r1.search('helloworld'): print 'search succeeds' else: print 'search fails'
说明一下:r是raw(原始)的意思。因为在表示字符串中有一些转义符,如表示回车'\n'。如果要表示\表需要写为'\\'。但如果我就是需要表示一个'\'+'n',不用r方式要写为:'\\n'。但使用r方式则为r'\n'这样清晰多了。
例:设置flag
#r2 = re.compile(r'n$', re.S) #r2 = re.compile('\n$', re.S) r2 = re.compile('World$', re.I) if r2.search('helloworld\n'): print 'search succeeds' else: print 'search fails'
例:直接调用
if re.search(r'abc','helloaaabcdworldn'): print 'search succeeds' else: print 'search fails'
split
re.split(pattern, string[, maxsplit=0, flags=0])
split(string[, maxsplit=0])
当我们传入3个参数的时候,系统会默认re.I是第三个参数。如果想让这里的re.I起作用,携程flags=re.I 即可
作用:可以将字符串匹配正则表达式的部分割开并返回一个列表
例:简单分析ip
#!/usr/bin/env python import re r1 = re.compile('W+') print r1.split('192.168.1.1') print re.split('(W+)','192.168.1.1') print re.split('(W+)','192.168.1.1', 1)
结果如下:
['192', '168', '1', '1'] ['192', '.', '168', '.', '1', '.', '1'] ['192', '.', '168.1.1']
findall
re.findall(pattern, string[, flags])
findall(string[, pos[, endpos]])
作用:在字符串中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并组成一个列表返回
例:查找[]包括的内容(贪婪和非贪婪查找)
*?,+?,??,{m,n}? 前面的*,+,?等都是贪婪匹配,也就是尽可能匹配,后面加?号使其变成惰性匹配
finditer
re.finditer(pattern, string[, flags])
finditer(string[, pos[, endpos]])
it = re.finditer(r"(?P<shuzi>\d+)", "你好啊, 我叫赛利亚123") print(it.__next__().group("shuzi"))
说明:和 findall 类似,在字符串中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并组成一个迭代器返回。同样 RegexObject 有:
sub
re.sub(pattern, repl, string[, count, flags])
sub(repl, string[, count=0])
说明:在字符串 string 中找到匹配正则表达式 pattern 的所有子串,用另一个字符串 repl 进行替换。如果没有找到匹配 pattern 的串,则返回未被修改的 string。Repl 既可以是字符串也可以是一个函数。
例:
#!/usr/bin/env python import re p = re.compile('(one|two|three)') print p.sub('num','one word two words three words apple', 2)
subn
re.subn(pattern, repl, string[, count, flags])
subn(repl, string[, count=0])
说明:该函数的功能和 sub() 相同,但它还返回新的字符串以及替换的次数。
fullmatch
从字符串开始匹配成功就返回re object 否则返回None
匹配电话号码:
p = re.compiler(r"\d{3}-\d{6}") print(p.findall("010-628888"))
"^1[358]\d{9}"
匹配邮箱
print(re.match('^[\w]*@(?:[A-Za-z0-9]+\.)+[A-Za-z]+', "1325@sina.cn").group())
匹配IP
print(re.search(r"(([01]?\d?\d|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])\.){3}([01]?\d?\d|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5]\.)", "192.168.1.1").group())


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号