算法基础<六> 加权无向图
加权无向图
最小生成树:一棵含有其所有顶点的无环连通子图,一幅加权无向图的最小生成树(MST)是它的一棵权值(树中所有边的权值之和)最小的生成时。
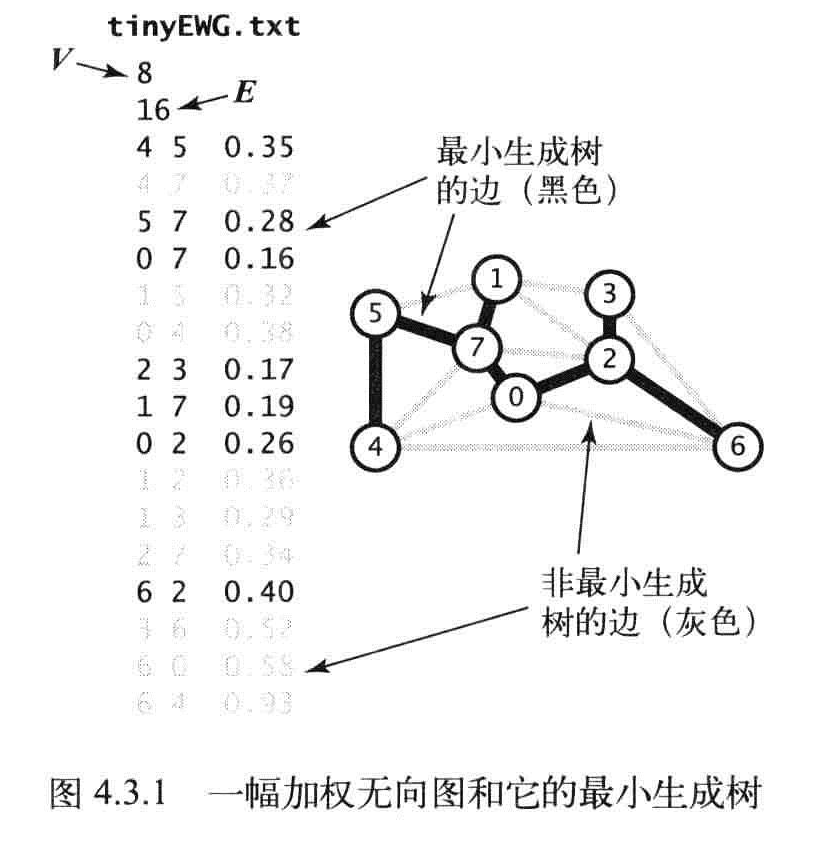
约定
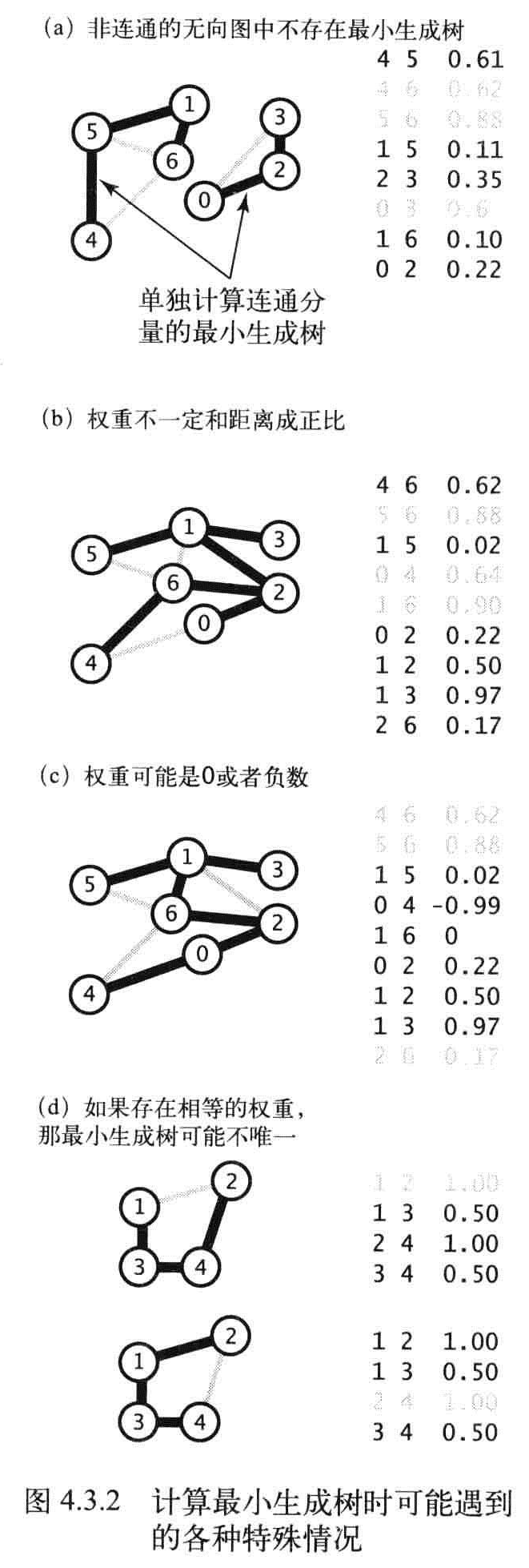
- 只考虑连通图
- 边的权重不一定表示距离
- 边的权重可能是0或者负数
- 所有边的权重都各不相同
public class Edge : IComparable<Edge>
{
private readonly int _v;//顶点总数
private readonly int _w;//边的总数
private readonly double _weight;//邻接表
public Edge(int v, int w, double weight)
{
if (v < 0) throw new ArgumentException("vertex index must be a nonnegative integer");
if (w < 0) throw new ArgumentException("vertex index must be a nonnegative integer");
if (Double.IsNaN(weight)) throw new ArgumentException("Weight is NaN");
this._v = v;
this._w = w;
this._weight = weight;
}
public double Weight()
{
return _weight;
}
public int Either()
{
return _v;
}
public int Other(int vertex)
{
if (vertex == _v) return _w;
else if (vertex == _w) return _v;
else throw new ArgumentException("Illegal endpoint");
}
public int CompareTo(Edge that)
{
return this._weight.CompareTo(that.Weight());
}
public override String ToString()
{
return $"{_v:D2}-{_w:D2} {_weight}";
}
}
public class EdgeWeightedGraph
{
private static readonly String NEWLINE = System.Environment.NewLine;
private readonly int _vertices;
private int _edge;
private LinkedBagNet<Edge>[] _adj;
public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V)
{
if (V < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of vertices must be nonnegative");
this._vertices = V;
this._edge = 0;
_adj = new LinkedBagNet<Edge>[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
_adj[v] = new LinkedBagNet<Edge>();
}
}
public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V, int E): this(V)
{
if (E < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
Random random=new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
int v = random.Next(V);
int w = random.Next(V);
double weight = Math.Round(100 * random.NextDouble()) / 100.0;
Edge e = new Edge(v, w, weight);
AddEdge(e);
}
}
public EdgeWeightedGraph(StreamReader stream)
{
if (stream == null) throw new ArgumentException("argument is null");
try
{
this._vertices = int.Parse(stream.ReadLine());
_adj = new LinkedBagNet<Edge>[_vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < _vertices; v++)
{
_adj[v] = new LinkedBagNet<Edge>();
}
int E = int.Parse(stream.ReadLine());
if (E < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
string line = stream.ReadLine().Trim();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(line) && line.Split(' ').Count() == 3)
{
int v = int.Parse(line.Split(' ')[0]);
int w = int.Parse(line.Split(' ')[1]);
double weight = double.Parse(line.Split(' ')[2]);
AddEdge(new Edge(v,w,weight));
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new ArgumentException("invalid input format in EdgeWeightedGraph constructor", e);
}
}
public EdgeWeightedGraph(EdgeWeightedGraph G):this(G._vertices)
{
this._edge = G.Edge();
for (int v = 0; v < G._vertices; v++)
{
Stack<Edge> reverse = new Stack<Edge>();
foreach (Edge e in G._adj[v])
{
reverse.Push(e);
}
foreach (Edge e in reverse)
{
_adj[v].Add(e);
}
}
}
public int Vertices()
{
return _vertices;
}
public int Edge()
{
return _edge;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
if (v < 0 || v >= _vertices)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (_vertices - 1));
}
public void AddEdge(Edge e)
{
int v = e.Either();
int w = e.Other(v);
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
_adj[v].Add(e);
_adj[w].Add(e);
_edge++;
}
public IEnumerable<Edge> Adj(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _adj[v];
}
public int Degree(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _adj[v].Length;
}
public IEnumerable<Edge> Edges()
{
LinkedBagNet<Edge> list = new LinkedBagNet<Edge>();
for (int v = 0; v < _vertices; v++)
{
int selfLoops = 0;
foreach (Edge e in _adj[v])
{
if (e.Other(v) > v)
{
list.Add(e);
}
// add only one copy of each self loop (self loops will be consecutive)
else if (e.Other(v) == v)
{
if (selfLoops % 2 == 0) list.Add(e);
selfLoops++;
}
}
}
return list;
}
public override String ToString()
{
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.Append(_vertices + " " + _edge + NEWLINE);
for (int v = 0; v < _vertices; v++)
{
s.Append(v + ": ");
foreach (Edge e in _adj[v])
{
s.Append(e + " ");
}
s.Append(NEWLINE);
}
return s.ToString();
}
}

树的两条最重要的性质:
- 用一条边连接树中的任意两个顶点都会产生一个新的环
- 从树中删去一条边将会得到两棵独立的树。
切分定理:图的一种切分是将图的所有顶点分为两个非空且不重复的两个集合。横切边的一条连接两个属于不同集合的顶点的边。
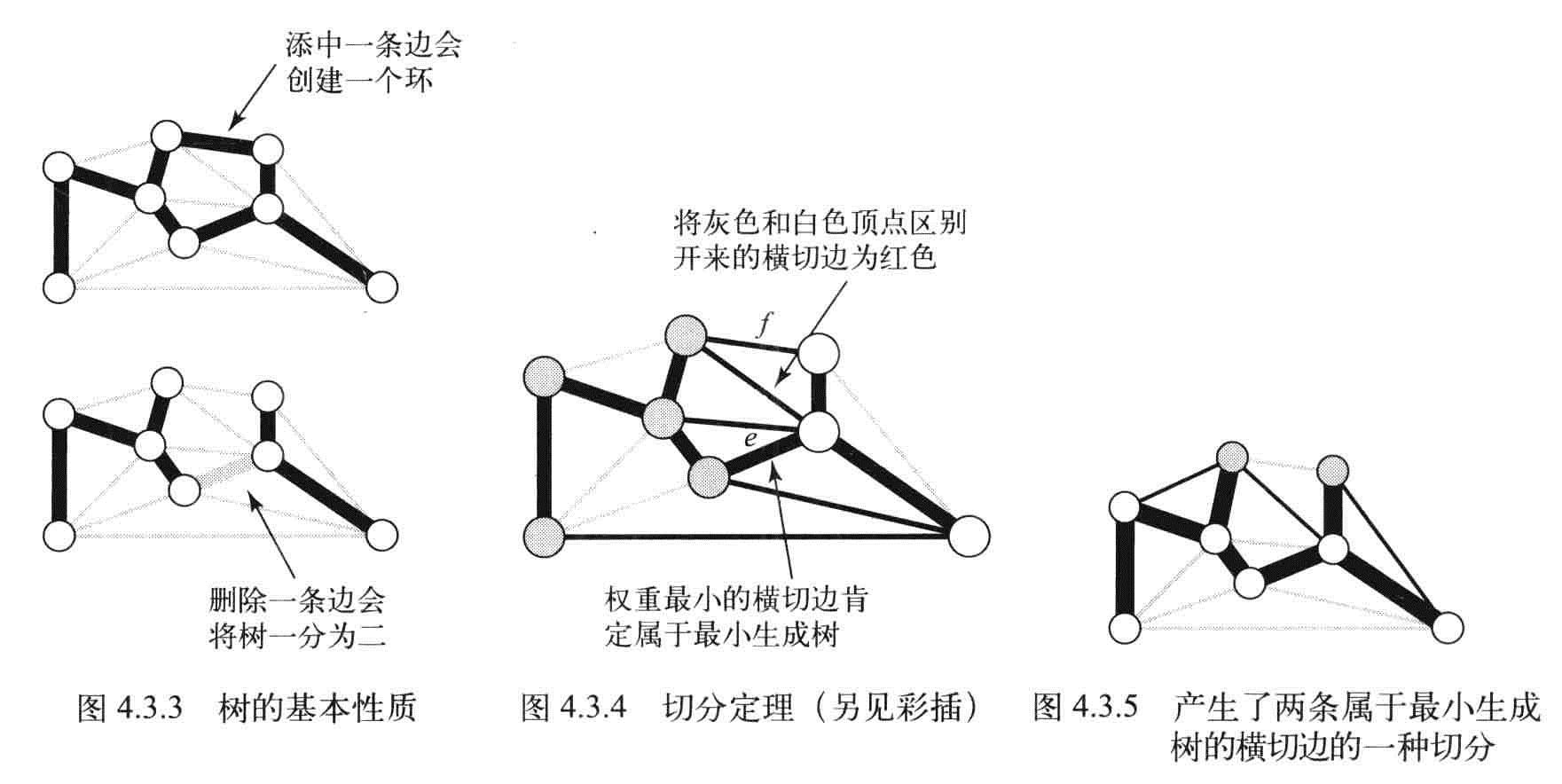
命题J(切分定理):在一幅加权图中,给定任意的切分,它的横切边中的权重最小者必然属于图的最小生成树。
贪心算法
使用切分定理找到最小生成树的一条边,不断重复直到找到最小生成树的所有边。

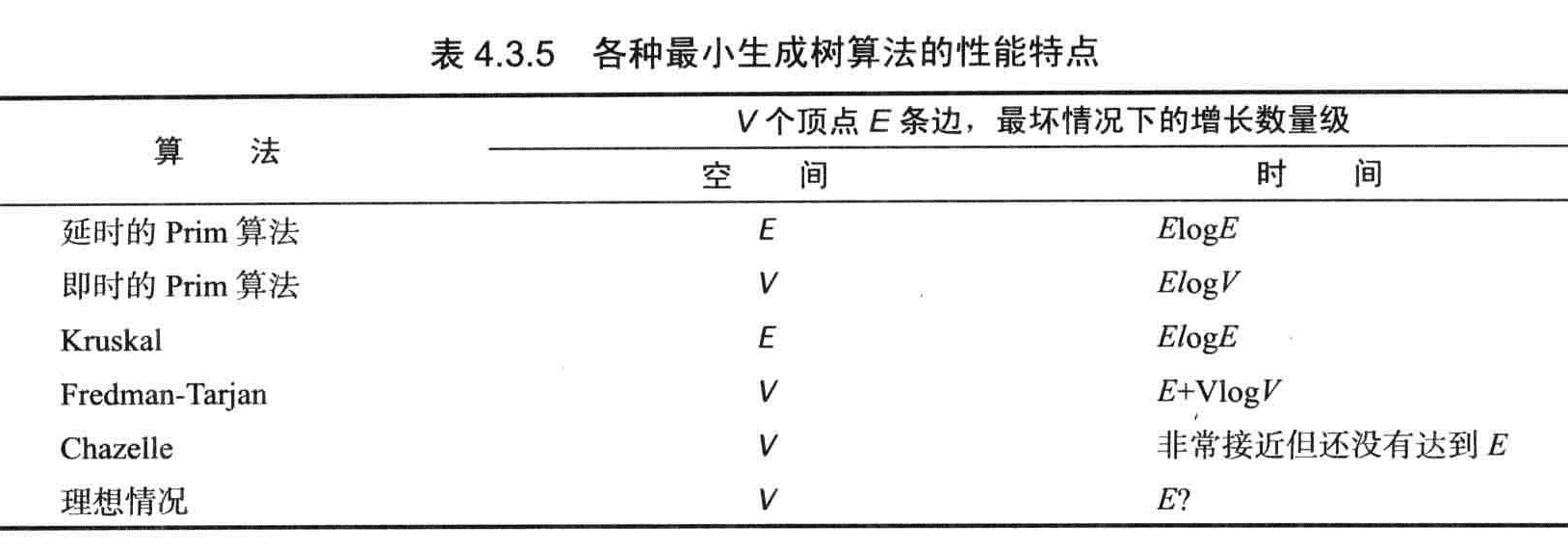
Prim算法
Prim算法能够得到任意加权无向图的最小生成树。
每一步都会为一棵生长中的树添加一条边。一开始这棵树只有一个顶点,然后会向它添加V-1条边。
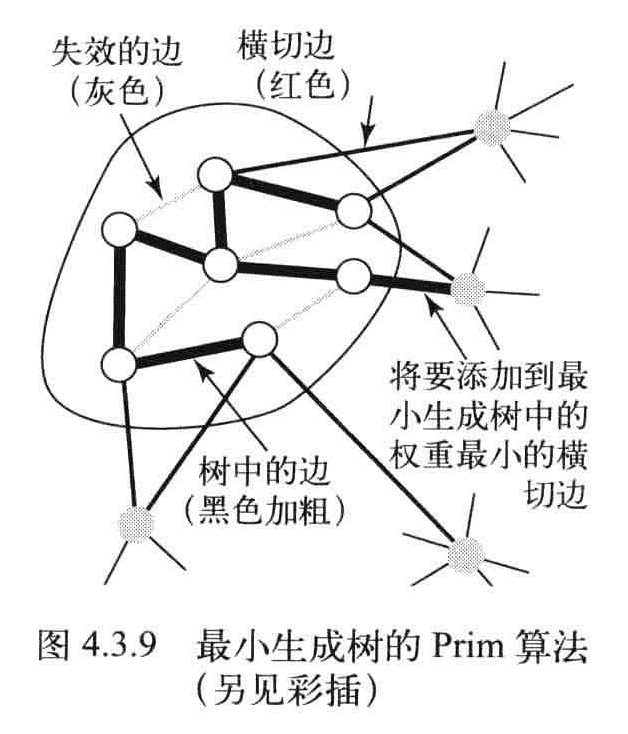
prim算法的核心是如何快速高校找到最小权重的横切边。失效的边是连接到已经在最小数的顶点,直到将所有顶点添加到最小树
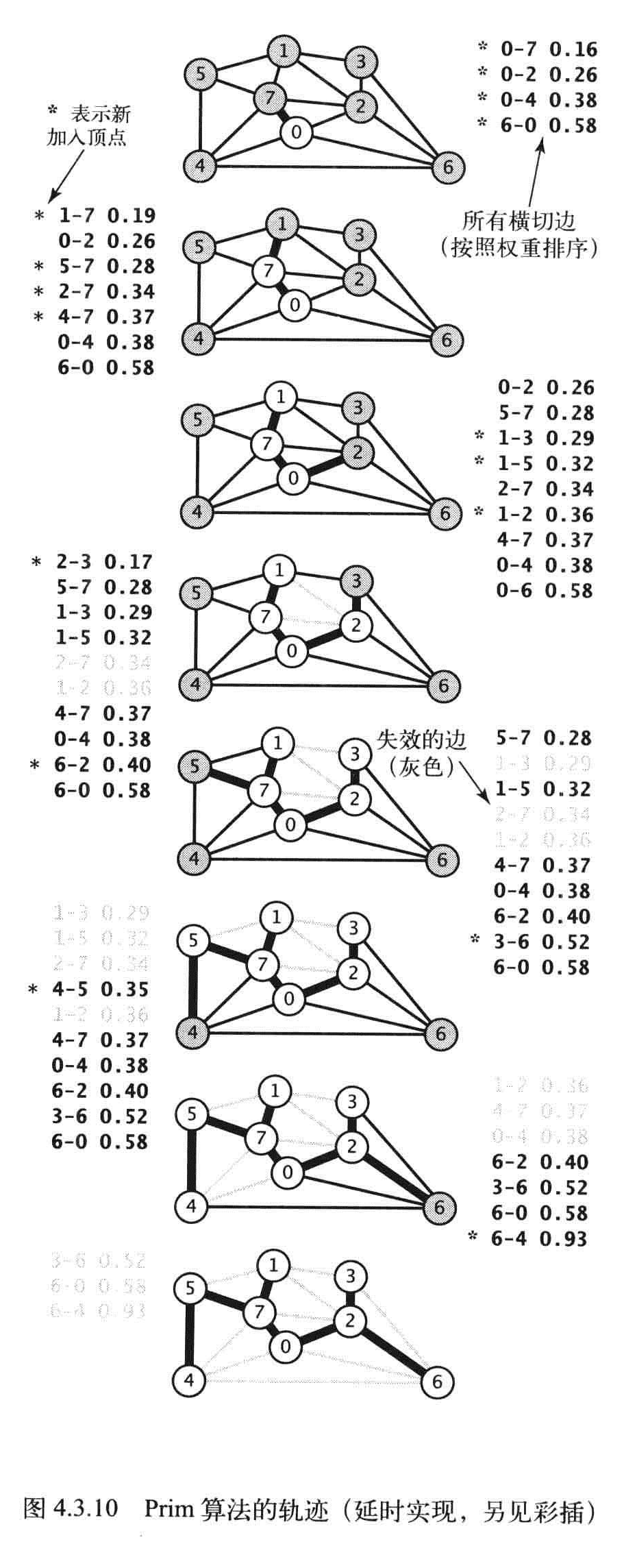
Prim算法的延时实现计算一幅含有V个顶点和E条边的连通加权无向图的最小生成树所需的空间与E成正比,所需的时间与ElogE成正比。
/// <summary>
/// 最小生成树
/// </summary>
public class LazyPrimMST
{
private static readonly double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12;//ε
private double _weight; // 最小生成树的总权重
private Queue<Edge> _mst; // 最小生成树的边
private bool[] _marked;
private MinPQNet<Edge> _pq; // 横切边(包括失效的边)
public LazyPrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G)
{
_mst = new Queue<Edge>();
_pq = new MinPQNet<Edge>();//最小优先队列,因为要找到最小的邻接边
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices(); v++)
if (!_marked[v]) prim(G, v);
}
private void prim(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int s)
{
scan(G, s);
while (_pq.Any())//直到优先队列中没有边
{
Edge e = _pq.DeleteMin(); // 找到最小优先队列
int v = e.Either(), w = e.Other(v); // 该边的两个顶点
if (_marked[v] && _marked[w]) continue;// lazy,这两个顶点已经被访问过就是失效边
_mst.Enqueue(e); // 另一个顶点没有访问过,就添加到最小生成树
_weight += e.Weight(); //计算总权重
if (!_marked[v]) scan(G, v);
if (!_marked[w]) scan(G, w); // 将新添加顶点的邻接表对应的边添加到最小优先队列
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 将其邻接表添加到队列中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="G"></param>
/// <param name="v"></param>
private void scan(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v)
{
_marked[v] = true;
foreach (Edge e in G.Adj(v))
if (!_marked[e.Other(v)]) _pq.Insert(e);//如果另一个顶点没有被访问过就将与该顶点的边添加到最小优先队列,不然就是失效边
}
public IEnumerable<Edge> Edges()
{
return _mst;
}
public double Weight()
{
return _weight;
}
private bool check(EdgeWeightedGraph G)
{
// check weight
double totalWeight = 0.0;
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
totalWeight += e.Weight();
}
if (Math.Abs(totalWeight - Weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON)
{
Console.Write($"Weight of edges does not equal weight(): {totalWeight} vs. {Weight()}\n");
return false;
}
// check that it is acyclic
UF uf = new UF(G.Vertices());
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
int v = e.Either(), w = e.Other(v);
if (uf.Find(v) == uf.Find(w))
{
Console.Write("Not a forest");
return false;
}
uf.Union(v, w);
}
// check that it is a spanning forest
foreach (Edge e in G.Edges())
{
int v = e.Either(), w = e.Other(v);
if (uf.Find(v) != uf.Find(w))
{
Console.Write("Not a spanning forest");
return false;
}
}
// check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions)
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
// all edges in MST except e
uf = new UF(G.Vertices());
foreach (Edge f in _mst)
{
int x = f.Either(), y = f.Other(x);
if (f != e) uf.Union(x, y);
}
// check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut
foreach (Edge f in G.Edges())
{
int x = f.Either(), y = f.Other(x);
if (uf.Find(x) != uf.Find(y))
{
if (f.Weight() < e.Weight())
{
Console.Write("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions");
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void LazyPrimMSTTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyEWG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedGraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedGraph(stream);
LazyPrimMST mst = new LazyPrimMST(G);
foreach (Edge e in mst.Edges())
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
Console.Write($"{mst.Weight()}\n");
}
//00 - 07 0.16
//01 - 07 0.19
//00 - 02 0.26
//02 - 03 0.17
//05 - 07 0.28
//04 - 05 0.35
//06 - 02 0.4
//1.81
}
Prim即时算法
改进上面的Prim算法
- 在优先队列中删除失效的边,优先队列中只包含树顶点和非树顶点之间的横切边。
- 在添加V之后只会更新W到最小树的权重。只需要保存最小的权重边即可。
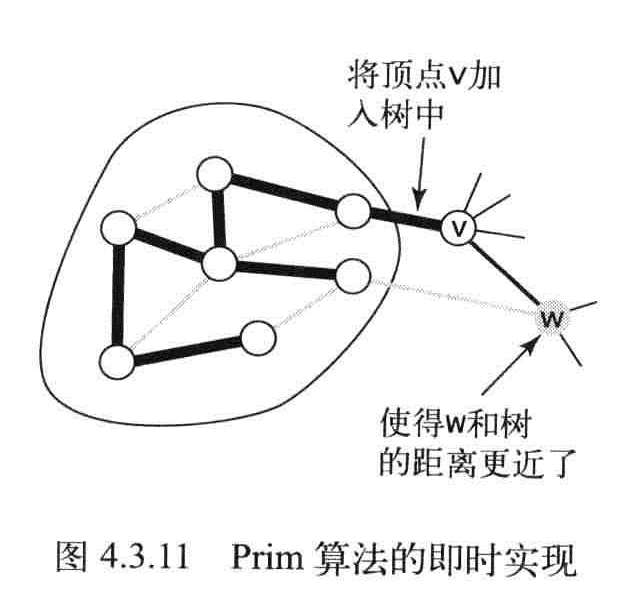
- 如果顶点v不在树中但至少含有一条边和树相连,那么edgeTo[v]是将v和树连接的最短边,distTo[v]为这条边的权重。
- 所有这类顶点v都保存在一条索引优先队列中,索引v关联的值是edgeTo[v]的边的权重
关键在于优先队列中的最小键即是权重最小的横切边的权重了,而和它相关联的顶点v就是下一个将被添加到树种的顶点。
public class PrimMST
{
private static readonly double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12;
private Edge[] edgeTo; //顶点v距离树最近的边
private double[] distTo; // 顶点v距离树最近的权重
private bool[] marked; // 如果v在树中则为true
private KeyMinPQNet<Double> pq;//有效的横切边
public PrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G)
{
edgeTo = new Edge[G.Vertices()];
distTo = new double[G.Vertices()];
marked = new bool[G.Vertices()];
pq = new KeyMinPQNet<Double>(G.Vertices());
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.PositiveInfinity;//正无穷,为常数,应该是最大数
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices(); v++)
if (!marked[v]) prim(G, v);
}
private void prim(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int s)
{
distTo[s] = 0.0;//distTo[s]=0.0
pq.Insert(s, distTo[s]);//将序号和权重压入
while (!pq.IsEmpty)
{
int v = pq.DeleteMin();//找到最小的权重
scan(G, v);
}
}
private void scan(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v)
{
marked[v] = true;
foreach (Edge e in G.Adj(v))//查找v的邻接边
{
int w = e.Other(v);//获取边对应的顶点
if (marked[w]) continue; //邻接顶点访问过
if (e.Weight() < distTo[w])//更新权重
{
distTo[w] = e.Weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
if (pq.Contains(w)) pq.DecreaseKey(w, distTo[w]);//更新
else pq.Insert(w, distTo[w]);//添加
}
}
}
public IEnumerable<Edge> Edges()
{
Queue<Edge> mst = new Queue<Edge>();
for (int v = 0; v < edgeTo.Length; v++)
{
Edge e = edgeTo[v];
if (e != null)
{
mst.Enqueue(e);
}
}
return mst;
}
public double Weight()
{
double weight = 0.0;
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
weight += e.Weight();
return weight;
}
private bool check(EdgeWeightedGraph G)
{
// check weight
double totalWeight = 0.0;
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
totalWeight += e.Weight();
}
if (Math.Abs(totalWeight - Weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON)
{
Console.Write($"Weight of edges does not equal weight():{totalWeight} vs. { Weight()}\n");
return false;
}
// check that it is acyclic
UF uf = new UF(G.Vertices());
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
int v = e.Either(), w = e.Other(v);
if (uf.Find(v) == uf.Find(w))
{
Console.Write("Not a forest");
return false;
}
uf.Union(v, w);
}
// check that it is a spanning forest
foreach (Edge e in G.Edges())
{
int v = e.Either(), w = e.Other(v);
if (uf.Find(v) != uf.Find(w))
{
Console.Write("Not a spanning forest");
return false;
}
}
// check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions)
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
// all edges in MST except e
uf = new UF(G.Vertices());
foreach (Edge f in Edges())
{
int x = f.Either(), y = f.Other(x);
if (f != e) uf.Union(x, y);
}
// check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut
foreach (Edge f in G.Edges())
{
int x = f.Either(), y = f.Other(x);
if (uf.Find(x) != uf.Find(y))
{
if (f.Weight() < e.Weight())
{
Console.Write("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions");
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void PrimMSTTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyEWG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedGraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedGraph(stream);
PrimMST mst = new PrimMST(G);
foreach (Edge e in mst.Edges())
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
Console.Write($"{mst.Weight()}\n");
}
//01 - 07 0.19
//00 - 02 0.26
//02 - 03 0.17
//04 - 05 0.35
//05 - 07 0.28
//06 - 02 0.4
//00 - 07 0.16
//1.81
}
算法轨迹
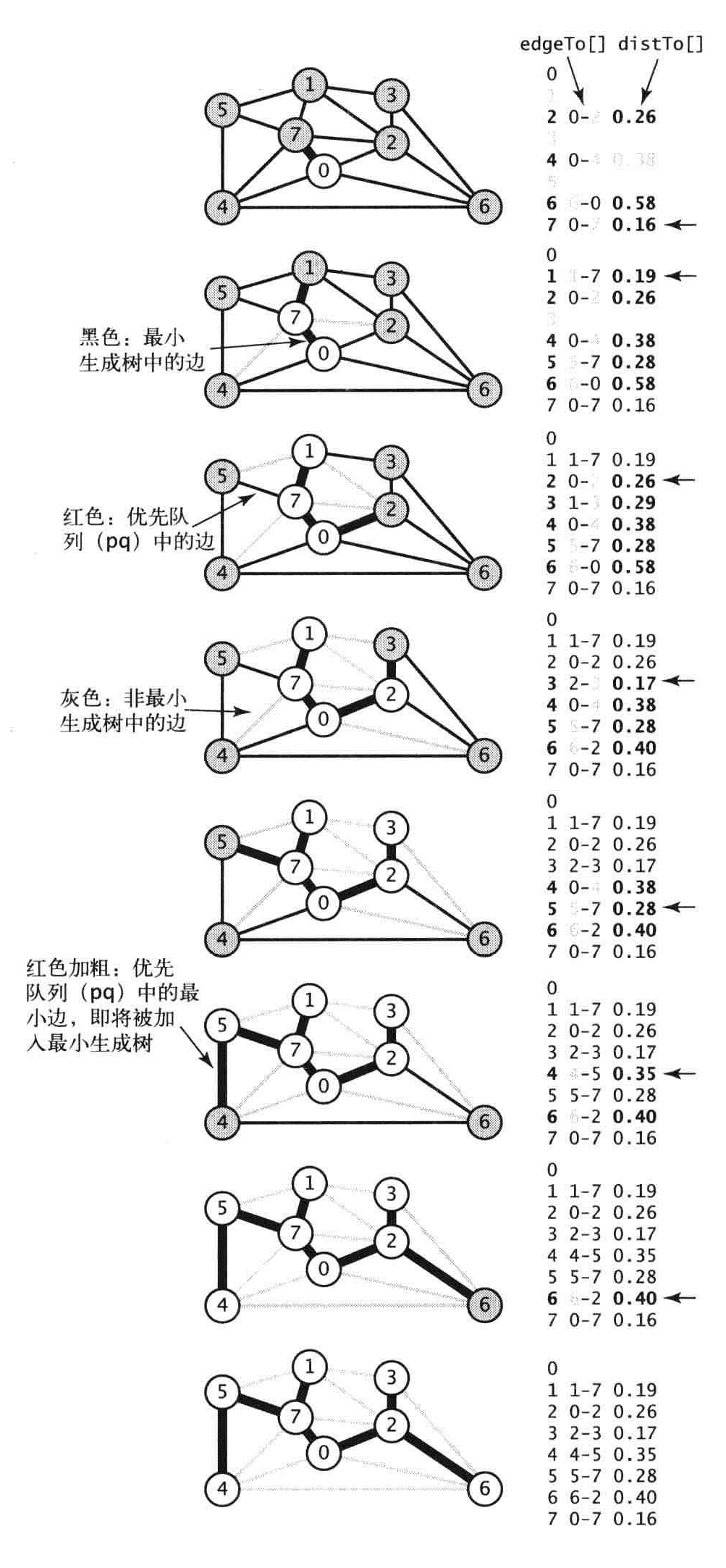
找到一幅连通的加权无向图的最小生成树,所需的时间ElogV成正比。
命题N:Prim算法的即时实现计算一幅含有V个顶点和E条边的连通加权无向图的最小生成树所需的空间和V成正比,所需的时间和ElogV成正比。
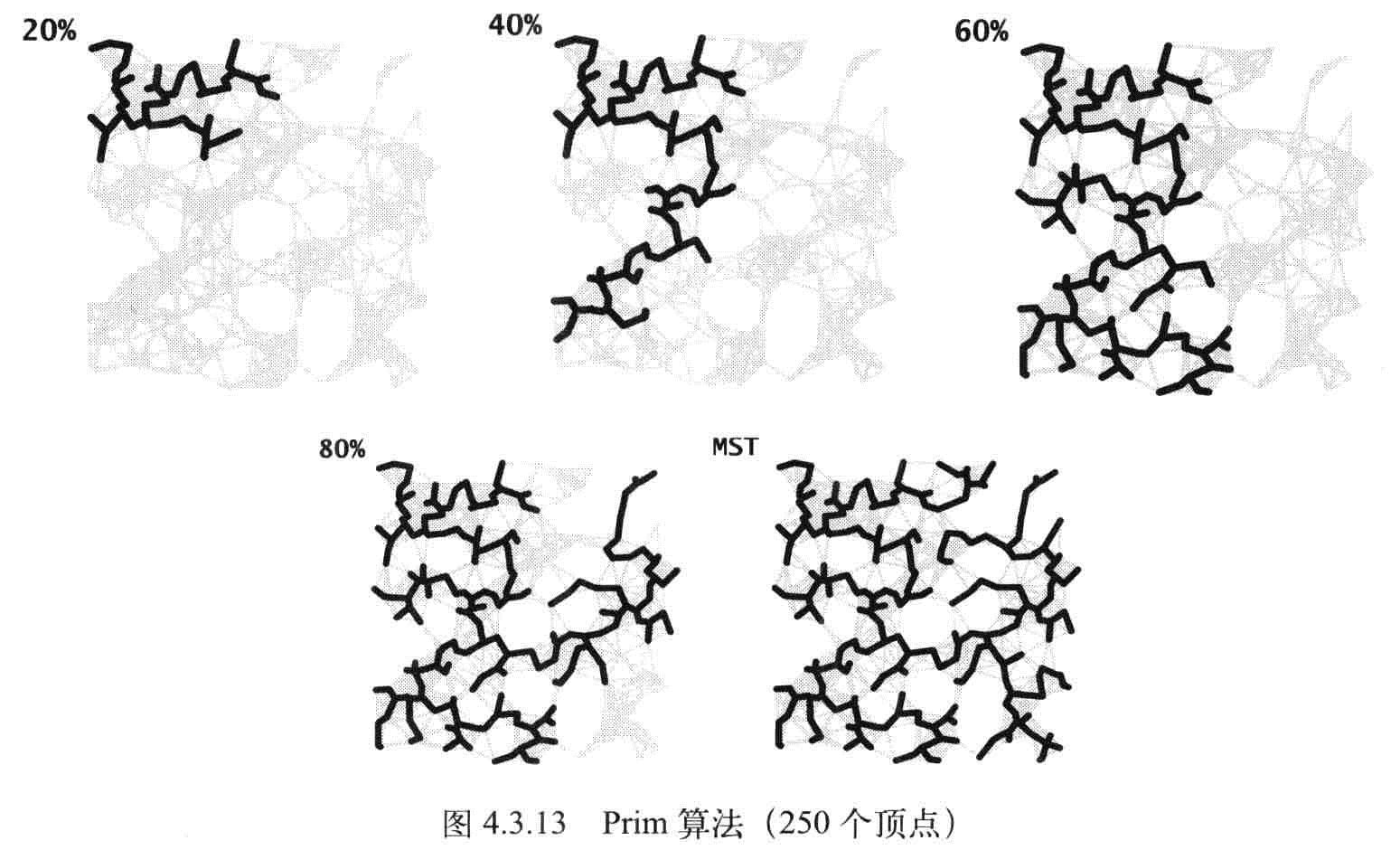
Kruskal算法
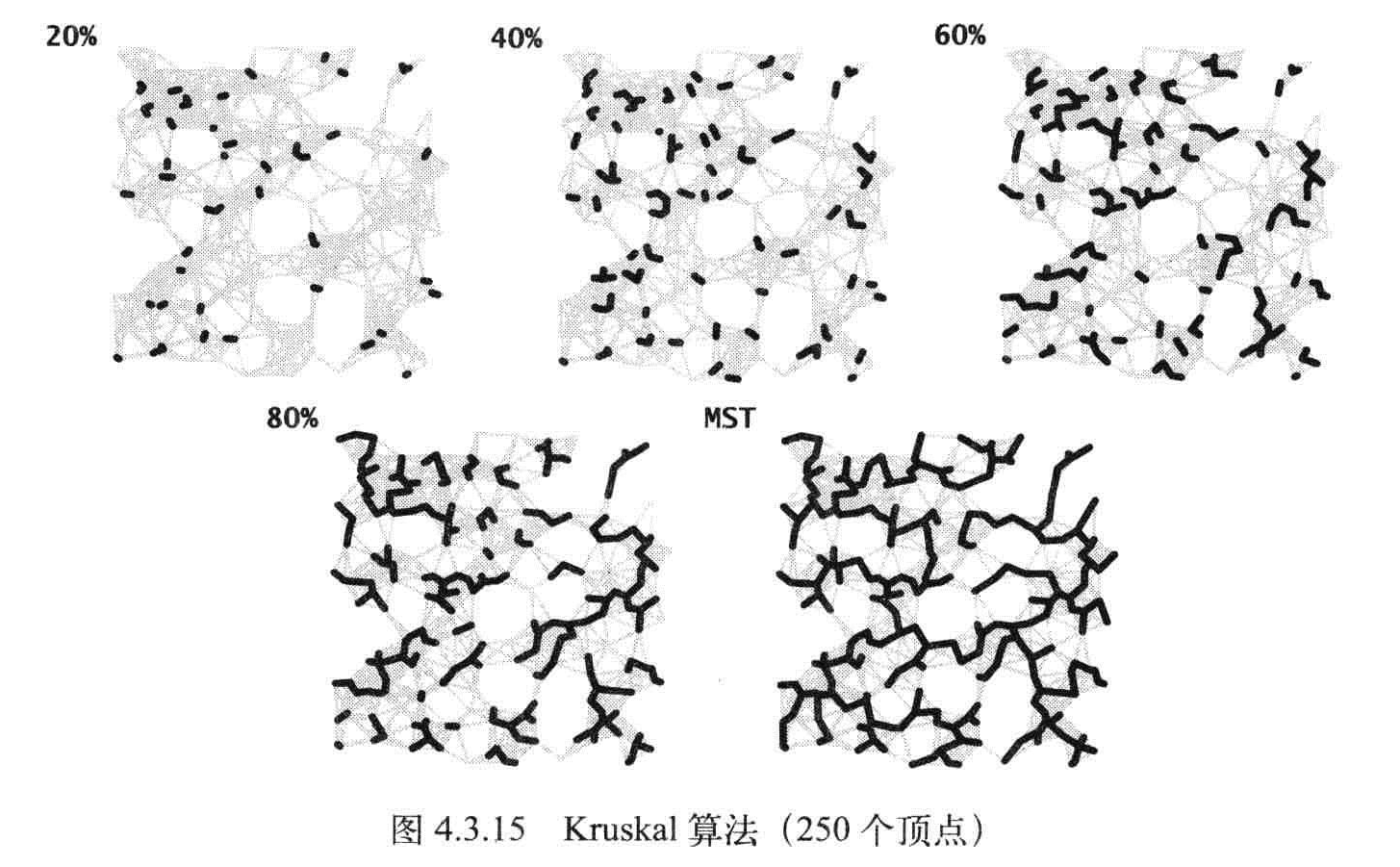
主要思想:按照边的权重顺序(从小到大)处理它们,将边加入最小生成树种(图种的黑色边),加入的边不会与已经加入的边构成环,直到树中含有V-1条边为止。
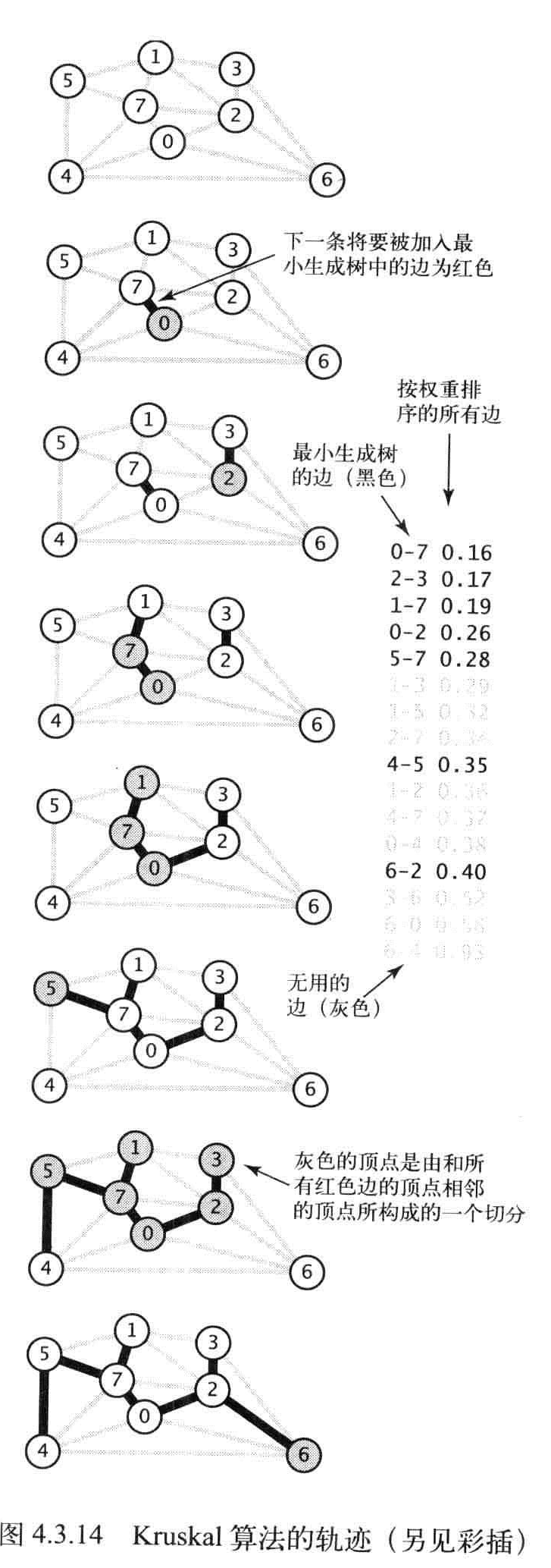
命题O:Kruskal算法能够计算任意加权无向图的最小生成树。
Kruskal实现:将会使用一条优先队列来将边按照权重排序,用一个union-find数据结构来识别会形成环的边,以及一条队列来保存最小生成树的所有边。
Kruskal:计算一幅含有V个顶点和E条边的连通加权无向图的最小生成树所需的空间和E成正比,所需的时间和ElogE成正比。

public class KruskalMST
{
private static readonly double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12;
private double _weight;
private Queue<Edge> _mst = new Queue<Edge>();
public KruskalMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G)
{
MinPQNet<Edge> pq = new MinPQNet<Edge>();
foreach (Edge e in G.Edges())
{
pq.Insert(e);//将所有边接入优先队列
}
UF uf = new UF(G.Vertices());
while (!pq.IsEmpty && _mst.Count() < G.Vertices() - 1)
{
Edge e = pq.DeleteMin();//找到最小权重边
int v = e.Either();//边的两个顶点
int w = e.Other(v);
if (uf.Find(v) != uf.Find(w))//标识符不相等,不连通
{
uf.Union(v, w); // 添加连通
_mst.Enqueue(e); // 将边压入
_weight += e.Weight();
}
}
}
public IEnumerable<Edge> Edges()
{
return _mst;
}
public double Weight()
{
return _weight;
}
private bool check(EdgeWeightedGraph G)
{
// check total weight
double total = 0.0;
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
total += e.Weight();
}
if (Math.Abs(total - Weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON)
{
Console.Write($"Weight of edges does not equal weight(): {total} vs. {Weight()}\n");
return false;
}
// check that it is acyclic
UF uf = new UF(G.Vertices());
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
int v = e.Either(), w = e.Other(v);
if (uf.Find(v) == uf.Find(w))
{
Console.Write("Not a forest");
return false;
}
uf.Union(v, w);
}
// check that it is a spanning forest
foreach (Edge e in G.Edges())
{
int v = e.Either(), w = e.Other(v);
if (uf.Find(v) != uf.Find(w))
{
Console.Write("Not a spanning forest");
return false;
}
}
// check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions)
foreach (Edge e in Edges())
{
// all edges in MST except e
uf = new UF(G.Vertices());
foreach (Edge f in _mst)
{
int x = f.Either(), y = f.Other(x);
if (f != e) uf.Union(x, y);
}
// check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut
foreach (Edge f in G.Edges())
{
int x = f.Either(), y = f.Other(x);
if (uf.Find(x) != uf.Find(y))
{
if (f.Weight() < e.Weight())
{
Console.Write("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions");
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void KruskalMSTTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyEWG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedGraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.EdgeWeightedGraph(stream);
KruskalMST mst = new KruskalMST(G);
foreach (Edge e in mst.Edges())
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
Console.Write($"{mst.Weight()}\n");
}
//00 - 07 0.16
//02 - 03 0.17
//01 - 07 0.19
//00 - 02 0.26
//05 - 07 0.28
//04 - 05 0.35
//06 - 02 0.4
//1.81
}

您的资助是我最大的动力!
金额随意,欢迎来赏!
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/lovexinyi/
版权:本文版权归作者和博客园共有
转载:欢迎转载,但未经作者同意,必须保留此段声明;必须在文章中给出原文链接;否则必究法律责任

