逻辑回归---梯度下降法
前言:
线性关系主要解决一类事物的特点,而逻辑回归注重于解决分类问题,试图寻找多种事物的边界所在,因此掌握逻辑回归是十分必要的!
正文:
#老朋友
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
#做模型评估的,正确率,召回率等
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
#数据是否需要标准化,可以做也可以不做
from sklearn import preprocessing
#False代表不做,True代表做
#做标准化会使数据变得更加准确更加平滑,推荐做
scale = True
#载入数据
data = np.genfromtxt("LR-testSet.csv",delimiter = ",")
#切分数据,从第1列到最后一列但不包括最后一列
x_data = data[:,:-1]
#最后一列
y_data = data[:,-1]
#定义画图函数
def plot():
x0 = []
x1 = []
y0 = []
y1 = []
#切分不同类别的数据
#有多少数据,循环多少次
for i in range(len(x_data)):
#如果数据属于y=0这个类别
if y_data[i] == 0:
#把每行第一个数据送给x0
x0.append(x_data[i,0])
#把每行第二个数据送给y0
y0.append(x_data[i,1])
#如果这个数据属于y=1这个类别
else:
#把每行第一个数据送给x0
x1.append(x_data[i,0])
#把每行第二个数据送给y0
y1.append(x_data[i,1])
#开始画图
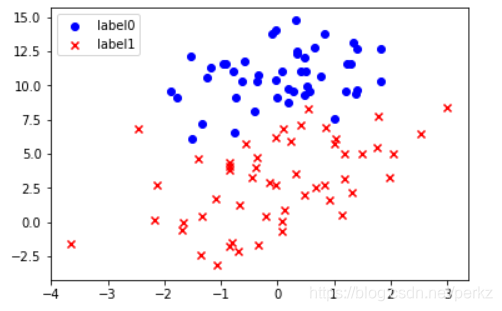
#把属于0的点画成点
scatter0 = plt.scatter(x0,y0,c = 'b',marker = 'o')
#把属于1的点画成叉
scatter1 = plt.scatter(x1,y1,c = 'r',marker = 'x')
#画图例
#handles表示你要画图例的数据,labels是图例的名称,loc=‘best’表示自动适配
plt.legend(handles=[scatter0,scatter1],labels=['label0','label1'],loc='best')
plot()
plt.show()
执行效果如下:
#数据处理,添加偏置项
x_data = data[:,:-1]
#这里注意要给y_data增加维度,让他也变成二维数据来适配函数mat
y_data = data[:,-1,np.newaxis]
print(np.mat(x_data).shape)
print(np.mat(y_data).shape)
#给样本添加偏置项
#concatenate函数可以改变axis的值来进行数据拼接
#axis的值为0时,不改变列数,将数据向下拼接
#axis的值为1时,不改变行数,将数据向右拼接
X_data = np.concatenate((np.ones((100,1)),x_data),axis=1)
print(X_data.shape)
打印出来的data格式如下:
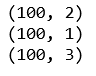
#预测函数
def sigmoid(x):
return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x))
#代价函数
def cost(xMat,yMat,ws):
#函数multiply是按位相乘
left = np.multiply(yMat,np.log(sigmoid(xMat*ws)))
right = np.multiply(1-yMat,np.log(1-sigmoid(xMat*ws)))
#返回公式
return np.sum(left + right) / -(len(xMat))
def gradAscent(xArr,yArr):
if scale == True:
xArr = preprocessing.scale(xArr)
#将数据变成矩阵形式
xMat = np.mat(xArr)
yMat = np.mat(yArr)
#定义学习率
lr = 0.001
#定义循环次数
epochs = 10000
#将代价函数的值定义在一个列表
costList = []
#计算数据的行列数
#行代表数据个数,列代表权值个数
m,n = np.shape(xMat)
#初始化权值
ws = np.mat(np.ones((n,1)))
for i in range(epochs+1):
#xMat和weights矩阵相乘
h = sigmoid(xMat*ws)
#计算误差
#给xMat的矩阵进行转置,才能进行正常的矩阵乘法
#h-yMat的格式是100*1,xMat.T的矩阵的格式是3*100
ws_grad = xMat.T*(h-yMat)/m
#更新ws的值
ws = ws-lr*ws_grad
#循环每进行50次,就将更新好的代价函数值代入
if i%50 == 0:
costList.append(cost(xMat,yMat,ws))
return ws,costList
#训练模型,得到权值和cost值的变换
#注意这里的X_data是大写字母
ws,costList = gradAscent(X_data,y_data)
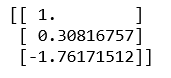
print(ws)
训练后的权值如下:
#不进行数据标准化时
if scale == False:
#画图决策边界
plot()
x_test = [[-4],[3]]
y_test = (-ws[0]-x_test*ws[1])/ws[2]
plt.plot(x_test,y_test,'k')
plt.show()
#画图 loss值的变化
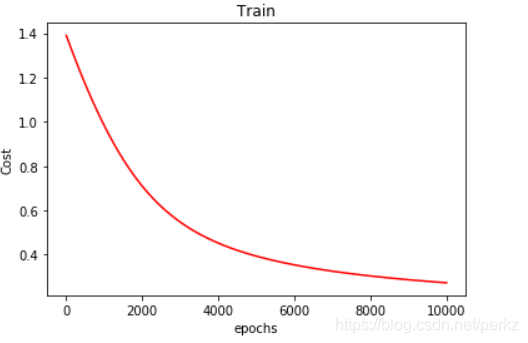
#定义图像范围
x = np.linspace(0,10000,201)
#给图像起名贴标签
plt.plot(x,costList,c = 'r')
plt.title('Train')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.show()
图片展示如下:
#预测
def predict(x_data,ws):
if scale == True:
x_data = preprocessing.scale(x_data)
xMat = np.mat(x_data)
ws = np.mat(ws)
return [1 if x>=0.5 else 0 for x in sigmoid(xMat*ws)]
predictions = predict(X_data,ws)
#classification_report计算准确率,召回率
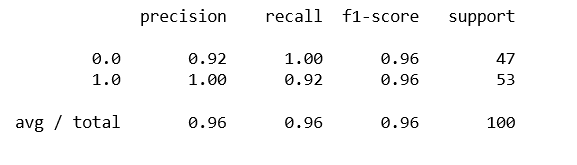
print(classification_report(y_data,predictions))
三种率运算如下:
总结:
可以看出工作量很高,检查很频繁,容易报错,尤其要求对参数格式的转化,期待sklearn库能使工作变得轻松愉悦!




