第四届“网鼎杯”网络安全大赛 - 青龙组
Crypto
CRYPTO01
2023 年江苏省领航杯 bd 原题:
题目:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from secret import flag
p = getPrime(512)
q = getPrime(512)
n = p * q
d = getPrime(299)
e = inverse(d,(p-1)*(q-1))
m = bytes_to_long(flag)
c = pow(m,e,n)
hint1 = p >> (512-70)
hint2 = q >> (512-70)
print(f"n = {n}")
print(f"e = {e}")
print(f"c = {c}")
print(f"hint1 = {hint1}")
print(f"hint2 = {hint2}")
n = 95987463597889741532025162535631829592517704738860431905943824498597890101136796870879646153634795544527837591685182170270252555997933421564167468816667980089869165228796395618775798781717091178143300536302805947806332962230499807469654672313206953750808878098101882367253566423367338396717229488061237787619
e = 12761568528114005244342182138319275328501544878744699681091257281459893043102455333575012392492554249378138377894473691530001400901111860569849400611145049669197371290112261284014768486937294128410391332641648640840309135718123516725634190495261570498188176102281061084366456374907755950527213961595506707585
c = 35154471719082941146017277238175991504655570882040897713927696748547265178059291385527810510087300325678561502592029686486144851647754163110759942860051150957340793828236482243293747881251009434747066136505663782280758979333019882382608002308773317613847702048959887017010151916544703971113441862351668075919
hint1 = 1175980694459189065778
hint2 = 632846170973644915854
思路:
利用上高位的boneh_durfee攻击
参考论文:
[367.pdf (iacr.org)](https://eprint.iacr.org/2023/367.pdf)
exp:
先恢复 d
import time
time.clock = time.time
debug = True
strict = False
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # 如果晶格达到该尺寸,则停止移除
# 显示有用矢量的统计数据
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii,ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
# 显示带有 0 和 X 的矩阵
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii,jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
#print (a)
# 尝试删除无用的向量
# 从当前 = n-1(最后一个向量)开始
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# 我们从当前 = n-1(最后一个向量)开始
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# 开始从后面检查
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# 如果它没有用
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# 让我们检查它是否影响其他向量
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# 如果另一个向量受到影响:
# 我们增加计数
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# 等级:0
# 如果没有其他载体最终受到影响
# 我们删除它
if affected_vectors == 0:
#print ("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# 等级:1
#如果只有一个受到影响,我们会检查
# 如果它正在影响别的向量
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# 如果它影响哪怕一个向量
# 我们放弃这个
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# 如果没有其他向量受到影响,则将其删除,并且
# 这个有用的向量不够有用
#与我们无用的相比
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(bound - BB[ii, ii]):
#print ("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 如果 "strict=true",并且行列式不受约束
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
在以下情况下找到解决方案:
* d < N^delta
* |x|< e^delta
* |y|< e^0.5
每当 delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.<u, x, y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ) #多项式环
Q = PR.quotient(x*y + 1 - u) # u = xy + 1
polZ = Q(pol).lift()
UU = XX*YY + 1
# x-移位
gg = []
for kk in range(mm + 1):
for ii in range(mm - kk + 1):
xshift = x^ii * modulus^(mm - kk) * polZ(u, x, y)^kk
gg.append(xshift)
gg.sort()
# 单项式 x 移位列表
monomials = []
for polynomial in gg:
for monomial in polynomial.monomials(): #对于多项式中的单项式。单项式():
if monomial not in monomials: # 如果单项不在单项中
monomials.append(monomial)
monomials.sort()
# y-移位
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
yshift = y^jj * polZ(u, x, y)^kk * modulus^(mm - kk)
yshift = Q(yshift).lift()
gg.append(yshift) # substitution
# 单项式 y 移位列表
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
monomials.append(u^kk * y^jj)
# 构造格 B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0, 0)
for jj in range(1, ii + 1):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
#约化格的原型
if helpful_only:
# #自动删除
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus^mm, nn-1)
# 重置维度
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print ("failure")
return 0,0
# 检查向量是否有帮助
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus^mm)
# 检查行列式是否正确界定
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus^(mm*nn)
if det >= bound:
print ("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
print ("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
print ("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print ("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus^mm)
# LLL
if debug:
print ("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
#BB = BB.BKZ(block_size=25)
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print ("LLL is done!")
# 替换向量 i 和 j ->多项式 1 和 2
if debug:
print ("在格中寻找线性无关向量")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# 对于i and j, 构造两个多项式
PR.<w,z> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
pol2 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# 结果
PR.<q> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
print ("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
print ("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
print ("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
return solx, soly
def example():
############################################
# 随机生成数据
##########################################
#start_time =time.perf_counter
start =time.clock()
size=512
length_N = 2*size;
ss=0
s=70;
M=1 # the number of experiments
delta = 299/1024
# p = random_prime(2^512,2^511)
for i in range(M):
# p = random_prime(2^size,None,2^(size-1))
# q = random_prime(2^size,None,2^(size-1))
# if(p<q):
# temp=p
# p=q
# q=temp
N = 95987463597889741532025162535631829592517704738860431905943824498597890101136796870879646153634795544527837591685182170270252555997933421564167468816667980089869165228796395618775798781717091178143300536302805947806332962230499807469654672313206953750808878098101882367253566423367338396717229488061237787619
e = 12761568528114005244342182138319275328501544878744699681091257281459893043102455333575012392492554249378138377894473691530001400901111860569849400611145049669197371290112261284014768486937294128410391332641648640840309135718123516725634190495261570498188176102281061084366456374907755950527213961595506707585
c = 35154471719082941146017277238175991504655570882040897713927696748547265178059291385527810510087300325678561502592029686486144851647754163110759942860051150957340793828236482243293747881251009434747066136505663782280758979333019882382608002308773317613847702048959887017010151916544703971113441862351668075919
hint1 = 1175980694459189065778
hint2 = 632846170973644915854
# print ("p真实高",s,"比特:", int(p/2^(512-s)))
# print ("q真实高",s,"比特:", int(q/2^(512-s)))
# N = p*q;
# 解密指数d的指数( 最大0.292)
m = 7 # 格大小(越大越好/越慢)
t = round(((1-2*delta) * m)) # 来自 Herrmann 和 May 的优化
X = floor(N^delta) #
Y = floor(N^(1/2)/2^s) # 如果 p、 q 大小相同,则正确
for l in range(int(hint1),int(hint1)+1):
print('\n\n\n l=',l)
pM=l;
p0=pM*2^(size-s)+2^(size-s)-1;
q0=N/p0;
qM=int(q0/2^(size-s))
A = N + 1-pM*2^(size-s)-qM*2^(size-s);
#A = N+1
P.<x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol = 1 + x * (A + y) #构建的方程
# Checking bounds
#if debug:
#print ("=== 核对数据 ===")
#print ("* delta:", delta)
#print ("* delta < 0.292", delta < 0.292)
#print ("* size of e:", ceil(log(e)/log(2))) # e的bit数
# print ("* size of N:", len(bin(N))) # N的bit数
#print ("* size of N:", ceil(log(N)/log(2))) # N的bit数
#print ("* m:", m, ", t:", t)
# boneh_durfee
if debug:
##print ("=== running algorithm ===")
start_time = time.time()
solx, soly = boneh_durfee(pol, e, m, t, X, Y)
if solx > 0:
#print ("=== solution found ===")
if False:
print ("x:", solx)
print ("y:", soly)
d_sol = int(pol(solx, soly) / e)
ss=ss+1
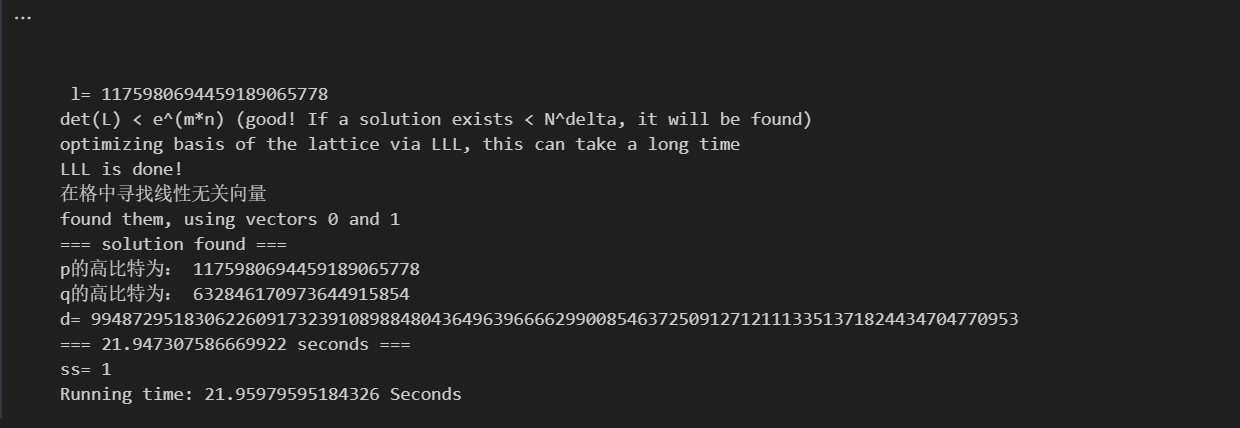
print ("=== solution found ===")
print ("p的高比特为:",l)
print ("q的高比特为:",qM)
print ("d=",d_sol)
if debug:
print("=== %s seconds ===" % (time.time() - start_time))
#break
print("ss=",ss)
#end=time.process_time
end=time.clock()
print('Running time: %s Seconds'%(end-start))
if __name__ == "__main__":
example()
然后再正常解 rsa
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import gmpy2
n = 95987463597889741532025162535631829592517704738860431905943824498597890101136796870879646153634795544527837591685182170270252555997933421564167468816667980089869165228796395618775798781717091178143300536302805947806332962230499807469654672313206953750808878098101882367253566423367338396717229488061237787619
e = 12761568528114005244342182138319275328501544878744699681091257281459893043102455333575012392492554249378138377894473691530001400901111860569849400611145049669197371290112261284014768486937294128410391332641648640840309135718123516725634190495261570498188176102281061084366456374907755950527213961595506707585
c = 35154471719082941146017277238175991504655570882040897713927696748547265178059291385527810510087300325678561502592029686486144851647754163110759942860051150957340793828236482243293747881251009434747066136505663782280758979333019882382608002308773317613847702048959887017010151916544703971113441862351668075919
hint1 = 1175980694459189065778
hint2 = 632846170973644915854
d = 994872951830622609173239108988480436496396666299008546372509127121113351371824434704770953
m = pow(c,d,n)
print(long_to_bytes(m))
flag: wdflag{a14a7fa0-4e7b-4624-ad0c-36c31dd8012e}
CRYPTO02
题目:
# coding: utf-8
#!/usr/bin/env python2
import gmpy2
import random
import binascii
from hashlib import sha256
from sympy import nextprime
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
from FLAG import flag
#flag = 'wdflag{123}'
def victory_encrypt(plaintext, key):
key = key.upper()
key_length = len(key)
plaintext = plaintext.upper()
ciphertext = ''
for i, char in enumerate(plaintext):
if char.isalpha():
shift = ord(key[i % key_length]) - ord('A')
encrypted_char = chr((ord(char) - ord('A') + shift) % 26 + ord('A'))
ciphertext += encrypted_char
else:
ciphertext += char
return ciphertext
victory_key = "WANGDINGCUP"
victory_encrypted_flag = victory_encrypt(flag, victory_key)
p = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffefffffc2f
a = 0
b = 7
xG = 0x79be667ef9dcbbac55a06295ce870b07029bfcdb2dce28d959f2815b16f81798
yG = 0x483ada7726a3c4655da4fbfc0e1108a8fd17b448a68554199c47d08ffb10d4b8
G = (xG, yG)
n = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141
h = 1
zero = (0,0)
dA = nextprime(random.randint(0, n))
if dA > n:
print("warning!!")
def addition(t1, t2):
if t1 == zero:
return t2
if t2 == zero:
return t2
(m1, n1) = t1
(m2, n2) = t2
if m1 == m2:
if n1 == 0 or n1 != n2:
return zero
else:
k = (3 * m1 * m1 + a) % p * gmpy2.invert(2 * n1 , p) % p
else:
k = (n2 - n1 + p) % p * gmpy2.invert((m2 - m1 + p) % p, p) % p
m3 = (k * k % p - m1 - m2 + p * 2) % p
n3 = (k * (m1 - m3) % p - n1 + p) % p
return (int(m3),int(n3))
def multiplication(x, k):
ans = zero
t = 1
while(t <= k):
if (k &t )>0:
ans = addition(ans, x)
x = addition(x, x)
t <<= 1
return ans
def getrs(z, k):
(xp, yp) = P
r = xp
s = (z + r * dA % n) % n * gmpy2.invert(k, n) % n
return r,s
z1 = random.randint(0, p)
z2 = random.randint(0, p)
k = random.randint(0, n)
P = multiplication(G, k)
hA = multiplication(G, dA)
r1, s1 = getrs(z1, k)
r2, s2 = getrs(z2, k)
print("r1 = {}".format(r1))
print("r2 = {}".format(r2))
print("s1 = {}".format(s1))
print("s2 = {}".format(s2))
print("z1 = {}".format(z1))
print("z2 = {}".format(z2))
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(dA)).digest()
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC)
iv = cipher.iv
encrypted_flag = cipher.encrypt(pad(victory_encrypted_flag.encode(), AES.block_size))
encrypted_flag_hex = binascii.hexlify(iv + encrypted_flag).decode('utf-8')
print("Encrypted flag (AES in CBC mode, hex):", encrypted_flag_hex)
# output
# r1 = 11455446275324978121918764201975007376236576456980676251003353868423934779741
# r2 = 11455446275324978121918764201975007376236576456980676251003353868423934779741
# s1 = 40939314972385973234538799073526528418921185412931089406906904671430814294251
# s2 = 20521265832237322311837491925934175279870547563516618597235100170259508682349
# z1 = 86373733089658748931377346977504497606857910789811212034370600969224209571891
# z2 = 114906325375159287808320541183977807561041047925384600130919891200501605749979
# ('Encrypted flag (AES in CBC mode, hex):', u'57608ba208813e738e7a354399e77272017548f9abf0da7a179a1136cda57579720b68a3ed46d85f5997c35af18f42175f43e856a0f64d964e7ab1e8a672b689')
思路:
**直接拷问 ai**

先求出,dA
k = ((z1 - z2) * inverse(s1 - s2, n)) % n
# print(k)
dA = ((s1 * k - z1) * inverse(r1, n)) % n
# print(dA)
接下来,我们使用 AES 密钥和 CBC 模式解密 encrypted_flag:
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import unpad
import binascii
# 解密 AES 加密的 flag
encrypted_flag_hex = '57608ba208813e738e7a354399e77272017548f9abf0da7a179a1136cda57579720b68a3ed46d85f5997c35af18f42175f43e856a0f64d964e7ab1e8a672b689'
iv_and_encrypted_flag = binascii.unhexlify(encrypted_flag_hex)
iv = iv_and_encrypted_flag[:16]
encrypted_flag = iv_and_encrypted_flag[16:]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
decrypted_flag = unpad(cipher.decrypt(encrypted_flag), AES.block_size)
最后一步是解密胜利密码。由于胜利密码是一个简单的多表替换密码,我们只需要反转加密过程即可解密:
def victory_decrypt(ciphertext, key):
key = key.upper()
key_length = len(key)
plaintext = ''
for i, char in enumerate(ciphertext):
if char.isalpha():
shift = ord(key[i % key_length]) - ord('A')
decrypted_char = chr((ord(char) - ord('A') - shift) % 26 + ord('A'))
plaintext += decrypted_char
else:
plaintext += char
return plaintext
# 解密胜利密码
victory_key = "WANGDINGCUP"
decrypted_flag = victory_decrypt(decrypted_flag.decode(), victory_key)
print("Decrypted flag:", decrypted_flag)
完整exp:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import gmpy2
from hashlib import sha256
p = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffefffffc2f
a = 0
b = 7
xG = 0x79be667ef9dcbbac55a06295ce870b07029bfcdb2dce28d959f2815b16f81798
yG = 0x483ada7726a3c4655da4fbfc0e1108a8fd17b448a68554199c47d08ffb10d4b8
G = (xG, yG)
n = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141
h = 1
zero = (0,0)
r1 = 11455446275324978121918764201975007376236576456980676251003353868423934779741
r2 = 11455446275324978121918764201975007376236576456980676251003353868423934779741
s1 = 40939314972385973234538799073526528418921185412931089406906904671430814294251
s2 = 20521265832237322311837491925934175279870547563516618597235100170259508682349
z1 = 86373733089658748931377346977504497606857910789811212034370600969224209571891
z2 = 114906325375159287808320541183977807561041047925384600130919891200501605749979
c = '57608ba208813e738e7a354399e77272017548f9abf0da7a179a1136cda57579720b68a3ed46d85f5997c35af18f42175f43e856a0f64d964e7ab1e8a672b689'
k = ((z1 - z2) * inverse(s1 - s2, n)) % n
# print(k)
dA = ((s1 * k - z1) * inverse(r1, n)) % n
# print(dA)
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(dA)).digest()
print(key)
# 解密aes
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import unpad
import binascii
# 解密 AES 加密的 flag
encrypted_flag_hex = '57608ba208813e738e7a354399e77272017548f9abf0da7a179a1136cda57579720b68a3ed46d85f5997c35af18f42175f43e856a0f64d964e7ab1e8a672b689'
iv_and_encrypted_flag = binascii.unhexlify(encrypted_flag_hex)
iv = iv_and_encrypted_flag[:16]
encrypted_flag = iv_and_encrypted_flag[16:]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
decrypted_flag = unpad(cipher.decrypt(encrypted_flag), AES.block_size)
def victory_decrypt(ciphertext, key):
key = key.upper()
key_length = len(key)
plaintext = ''
for i, char in enumerate(ciphertext):
if char.isalpha():
shift = ord(key[i % key_length]) - ord('A')
decrypted_char = chr((ord(char) - ord('A') - shift) % 26 + ord('A'))
plaintext += decrypted_char
else:
plaintext += char
return plaintext
# 解密胜利密码
victory_key = "WANGDINGCUP"
decrypted_flag = victory_decrypt(decrypted_flag.decode(), victory_key)
# 转小写
print("Decrypted flag:", decrypted_flag.lower())
flag: wdflag{8ed62e3b409bb214e6fdb0a78f63569c}
Misc
MISC01
描述:
某单位网络遭到非法的攻击,安全人员对流量调查取证之后保存了关键证据,发现人员的定位信息存在泄露,请对其进行分析。flag为用户位置信息进行32位md5哈希值
提交的flag格式:wdflag
学习:Diameter协议摘要 - StevensFollower - 博客园
思路:
分析流量包发现是一个 diameter 协议分析,先过滤一下 diameter,
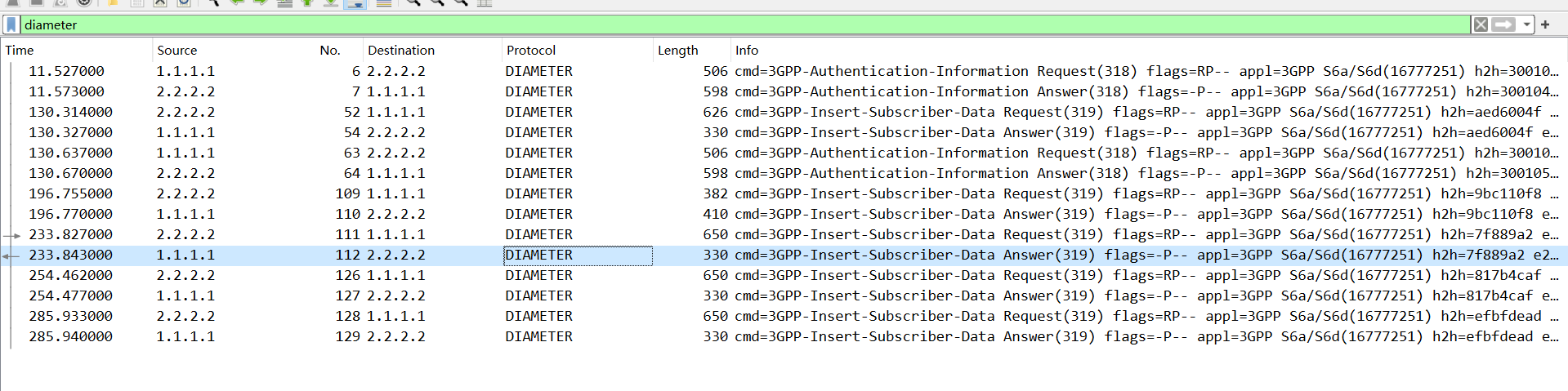
然后往下看 AVP 其中有条消息表示的是地理位置,
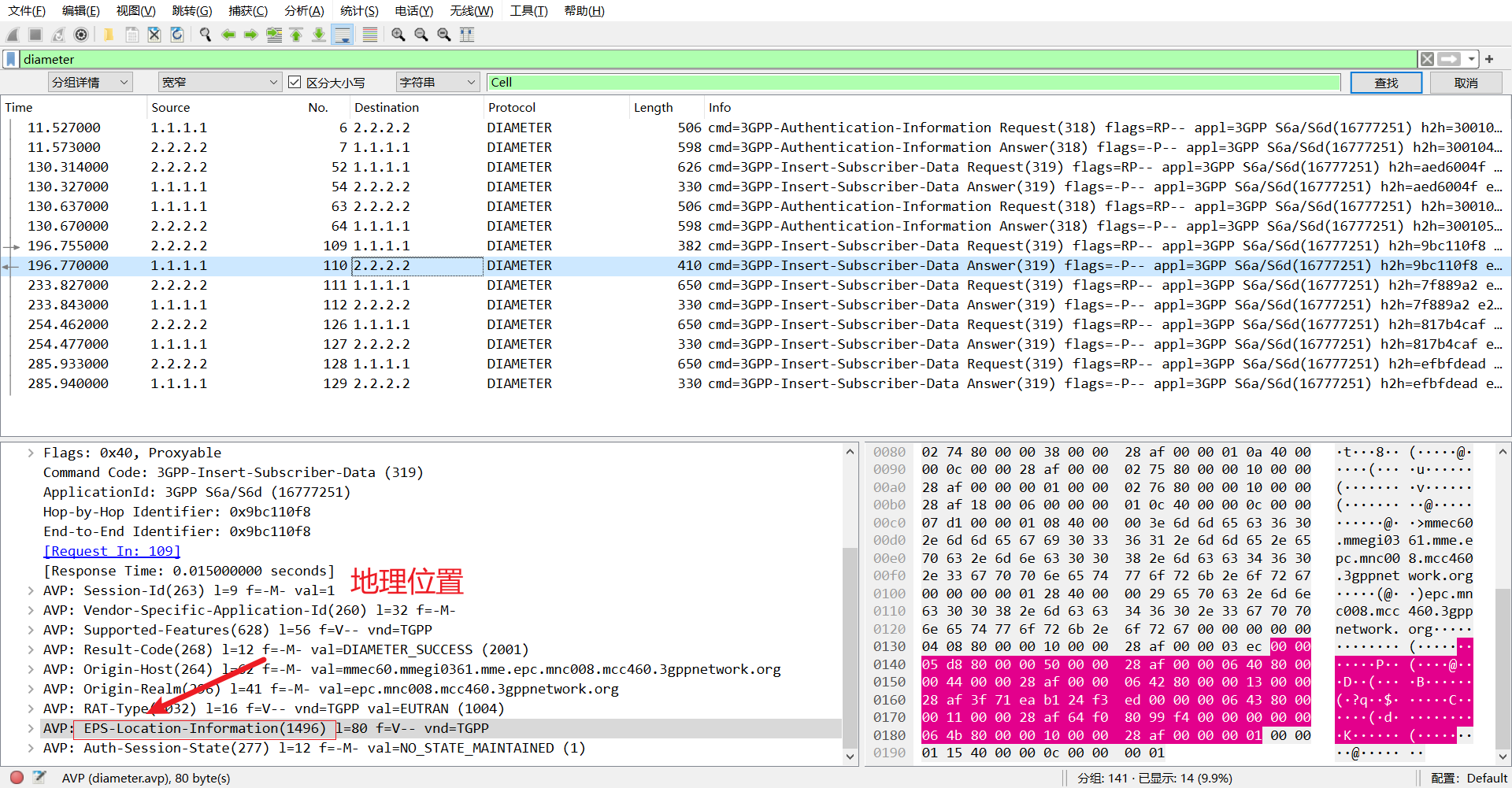
可以发现 E-UTRAN-Cell-Global-Identit 就是的 val,就表示泄露的信息,可以复制出来丢给 chat 分析一下
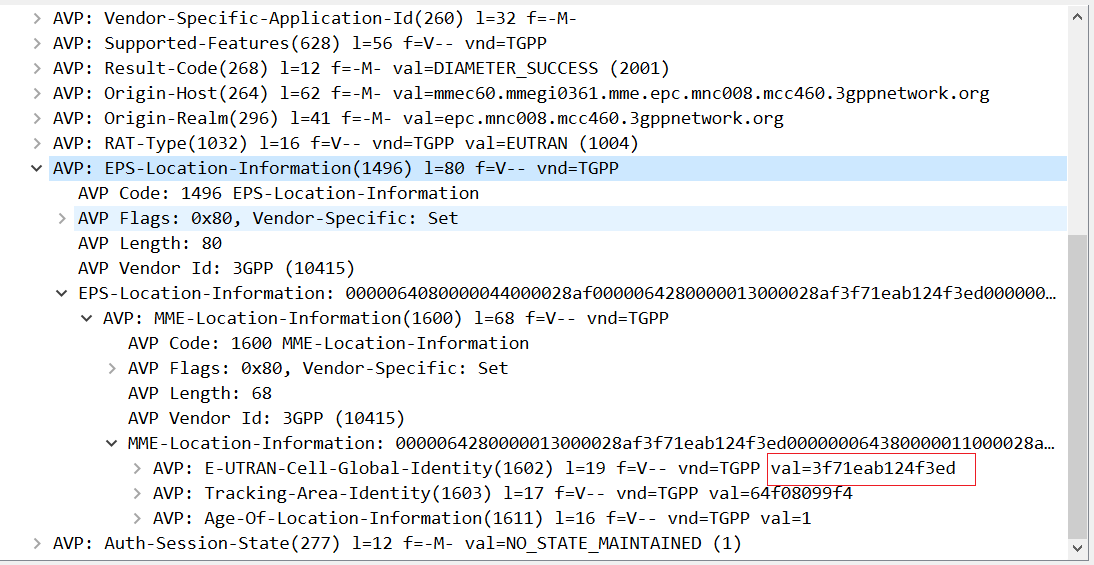

最后 md5 加密一下就行
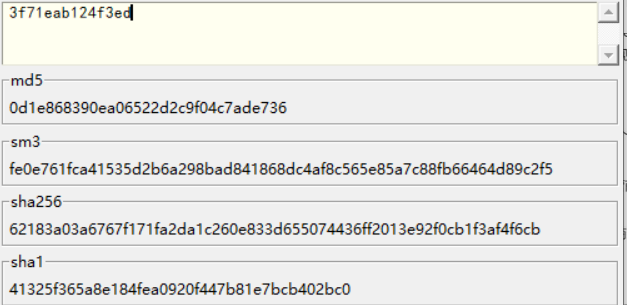
flag: wdflag{0d1e868390ea06522d2c9f04c7ade736}
MISC03
题目:
近日某公司服务器遭到恶意攻击,随后公司立即对流量监测系统中遭受攻击时段的流量进行了取证,但是公司某一网络安全实习生进行分析溯源后并未找到攻击者的攻击IP,于是公司决定将这个任务重新交给更具经验的你来进行,接手工作后,你立即对其进行了深入调查!
提交的flag格式:wdflag
分析流量包,过滤 http 流,查看 200 的返回包,可以发现,这里 hacker.php 恶意操作了
ip 为 39.168.5.60
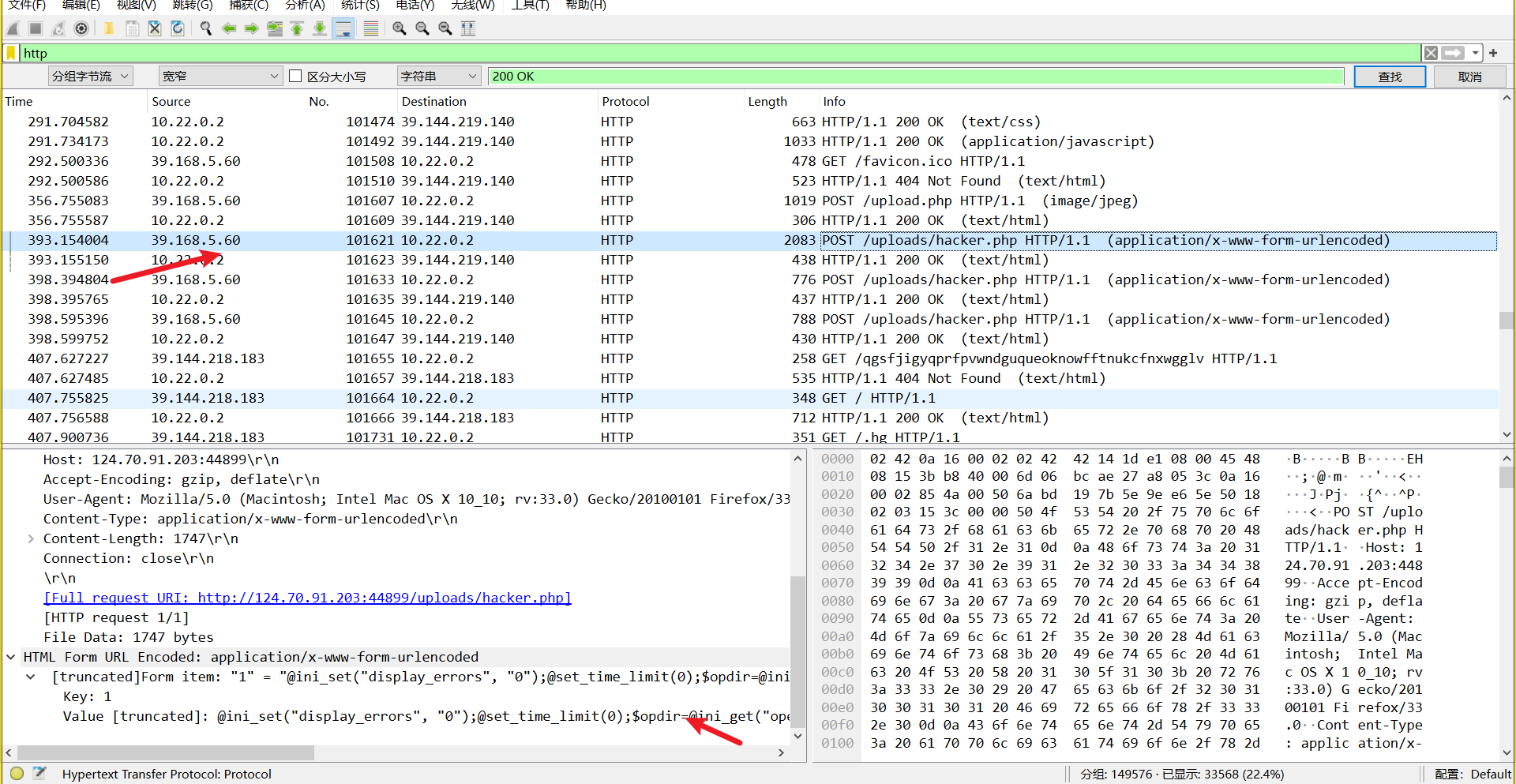
flag: wdflag{39.168.5.60}
MISC04
IrisCTF-2024-Challenges/peanoscramble at main · IrisSec/IrisCTF-2024-Challenges
(皮亚诺)曲线 【分形几何】05.Peano(皮亚诺)曲线 - 知乎
推测应该是按着曲线的轨迹将像素还原到原来的位置,编写脚本
exp:
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
def peano(n):
if n == 0:
return [[0,0]]
else:
in_lst = peano(n - 1)
lst = in_lst.copy()
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + 1 + i[0], py - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py - 1 - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py - 1 - i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + 1 + i[0], py + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px - i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
px,py = lst[-1]
lst.extend([px + i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst)
return lst
order = peano(6)
img = Image.open('1.png')
width, height = img.size
block_width = width # // 3
block_height = height # // 3
new_image = Image.new("RGB", (width, height))
for i, (x, y) in tqdm(enumerate(order)):
# 根据列表顺序获取新的坐标
new_x, new_y = i % width, i // width
# 获取原图像素
pixel = img.getpixel((x, height - 1 - y))
# 在新图像中放置像素
new_image.putpixel((new_x, new_y), pixel)
new_image.save("rearranged_image.jpg")
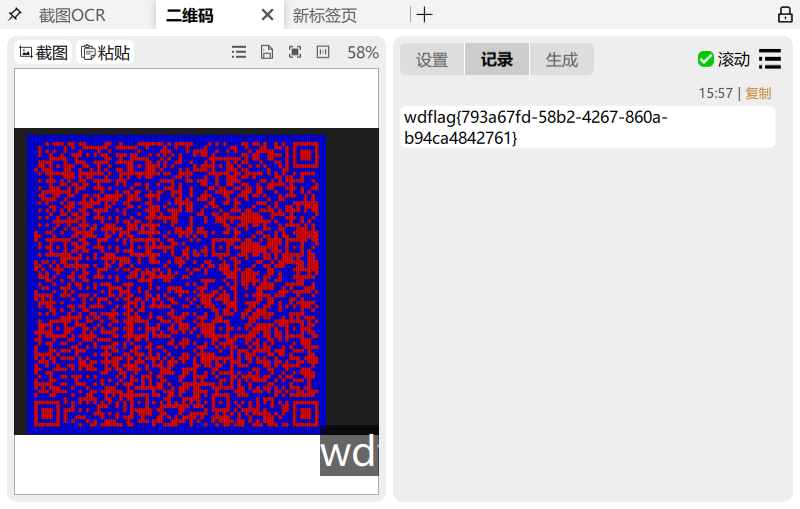
flag: wdflag{793a67fd-58b2-4267-860a-b94ca4842761}
Reverse
REVERSE01
一个安卓逆向题,分析一下主程序
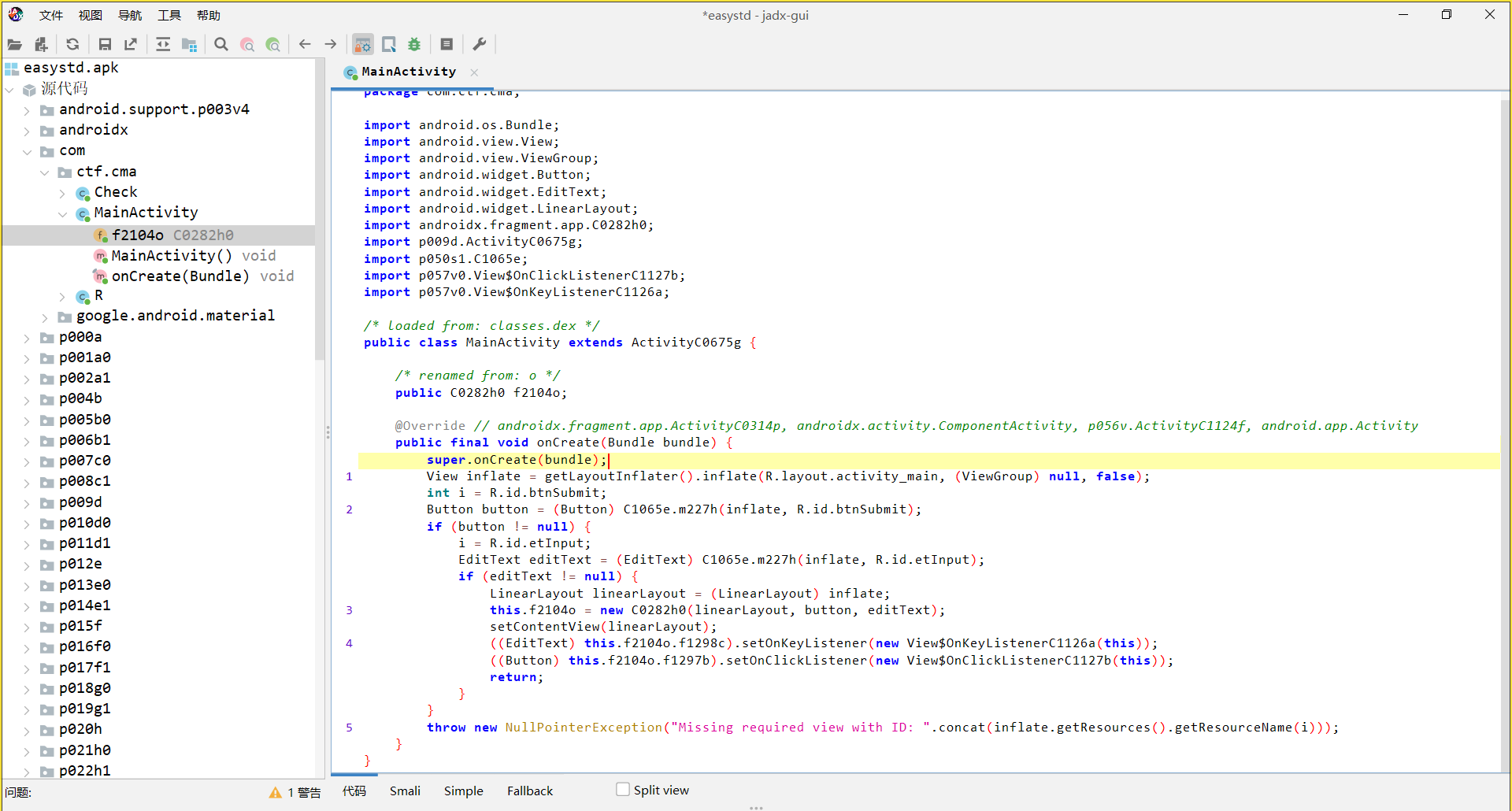
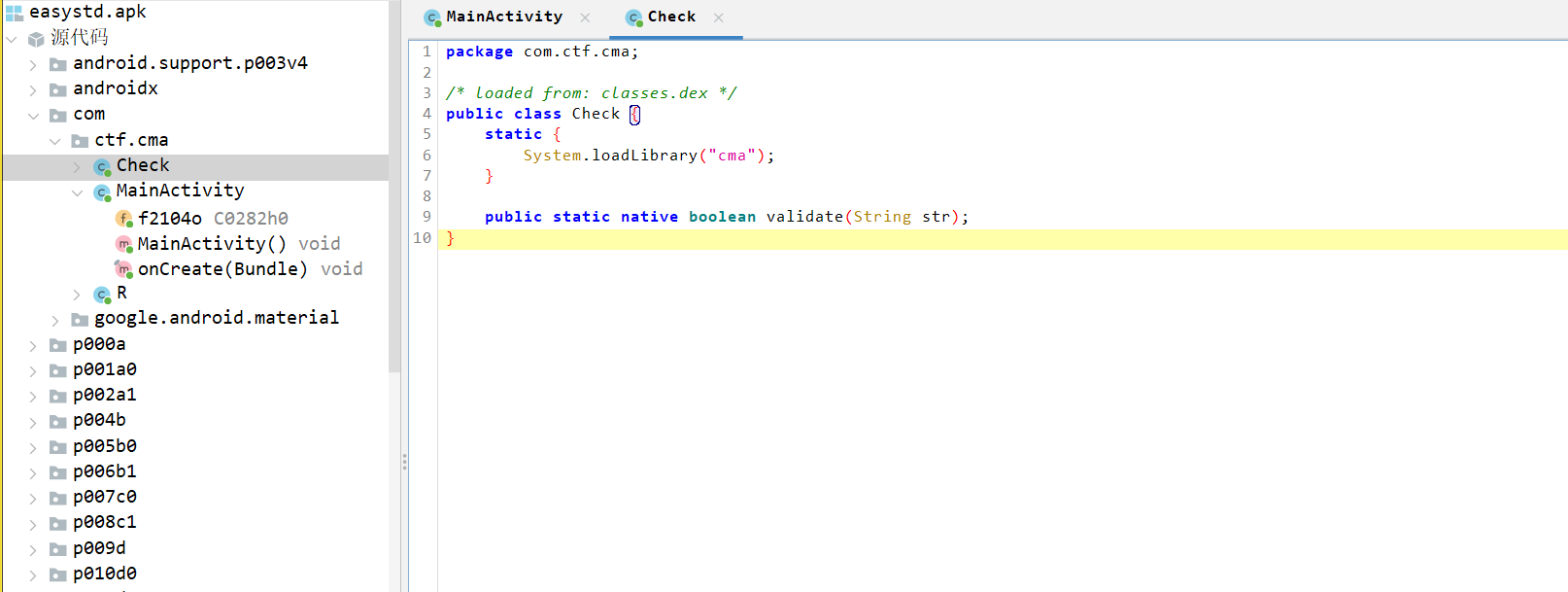
加载了一个 so 文件
逆向一下 so 程序
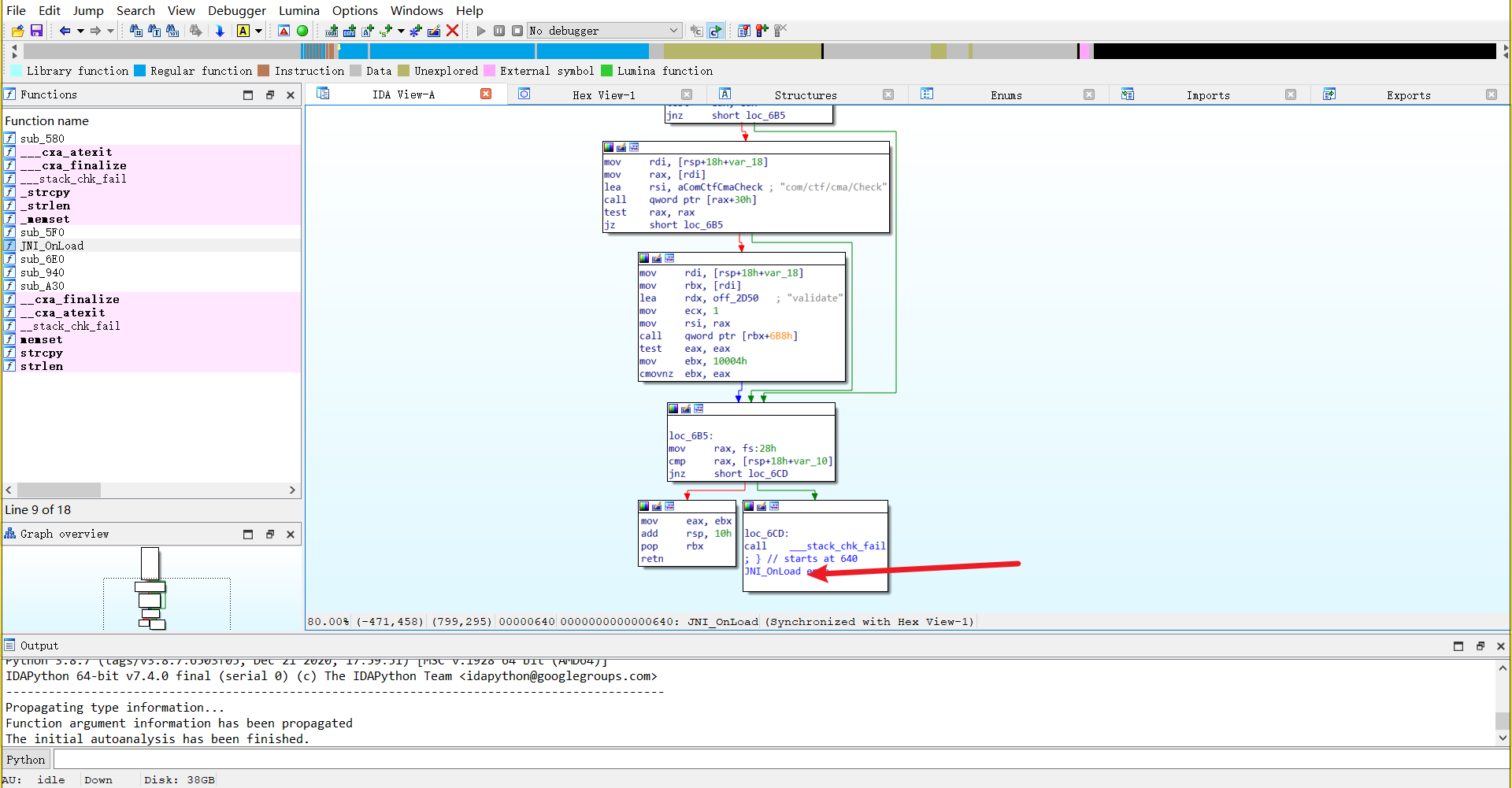
在 sub_940 发现 sm4 加密,key 是 16 字节
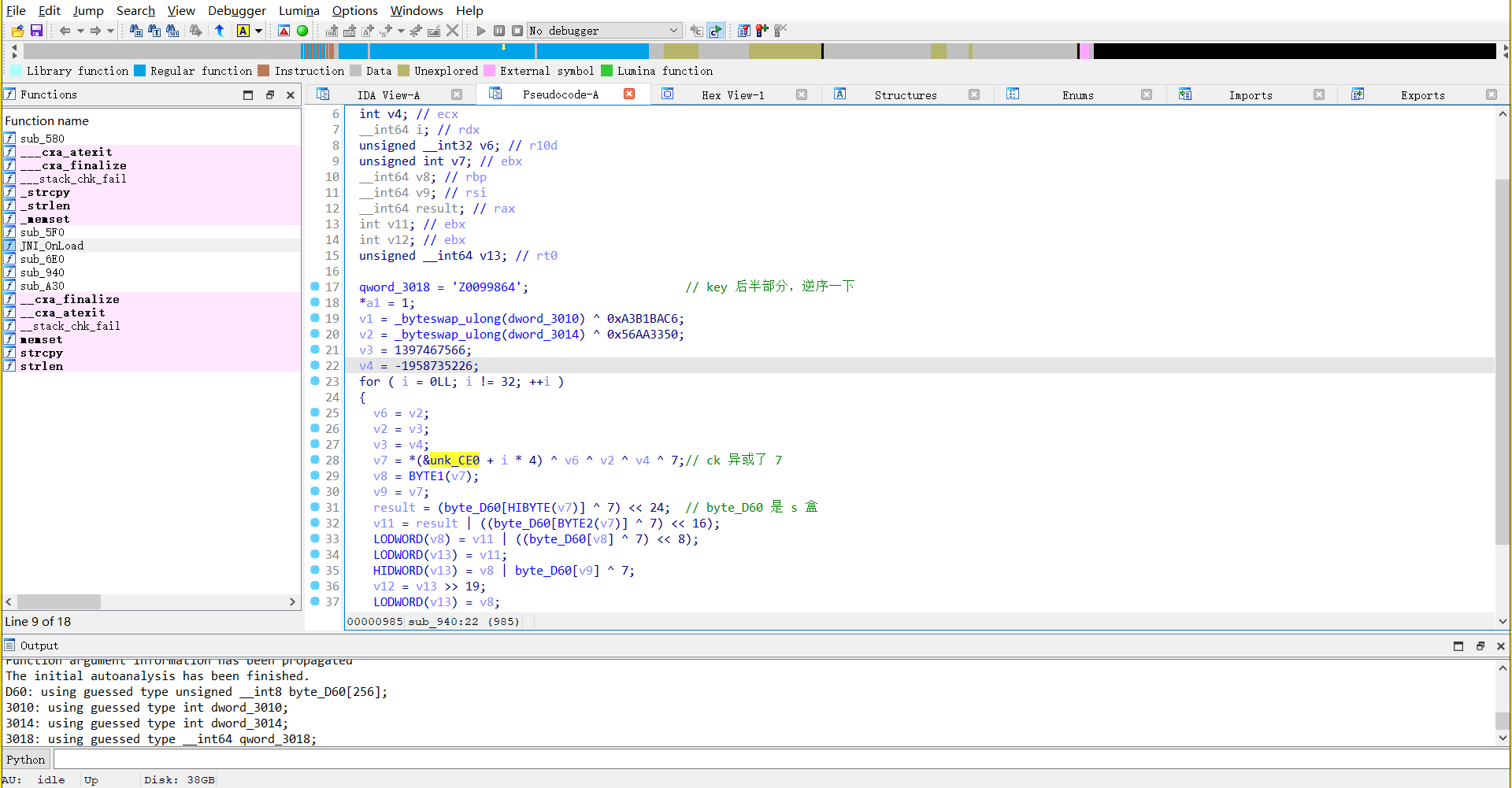
key 的后一半
key:A11223574689900Z
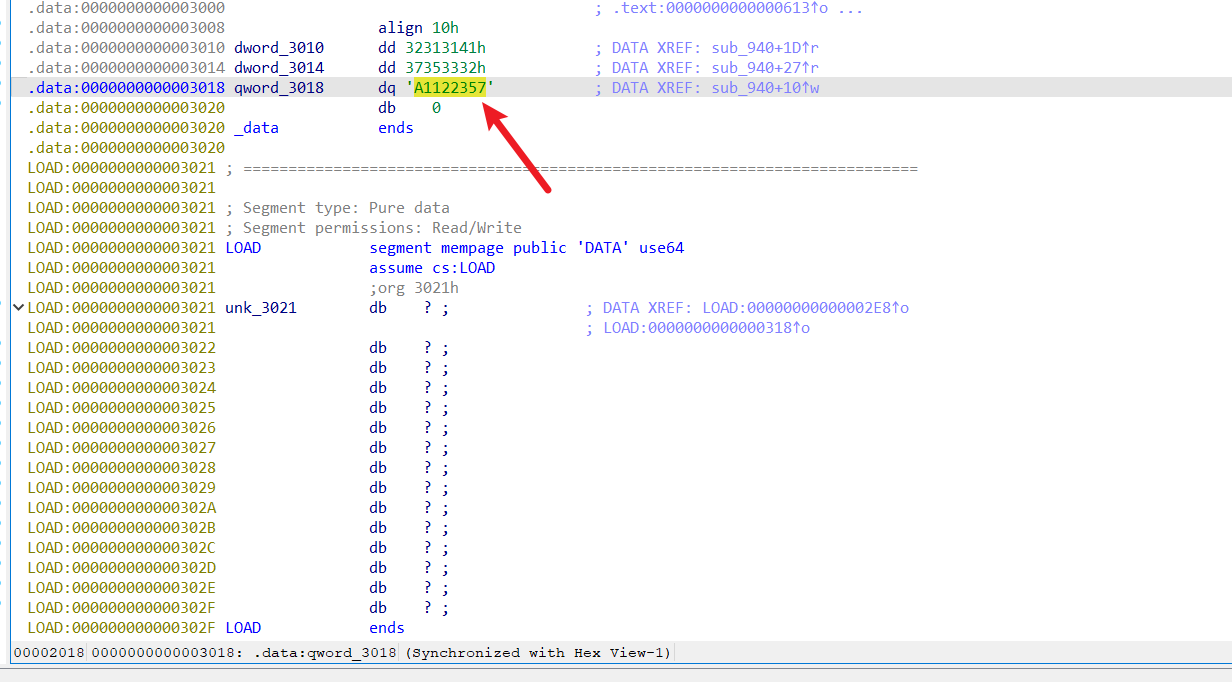
提取密文
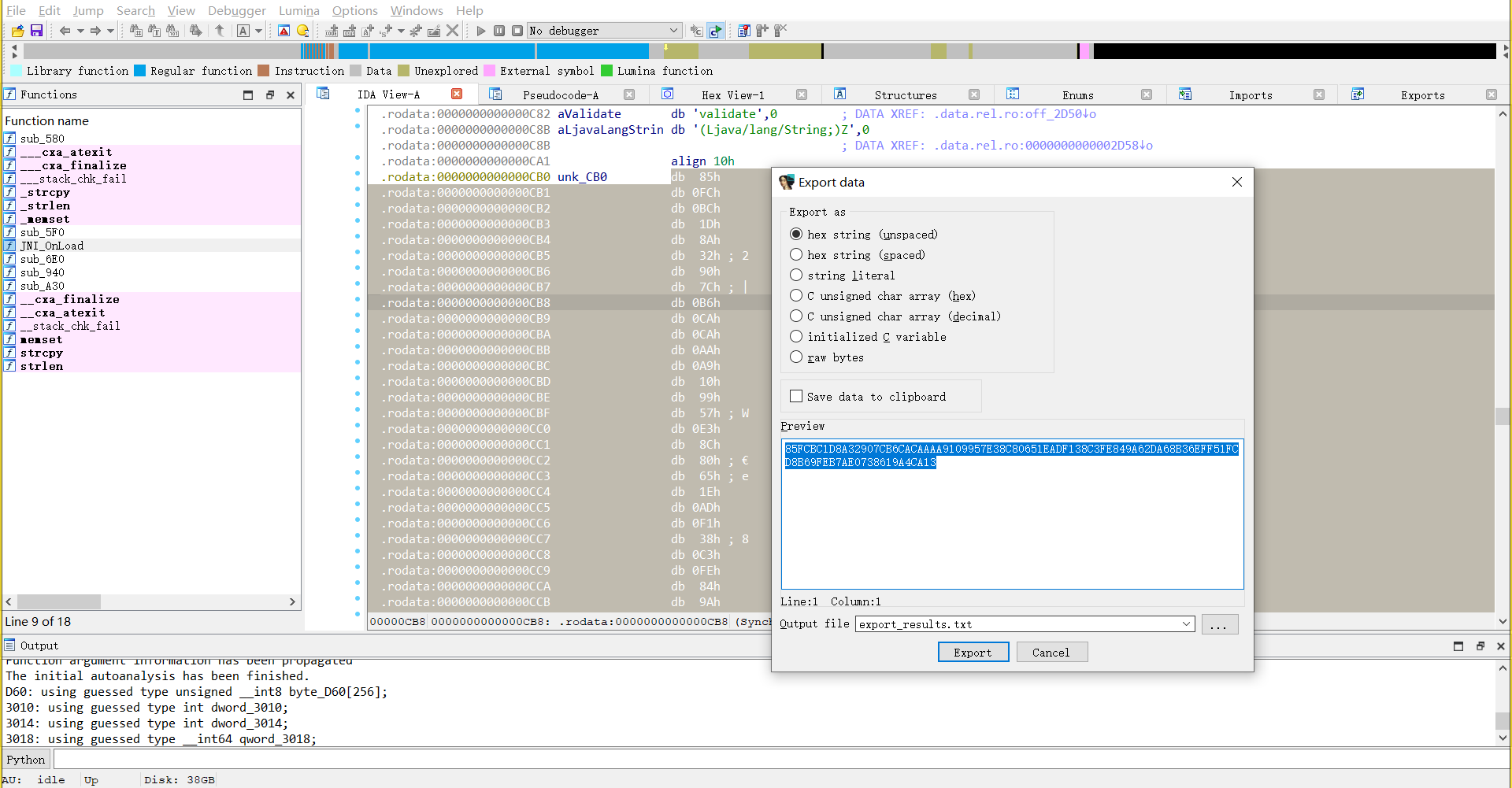
85FCBC1D8A32907CB6CACAAAA9109957E38C80651EADF138C3FE849A62DA68B36EFF51FCD8B69FEB7AE0738619A4CA13
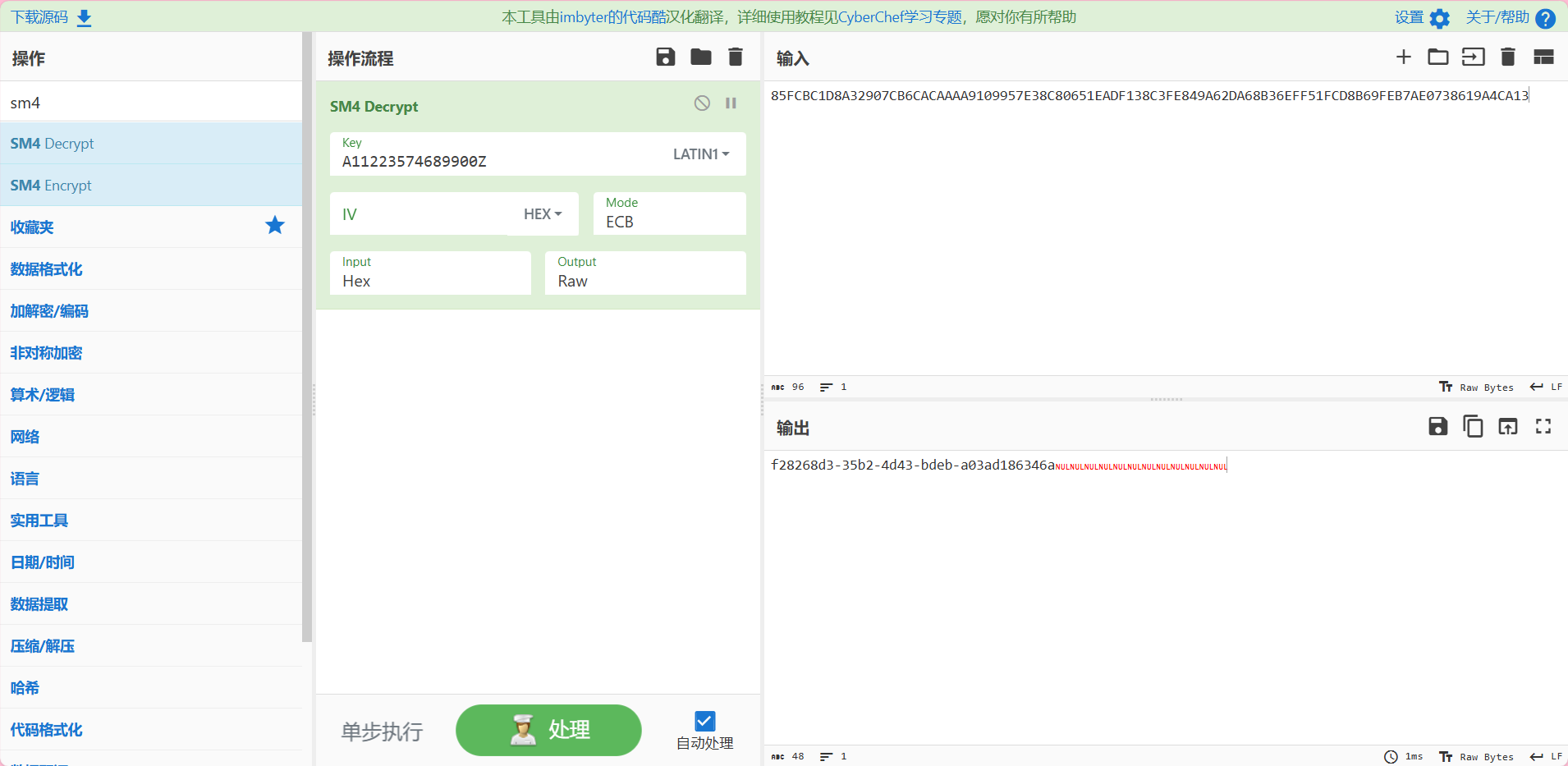
flag: wdflag{f28268d3-35b2-4d43-bdeb-a03ad186346a}
REVERSE02
思路:
查壳,然后使用 ida64 打开,分析一下 main 函数,将 flag 分成了 4 段,解释在注释里面
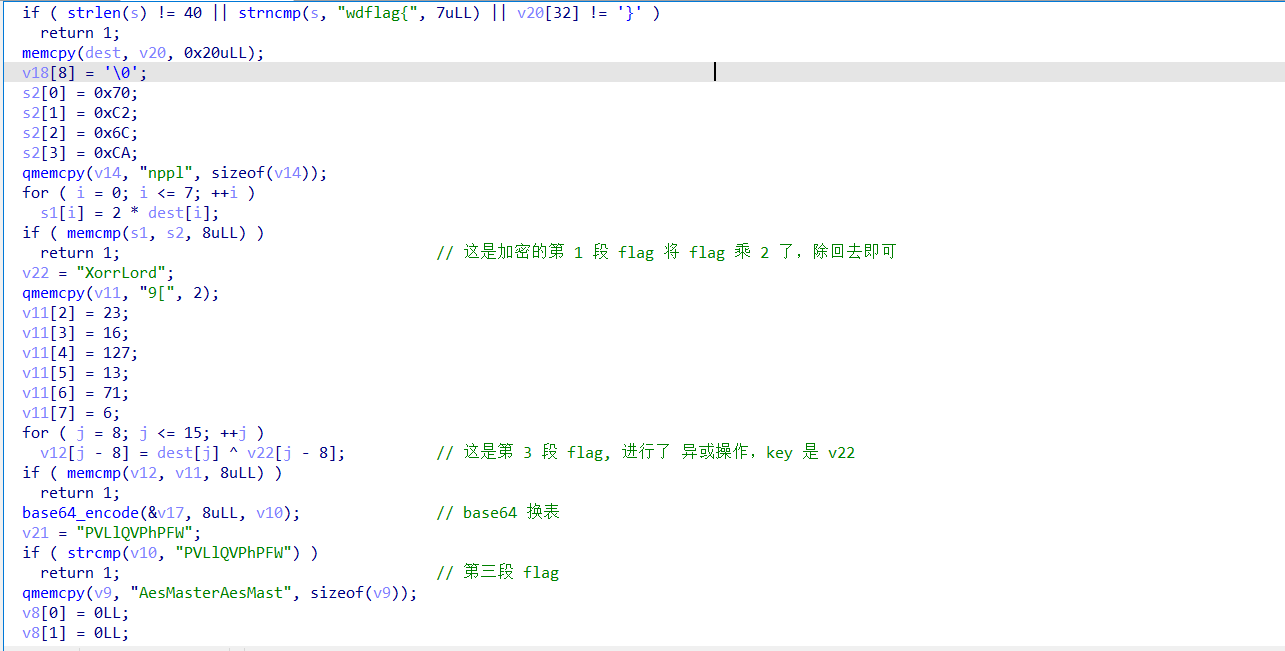
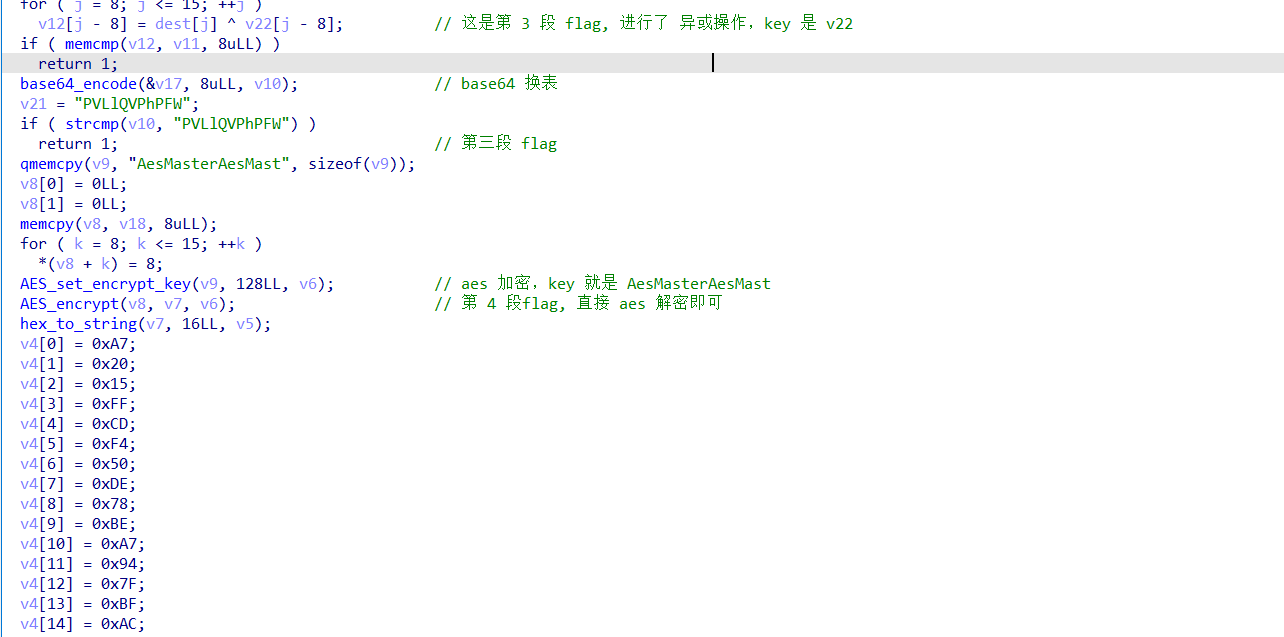
直接进行解密即可,base64 表,追踪 base64_encode 这个函数,就能发现
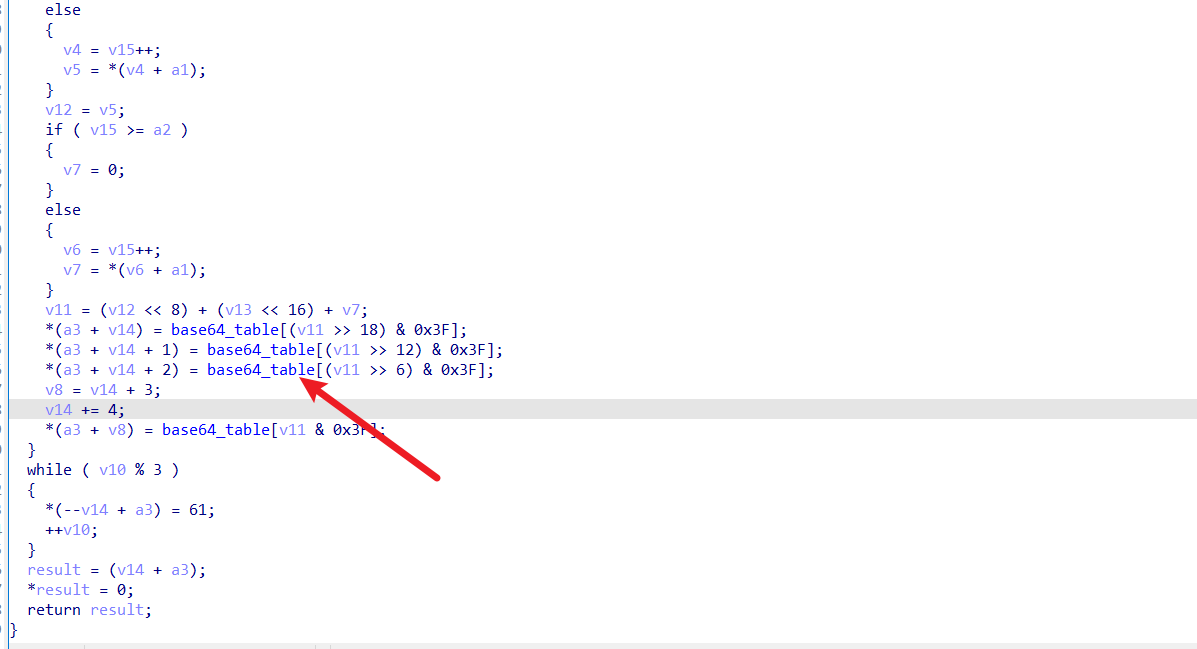
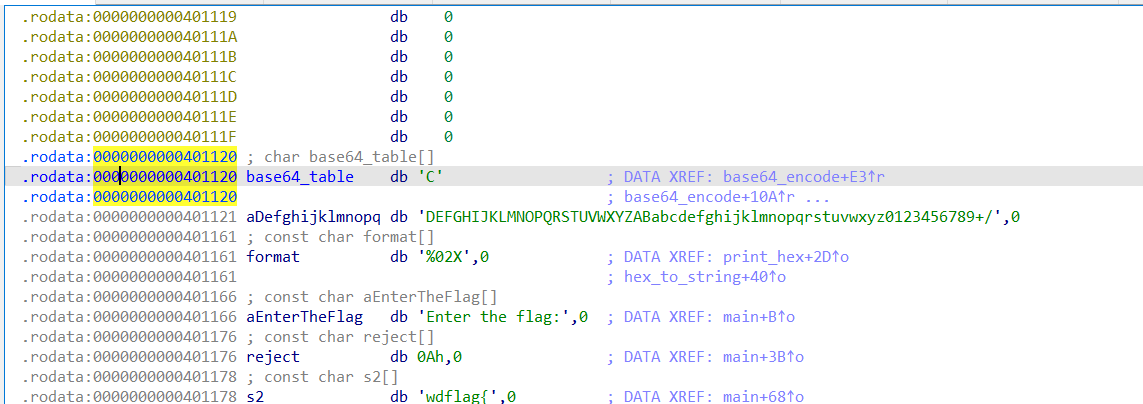
exp:
# 第一段
s2 = [0x70, 0xC2, 0x6C, 0xCA]
s1 = [ord(c) for c in "nppl"]
s = s2 + s1
dest = [s[i] // 2 for i in range(8)]
flag1 = ''.join(chr(i) for i in dest)
print('flag1 = ', flag1)
# 第二段
# 定义 v11 和 v22
v11 = [ord('9'), ord('['), 23, 16, 127, 13, 71, 6]
v22 = [ord(c) for c in "XorrLord"]
# 初始化 dest 数组
dest = [0] * 8
flag2 = []
for i in range(8):
for j in range(1, 128):
if j ^ v22[i] == v11[i]:
flag2.append(j)
break
# 计算 dest 的第8到第15个元素
# for j in range(8):
# dest[j] = v11[j - 8] ^ v22[j - 8]
# print("dest =", ''.join(chr(i) for i in dest))
flag2 = ''.join(chr(i) for i in flag2)
print('flag2 = ', flag2)
# 第三段
import base64
import string
str1 = "PVLlQVPhPFW"
string1 = "CDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/"
string2 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/"
# 转换字符串
translated_str = str1.translate(str.maketrans(string1,string2))
# 为 Base64 解码添加填充
padding_needed = len(translated_str) % 4
if padding_needed:
translated_str += '=' * (4 - padding_needed)
# 解码并打印结果
try:
flag3 = base64.b64decode(translated_str).decode()
print("flag3 = ", flag3)
except Exception as e:
print("解码错误:", e)
# 第四段
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
key = b"AesMasterAesMast"
c = [0xA7, 0x20, 0x15, 0xFF, 0xCD, 0xF4, 0x50, 0xDE, 0x78, 0xBE, 0xA7, 0x94, 0x7F, 0xBF, 0xAC, 0xC5]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
flag4 = cipher.decrypt(bytes(c)).decode()
print("flag4 = ", flag4)
flag = flag1 + flag2 + flag3 + flag4
print("flag = ", "wdflag{" + flag )
print(len(flag))
flag: wdflag{8a6e7886a4eb3b5b52e93a4506d28a04}
 第四届“网鼎杯”网络安全大赛 - 青龙组
第四届“网鼎杯”网络安全大赛 - 青龙组

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号