Java学习笔记-基础语法Ⅵ-异常
异常
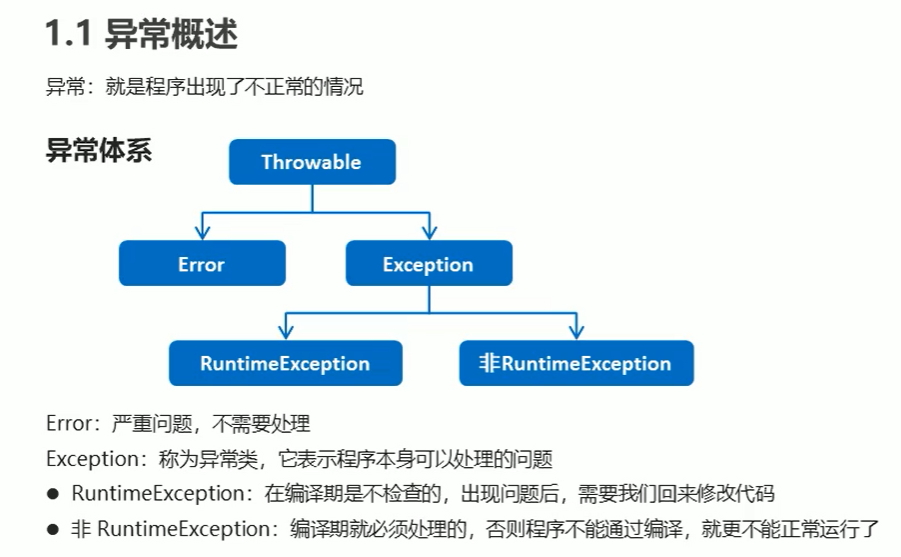

对于异常,JVM默认处理方案为:把异常名称、异常原因以及异常出现的位置等信息输出在控制台,并且程序停止执行
异常处理方式一:try ... catch
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
show();
System.out.println("结束");
}
public static void show(){
int [] arr = {1,2,3};
try {
System.out.println(arr[2]);
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println(arr[3]);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Throwable三个主要成员方法:printStackTrace、getMessage、toString
编译时异常表示有可能出现异常,需要处理
异常处理方式二:throws
throws抛出异常给上级,实际上并没有解决异常,等到上级调用时再使用try catch或者继续抛出
也可以自定义异常(个人感觉不是很常用,因为有需要的话,写个if语句就可以)
// 先定义一个异常,这个异常继承Exception
public class ScoreException extends Exception{
public ScoreException(){}
public ScoreException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
// 再写一个类,这个类中的方法语句可以抛出异常对象,方法名抛出异常类
public class Teacher {
public void checkScore(int score) throws ScoreException {
if(score<0||score>100){
throw new ScoreException("分数有误");
}else{
System.out.println("分数正常");
}
}
}
// 测试类
public class TeacherDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入分数");
int score = sc.nextInt();
Teacher t = new Teacher();
try {
t.checkScore(score);
} catch (ScoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这里测试类中采用的是try catch方法,如果在main中throws也是可以的,那这样相当于抛给了main这个静态方法去解决





