数据结构-链表
链表一般分为两种:1)单链表 2)双链表,二者是及其相似的,但双链表有两个指针
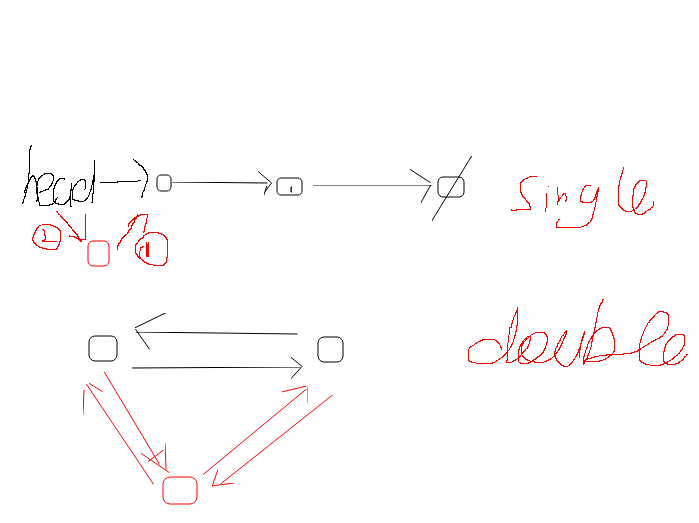
1.单链表:
//数组模拟链表(快) #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #define ll long long const int N=1e6+10; using namespace std; typedef pair<int,int>PII; //head 表示头节点的下标 //e[i] 表示结点的value //ne[i] 表示节点i的next指针是多少 //idx 存储当前的已经用到了哪个点 int head,e[N],ne[N],idx; //初始化 void init(){ head=-1; idx=0; } //将x插到头节点 void add_to_head(int x){ e[idx]=x; //3 ne[idx]=head; //1 head=idx; //2 idx++; //4 } //将x插到下标是k的点的后面 void add(int k,int x){ e[idx]=x; ne[idx]=ne[k]; ne[k]=idx; idx++; } //将下标是k的后面的点删去 void remove(int k){ ne[k]=ne[ne[k]]; } int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); return 0; }
2.双链表
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #define ll long long const int N=1e6+10; using namespace std; typedef pair<int,int>PII; int m; int e[N],l[N],r[N],idx; //初始化 void init(){ // 0表示左端点,1表示右端点 r[0]=1,l[1]=0; idx=2; } //在下标是k的点的右边,插入x void add(int k,int x){ e[idx]=x; r[idx]=r[k]; l[idx]=k; l[r[k]]=idx; r[k]=idx; } //删除第k个点 void remove(int k){ r[l[k]]=r[k]; l[r[k]]=l[k]; } int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); return 0; }
𝓐𝓬𝓱𝓲𝓮𝓿𝓮𝓶𝓮𝓷𝓽 𝓹𝓻𝓸𝓿𝓲𝓭𝓮𝓼 𝓽𝓱𝓮 𝓸𝓷𝓵𝔂 𝓻𝓮𝓪𝓵
𝓹𝓵𝓮𝓪𝓼𝓾𝓻𝓮 𝓲𝓷 𝓵𝓲𝓯𝓮

