MongoDB中聚合工具Aggregate等的介绍与使用
Aggregate是MongoDB提供的众多工具中的比较重要的一个,类似于SQL语句中的GROUP BY。聚合工具可以让开发人员直接使用MongoDB原生的命令操作数据库中的数据,并且按照要求进行聚合。
MongoDB提供了三种执行聚合的方法:Aggregation Pipleline,map-reduce功能和 Single Purpose Aggregation Operations
其中用来做聚合操作的几个函数是
-
aggregate(pipeline,options)指定 group 的 keys, 通过操作符$push/$addToSet/$sum等实现简单的 reduce, 不支持函数/自定义变量 -
group({ key, reduce, initial [, keyf] [, cond] [, finalize] })支持函数(keyf)mapReduce的阉割版本 -
mapReduce -
count(query) -
distinct(field,query)
1、Aggregation Pipleline
MongoDB’s aggregation framework is modeled on the concept of data processing pipelines. Documents enter a multi-stage pipeline that transforms the documents into an aggregated result.
管道在*nix中将上一个命令输出的数据作为下一个命令的参数。MongoDB中的管道聚合非常实用,提供高效的数据聚合,并且是MongoDB中数据聚合的首选方法
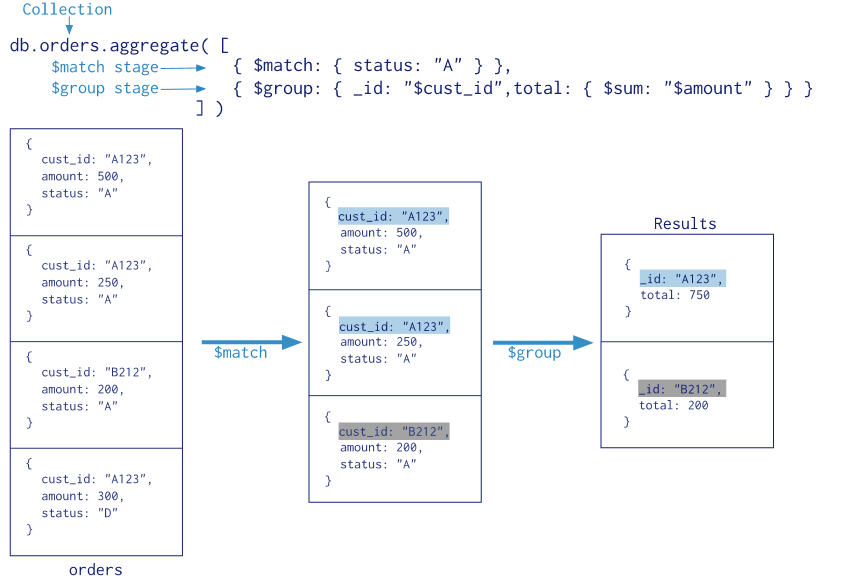
官方给的图:
|
1
2
3
4
|
[ {$match: {status: "A"}}, {$group: {_id: "$cust_id", total: {$sum: "$amount"}}}] |
aggreagte是一个数组,其中包含多个对象(命令),通过遍历Pipleline数组对collection中的数据进行操作。
$match:查询条件
$group:聚合的配置
-
_id代表你想聚合的数据的主键,上述数据中,你想聚合所有cust_id相同的条目的amount的总和,那_id即被设置为cust_id。_id为必须,你可以填写一个空值。 -
total代表你最后想输出的数据之一,这里total是每条结果中amount的总和。 -
$sum是一个聚合的操作符,另外的操作符你可以在官方文档中找到。上图中的命令表示对相同主键(_id)下的amount进行求和。如果你想要计算主键出现的次数,可以把命令写成如下的形式{$sum: 1}
聚合的过程
看一下图例,所有的数据先经过$match命令,只留下了status为A的数据,接着,对筛选出的数据进行聚合操作,对相同cust_id的数据进行计算amount总和的操作,最后输出结果。
二、aggregate具体介绍
接受两个参数 pipeline/options, pipeline 是 array, 相同的 operator 可以多次使用
pipeline 支持的方法
-
$geoNeargeoNear命令可以在查询结果中返回每个点距离查询点的距离 -
$group指定 group 的_id(key/keys) 和基于操作符($push/$sum/$addToSet/...) 的累加运算 -
$limit限制条件 -
$match输入过滤条件 -
$out将输出结果保存到collection -
$project修改数据流中的文档结构 -
$redact是$project/$match功能的合并 -
$skip 跳过 -
$sort对结果排序 -
$unwind拆解数据
$group 允许用的累加操作符 $addToSet/$avg/$first/$last/$max/$min/$push/$sum,不被允许的累加操作符$each... ,默认最多可以用 100MB RAM, 增加allowDiskUse可以让$group操作更多的数据
下面是aggregate的用法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
db.newtest.aggregate([ {$match: {}}, {$skip: 10}, // 跳过 collection 的前 10 行 {$project: {group: 1, datetime: 1, category: 1, count: 1}}, // 如果不选择 {count: 1} 最后的结果中 count_all/count_avg = 0 {$redact: { // redact 简单用法 过滤 group != 'A' 的行 $cond: [{$eq: ["$group", "A"]}, "$$DESCEND", "$$PRUNE"] }}, {$group: { _id: {year: {$year: "$datetime"}, month: {$month: "$datetime"}, day: {$dayOfMonth: "$datetime"}}, group_unique: {$addToSet: "$group"}, category_first: {$first: "$category"}, category_last: {$last: "$category"}, count_all: {$sum: "$count"}, count_avg: {$avg: "$count"}, rows: {$sum: 1} }}, // 拆分 group_unique 如果开启这个选项, 会导致 _id 重复而无法写入 out 指定的 collection, 除非再 $group 一次 // {$unwind: "$group_unique"}, // 只保留这两个字段 {$project: {group_unique: 1, rows: 1}}, // 结果按照 _id 排序 {$sort: {"_id": 1}}, // 只保留 50 条结果 // {$limit: 50}, // 结果另存 {$out: "data_agg_out"},], { explain: true, allowDiskUse: true, cursor: {batchSize: 0}})db.data_agg_out.find()db.data_agg_out.aggregate([ {$group: { _id: null, rows: {$sum: '$rows'} }}])db.data_agg_out.drop() |
-
$match聚合前数据筛选 -
$skip跳过聚合前数据集的 n 行, 如果{$skip: 10}, 最后rows = 5000000 - 10 -
$project之选择需要的字段, 除了_id之外其他的字段的值只能为 1 -
$redact看了文档不明其实际使用场景, 这里只是简单筛选聚合前的数据 -
$group指定各字段的累加方法 -
$unwind拆分 array 字段的值, 这样会导致_id重复 -
$project可重复使用多次 最后用来过滤想要存储的字段 -
$out如果$group/$project/$redact的_id没有重复就不会报错 -
以上方法中
$project/$redact/$group/$unwind可以使用多次
二、group
group 比 aggregate 好的一个地方是 map/reduce 都支持用 function 定义, 下面是支持的选项
ns如果用db.runCommand({group: {}})方式调用, 需要ns指定 collectioncond聚合前筛选key聚合的 keyinitial初始化 累加 结果$reduce接受(curr, result)参数, 将curr累加到resultkeyf代替key用函数生成聚合用的主键finalize结果处理
需要保证输出结果小于 16MB 因为 group 没有提供转存选项
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
db.data.group({ cond: {'group': 'A'}, // key: {'group': 1, 'category': 1}, keyf: function(doc) { var dt = new Date(doc.created); // or // var dt = doc.datetime; return { year: doc.datetime.getFullYear(), month: doc.datetime.getMonth() + 1, day: doc.datetime.getDate() } }, initial: {count: 0, category: []}, $reduce: function(curr, result) { result.count += curr.count; if (result.category.indexOf(curr.category) == -1) { result.category.push(curr.category); } }, finalize: function(result) { result.category = result.category.join(); }}) |
如果要求聚合大量数据, 就需要用到 mapReduce
三、mapReduce
query聚合前筛选sort对聚合前的数据排序 用来优化 reducelimit限制进入 map 的数据map(function) emit(key, value) 在函数中指定聚合的 K/Vreduce(function) 参数(key, values)key在 map 中定义了,values是在这个 K 下的所有 V 数组finalize处理最后结果out结果转存 可以选择另外一个 dbscope设置全局变量jdMode(false) 是否(默认是)把 map/reduce 中间结果转为 BSON 格式, BSON 格式可以利用磁盘空间, 这样就可以处理大规模的数据集verbose(true) 详细信息
如果设 jsMode 为 true 不进行 BSON 转换, 可以优化 reduce 的执行速度, 但是由于内存限制最大在 emit 数量小于 500,000 时使用
写 mapReduce 时需要注意
- emit 返回的 value 必须和 reduce 返回的 value 结构一致
reduce函数必须幂等- 详见 Troubleshoot the Reduce Function
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
db.data.mapReduce(function() { var d = this.datetime; var key = { year: d.getFullYear(), month: d.getMonth() + 1, day: d.getDate(), }; var value = { count: this.count, rows: 1, groups: [this.group], } emit(key, value);}, function(key, vals) { var reducedVal = { count: 0, groups: [], rows: 0, }; for(var i = 0; i < vals.length; i++) { var v = vals[i]; reducedVal.count += v.count; reducedVal.rows += v.rows; for(var j = 0; j < v.groups.length; j ++) { if (reducedVal.groups.indexOf(v.groups[j]) == -1) { reducedVal.groups.push(v.groups[j]); } } } return reducedVal;}, { query: {}, sort: {datetime: 1}, // 需要索引 否则结果返回空 limit: 50000, finalize: function(key, reducedVal) { reducedVal.avg = reducedVal.count / reducedVal.rows; return reducedVal; }, out: { inline: 1, // replace: "", // merge: "", // reduce: "", }, scope: {}, jsMode: true}) |
测试数据:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
> db.newtest.find(){ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544352ba57ccba824d7bf"), "group" : "E", "created" : 1402764223, "count" : 63, "datetime" : 1512391126, "title" : "aa", "category" : "C8" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544512ba57ccba824d7c0"), "group" : "I", "created" : 1413086660, "count" : 93, "datetime" : 1512391261, "title" : "bb", "category" : "C10" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c1"), "group" : "H", "created" : 1440750343, "count" : 41, "datetime" : 1512391111, "title" : "cc", "category" : "C1" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c2"), "group" : "S", "created" : 1437710373, "count" : 14, "datetime" : 1512392136, "title" : "dd", "category" : "C10" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c3"), "group" : "Z", "created" : 1428307315, "count" : 78, "datetime" : 1512391166, "title" : "ee", "category" : "C5" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c4"), "group" : "R", "created" : 1402809274, "count" : 74, "datetime" : 1512391162, "title" : "ff", "category" : "C9" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c5"), "group" : "Y", "created" : 1400571321, "count" : 66, "datetime" : 1512139164, "title" : "gg", "category" : "C2" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c6"), "group" : "L", "created" : 1416562128, "count" : 5, "datetime" : 1512393165, "title" : "hh", "category" : "C1" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544562ba57ccba824d7c7"), "group" : "E", "created" : 1414057884, "count" : 12, "datetime" : 1512391165, "title" : "ii", "category" : "C3" }{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2544572ba57ccba824d7c8"), "group" : "L", "created" : 1418879346, "count" : 67, "datetime" : 1512391167, "title" : "gg", "category" : "C3" } |
四、总结
| method | allowDiskUse | out | function |
|---|---|---|---|
| aggregate | true | pipeline/collection | false |
| group | false | pipeline | true |
| mapReduce | jsMode | pipeline/collection | true |
aggregate基于累加操作的的聚合 可以重复利用$project/$group一层一层聚合数据, 可以用于大量数据(单输出结果小于 16MB) 不可用于分片数据mapReduce可以处理超大数据集 需要严格遵守 mapReduce 中的结构一致/幂等 写法, 可增量输出/合并, 见outoptionsgroupRDB 中的group by简单需求可用(只有 inline 输出) 会产生read lock
- 作者:踏雪无痕
- 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/chenpingzhao/
- 本文版权归作者和博客园共有,如需转载,请联系 pingzhao1990#163.com



