算法基础<七> 加权有向图
加权有向图
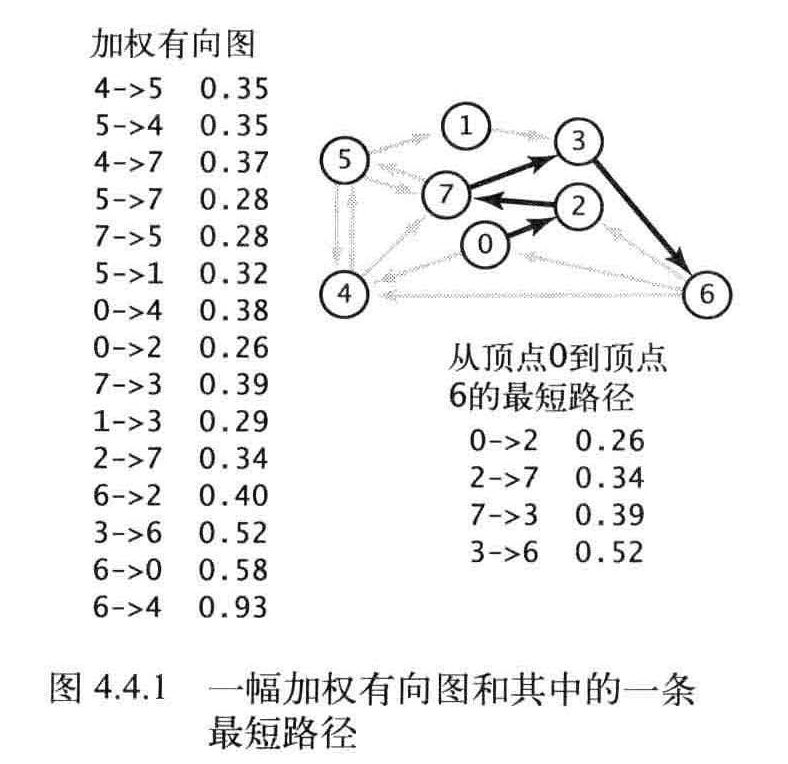
找到从一个顶点到达另一个顶点的成本最小的路径。
在一幅加权有向图中,从顶点s 到顶点t 的最短路径是所有从s 到t 的路径中的权重最小者。
最短路径性质
- 路径是有向的,
- 权重不一定等价于距离
- 并不是所有顶点都是可达的
- 负权重会使问题更复杂
- 最短路径不一定是唯一的。
- 可能存在平行边和自环。
我们的重点是单点最短路径问题,其中给出了起点s , 计算的结果是一棵最短路径树(SPT), 它包含了顶点s 到所有可达的顶点的最短路径。如图所示。
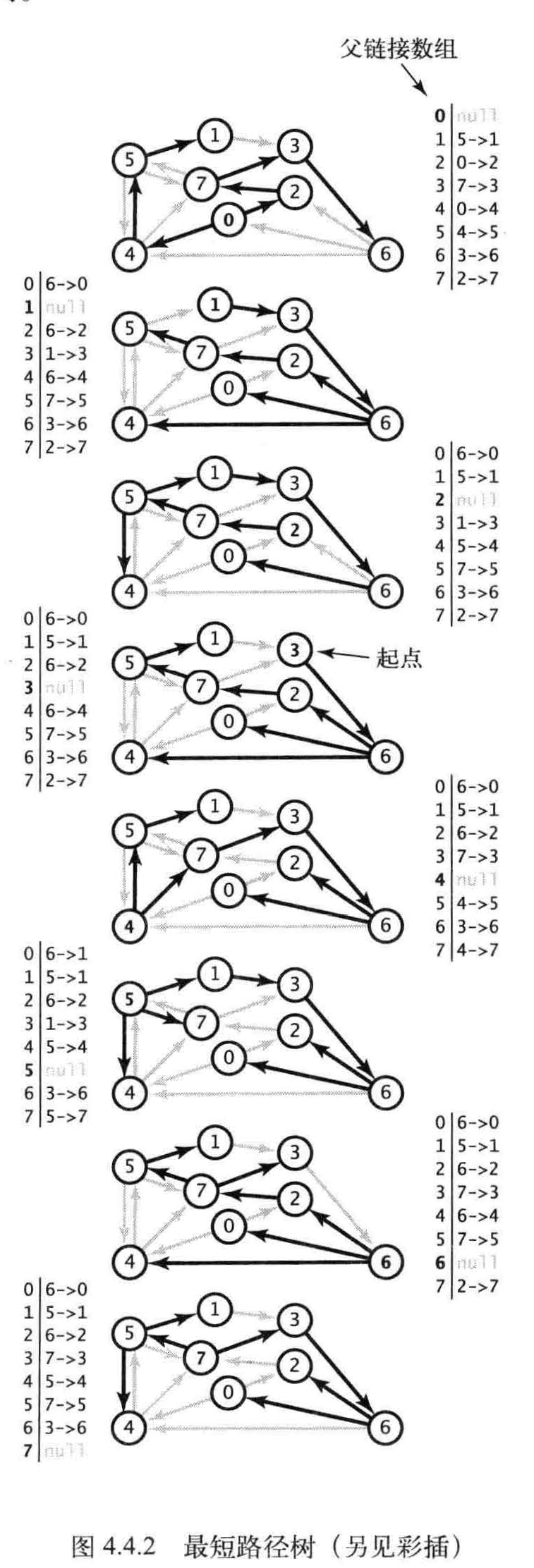
定义:给定一幅加权有向图和一个顶点s , 以s 为起点的一棵最短路径树是图的一幅子图,它包含s和从s 可达的所有顶点。这棵有向树的根结点为s,树的每条路径都是有向图中的一条最短路径。
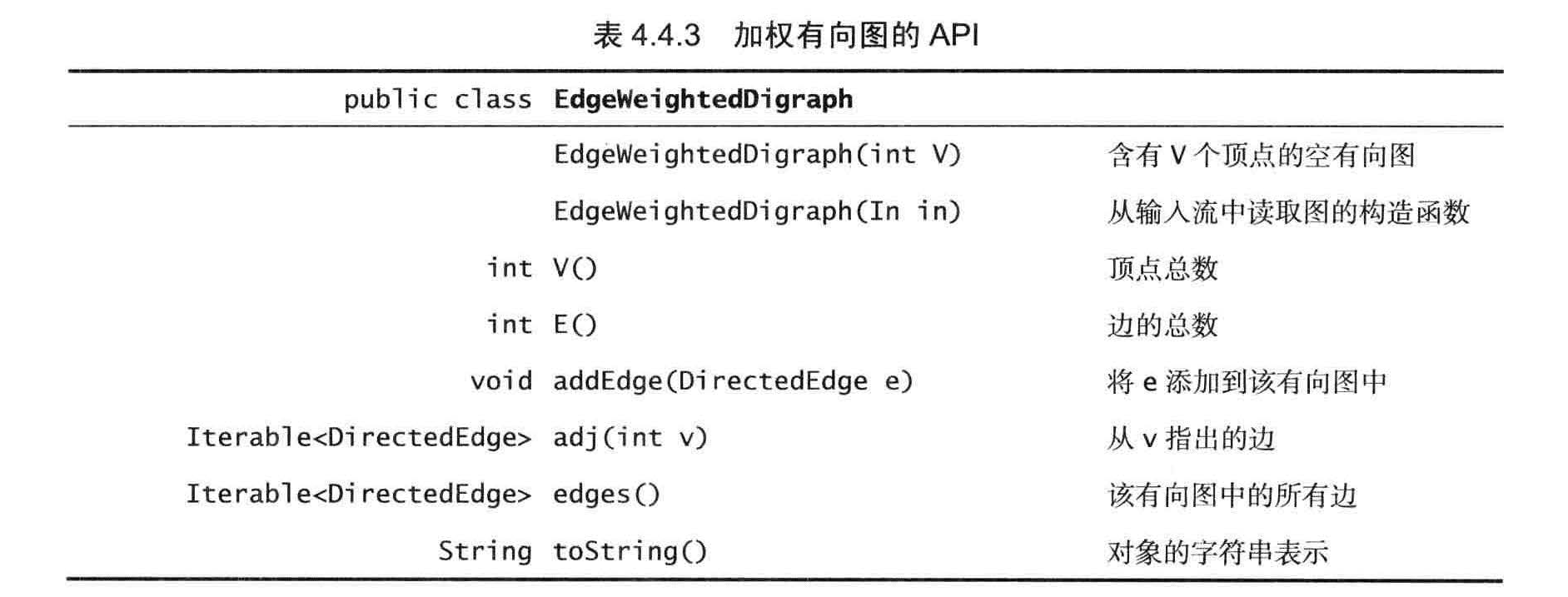
加权有向图的数据结构

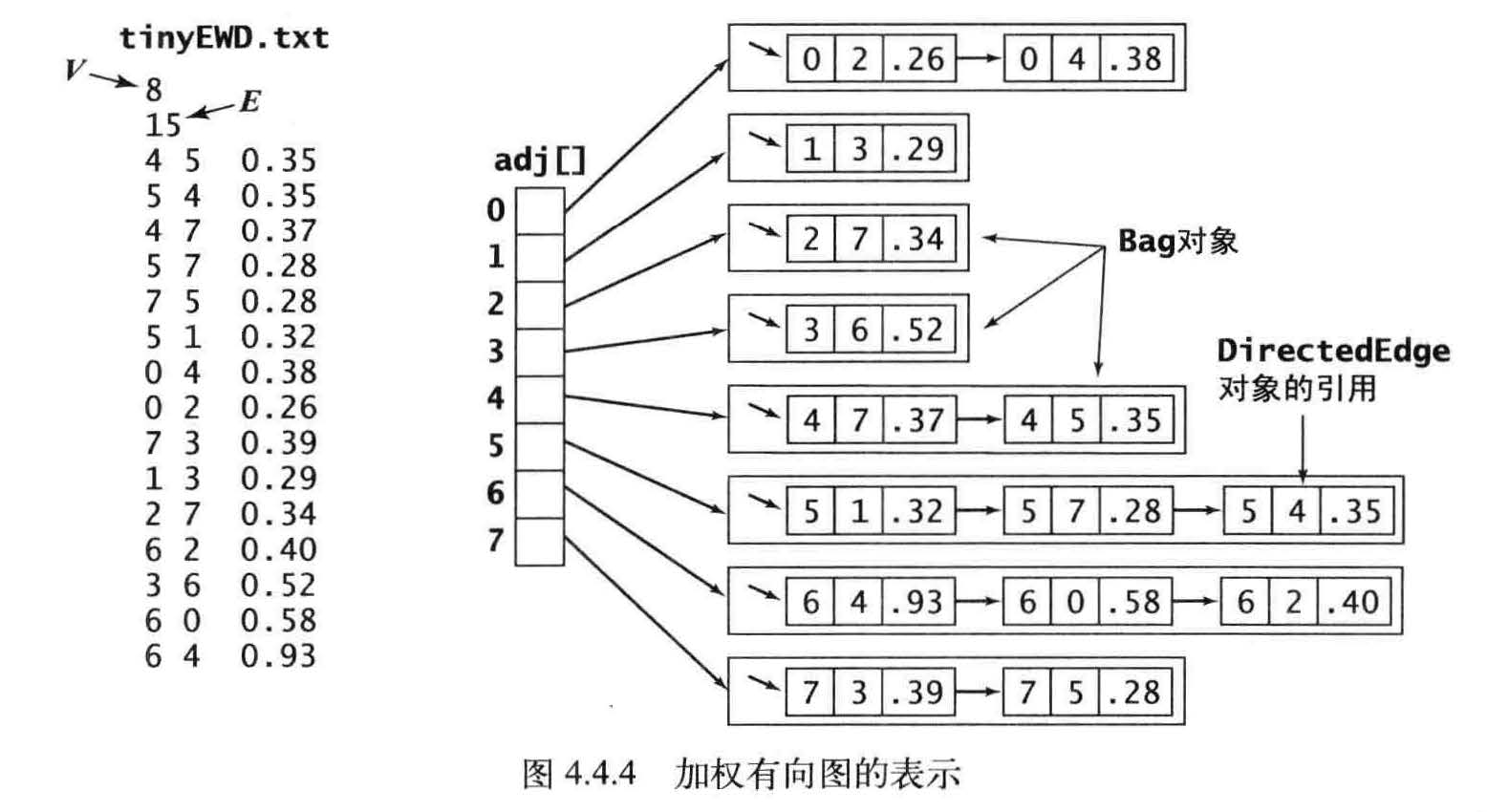
edgeTo[v]:最短路径树中的边,连接v和它父节点的边,
distTo[v] :到达起点的距离, 为从s 到v的已知最短路径的长度。该路径上的所有顶点均在树中且路径上的最后一条边为edgeTo[v]
using SuddenGale.AlgorithmEngine.Structure;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace SuddenGale.AlgorithmEngine.Graph
{
public class DirectedEdge:IComparable<DirectedEdge>
{
private readonly int v;//边的起点
private readonly int w;//边的终点
private readonly double weight;//边的权重
public DirectedEdge(int v, int w, double weight)
{
if (v < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Vertex names must be nonnegative integers");
if (w < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Vertex names must be nonnegative integers");
if (Double.IsNaN(weight)) throw new ArgumentException("Weight is NaN");
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int From()
{
return v;
}
public int To()
{
return w;
}
public double Weight()
{
return weight;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return $"{v}->{w} {weight:F2}";
}
public int CompareTo(DirectedEdge other)
{
return this.weight.CompareTo(other.Weight());
}
}
public class EdgeWeightedDigraph
{
private static readonly String NEWLINE = System.Environment.NewLine;
private readonly int V; // 顶点总数
private int E; // 边的总数
private LinkedBagNet<DirectedEdge>[] adj; // 顶点index的临接表
private int[] indegree; // vertex 的度
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V)
{
if (V < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
this.indegree = new int[V];
adj = new LinkedBagNet<DirectedEdge>[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
adj[v] = new LinkedBagNet<DirectedEdge>();
}
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V, int E):this(V)
{
if (E < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of edges in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
int v = random.Next(V);
int w = random.Next(V);
double weight = Math.Round(100 * random.NextDouble()) / 100.0;
DirectedEdge e = new DirectedEdge(v, w, weight);
AddEdge(e);
}
}
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(StreamReader stream)
{
if (stream == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("argument is null");
try
{
this.V = int.Parse(stream.ReadLine());
if (V < 0) throw new ArgumentException("number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
indegree = new int[V];
adj = new LinkedBagNet<DirectedEdge>[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
adj[v] = new LinkedBagNet<DirectedEdge>();
}
int E = int.Parse(stream.ReadLine());
if (E < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
string line = stream.ReadLine().Trim();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(line) && line.Split(' ').Count() == 3)
{
int v = int.Parse(line.Split(' ')[0]);
int w = int.Parse(line.Split(' ')[1]);
double weight = double.Parse(line.Split(' ')[2]);
AddEdge(new DirectedEdge(v, w, weight));
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new ArgumentException("invalid input format in EdgeWeightedDigraph constructor", e);
}
}
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(EdgeWeightedDigraph G): this(G.V)
{
this.E = G.Edge();
for (int v = 0; v < G.V; v++)
this.indegree[v] = G.Indegree(v);
for (int v = 0; v < G.V; v++)
{
// reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original
Stack<DirectedEdge> reverse = new Stack<DirectedEdge>();
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.adj[v])
{
reverse.Push(e);
}
foreach (DirectedEdge e in reverse)
{
adj[v].Add(e);
}
}
}
public int Vertic()
{
return V;
}
public int Edge()
{
return E;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
public void AddEdge(DirectedEdge e)
{
int v = e.From();
int w = e.To();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
adj[v].Add(e);
indegree[w]++;
E++;
}
public IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> Adj(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
public int Outdegree(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].Length;
}
public int Indegree(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return indegree[v];
}
public IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> Edges()
{
LinkedBagNet<DirectedEdge> list = new LinkedBagNet<DirectedEdge>();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
foreach (DirectedEdge e in Adj(v))
{
list.Add(e);
}
}
return list;
}
public override string ToString()
{
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.Append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
s.Append(v + ": ");
foreach (DirectedEdge e in adj[v])
{
s.Append(e + " ");
}
s.Append(NEWLINE);
}
return s.ToString();
}
}
}
边松弛
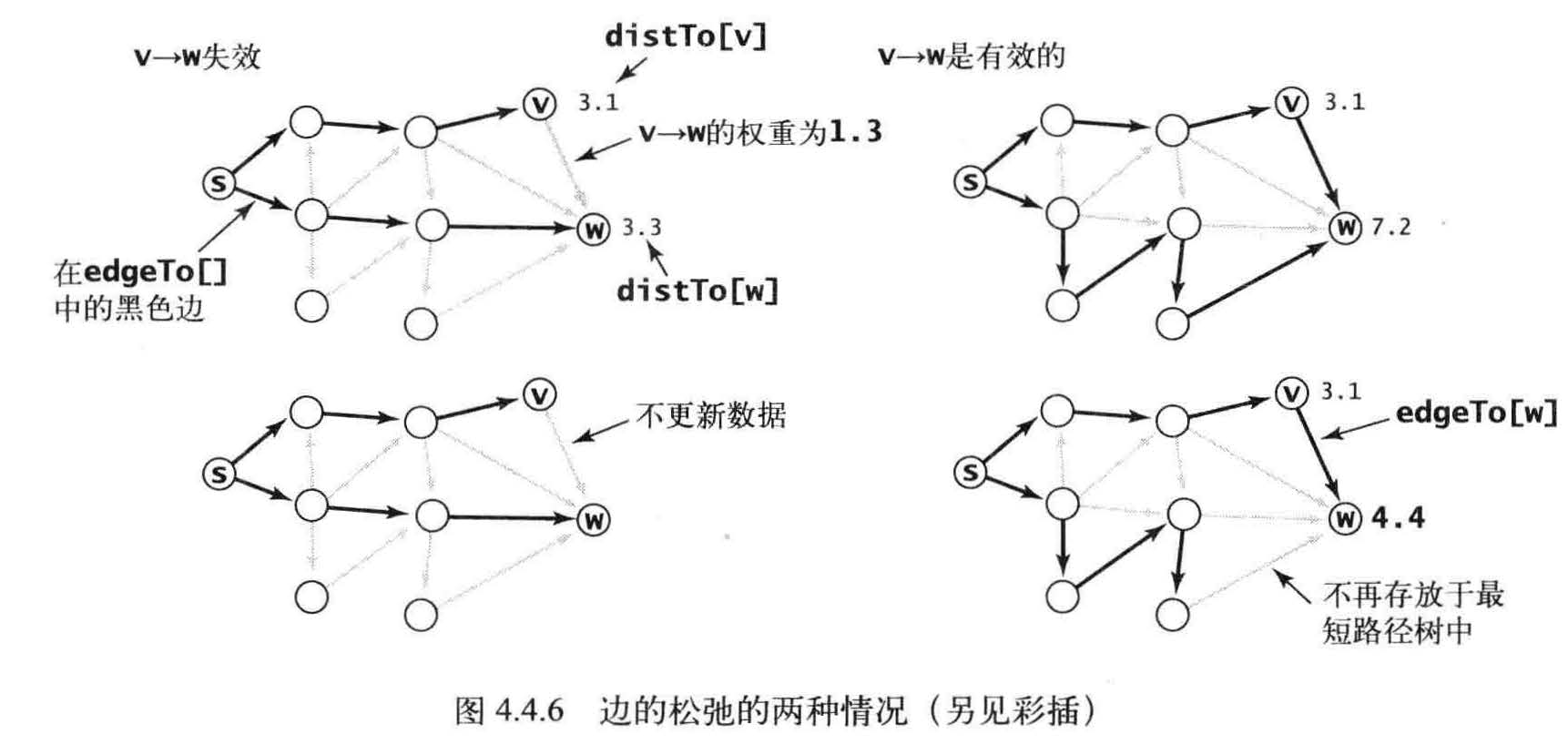
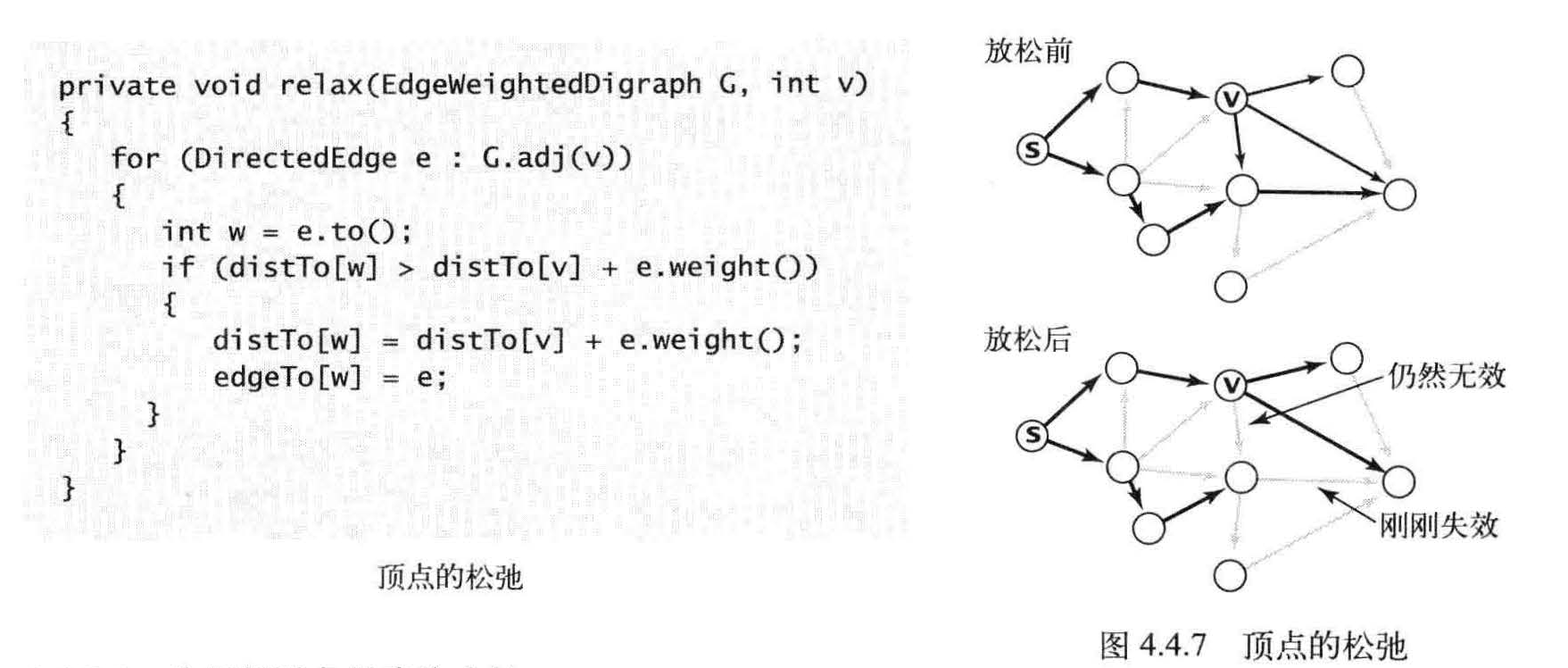
松弛( relaxation ):放松边V -> W 意味着检查从s 到w 的最短路径是否是先从s 到v , 然后再由v 到w 。如果是, 则根据这个情况更新数据结构的内容。由v 到达w 的最短路径是di stTo[v] 与e.weight() 之和一一如果这个值不小于distTo[w] , 称这条边失效了并将它忽略; 如果这个值更小,就更新数据。
一种情况是边失效(左边的例子),不更新任何数据;另一种情况是v -> w 就是到达w 的最短路径(右边的例子),这将会更新edgeTo[w]和distTo[w] (这可能会使另一些边失效,但也可能产生一些新的有效边)

Dijkstra算法
寻找加权无向图中的最小生成树的Prim 算法:构造最小生成树的每一步都向这棵树中添加一条新的边。Dijkstra 算法采用了类似的方法来计算最短路径树。首先将distTo[s]初始化为0, distTo[] 中的其他元素初始化为正无穷。然后将distTo [] 最小的非树顶点放松并加入树中,如此这般,直到所有的顶点都在树中或者所有的非树顶点的distTo[]值均为无穷大。
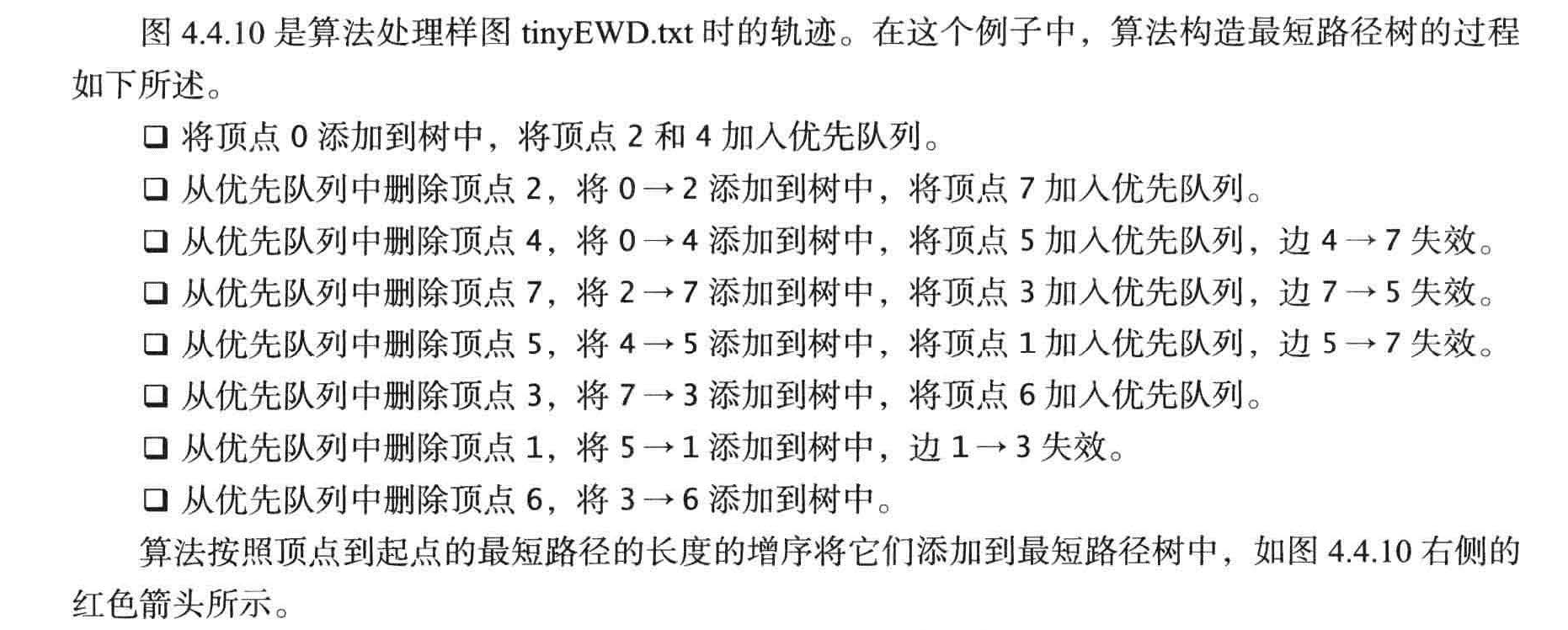
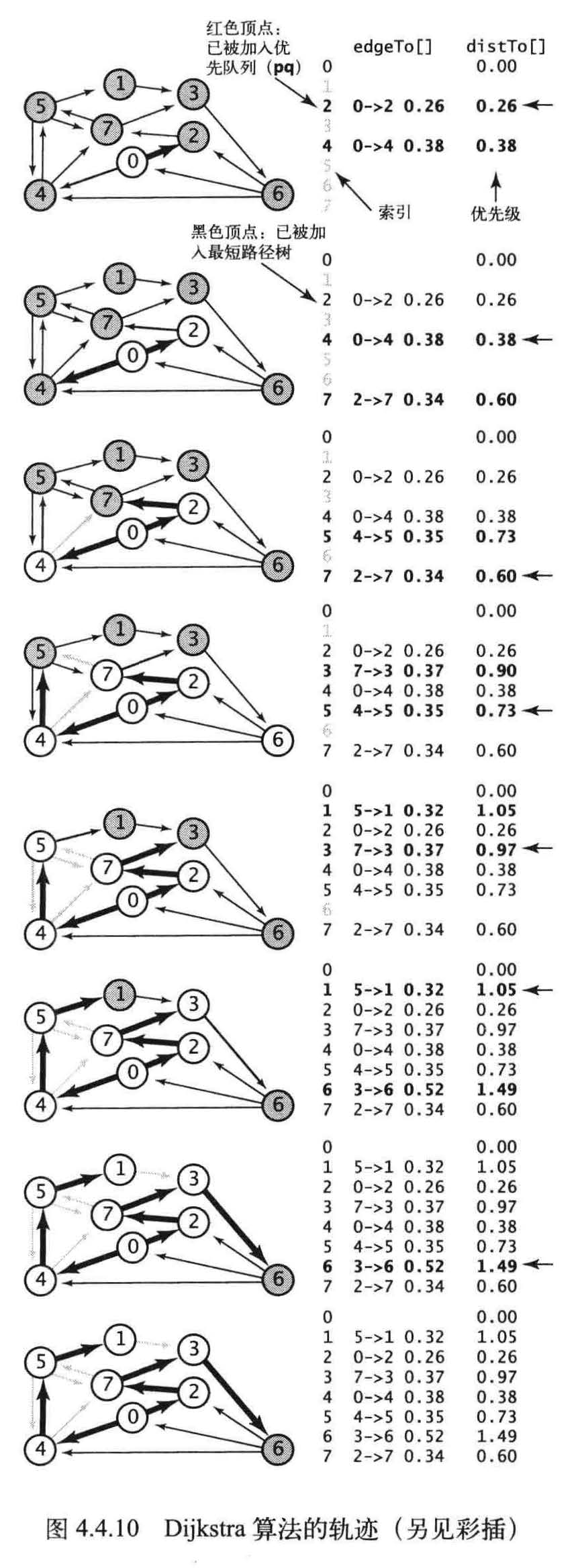
Prim 算法每次添加的都是离树最近的非树顶点, Dijkstra算法每次添加的都是离起点最近的非树顶点。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using SuddenGale.AlgorithmEngine.Structure;
namespace SuddenGale.AlgorithmEngine.Graph
{
public class DijkstraSP
{
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = distance of shortest s->v path,最小树的长度
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest s->v path,最小树中的边
private IndexMinPQ<Double> pq; //顶点优先队列,保存需要放松的下一个顶点,所有添加进最小树的边的To,每次放松最小值
public DijkstraSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s)
{
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.Edges())
{
if (e.Weight() < 0)
throw new ArgumentException("edge " + e + " has negative weight");
}
distTo = new double[G.Vertic()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.Vertic()];
ValidateVertex(s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.PositiveInfinity;
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// relax vertices in order of distance from s
pq = new IndexMinPQ<Double>(G.Vertic());
pq.Insert(s, distTo[s]);
while (!pq.IsEmpty())
{
int v = pq.DelMin();
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.Adj(v))
Relax(e);
}
// check optimality conditions
if(!Check(G, s))
throw new Exception("Check return false");
}
// relax edge e and update pq if changed
private void Relax(DirectedEdge e)
{
int v = e.From(), w = e.To();
if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.Weight())
{
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.Weight();//更新最小树的长度
edgeTo[w] = e;//更新最小树
if (pq.Contains(w)) pq.DecreaseKey(w, distTo[w]);
else pq.Insert(w, distTo[w]);
}
}
public double DistTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
return distTo[v];
}
public bool HasPathTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] < Double.PositiveInfinity;
}
public IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> PathTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
if (!HasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<DirectedEdge>();
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.From()])
{
path.Push(e);
}
return path;
}
private bool Check(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s)
{
// check that edge weights are nonnegative
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.Edges())
{
if (e.Weight() < 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("negative edge weight detected");
return false;
}
}
// check that distTo[v] and edgeTo[v] are consistent
if (distTo[s] != 0.0 || edgeTo[s] != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("distTo[s] and edgeTo[s] inconsistent");
return false;
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
if (v == s) continue;
if (edgeTo[v] == null && distTo[v] != Double.PositiveInfinity)
{
Console.WriteLine("distTo[] and edgeTo[] inconsistent");
return false;
}
}
// check that all edges e = v->w satisfy distTo[w] <= distTo[v] + e.weight()
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.Adj(v))
{
int w = e.To();
if (distTo[v] + e.Weight() < distTo[w])
{
Console.WriteLine("edge " + e + " not relaxed");
return false;
}
}
}
// check that all edges e = v->w on SPT satisfy distTo[w] == distTo[v] + e.weight()
for (int w = 0; w < G.Vertic(); w++)
{
if (edgeTo[w] == null) continue;
DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[w];
int v = e.From();
if (w != e.To()) return false;
if (distTo[v] + e.Weight() != distTo[w])
{
Console.WriteLine("edge " + e + " on shortest path not tight");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private void ValidateVertex(int v)
{
int V = distTo.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void DijkstraSPTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyEWG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph(stream);
int s = 0;
DijkstraSP sp = new DijkstraSP(G, s);
//打印最短路径
for (int t = 0; t < G.Vertic(); t++)
{
if (sp.HasPathTo(t))
{
Console.Write($"{s} to {t} {sp.DistTo(t):f2} ");
foreach (DirectedEdge e in sp.PathTo(t))
{
Console.Write(e + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"{s} to {t} no path");
}
}
}
// 0 to 0 0.00
// 0 to 1 no path
// 0 to 2 0.26 0->2 0.26
// 0 to 3 0.43 0->2 0.26 2->3 0.17
// 0 to 4 0.38 0->4 0.38
// 0 to 5 0.73 0->4 0.38 4->5 0.35
// 0 to 6 0.95 0->2 0.26 2->3 0.17 3->6 0.52
// 0 to 7 0.16 0->7 0.16
}
任意两点的最短路径
public class DijkstraAllPairsSP
{
private DijkstraSP[] all;
public DijkstraAllPairsSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G)
{
all = new DijkstraSP[G.Vertic()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
all[v] = new DijkstraSP(G, v);
}
public IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> Path(int s, int t)
{
ValidateVertex(s);
ValidateVertex(t);
return all[s].PathTo(t);
}
public bool HasPath(int s, int t)
{
ValidateVertex(s);
ValidateVertex(t);
return Dist(s, t) < Double.PositiveInfinity;
}
public double Dist(int s, int t)
{
ValidateVertex(s);
ValidateVertex(t);
return all[s].DistTo(t);
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void ValidateVertex(int v)
{
int V = all.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void DijkstraAllPairsSPTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyEWD.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph(stream);
DijkstraAllPairsSP spt = new DijkstraAllPairsSP(G);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{v}");
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
Console.Write($"{v}: ");
for (int w = 0; w < G.Vertic(); w++)
{
if (spt.HasPath(v, w)) Console.Write($"{spt.Dist(v, w)} ");
else Console.Write(" Inf ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine();
// print all-pairs shortest paths
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < G.Vertic(); w++)
{
if (spt.HasPath(v, w))
{
Console.Write($"{v} to {w} {spt.Dist(v, w)} ");
foreach (DirectedEdge e in spt.Path(v, w))
Console.Write(e + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"{v} to {w} no path", v, w);
}
}
}
}
}
}
无环加权有向图的最短路径
该算法的特点
- 能够在线性事件内解决单点的最短路径问题
- 能够处理负权重的边
- 能够解决相关的问题。例如找到最长的路径。
首先,将distTo[s] 初始化为0, 其他distTo[] 元素初始化为无穷大,然后一个一个地按照拓扑顺序放松所有顶点。
按照拓扑顺序放松顶点,就能在和E+V 成正比的时间内解决无环加权有向图的单点最短路径问题。

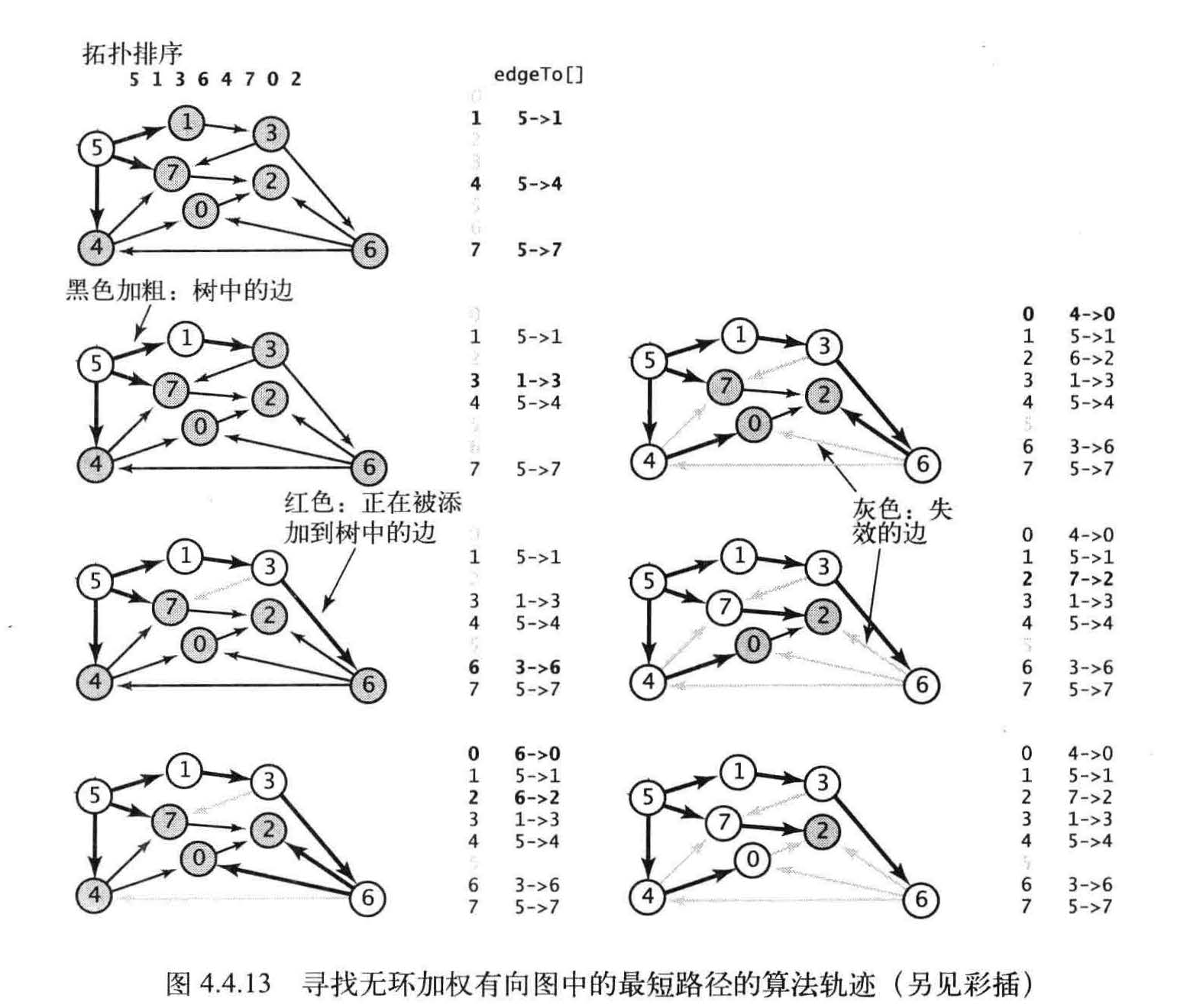
在拓扑排序后,构造函数会扫描整幅图并将每条边放松一次。在已知加权图是无环的情况下,它是找出最短路径的最好方法。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SuddenGale.AlgorithmEngine.Graph
{
public class AcyclicSP
{
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = distance of shortest s->v path
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest s->v path
public AcyclicSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s)
{
distTo = new double[G.Vertic()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.Vertic()];
ValidateVertex(s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.PositiveInfinity;
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// 拓扑排序
Topological topological = new Topological(G);
if (!topological.HasOrder())
throw new ArgumentException("Digraph is not acyclic.");
foreach (int v in topological.Order())
{
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.Adj(v))
Relax(e);
}
}
// relax edge e
private void Relax(DirectedEdge e)
{
int v = e.From(), w = e.To();
if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.Weight())
{
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.Weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
}
}
public double DistTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
return distTo[v];
}
public bool HasPathTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] < Double.PositiveInfinity;
}
public IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> PathTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
if (!HasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<DirectedEdge>();
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.From()])
{
path.Push(e);
}
return path;
}
private void ValidateVertex(int v)
{
int V = distTo.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
}
测试
public void AcyclicSPTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyEWDAG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph(stream);
int s = 5;
AcyclicSP sp = new AcyclicSP(G, s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
if (sp.HasPathTo(v))
{
Console.Write($"{s} to {v} ({sp.DistTo(v)}) ");
foreach (DirectedEdge e in sp.PathTo(v))
{
Console.Write(e + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"{s} to {v} no path.");
}
}
}
// 5 to 0 (0.73) 5->4 0.35 4->0 0.38
// 5 to 1 (0.32) 5->1 0.32
// 5 to 2 (0.62) 5->7 0.28 7->2 0.34
// 5 to 3 (0.61) 5->1 0.32 1->3 0.29
// 5 to 4 (0.35) 5->4 0.35
// 5 to 5 (0)
// 5 to 6 (1.13) 5->1 0.32 1->3 0.29 3->6 0.52
// 5 to 7 (0.28) 5->7 0.28
}
基于拓扑排序的方法比Dijkstra 算法快的倍数与Dijkstra 算法中所有优先队列操作的总成本成正比。
最长路径

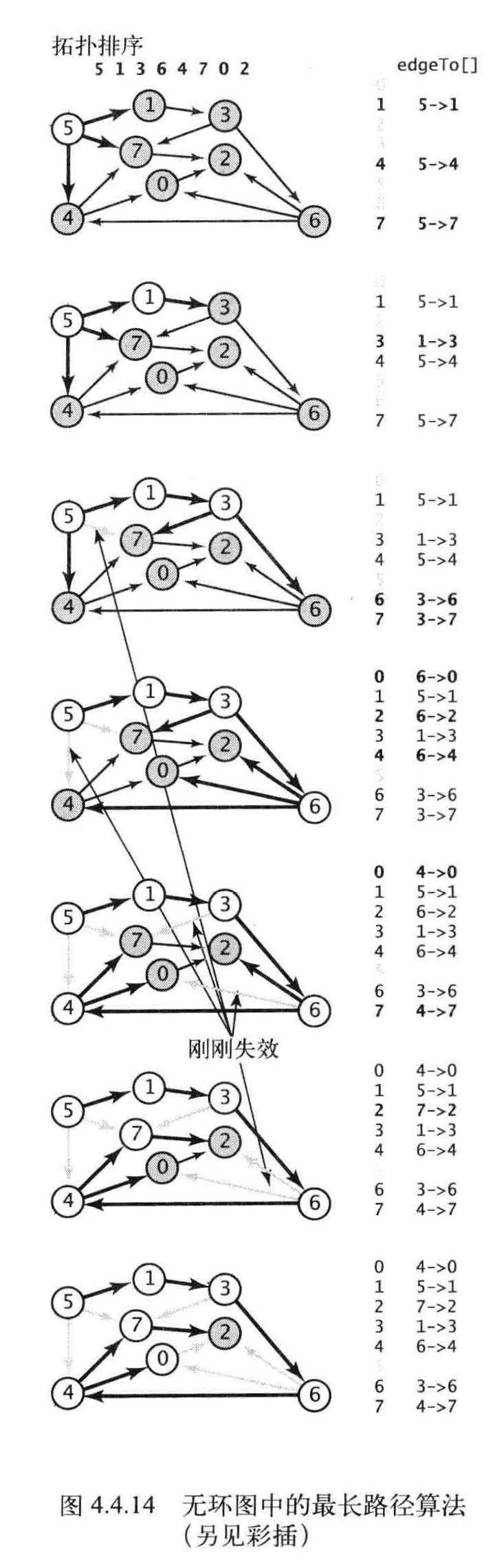
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SuddenGale.AlgorithmEngine.Graph
{
/// <summary>
/// 无环权重有向图的最长路径
/// </summary>
public class AcyclicLP
{
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = distance of longest s->v path
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on longest s->v path
public AcyclicLP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s)
{
distTo = new double[G.Vertic()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.Vertic()];
ValidateVertex(s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.NegativeInfinity;
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// relax vertices in topological order
Topological topological = new Topological(G);
if (!topological.HasOrder())
throw new ArgumentException("Digraph is not acyclic.");
foreach (int v in topological.Order())
{
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.Adj(v))
Relax(e);
}
}
// relax edge e, but update if you find a *longer* path
private void Relax(DirectedEdge e)
{
int v = e.From(), w = e.To();
if (distTo[w] < distTo[v] + e.Weight())
{
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.Weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
}
}
public double DistTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
return distTo[v];
}
public bool HasPathTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] > Double.NegativeInfinity;
}
public IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> PathTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
if (!HasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<DirectedEdge>();
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.From()])
{
path.Push(e);
}
return path;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void ValidateVertex(int v)
{
int V = distTo.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException($"vertex {v} is not between 0 and {V-1}");
}
}
}
测试
public void AcyclicLPTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyEWDAG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph(stream);
int s = 5;
AcyclicLP lp = new AcyclicLP(G, s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
if (lp.HasPathTo(v))
{
Console.Write($"{s} to {v} ({lp.DistTo(v)}) ");
foreach (DirectedEdge e in lp.PathTo(v))
{
Console.Write(e + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"{s} to {v} no path.");
}
}
}
// 5 to 0 (2.44) 5->1 0.32 1->3 0.29 3->6 0.52 6->4 0.93 4->0 0.38
// 5 to 1 (0.32) 5->1 0.32
// 5 to 2 (2.77) 5->1 0.32 1->3 0.29 3->6 0.52 6->4 0.93 4->7 0.37 7->2 0.34
// 5 to 3 (0.61) 5->1 0.32 1->3 0.29
// 5 to 4 (2.06) 5->1 0.32 1->3 0.29 3->6 0.52 6->4 0.93
// 5 to 5 (0)
// 5 to 6 (1.13) 5->1 0.32 1->3 0.29 3->6 0.52
// 5 to 7 (2.43) 5->1 0.32 1->3 0.29 3->6 0.52 6->4 0.93 4->7 0.37
}
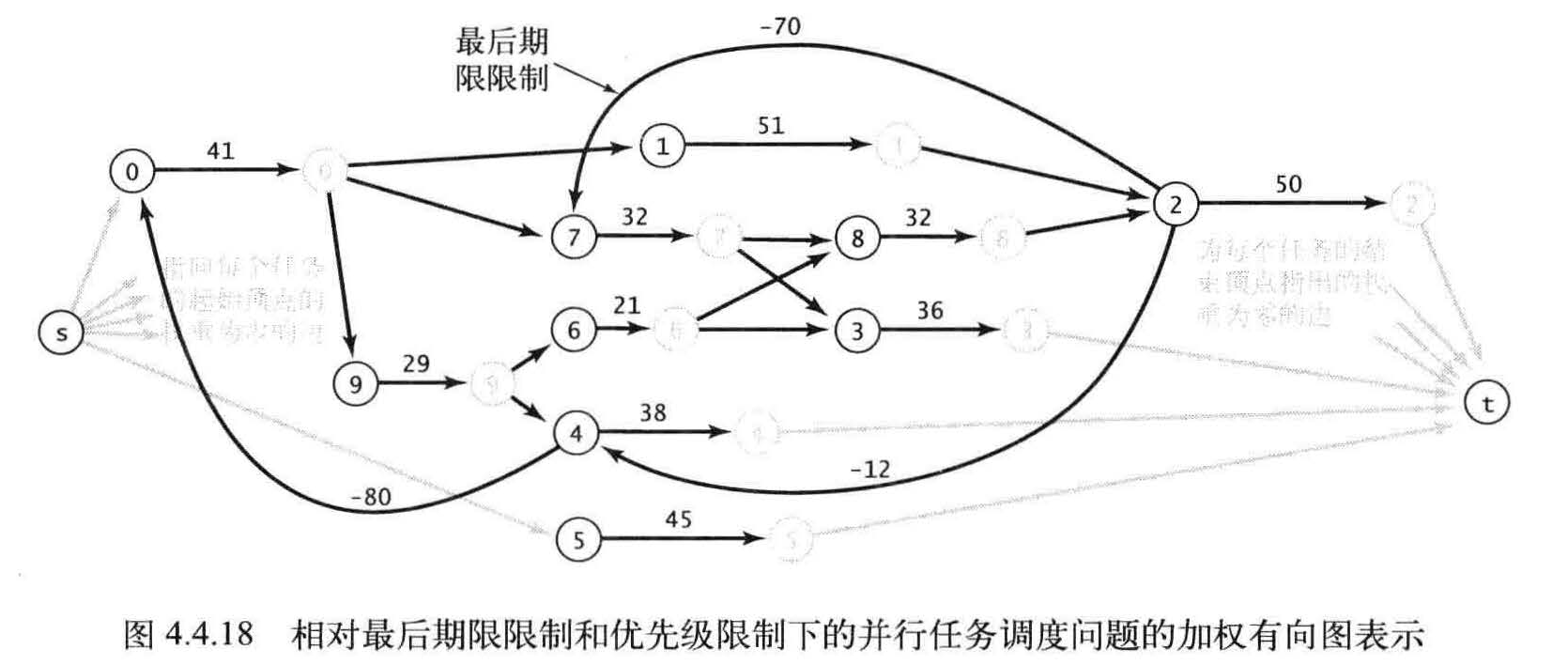
平行任务调度
优先级限制下的并行任务调度。给定一组需要完成的特定任务,以及一组关于任务完成的先后次序的优先级限制。在满足限制条件的前提下应该如何在若干相同的处理器上(数量不限)安排任务并在最短的时间内完成所有任务?
假设任意可用的处理器都能在任务所需的时间内完成它,那么
我们的重点就是尽早安排每一个任务。
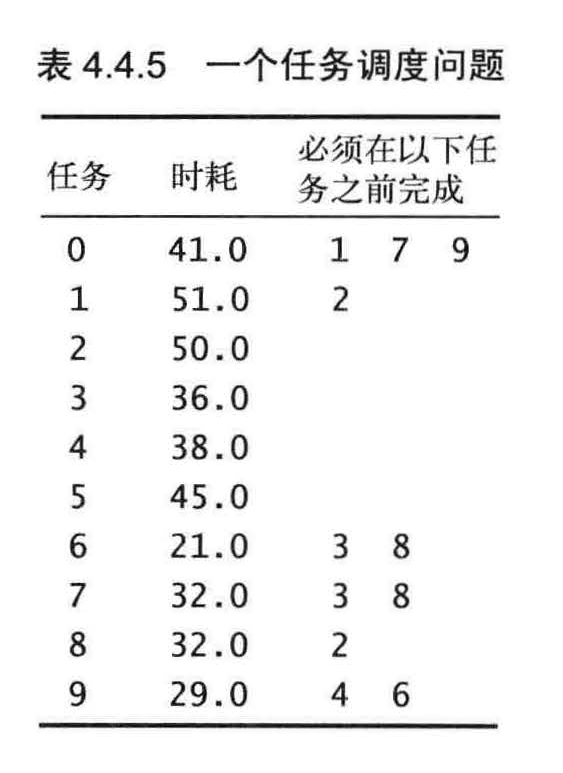
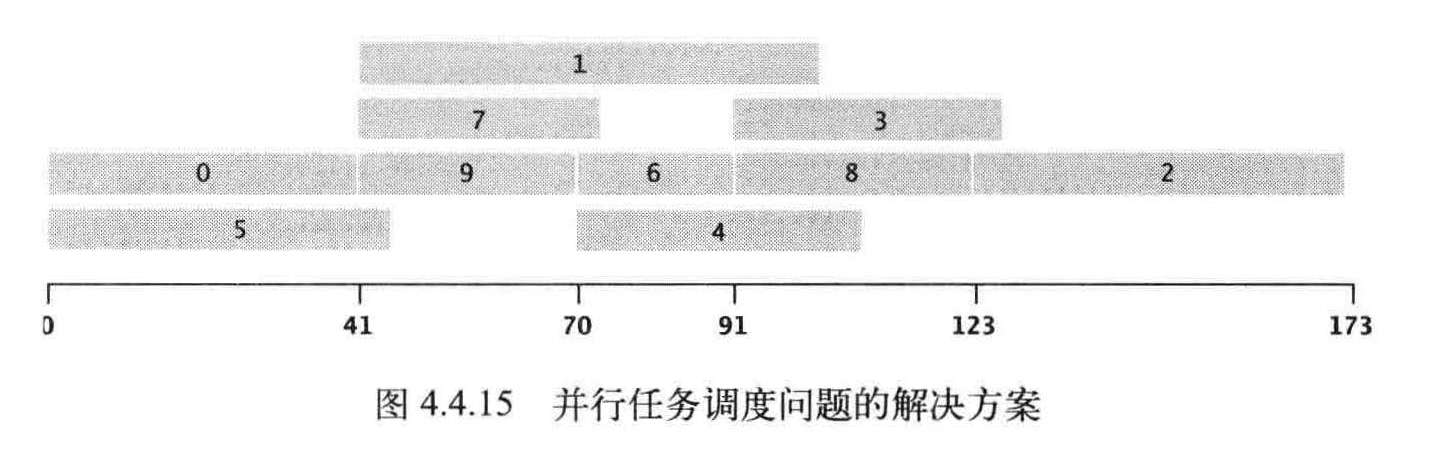
解决这个问题最主要的要解决关键路径
这个问题所需的最短时间为173.0 。这份调度方案满足了所有限制条件,没有其他调度方案能比它耗时更少,因为任务必须按照0 ----> 9 ----> 6 ----> 8 ----> 2 的顺序完成。这个顺序就是这个问题的关键路径。由优先级限制指定的每一列任务都代表了调度方案的一种可能的时间下限。如果将一系列任务的长度定义为完成所有任务的最早可能时间,那么最长的任务序列就是问题的关键路径,因为在这份任务序列中任何任务的启动延迟都会影响到整个项目的完成时间。
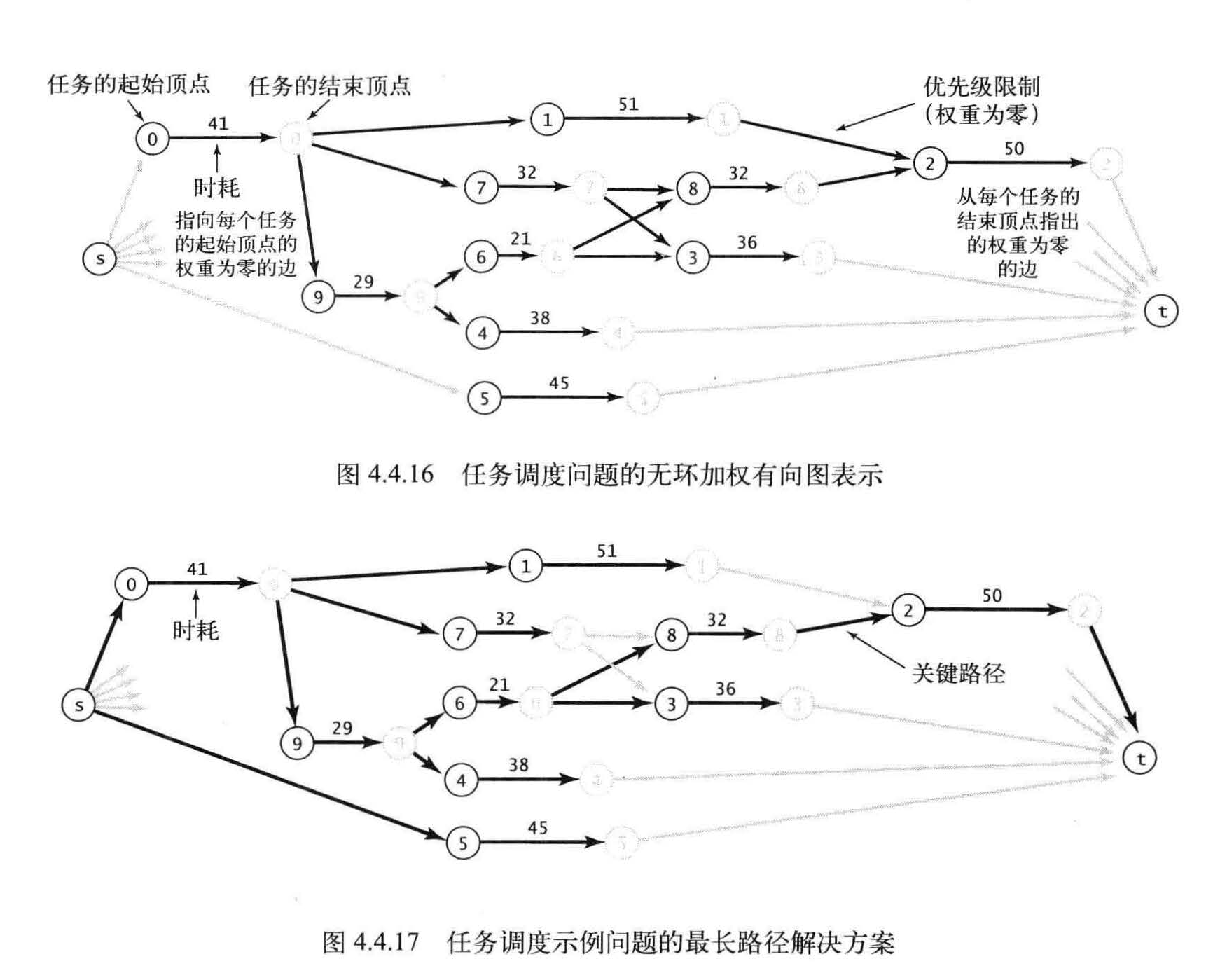
图4.4.16 显示的是示例任务所对应的图
图4.4 . 17 则显示的是最长路径的答案。
调度问题其实就是最长路径问题。
在图中每个任务都对应着三条边(从起点到起始顶点、从结束顶点到终点的权重为零的边,以及一条从起始顶点到结束顶点的边),每个优先级限制条件都对应着一条边。
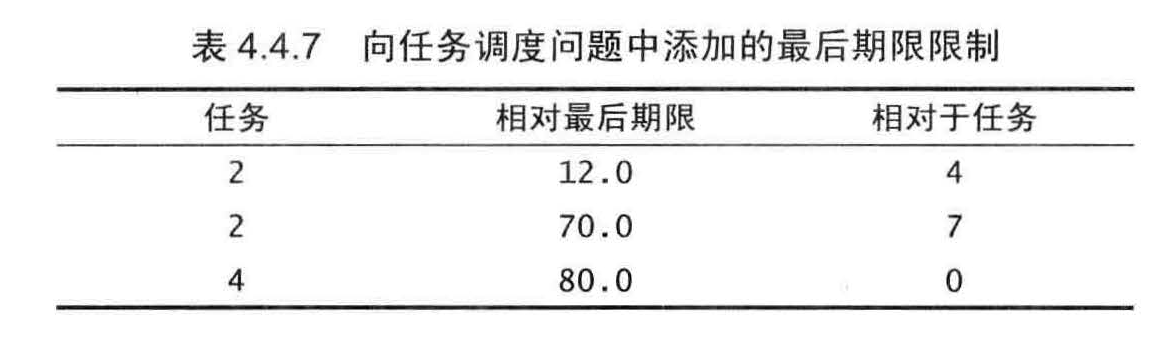
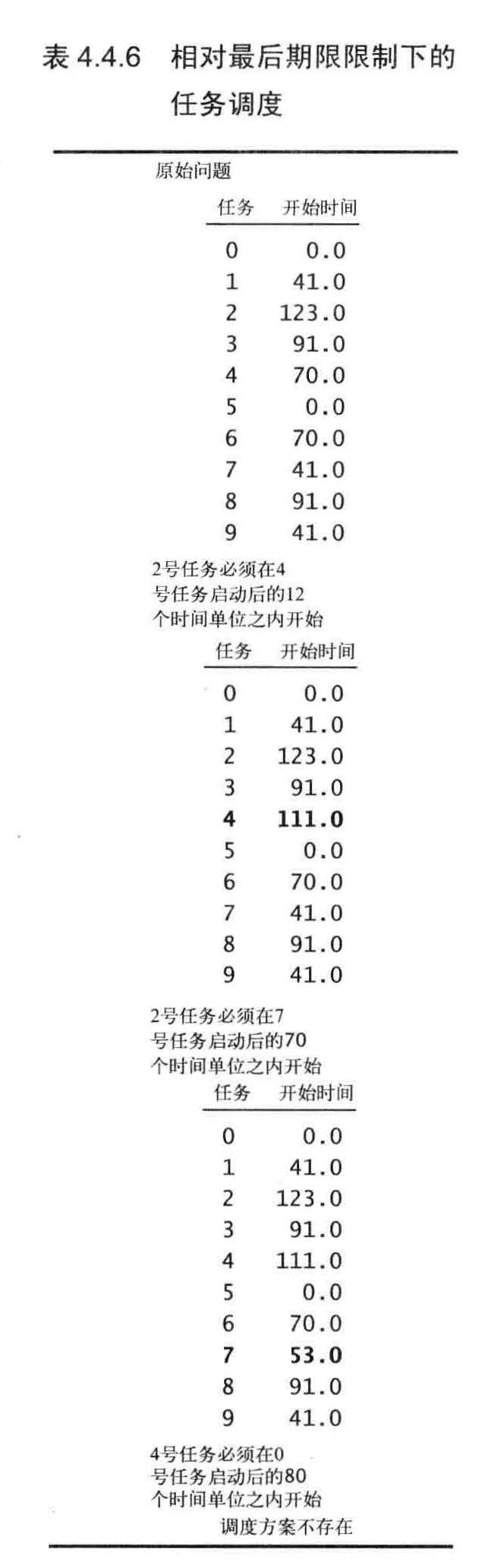
相对最后期限的并行任务调度
相对最后期限限制下的并行任务调度问题是一个加权有向图中的最短路径问题(可能存在环和负权重边) 。
负权重加权有向图的最短路径
也许最明显的改变就是当存在负权重的边时,权重较小的路径含有的边可能会比权重较大的路径更多。在只存在正权重的边时,我们的重点在于寻找近路;但当存在负权重的边时,我们可能会为了经过负权重的边而绕弯。这种效应使得我们要将查找“最短“路径的感觉转变为对算法本质的理解。
中间探究过程不说了,直接说结论
负权重环:加权有向图中的负权重环是一个总权重(环上的所有边的权重之和)为负的有向环。
假设从s 到可达的某个顶点v 的路径上的某个顶点在一个负权重环上。在这种情况下,从s 到v 的最短路径是不可能存在的,因为可以用这个负权重环构造权重任意小的路径。换句话说,在负权重环存在的情况下,最短路径问题是没有意义的
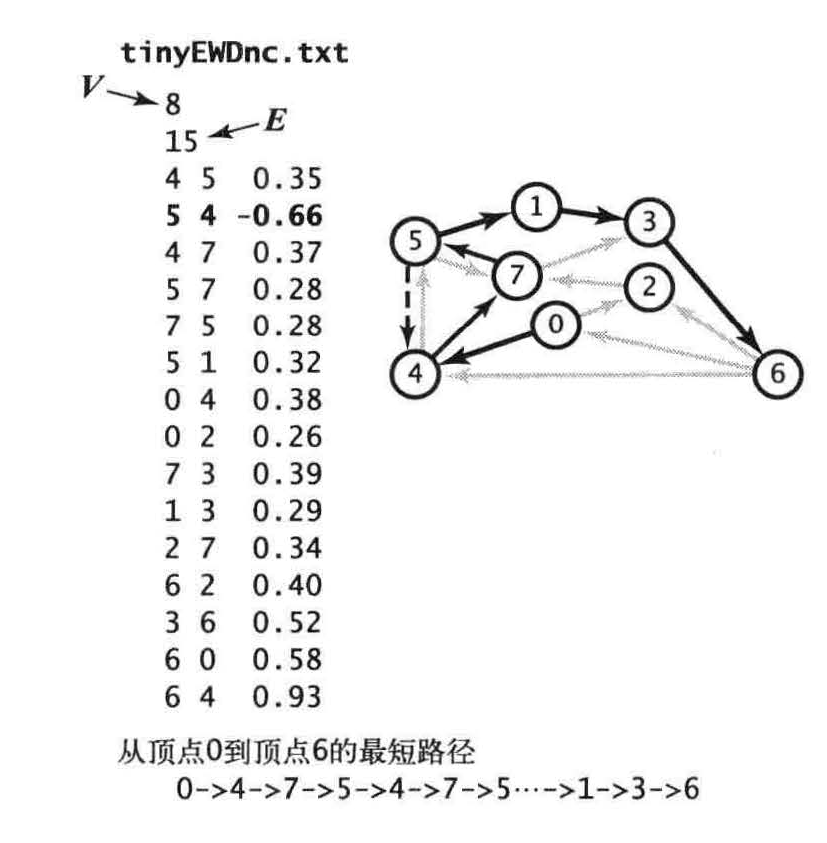
4,7,5,4,7,5不停兜圈子最短路径就会不停减少。所以最短路径失去了意义。
要求最短路径上的任意顶点都不存在负权重环意味着最短路径是简单的,而且与正权重边的图一样都能够得到此类顶点的最短路径树。
之前算法都是限制的。1:不允许负权重环的存在。2:不接受有向环。
基于队列的Bellman-Ford 算法
只有上一轮中的distTo[]值发生变化的顶点指出的边才能够改变其他distTo[] 元素的值。为了记录这样的顶点,
我们使用了一条FIFO 队列首先将起点加入队列,然后按照以下步骤计算最短路径树。
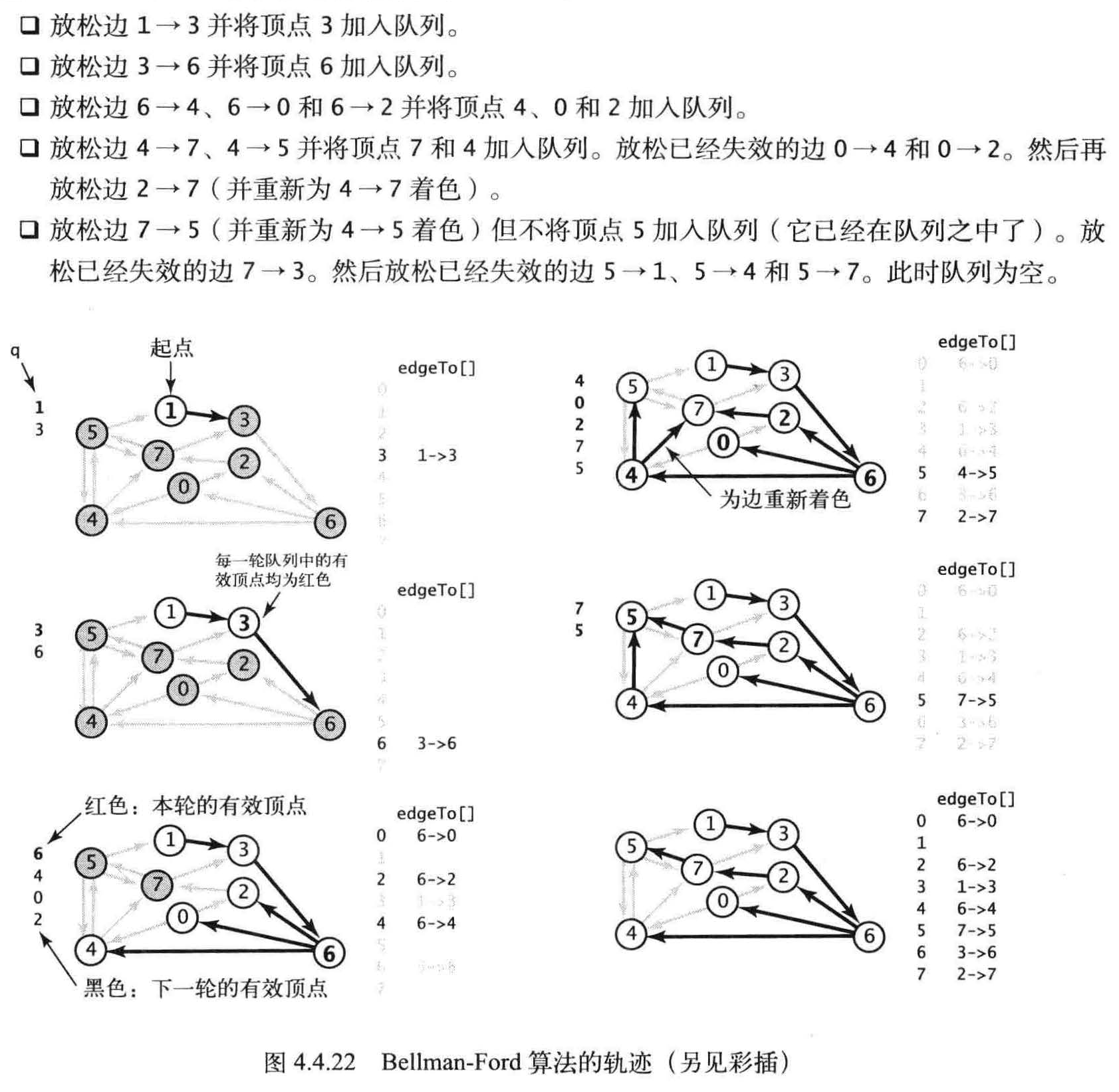
Bellman-Ford 算法基于以下两种其他的数据结构:
- 一条用来保存即将被放松的顶点的队列q ;
- 一个由顶点索引的boolean 数组onQ[] , 用来指示顶点是否已经存在于队列中,
顶点重复插入队列。
在某一轮中,改变了edgeTo[] 和distTo [] 的值的所有顶点都会在下一轮中处理。
负权重的边
- 放松边0→2 和0→4 并将顶点2 、4 加入队列。
- 放松边2→7 并将顶点7 加入队列。放松边4→5 并将顶点5 加入队列。然后放松失效的边
4→7 。 - 放松边7→3 和5 →1 并将顶点3 和1 加入队列。放松失效的边5 → 4 和5 →7 。
- 放松边3→6 并将顶点6 加入队列。放松失效的边1→3 。
- 放松边6→4 并将顶点4 加入队列。这条负权重边使得到顶点4 的路径变短, 因此它的边需要被再次放松(它们在第二轮中已经被放松过) 。从起点到顶点5 和1 的距离巳经失效并会在下一轮中修正。
- 放松边4 →5 并将顶点5 加入队列。放松失效的边4 →7 。
- 放松边5→1 并将顶点1 加入队列。放松失效的边5 →4 和5→7 。
- 放松无效的边1→3 。队列为空。
将所有边放松V 轮之后当且仅当队列非空时有向图中才存在从起点可达的负权重环。
如果是这样, edgeTo [] 数组所表示的子图中必然含有这个负权重环。因此,要实现
negativeCycl e() , 会根据edgeTo[] 中的边构造一幅加权有向图并在该图中检测环。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace SuddenGale.AlgorithmEngine.Graph
{
public class BellmanFordSP
{
// for floating-point precision issues
private static readonly double EPSILON = 1E-14;
/// <summary>
/// 从起点到某个顶点的路径长度,
/// distTo[v] = distance of shortest s->v path,
/// </summary>
private double[] distTo;
/// <summary>
/// 从起点到某个顶点的最后一条边,
/// edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest s->v path
/// </summary>
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo;
/// <summary>
/// onQueue[v] = is v currently on the queue?
/// 该顶点是否存在于队列中
/// </summary>
private bool[] onQueue;
/// <summary>
/// 正在被放松的顶点,
/// queue of vertices to relax
/// </summary>
private Queue<int> queue;
/// <summary>
/// relax的调用次数,
/// number of calls to relax(),
/// </summary>
private int cost;
/// <summary>
/// edgeTo[]中的是否有负权重环
/// negative cycle (or null if no such cycle)
/// </summary>
private IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> cycle;
public BellmanFordSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s)
{
distTo = new double[G.Vertic()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.Vertic()];
onQueue = new bool[G.Vertic()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.PositiveInfinity;
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// Bellman-Ford algorithm
queue = new Queue<int>();
queue.Enqueue(s);
onQueue[s] = true;
while (queue.Any() && !HasNegativeCycle())
{
int v = queue.Dequeue();
onQueue[v] = false;
Relax(G, v);
}
if(!Check(G, s))
throw new ArgumentException("check return false ");
}
// relax vertex v and put other endpoints on queue if changed
private void Relax(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int v)
{
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.Adj(v))
{
int w = e.To();
if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.Weight() + EPSILON)
{
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.Weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
if (!onQueue[w])//只有上一轮中发送变化的值才会改变,防止将顶点重复插入队列
{
queue.Enqueue(w);
onQueue[w] = true;
}
}
if (++cost % G.Vertic() == 0)//负环会造成循环,导致放松的次数一直增加,最总会达到顶点数,这个时候在最小生成树上一定能检测出负环
{
FindNegativeCycle();
if (HasNegativeCycle())
return; // found a negative cycle
}
}
}
public bool HasNegativeCycle()
{
return cycle != null;
}
public IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> NegativeCycle()
{
return cycle;
}
// by finding a cycle in predecessor graph
private void FindNegativeCycle()
{
int V = edgeTo.Length;
EdgeWeightedDigraph spt = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(V);//在最短路径上肯定存在负环
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (edgeTo[v] != null)
spt.AddEdge(edgeTo[v]);
EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle finder = new EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle(spt);//所以只在最短路径上寻找环,找到的环一定是负环
cycle = finder.Cycle();
}
public double DistTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
if (HasNegativeCycle())
throw new ArgumentException("Negative cost cycle exists");
return distTo[v];
}
public bool HasPathTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] < Double.PositiveInfinity;
}
public IEnumerable<DirectedEdge> PathTo(int v)
{
ValidateVertex(v);
if (HasNegativeCycle())
throw new ArgumentException("Negative cost cycle exists");
if (!HasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<DirectedEdge>();
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.From()])
{
path.Push(e);
}
return path;
}
// check optimality conditions: either
// (i) there exists a negative cycle reacheable from s
// or
// (ii) for all edges e = v->w: distTo[w] <= distTo[v] + e.weight()
// (ii') for all edges e = v->w on the SPT: distTo[w] == distTo[v] + e.weight()
private bool Check(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s)
{
// has a negative cycle
if (HasNegativeCycle())
{
double weight = 0.0;
foreach (DirectedEdge e in NegativeCycle())
{
weight += e.Weight();
}
if (weight >= 0.0)
{
Console.WriteLine("error: weight of negative cycle = " + weight);
return false;
}
}
// no negative cycle reachable from source
else
{
// check that distTo[v] and edgeTo[v] are consistent
if (distTo[s] != 0.0 || edgeTo[s] != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("distanceTo[s] and edgeTo[s] inconsistent");
return false;
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
if (v == s) continue;
if (edgeTo[v] == null && distTo[v] != Double.PositiveInfinity)
{
Console.WriteLine("distTo[] and edgeTo[] inconsistent");
return false;
}
}
// check that all edges e = v->w satisfy distTo[w] <= distTo[v] + e.weight()
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
foreach (DirectedEdge e in G.Adj(v))
{
int w = e.To();
if (distTo[v] + e.Weight() < distTo[w])
{
Console.WriteLine("edge " + e + " not relaxed");
return false;
}
}
}
// check that all edges e = v->w on SPT satisfy distTo[w] == distTo[v] + e.weight()
for (int w = 0; w < G.Vertic(); w++)
{
if (edgeTo[w] == null) continue;
DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[w];
int v = e.From();
if (w != e.To()) return false;
if (distTo[v] + e.Weight() != distTo[w])
{
Console.WriteLine("edge " + e + " on shortest path not tight");
return false;
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Satisfies optimality conditions");
return true;
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void ValidateVertex(int v)
{
int V = distTo.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
}
测试
public void BellmanFordSP()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyEWDn.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedDigraph(stream);
int s = 0;
BellmanFordSP sp = new BellmanFordSP(G, s);
if (sp.HasNegativeCycle())
{
Console.WriteLine($"{s} has negative cycle");
foreach (DirectedEdge e in sp.NegativeCycle())
{
Console.Write(e);
}
}
else
{
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertic(); v++)
{
if (sp.HasPathTo(v))
{
Console.Write($"{s} to {v} ({sp.DistTo(v)}) ");
foreach (DirectedEdge e in sp.PathTo(v))
{
Console.Write(e + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"{s} to {v} no path.");
}
}
}
}
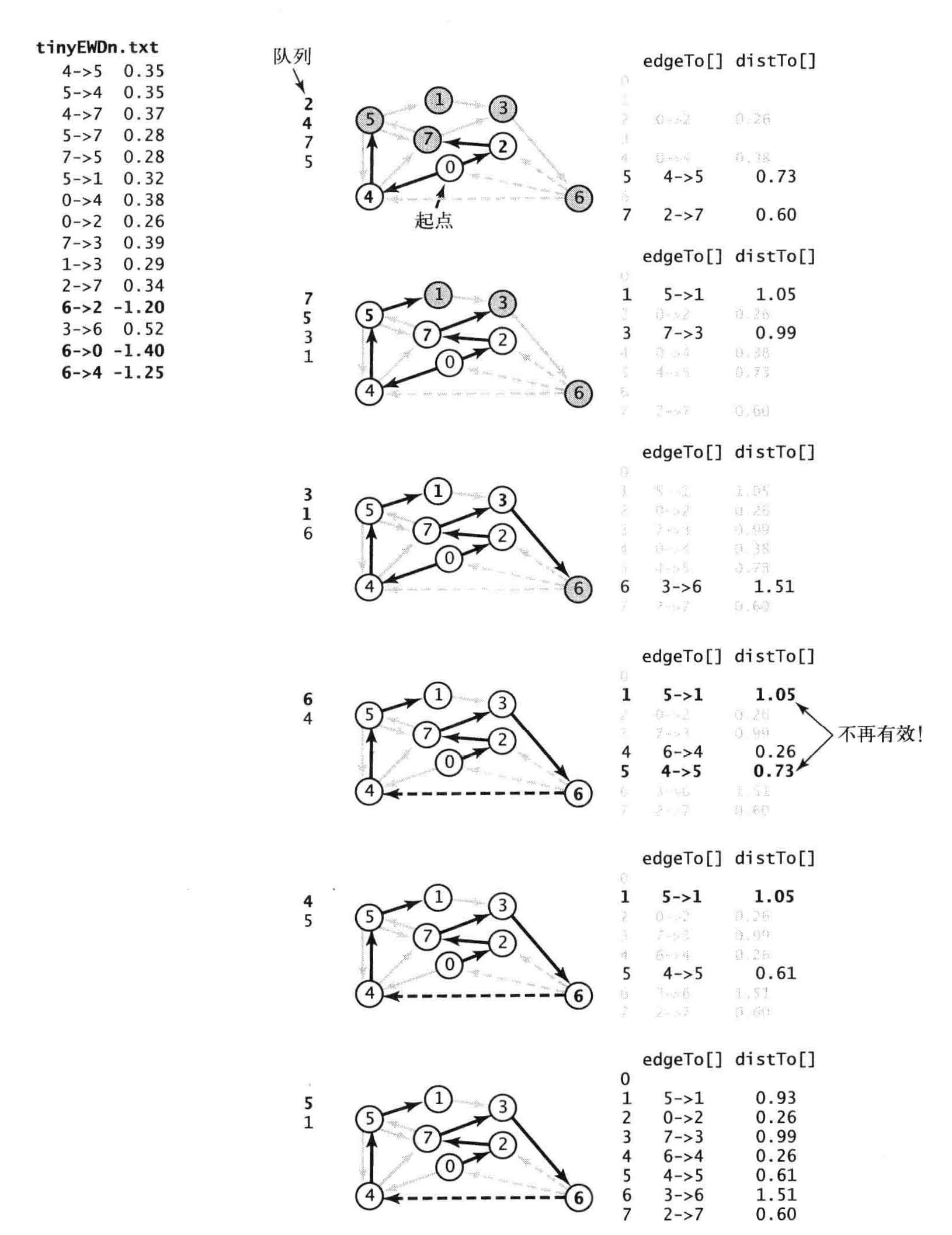
// 0 to 0 (0)
// 0 to 1 (0.93) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39 3->6 0.52 6->4 -1.25 4->5 0.35 5->1 0.32
// 0 to 2 (0.26) 0->2 0.26
// 0 to 3 (0.99) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39
// 0 to 4 (0.26) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39 3->6 0.52 6->4 -1.25
// 0 to 5 (0.61) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39 3->6 0.52 6->4 -1.25 4->5 0.35
// 0 to 6 (1.51) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34 7->3 0.39 3->6 0.52
// 0 to 7 (0.6) 0->2 0.26 2->7 0.34
}

您的资助是我最大的动力!
金额随意,欢迎来赏!
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/lovexinyi/
版权:本文版权归作者和博客园共有
转载:欢迎转载,但未经作者同意,必须保留此段声明;必须在文章中给出原文链接;否则必究法律责任


【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步