算法基础<五> 有向图
有向图
有向图:边是单向的,每条边所连接的两个顶点都是一个有序对。
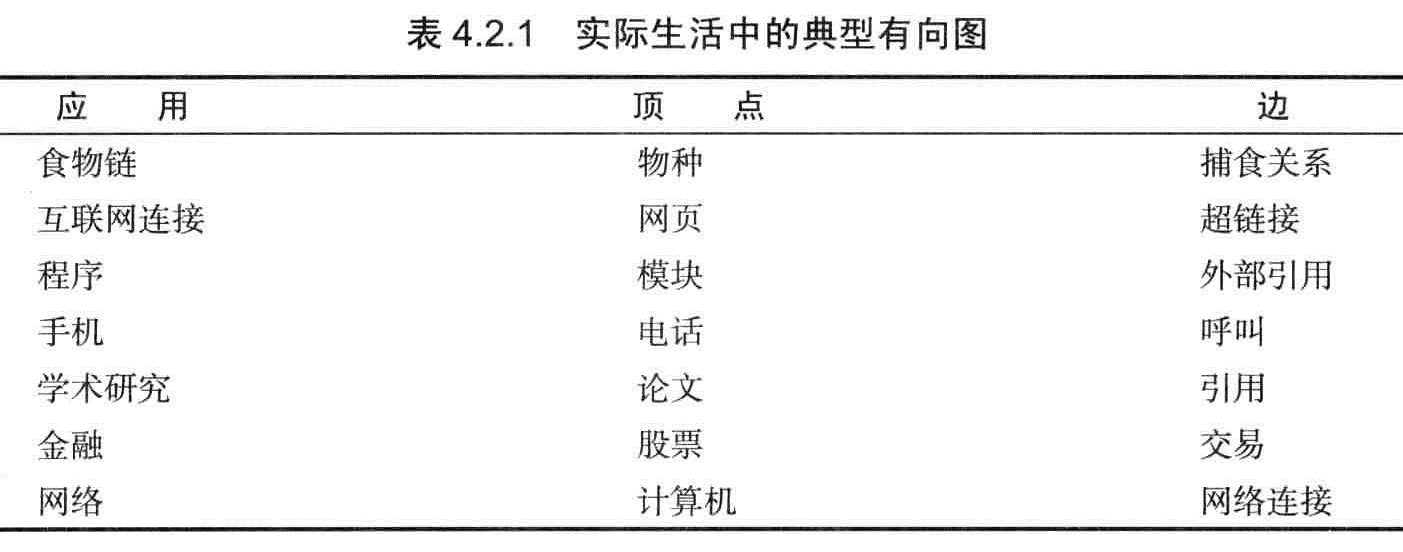
定义:一幅有方向性的图(或有向图)是由一组顶点和一组由方向的边组成的,每条有方向的边都连接这有序的一对顶点。
出度:该顶点指出边的总数。
入度:指向该顶点边的总数。
头:有向边的第一个顶点
尾:有向边的第二个顶点
有向路径:一系列顶点组成,每个顶点都存在一条有向边指向序列的下一个顶点。
有向环:一条至少含有一条边且起点和终点相同的有向路径。
简单有向环:一条(除起点和终点)不含有重复的顶点和边的环。
长度:路径或环的长度为边的数量。
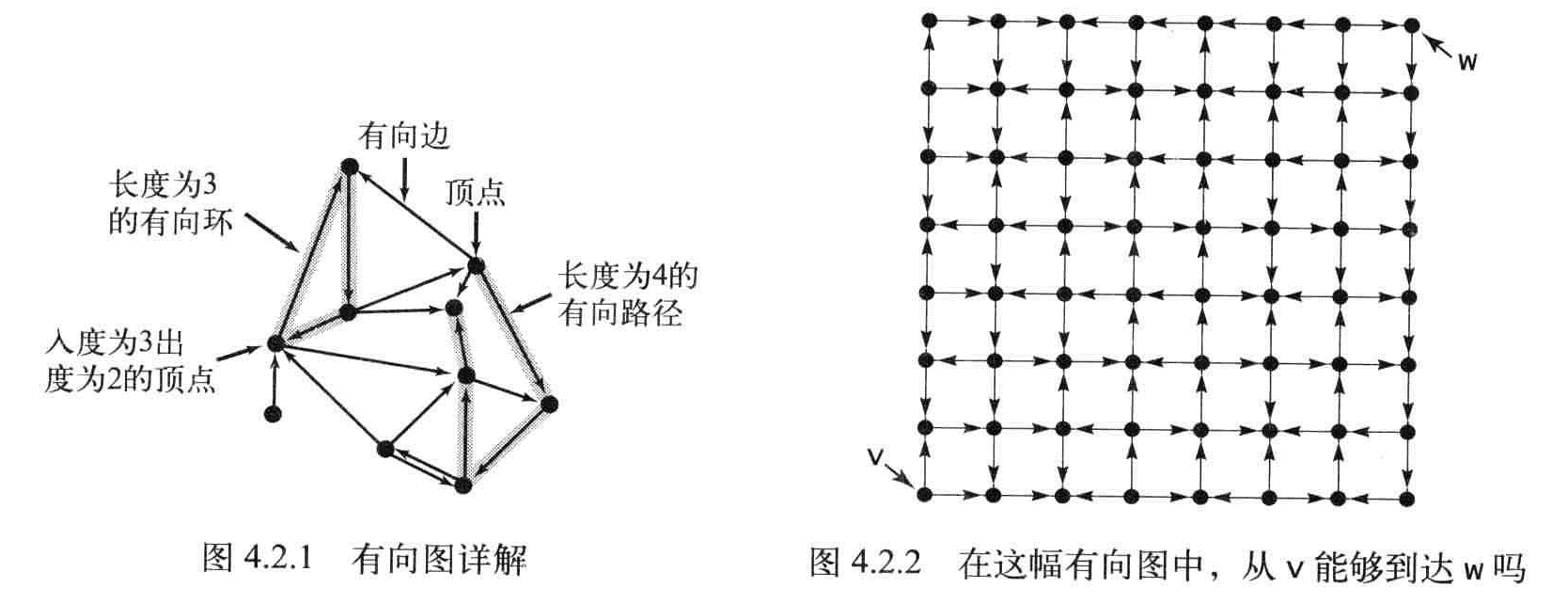
有向图的API
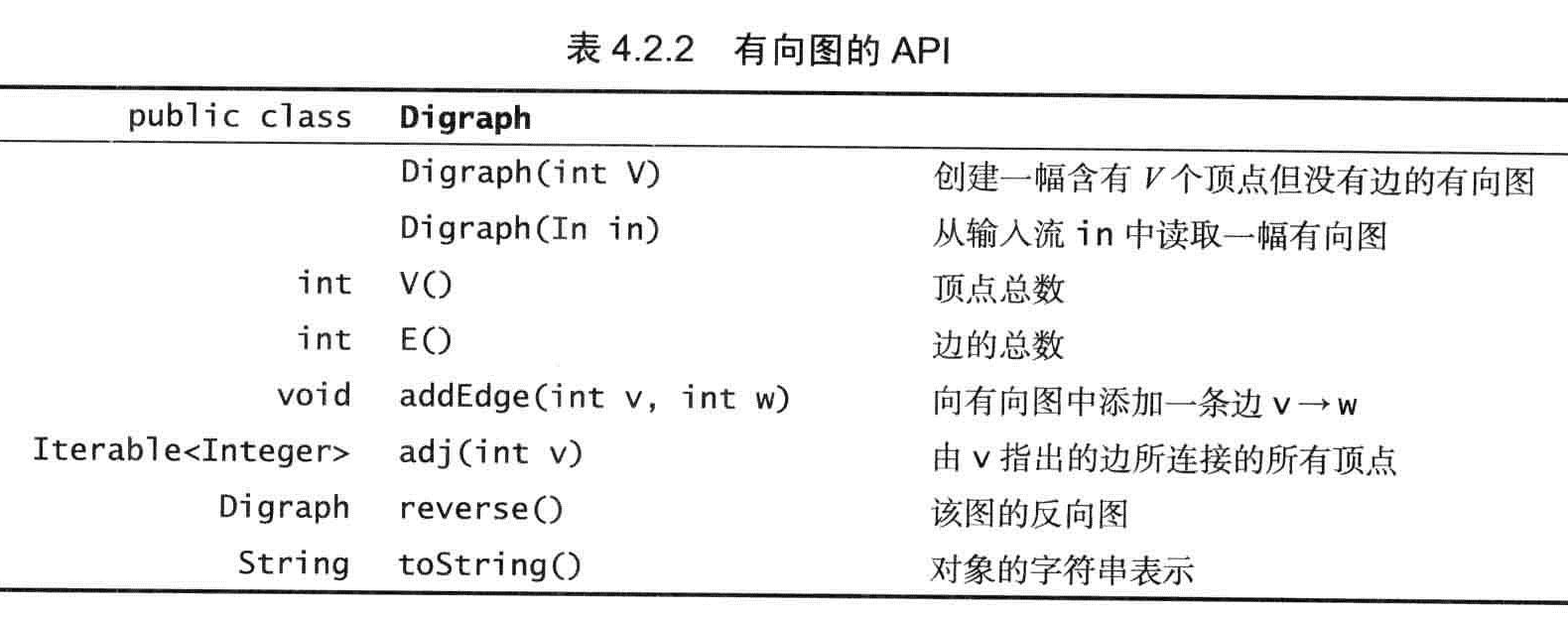
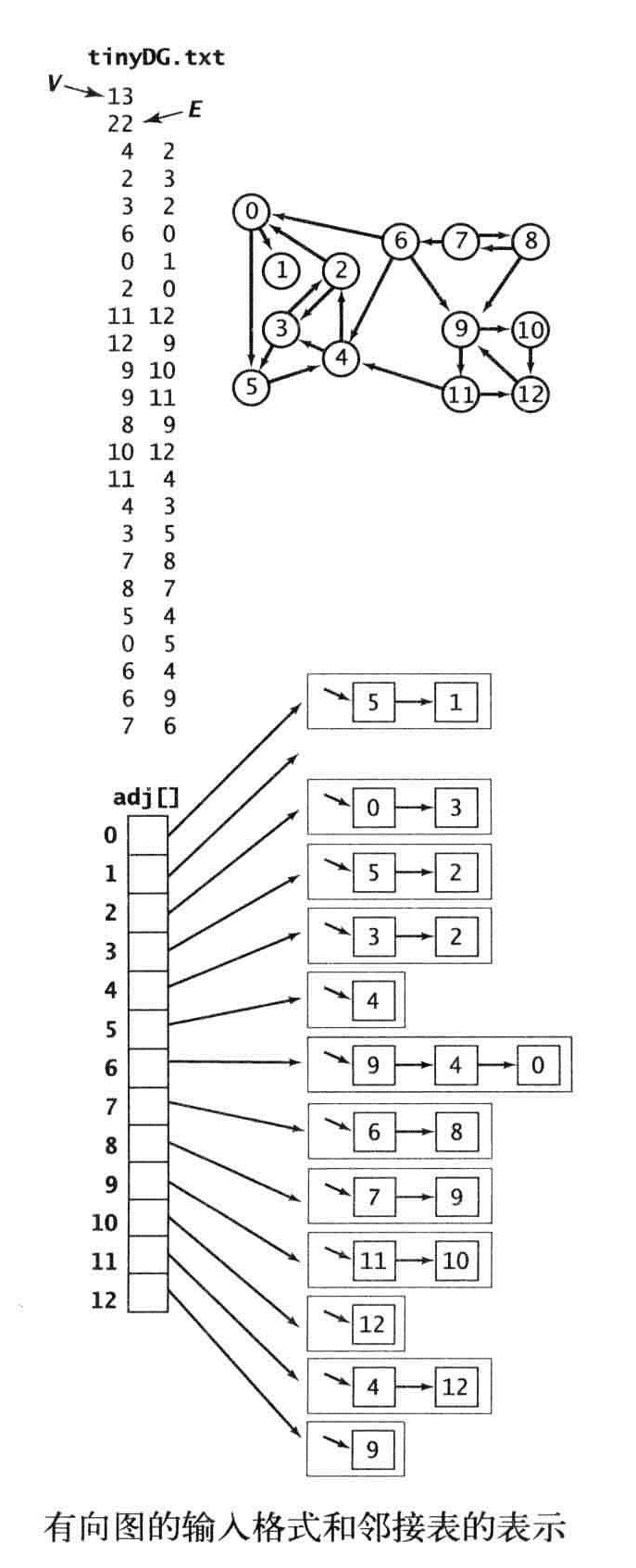
public class Digraph
{
private static readonly String NEWLINE = System.Environment.NewLine;
private readonly int _vertices; // 有向图顶点的数量
private int _edge; // 有向图边的数量
private LinkedBagNet<int>[] _adj; //有向图的邻接表
private int[] _indegree; // 有向图的度
/// <summary>
/// 顶点
/// </summary>
public int Vertices => _vertices;
/// <summary>
/// 边
/// </summary>
public int Edge => _edge;
/// <summary>
/// 顶点V的邻接图,也可以是顶点V射出边的数量
/// </summary>
public LinkedBagNet<int>[] Adj => _adj;
/// <summary>
/// 入射到顶点V的数量
/// </summary>
public int[] Indegree => _indegree;
public Digraph(int V)
{
if (V < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
this._vertices = V;
this._edge = 0;
_indegree = new int[V];
_adj = new LinkedBagNet<int>[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
_adj[v] = new LinkedBagNet<int>();
}
}
public Digraph(StreamReader stream)
{
if (stream == null) throw new ArgumentException("argument is null");
try
{
this._vertices = int.Parse(stream.ReadLine());
if (_vertices < 0) throw new ArgumentException("number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
_indegree = new int[_vertices];
_adj = new LinkedBagNet<int>[_vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < _vertices; v++)
{
_adj[v] = new LinkedBagNet<int>();
}
int E = int.Parse(stream.ReadLine());
if (E < 0) throw new ArgumentException("number of edges in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
string line = stream.ReadLine();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(line) && line.Split(' ').Count() == 2)
{
int v = int.Parse(line.Split(' ')[0]);
int w = int.Parse(line.Split(' ')[1]);
addEdge(v, w);
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new ArgumentException("invalid input format in Digraph constructor", e);
}
}
public Digraph(Digraph G)
{
if (G == null) throw new ArgumentException("argument is null");
this._vertices = G.Vertices;
this._vertices = G.Edge;
if (_vertices < 0) throw new ArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
// update indegrees
_indegree = new int[_vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < _vertices; v++)
this._indegree[v] = G._indegree[v];
// update adjacency lists
_adj = new LinkedBagNet<int>[_vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < _vertices; v++)
{
_adj[v] = new LinkedBagNet<int>();
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
// reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original
Stack<int> reverse = new Stack<int>();
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
reverse.Push(w);
}
foreach (int w in reverse)
{
_adj[v].Add(w);
}
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
if (v < 0 || v >= _vertices)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (Vertices - 1));
}
/// <summary>
/// Adds the directed edge v→w to this digraph.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="v"></param>
/// <param name="w"></param>
public void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
_adj[v].Add(w);
_indegree[w]++;
_edge++;
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回从顶点v射出是线数量
/// </summary>
/// <param name="v"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Outdegree(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _adj[v].Length;
}
/// <summary>
/// 逆转图
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Digraph Reverse()
{
Digraph reverse = new Digraph(_vertices);
for (int v = 0; v < _vertices; v++)
{
foreach (int w in Adj[v])
{
reverse.addEdge(w, v);
}
}
return reverse;
}
public override String ToString()
{
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.Append(_vertices + " vertices, " + _edge + " edges " + NEWLINE);
for (int v = 0; v < _vertices; v++)
{
s.Append(String.Format("%d: ", v));
foreach (int w in Adj[v])
{
s.Append(String.Format("%d ", w));
}
s.Append(NEWLINE);
}
return s.ToString();
}
}
符号有向图
和之前一样
public class SymbolDigraph
{
private ST<String, int> _st;
private String[] _keys;
private Digraph _graph;
public SymbolDigraph(String filename, String delimiter)
{
_st = new ST<String, int>();
// First pass builds the index by reading strings to associate
// distinct strings with an index
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(filename);
while (!reader.EndOfStream)
{
String[] a = reader.ReadLine().Split(delimiter.ToCharArray());
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
if (!_st.Contains(a[i]))
_st.Add(a[i], _st.Count());
}
}
// inverted index to get string keys in an array
_keys = new String[_st.Count()];
foreach (String name in _st.Keys())
{
_keys[_st.Get(name)] = name;
}
// second pass builds the digraph by connecting first vertex on each
// line to all others
_graph = new Digraph(_st.Count());
reader = new StreamReader(filename);
while (!reader.EndOfStream) {
String[] a = reader.ReadLine().Split(delimiter.ToCharArray());
int v = _st.Get(a[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < a.Length; i++)
{
int w = _st.Get(a[i]);
_graph.AddEdge(v, w);
}
}
}
public bool Contains(String s)
{
return _st.Contains(s);
}
public int Index(String s)
{
return _st.Get(s);
}
public int IndexOf(String s)
{
return _st.Get(s);
}
public String Name(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _keys[v];
}
public String NameOf(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _keys[v];
}
public Digraph G()
{
return _graph;
}
public Digraph Digraph()
{
return _graph;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _graph.Vertices;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void SymbolDigraphTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\routes.txt");
SymbolDigraph sg = new SymbolDigraph(data, " ");
Digraph graph = sg.Digraph();
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(data);
while (!reader.EndOfStream)
{
String source = reader.ReadLine().Split(' ')[0];
if (sg.Contains(source))
{
Console.Write($"{source} :");
int s = sg.Index(source);
foreach (int v in graph.Adj[s])
{
Console.Write(" " + sg.Name(v));
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("input not contain '" + source + "'");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
//JFK: ORD ATL MCO
//ORD : ATL PHX DFW HOU DEN
//ORD : ATL PHX DFW HOU DEN
//DFW : HOU PHX
//JFK: ORD ATL MCO
//ORD : ATL PHX DFW HOU DEN
//ORD : ATL PHX DFW HOU DEN
//ATL : MCO HOU
//DEN: LAS PHX
//PHX: LAX
//JFK : ORD ATL MCO
//DEN : LAS PHX
//DFW: HOU PHX
//ORD: ATL PHX DFW HOU DEN
//LAS : PHX LAX
//ATL: MCO HOU
//HOU: MCO
//LAS : PHX LAX
}
查找所有节点
可达性:是否存在一条从S到达顶点V的有向路径

深度搜索
public class DirectedDFS
{
private bool[] _marked;
private int _count; //顶点数量
public DirectedDFS(Digraph G, int s)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
validateVertex(s);
dfs(G, s);
}
public DirectedDFS(Digraph G, IEnumerable<int> sources)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
validateVertices(sources);
foreach (int v in sources)
{
if (!_marked[v]) dfs(G, v);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 深度搜素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="G"></param>
/// <param name="v"></param>
private void dfs(Digraph G, int v)
{
_count++;
_marked[v] = true;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w]) dfs(G, w);
}
}
public bool Marked(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _marked[v];
}
public int Count()
{
return _count;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertices(IEnumerable<int> vertices)
{
if (vertices == null)
{
throw new ArgumentException("argument is null");
}
foreach (int v in vertices)
{
if (v == default)
{
throw new ArgumentException("vertex is null");
}
validateVertex(v);
}
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void DirectedDFSTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
DirectedDFS dfs=new DirectedDFS(G,9);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
if (dfs.Marked(v)) Console.Write(v + " ");
}
}
}
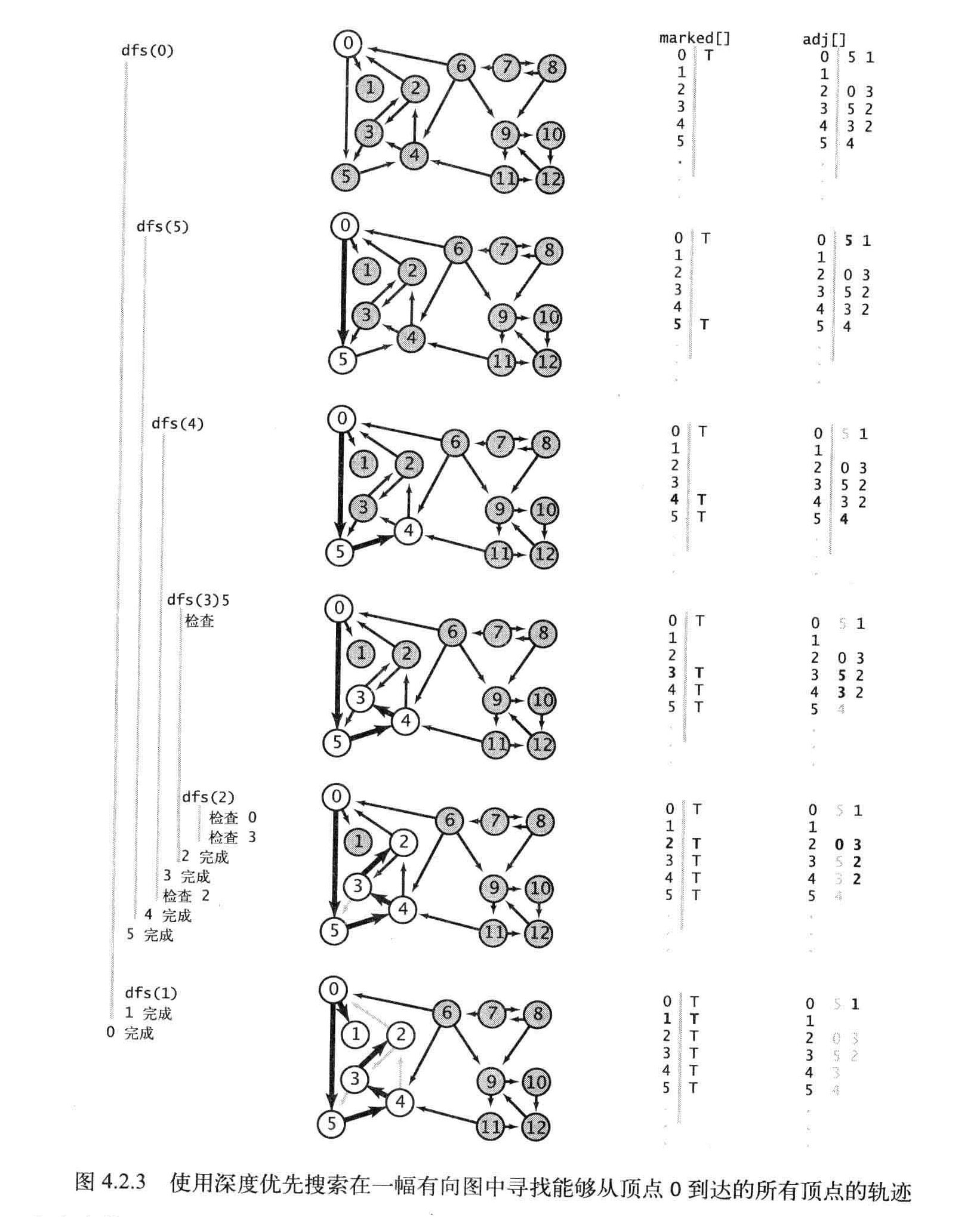
可达性非递归
public class NonrecursiveDirectedDFS
{
private bool[] _marked;
public NonrecursiveDirectedDFS(Digraph G, int s)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
validateVertex(s);
IEnumerator<int>[] adj =new IEnumerator<int>[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
adj[v] = G.Adj[v].GetEnumerator();
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
_marked[s] = true;
stack.Push(s);
while (stack.Any())
{
int v = stack.Peek();
if (adj[v].MoveNext())
{
int w = adj[v].Current;
if (!_marked[w])
{
_marked[w] = true;
stack.Push(w);
}
}
else
{
stack.Pop();
}
}
}
public bool Marked(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _marked[v];
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
寻找所有路径
深度搜索
public class DepthFirstDirectedPaths
{
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _edgeTo;
private readonly int s; // 起点
public DepthFirstDirectedPaths(Digraph G, int s)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
this.s = s;
validateVertex(s);
dfs(G, s);
}
private void dfs(Digraph G, int v)
{
_marked[v] = true;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;
dfs(G, w);
}
}
}
public bool HasPathTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _marked[v];
}
public IEnumerable<int> PathTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
if (!HasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<int> path = new Stack<int>();
for (int x = v; x != s; x = _edgeTo[x])
path.Push(x);
path.Push(s);
return path;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void DepthFirstDirectedPathsTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
DepthFirstDirectedPaths dfs=new DepthFirstDirectedPaths(G,9);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
if (dfs.HasPathTo(v))
{
Console.Write($"{9} to {v}: ");
foreach (int x in dfs.PathTo(v))
{
if (x == 9) Console.Write(x);
else Console.Write("-" + x);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.Write($"9 to {v}: not connected\n");
}
}
}
//9 to 0: 9 - 11 - 4 - 3 - 2 - 0
//9 to 1: 9 - 11 - 4 - 3 - 2 - 0 - 1
//9 to 2: 9 - 11 - 4 - 3 - 2
//9 to 3: 9 - 11 - 4 - 3
//9 to 4: 9 - 11 - 4
//9 to 5: 9 - 11 - 4 - 3 - 5
//9 to 6: not connected
//9 to 7: not connected
//9 to 8: not connected
//9 to 9: 9
//9 to 10: 9 - 10
//9 to 11: 9 - 11
//9 to 12: 9 - 11 - 12
}
广度搜索
广度搜索需要一个队列辅助,基本和无向图一样
public class BreadthFirstDirectedPaths
{
private static readonly int INFINITY = int.MaxValue;
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _edgeTo;
private int[] _distTo;
public BreadthFirstDirectedPaths(Digraph G, int s)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_distTo = new int[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
_distTo[v] = INFINITY;
validateVertex(s);
bfs(G, s);
}
public BreadthFirstDirectedPaths(Digraph G, IEnumerable<int> sources)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_distTo = new int[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
_distTo[v] = INFINITY;
validateVertices(sources);
bfs(G, sources);
}
// BFS from single source
private void bfs(Digraph G, int s)
{
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
_marked[s] = true;
_distTo[s] = 0;
q.Enqueue(s);
while (q.Any())
{
int v = q.Dequeue();
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;
_distTo[w] = _distTo[v] + 1;
_marked[w] = true;
q.Enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
// BFS from multiple sources
private void bfs(Digraph G, IEnumerable<int> sources)
{
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
foreach (int s in sources)
{
_marked[s] = true;
_distTo[s] = 0;
q.Enqueue(s);
}
while (q.Any())
{
int v = q.Dequeue();
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;
_distTo[w] = _distTo[v] + 1;
_marked[w] = true;
q.Enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
public bool HasPathTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _marked[v];
}
public int DistTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _distTo[v];
}
public IEnumerable<int> PathTo(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
if (!HasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<int> path = new Stack<int>();
int x;
for (x = v; _distTo[x] != 0; x = _edgeTo[x])
path.Push(x);
path.Push(x);
return path;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertices(IEnumerable<int> vertices)
{
if (vertices == null)
{
throw new ArgumentException("argument is null");
}
foreach (int v in vertices)
{
if (v == default)
{
throw new ArgumentException("vertex is null");
}
validateVertex(v);
}
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void BreadthFirstDirectedPathsTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
BreadthFirstDirectedPaths bfs = new BreadthFirstDirectedPaths(G, 9);
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
if (bfs.HasPathTo(v))
{
Console.Write($"{9} to {v}: ");
foreach (int x in bfs.PathTo(v))
{
if (x == 9) Console.Write(x);
else Console.Write("-" + x);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.Write($"9 to {v}: not connected\n");
}
}
}
//9 to 0: 9 - 11 - 4 - 2 - 0
//9 to 1: 9 - 11 - 4 - 2 - 0 - 1
//9 to 2: 9 - 11 - 4 - 2
//9 to 3: 9 - 11 - 4 - 3
//9 to 4: 9 - 11 - 4
//9 to 5: 9 - 11 - 4 - 3 - 5
//9 to 6: not connected
//9 to 7: not connected
//9 to 8: not connected
//9 to 9: 9
//9 to 10: 9 - 10
//9 to 11: 9 - 11
//9 to 12: 9 - 11 - 12
}
广度搜索和深度搜索的路径是不一样的,广度搜索的路径是最短路径。
寻找有向环
调度问题
一种广泛的模型是给定一组任务并安排它们的执行顺序,限制条件是这些任务的执行方法和起始时间。哪些任务必须在哪些任务之前完成,最重要的限制条件叫优先级限制。
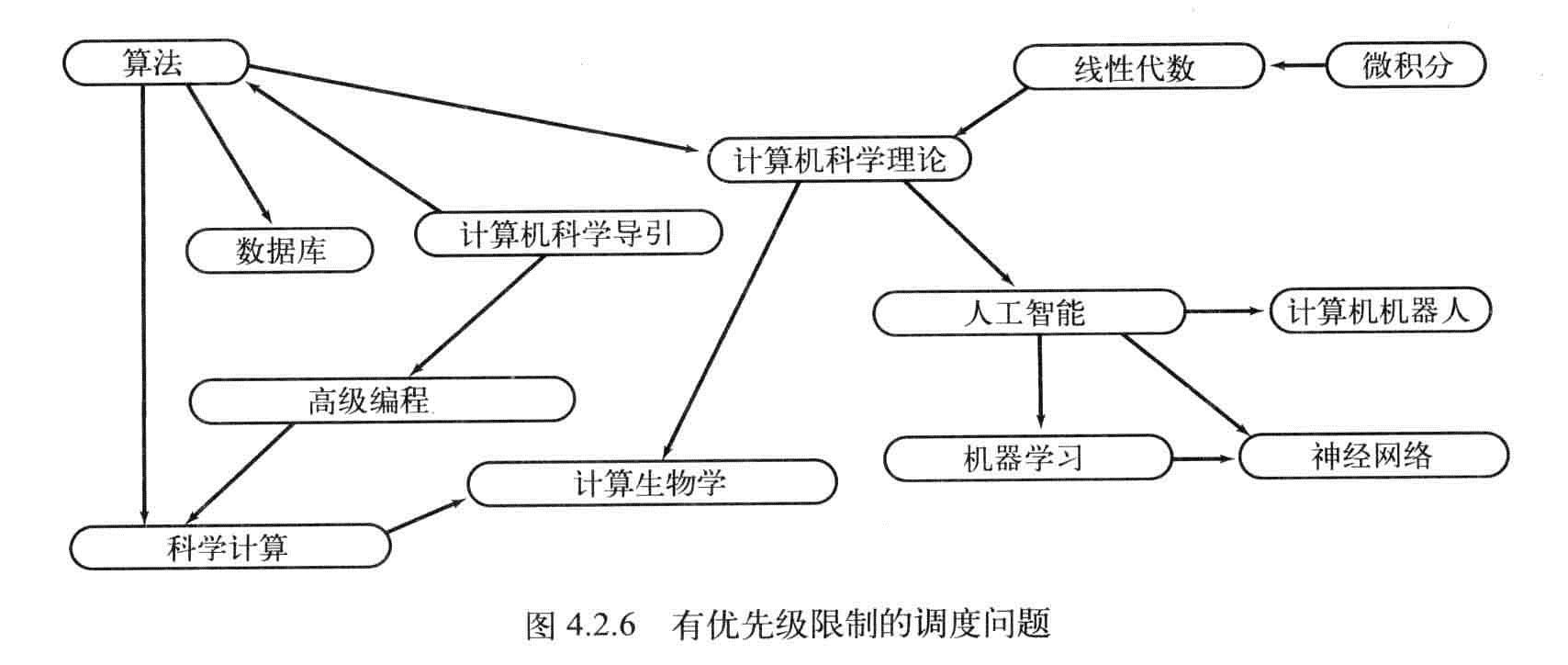
优先级限制下调度问题:一组关于任务完成的先后次序的优先级限制。

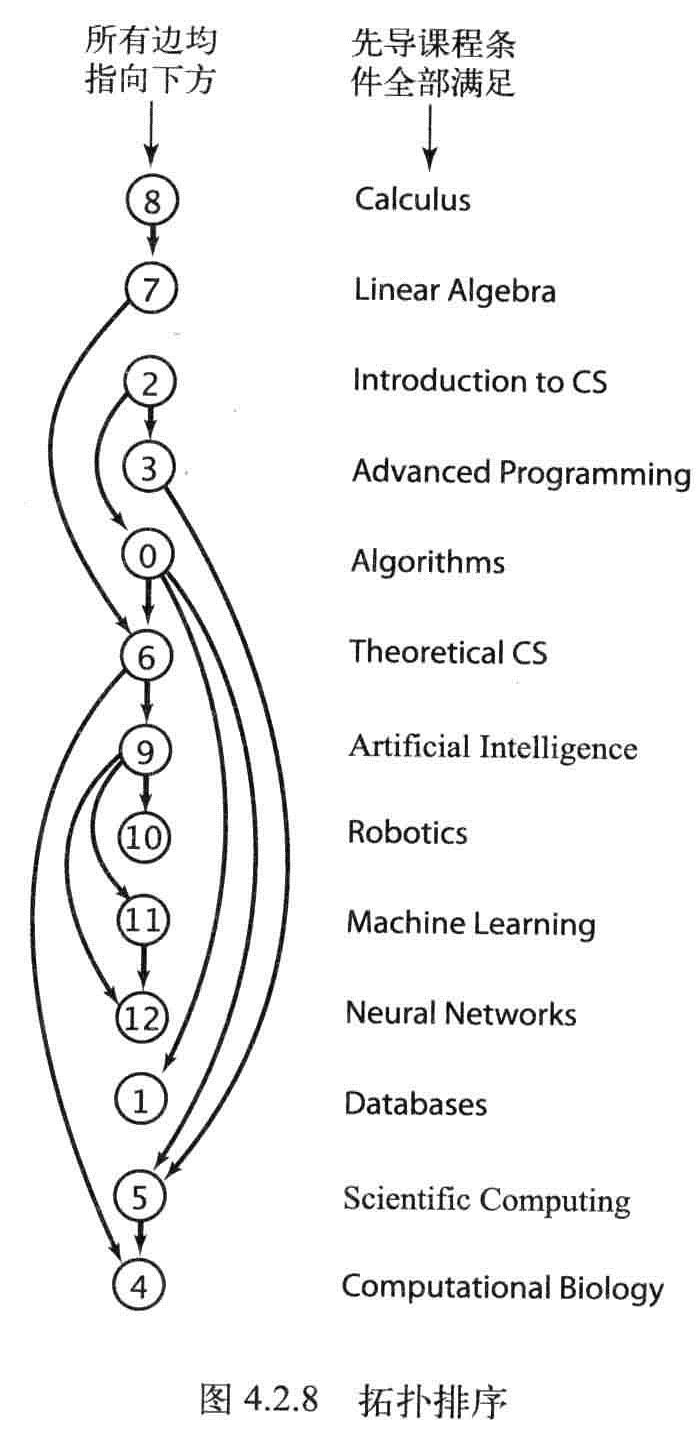
拓扑排序:有向图,将所有的顶点排序,使得所有的有向边均从排在前面的元素指向排在后面的元素(或者说明无法做到这一点)。
如果一个有优先级限制的问题中存在有向环,那么这个问题无解。
有向无环图(DAG):不含有环的有向图。

深度搜索,就跟拿根绳走迷宫是一样的
public class DirectedCycle
{
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _edgeTo;
private bool[] _onStack; //该顶点是否在栈
private Stack<int> _cycle; // 环栈
public DirectedCycle(Digraph G)
{
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_onStack = new bool[G.Vertices];
_edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (!_marked[v] && _cycle == null) dfs(G, v);
}
private void dfs(Digraph G, int v)
{
_onStack[v] = true;
_marked[v] = true;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
// 环已经被发现
if (_cycle != null) return;
// 新的顶点且环没有被发现
else if (!_marked[w])
{
_edgeTo[w] = v;
dfs(G, w);
}
else if (_onStack[w])//查找到环,压入环栈
{
_cycle = new Stack<int>();
for (int x = v; x != w; x = _edgeTo[x])
{
_cycle.Push(x);
}
_cycle.Push(w);
_cycle.Push(v);
}
}
_onStack[v] = false;
}
public bool HasCycle()
{
return _cycle != null;
}
public IEnumerable<int> Cycle()
{
return _cycle;
}
private bool check()
{
if (HasCycle())
{
// verify cycle
int first = -1, last = -1;
foreach (int v in _cycle)
{
if (first == -1) first = v;
last = v;
}
if (first != last)
{
Console.Write("cycle begins with %d and ends with %d\n", first, last);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void DirectedCycleTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
DirectedCycle finder = new DirectedCycle(G);
if (finder.HasCycle())
{
Console.Write("Directed cycle: ");
foreach (int v in finder.Cycle())//只能找到一个环
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No directed cycle");
}
//Directed cycle: 3 5 4 3
}
}
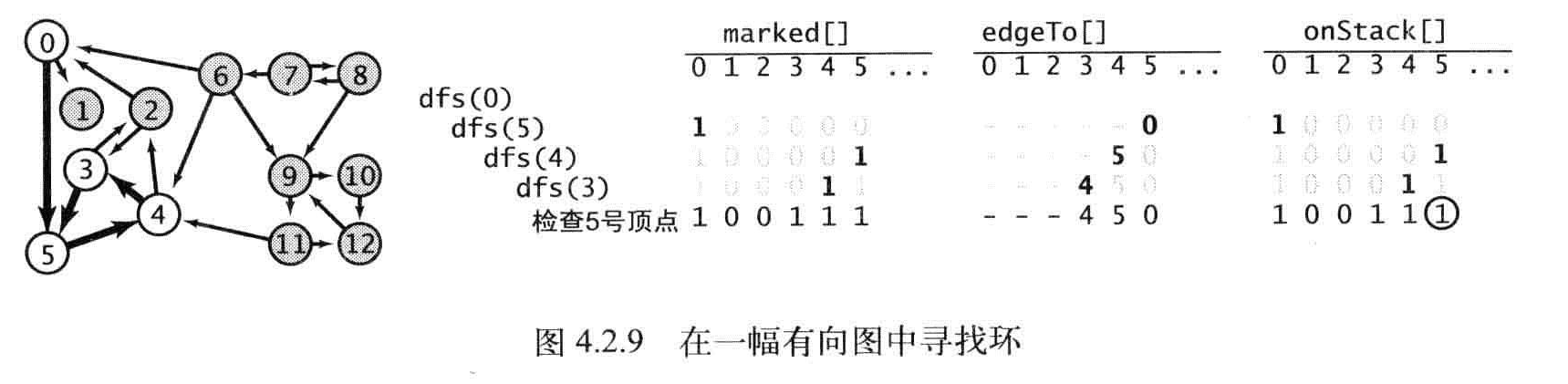
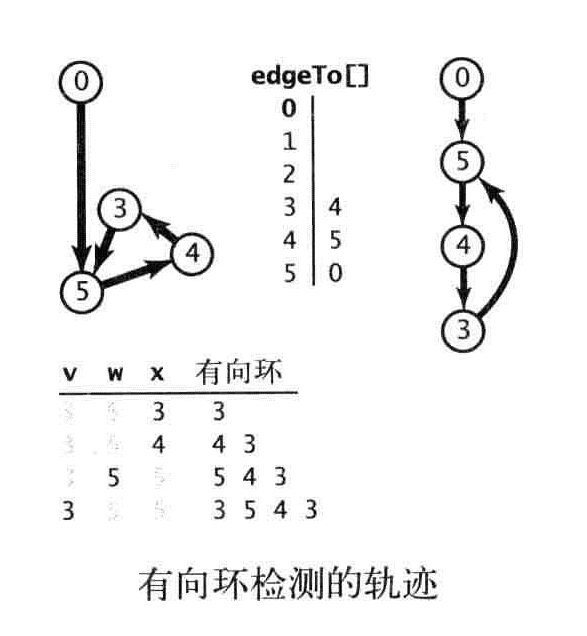
广度搜索,就像一个人有影分身走不同的路径
public class DirectedCycleX
{
private Stack<int> _cycle;
public DirectedCycleX(Digraph G)
{
int[] indegree = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
indegree[v] = G.Indegree[v];
}
//所有没有入射边的顶点压入队列
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (indegree[v] == 0) queue.Enqueue(v);
while (queue.Any())//广度搜索
{
int v = queue.Dequeue();
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
indegree[w]--;//去除掉从没有入射边顶点射出的边,并查看是否有没有入射边的顶点
if (indegree[w] == 0) queue.Enqueue(w);
}
}
int[] edgeTo = new int[G.Vertices];
int root = -1;
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
if (indegree[v] == 0) continue;
else root = v;//入射边大于0的顶点,有环
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (indegree[w] > 0)
{
edgeTo[w] = v;
}
}
}
if (root != -1)
{
// find any vertex on cycle
bool[] visited = new bool[G.Vertices];
while (!visited[root])
{
visited[root] = true;
root = edgeTo[root];
}
// extract cycle
_cycle = new Stack<int>();
int v = root;
do
{
_cycle.Push(v);
v = edgeTo[v];
} while (v != root);
_cycle.Push(root);
}
}
public IEnumerable<int> Cycle()
{
return _cycle;
}
public bool HasCycle()
{
return _cycle != null;
}
private bool check()
{
if (HasCycle())
{
int first = -1, last = -1;
foreach (int v in _cycle)
{
if (first == -1) first = v;
last = v;
}
if (first != last)
{
Console.Write("cycle begins with %d and ends with %d\n", first, last);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod]
public void DirectedCycleXTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
DirectedCycleX finder = new DirectedCycleX(G);
if (finder.HasCycle())
{
Console.Write("Directed cycle: ");
foreach (int v in finder.Cycle())
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No directed cycle");
}
//Directed cycle: 12 9 11 12
}
}
顶点排序
基于深度优先搜索的顶点排序,深度优先搜索正好只会访问每个顶点一次。
如果将dfs()的参数顶点保存在一个数据结构中,遍历这个数据结构实际上就能够访问图中的所有顶点。
要讨论的是需要在递归前保存顶点,还是递归后保存顶点。
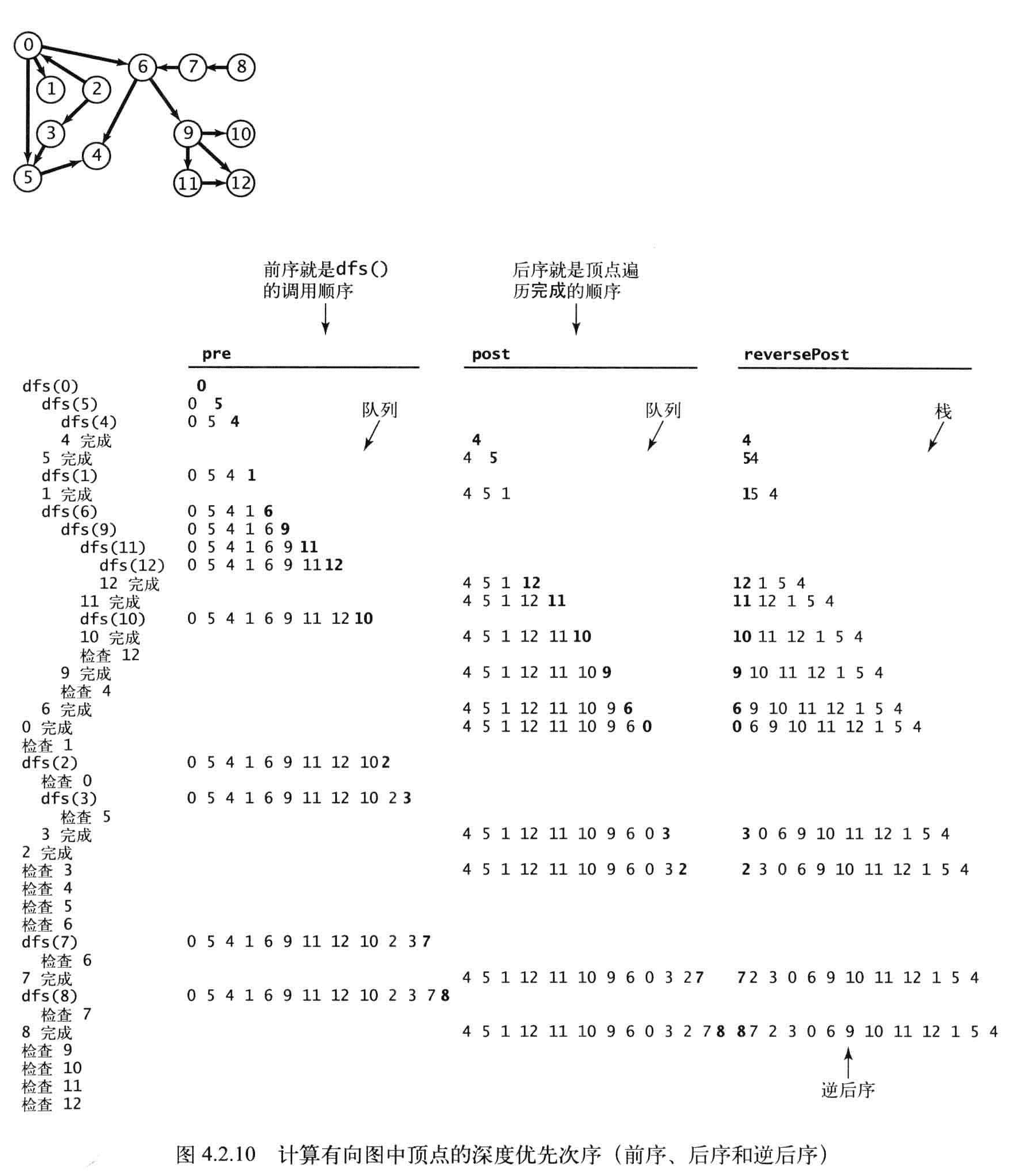
public class DepthFirstOrder
{
private bool[] _marked;
private int[] _pre;
private int[] _post;
private Queue<int> _preorder; //在递归之前将顶点保存,顺序正确
private Queue<int> _postorder; //在递归之后将顶点保存,最后顺序应该倒一下。
private int _preCounter;
private int _postCounter;
public DepthFirstOrder(Digraph G)
{
_pre = new int[G.Vertices];
_post = new int[G.Vertices];
_postorder = new Queue<int>();
_preorder = new Queue<int>();
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (!_marked[v]) dfs(G, v);
}
private void dfs(Digraph G, int v)
{
_marked[v] = true;
_pre[v] = _preCounter++;
_preorder.Enqueue(v);
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w])
{
dfs(G, w);
}
}
_postorder.Enqueue(v);
_post[v] = _postCounter++;
}
public int Pre(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _pre[v];
}
public int Post(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _post[v];
}
public IEnumerable<int> Post()
{
return _postorder;
}
public IEnumerable<int> Pre()
{
return _preorder;
}
public IEnumerable<int> ReversePost()//通过栈进行反转
{
Stack<int> reverse = new Stack<int>();
foreach (int v in _postorder)
reverse.Push(v);
return reverse;
}
private bool check()
{
// check that post(v) is consistent with post()
int r = 0;
foreach (int v in _post)
{
if (_post[v] != r)
{
Console.Write("post(v) and post() inconsistent");
return false;
}
r++;
}
// check that pre(v) is consistent with pre()
r = 0;
foreach (int v in _pre)
{
if (_pre[v] != r)
{
Console.Write("pre(v) and pre() inconsistent");
return false;
}
r++;
}
return true;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void DepthFirstOrderTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDAG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
DepthFirstOrder dfs = new DepthFirstOrder(G);
Console.WriteLine("v pre post");
Console.WriteLine("--------------");
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
Console.Write($"{v} {dfs.Pre(v)} {dfs.Post(v)}\n");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("Preorder: ");
foreach (int v in dfs.Pre())
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("Postorder: ");
foreach (int v in dfs.Post())
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("Reverse postorder: ");
foreach (int v in dfs.ReversePost())
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
//v pre post
//--------------
//0 0 8
//1 3 2
//2 9 10
//3 10 9
//4 2 0
//5 1 1
//6 4 7
//7 11 11
//8 12 12
//9 5 6
//10 8 5
//11 6 4
//12 7 3
//Preorder: 0 5 4 1 6 9 11 12 10 2 3 7 8
//Postorder: 4 5 1 12 11 10 9 6 0 3 2 7 8
//Reverse postorder: 8 7 2 3 0 6 9 10 11 12 1 5 4
}
拓扑排序
命题E:当且仅当一幅有向图是无环图时它才能进行拓扑排序
命题F:一幅有向无环图的拓扑排序即为所有顶点的逆后序排序。
命题G:使用深度优先搜索对有向无环图进行拓扑排序所需的时间和V+E成正比。
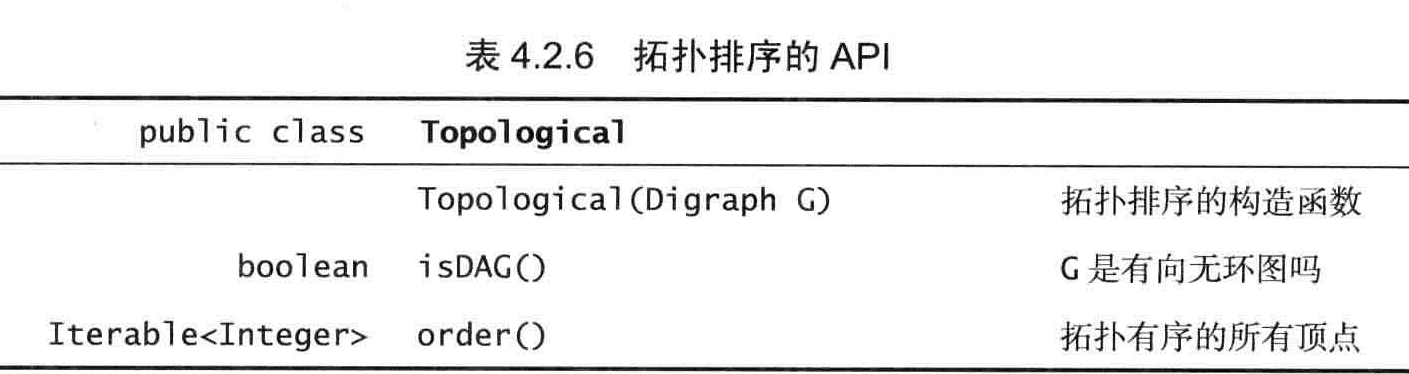
public class Topological
{
private IEnumerable<int> _order; //顶点的拓扑顺序
private int[] _rank;
public Topological(Digraph G)
{
DirectedCycle finder = new DirectedCycle(G);//先检测一下是否有环
if (!finder.HasCycle())
{
DepthFirstOrder dfs = new DepthFirstOrder(G);//顶点排序
_order = dfs.ReversePost();//后续插入反转就是拓扑排序,又称逆后续
_rank = new int[G.Vertices];
int i = 0;
foreach (int v in _order)
_rank[v] = i++;
}
}
public IEnumerable<int> Order()
{
return _order;
}
public bool HasOrder()
{
return _order != null;
}
public bool IsDAG()
{
return HasOrder();
}
public int Rank(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
if (HasOrder()) return _rank[v];
else return -1;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _rank.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void TopologicalTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDAG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
Topological topological = new Topological(G);
foreach (int v in topological.Order())
{
Console.Write(v+" ");
}
}
//8 7 2 3 0 6 9 10 11 12 1 5 4
}
逆后序就是顶点遍历完成顺序的逆,从下往上
更流性的一种拓扑算法,其实就是广度搜索
public class TopologicalX
{
private Queue<int> _order; // 顶点的拓扑顺序
private int[] _ranks;
public TopologicalX(Digraph G)
{
//入射到顶点的边的数量
int[] indegree = new int[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
indegree[v] = G.Indegree[v];
}
// initialize
_ranks = new int[G.Vertices];
_order = new Queue<int>();
int count = 0;
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
if (indegree[v] == 0) queue.Enqueue(v);//将没有入射的压入
while (queue.Any())
{
int v = queue.Dequeue();
_order.Enqueue(v);
_ranks[v] = count++;
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
indegree[w]--;
if (indegree[w] == 0) queue.Enqueue(w);//广度搜索
}
}
if (count != G.Vertices)
{
_order = null;
}
}
public IEnumerable<int> Order()
{
return _order;
}
public bool HasOrder()
{
return _order != null;
}
public int Rank(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
if (HasOrder()) return _ranks[v];
else return -1;
}
private bool check(Digraph G)
{
// digraph is acyclic
if (HasOrder())
{
// check that ranks are a permutation of 0 to V-1
bool[] found = new bool[G.Vertices];
for (int i = 0; i < G.Vertices; i++)
{
found[_ranks[i]] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < G.Vertices; i++)
{
if (!found[i])
{
Console.Write("No vertex with rank " + i);
return false;
}
}
// check that ranks provide a valid topological order
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (Rank(v) > Rank(w))
{
Console.Write($"{v}-{w}: rank({v}) = {Rank(v)}, rank({w}) = {Rank(w)}\n");
return false;
}
}
}
// check that order() is consistent with rank()
int r = 0;
foreach (int v in Order())
{
if (Rank(v) != r)
{
Console.Write("order() and rank() inconsistent");
return false;
}
r++;
}
}
return true;
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _ranks.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试:
[TestMethod()]
public void TopologicalXTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDAG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
TopologicalX topological = new TopologicalX(G);
foreach (int v in topological.Order())
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
}
//2 8 0 3 7 1 5 6 9 4 11 10 12
}
解决任务调度类通常由3步:
- 指明任务和优先级条件
- 不断检测并去除有向图中的所有环,以确保存在可行方案的
- 使用拓扑排序解决调度问题。
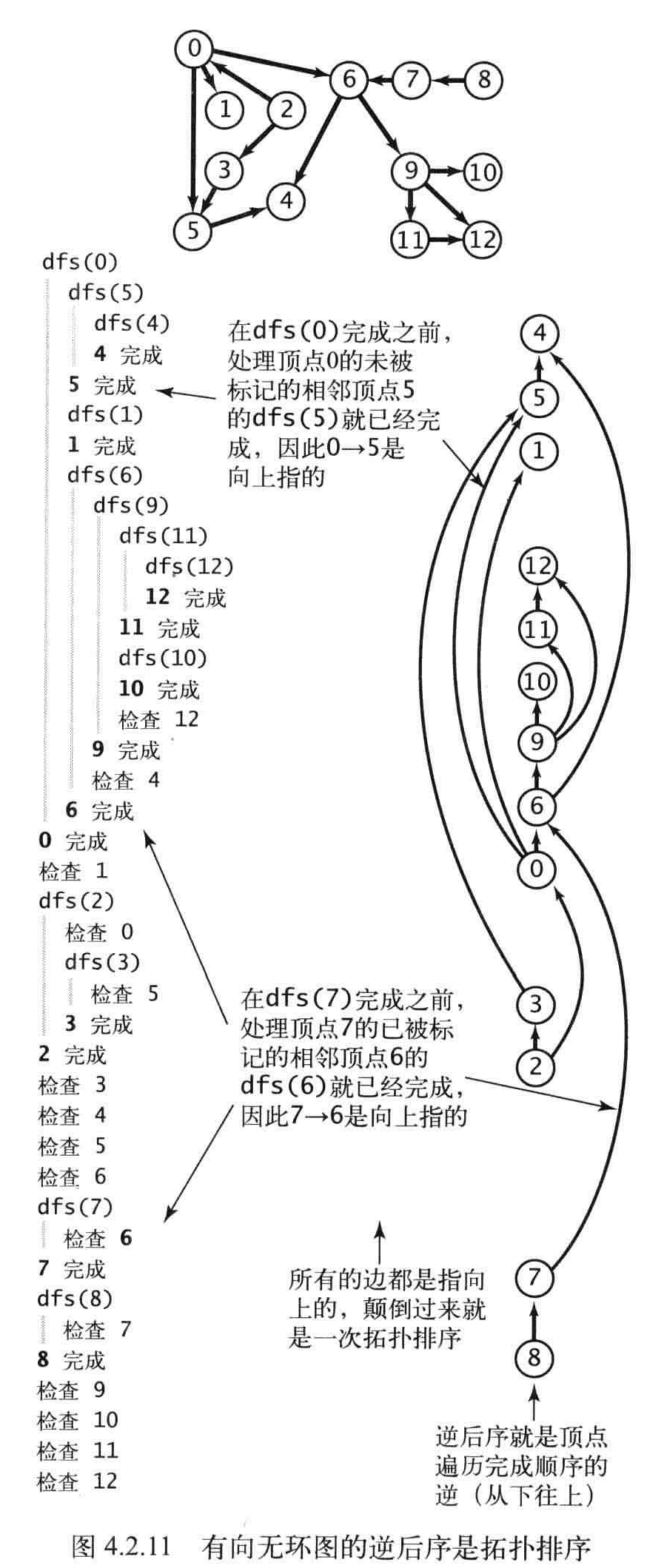
强连通性问题
强连通:如果两个顶点v和w是相互可达的,则称它们为强连通。
两个顶点是强连通的当且仅当它们都在一个普通的有向环中。
性质:
- 自反性:任意顶点V和自己都是强连通的
- 对称性:如果v和w是强连通的,那么w和v也是强连通的。
- 传递性:如果v和w是强连通的且w和x也是强连通的,那么v和x也是强连通的。
强连通可以帮助进行归类,可以帮助生物学家解决生态的问题
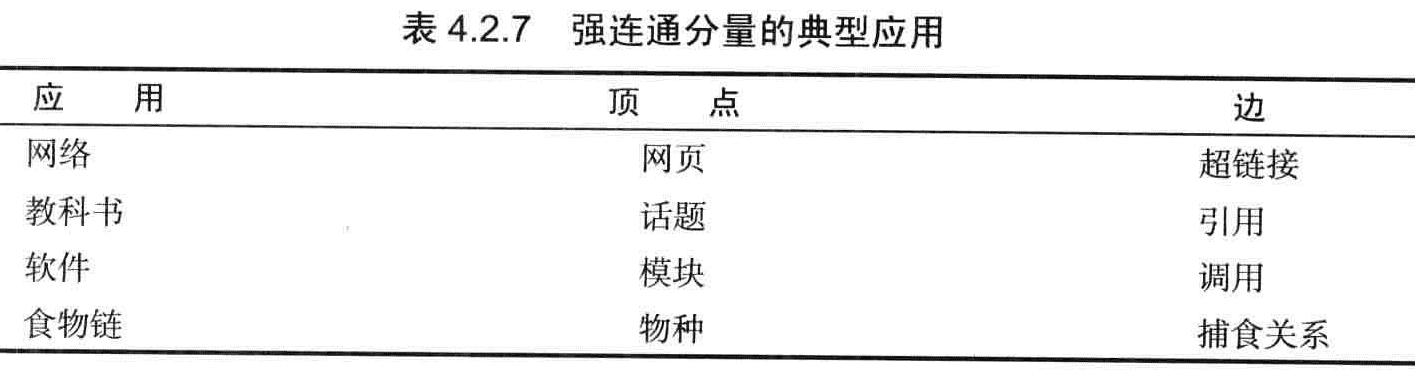
Kosaraju算法
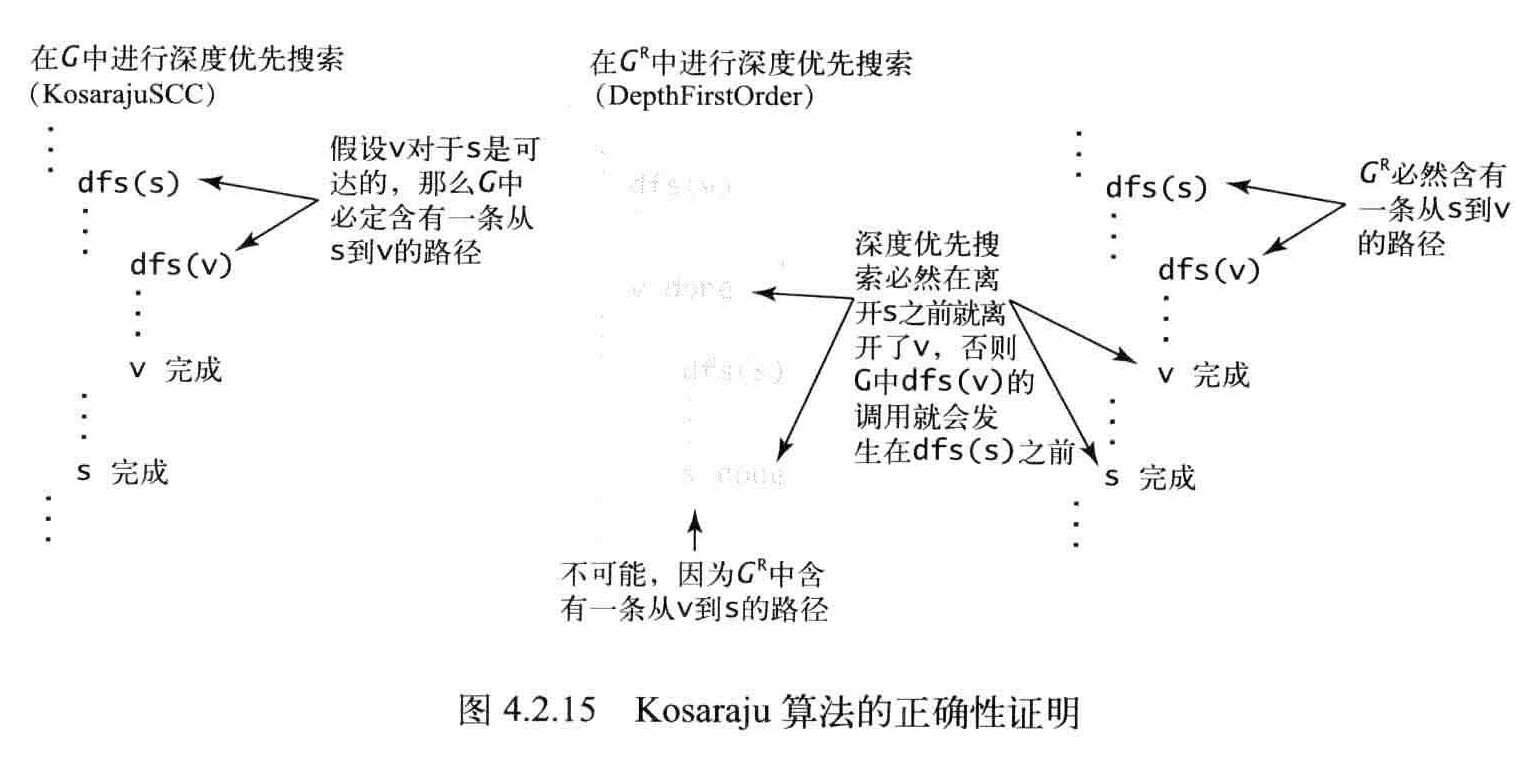
Kosaraju算法的步骤
- 对给定的G,使用DepthFirstOrder来计算它的反向图G的逆后序排序。
- 在G中进行标准的深度优先搜索,按照上一步的顺序来访问所有未被标记过的顶点。
- 在构造函数中,所有在同一个递归dfs()调用中被访问到的顶点都在同一个强连通分量中,将它们按照和CC相同的方式识别出来。
/// <summary>
/// Kosaraju算法
/// </summary>
public class KosarajuSharirSCC
{
private bool[] _marked; //已访问过的顶点
private int[] _id; //强连通分量的标识符
private int _count; //强连通分量的数量
public KosarajuSharirSCC(Digraph G)
{
DepthFirstOrder dfo = new DepthFirstOrder(G.Reverse());//这边注意是G.Reverse
_marked = new bool[G.Vertices];
_id = new int[G.Vertices];
foreach (int v in dfo.ReversePost())//拓扑排序的顶点
{
if (!_marked[v])//遍历拓扑排序的顶点
{
dfs(G, v);//
_count++;//找到一个新的连通量
}
}
}
private void dfs(Digraph G, int v)
{
_marked[v] = true;
_id[v] = _count;//强连通分量的顶点对应的id都一样
foreach (int w in G.Adj[v])
{
if (!_marked[w]) dfs(G, w);
}
}
public int Count()
{
return _count;
}
public bool StronglyConnected(int v, int w)
{
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return _id[v] == _id[w];
}
public int Id(int v)
{
validateVertex(v);
return _id[v];
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = _marked.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试
[TestMethod()]
public void KosarajuTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
KosarajuSharirSCC scc=new KosarajuSharirSCC(G);
// number of connected components
int m = scc.Count();
Console.WriteLine(m + " strong components");
// compute list of vertices in each strong component
Queue<int>[] components = new Queue<int>[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
components[i] = new Queue<int>();
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
components[scc.Id(v)].Enqueue(v);//将每一种连通向都
}
// print results
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
foreach (int v in components[i])
{
Console.Write(v + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
//5 strong components
//1
//0 2 3 4 5
//9 10 11 12
//6 8
//7
}
命题H:使用深度优先搜索查找给定有向图G的反向图GR(也就是上面的拓扑排序),根据由此得到的所有顶点的逆后序再次用深度优先搜索处理有向图G(Kosaraju算法),其构造函数中的每一次递归调用所标记的顶点都在同一个强连通分量之中。

顶点对的可达性
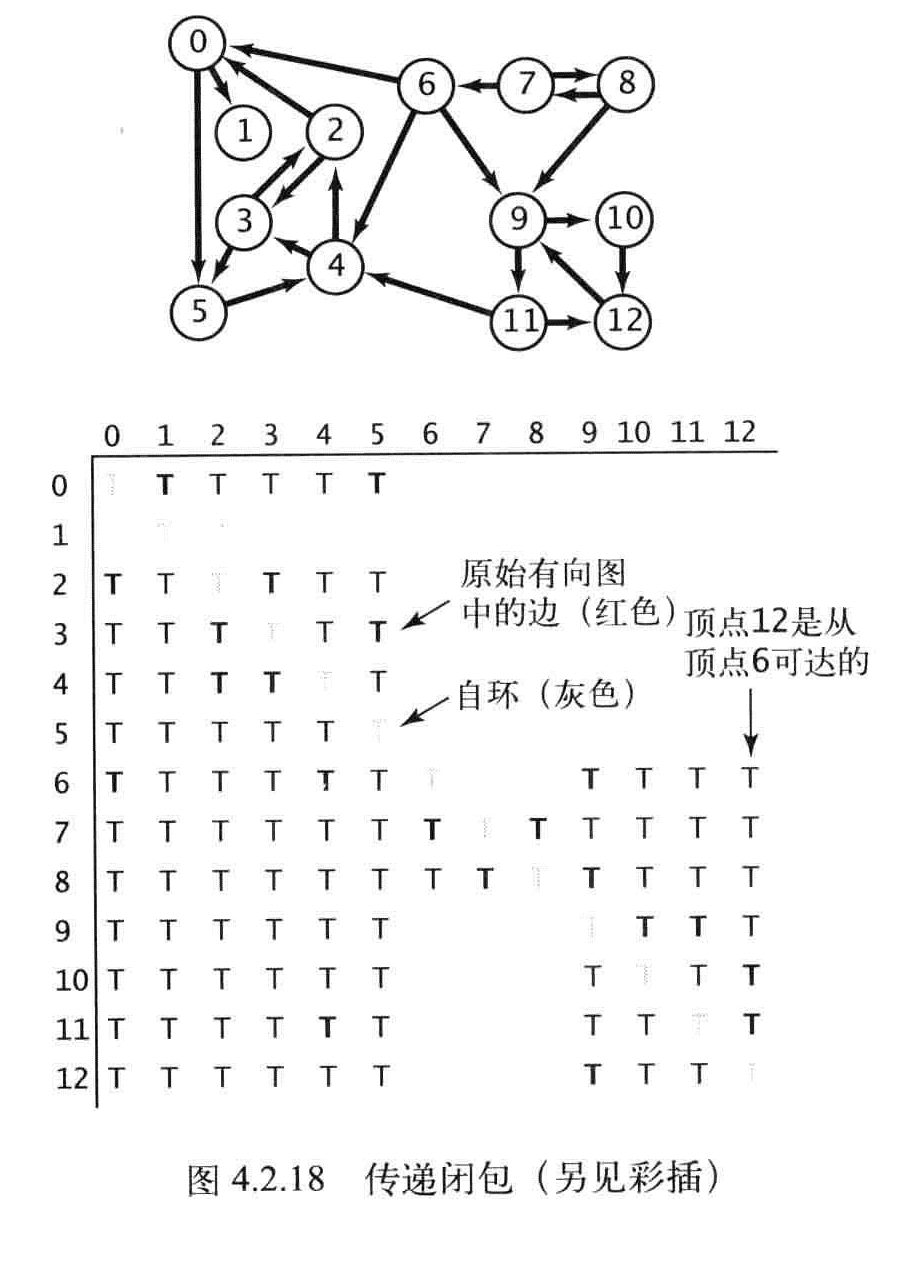
有向图G的传递闭包是由相同的一组顶点组成的另一幅有向图,在传递闭包中存在一条从v指向w的边当且仅当在G中w是从v可达的。
传递闭包不如用深度优先搜索算法
public class TransitiveClosure
{
private DirectedDFS[] tc;
public TransitiveClosure(Digraph G)
{
tc = new DirectedDFS[G.Vertices];
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
tc[v] = new DirectedDFS(G, v);
}
public bool Reachable(int v, int w)
{
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return tc[v].Marked(w);
}
private void validateVertex(int v)
{
int V = tc.Length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new ArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
}
测试:
[TestMethod()]
public void TransitiveClosureTest()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\\tinyDG.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph G = new AlgorithmEngine.Graph.Digraph(stream);
TransitiveClosure tc = new TransitiveClosure(G);
// print header
Console.Write("// ");
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
Console.Write($" {v:D2}");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("//--------------------------------------------");
// print transitive closure
for (int v = 0; v < G.Vertices; v++)
{
Console.Write($"// {v:D2}: ");
for (int w = 0; w < G.Vertices; w++)
{
if (tc.Reachable(v, w)) Console.Write(" T");
else Console.Write(" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12
//--------------------------------------------
// 00: T T T T T T
// 01: T
// 02: T T T T T T
// 03: T T T T T T
// 04: T T T T T T
// 05: T T T T T T
// 06: T T T T T T T T T T T T
// 07: T T T T T T T T T T T T T
// 08: T T T T T T T T T T T T
// 09: T T T T T T T T T T
// 10: T T T T T T T T T T
// 11: T T T T T T T T T T
// 12: T T T T T T T T T T
}
总结

您的资助是我最大的动力!
金额随意,欢迎来赏!
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/lovexinyi/
版权:本文版权归作者和博客园共有
转载:欢迎转载,但未经作者同意,必须保留此段声明;必须在文章中给出原文链接;否则必究法律责任


