Problem B. Full Binary Tree
题目
链接:http://code.google.com/codejam/contest/2984486/dashboard#s=p1
googlde code jam 2014 Round1A
解题报告下载
归类
动态规划,DFS
解法1[最优解]
耗时
1秒左右
分析
使用DFS和DP。目前为止的最优方案。
关键是用二维数组children_nodes[1001][1001]来表示父节点下的子节点的个数,例如
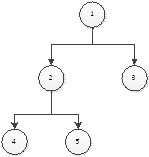
children_nodes[4][2]表示当2节点作为4节点的父亲的时候,4节点极其孩子节点的个数,当然前提是满足full binary tree。
children_nodes[4][2] = 1;
children_nodes[5][2] = 1;
children_nodes[2][1] = 3;
children_nodes[3][1] = 1;
通过children_nodes来记录计算的中间结果,可以大大加速DFS递归。
源码
#include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <fstream> #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <iterator> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::fstream; using std::map; using std::stringstream; using std::string; using std::vector; int get_result(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix); int get_max(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix, const int _child_row, const int _parent); int children_nodes[1001][1001]; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int case_amount = 0; cin >> case_amount; for (int i = 0; i < case_amount; ++i) { memset(children_nodes, 0, sizeof(children_nodes)); int N = 0; cin >> N; // Step1: Init vector<vector<int> > matrix(N + 1, vector<int>()); for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; ++j) { int row = 0, column = 0; cin >> row >> column; matrix[row].push_back(column); matrix[column].push_back(row); } const int result = get_result(matrix); cout << "Case #" << 1 + i << ": " << result << endl; } return 0; } int get_result(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix) { int max = 0; for (int i = 1; i < _matrix.size(); ++i) { const int result = get_max(_matrix, i, 0); if (max < result) max = result; } return _matrix.size() - max - 1; } int get_max(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix, const int _child_row, const int _parent) { if (0 == children_nodes[_child_row][_parent]) { vector<int> children; for (int i = 0; i < _matrix[_child_row].size(); ++i) { if (_parent != _matrix[_child_row][i]) children.push_back(get_max(_matrix, _matrix[_child_row][i], _child_row)); } std::sort(children.begin(), children.end(), std::greater<int>()); if (children.size() < 2) children_nodes[_child_row][_parent] = 1; else children_nodes[_child_row][_parent] = 1 + children[0] + children[1]; } return children_nodes[_child_row][_parent]; }
解法2[原来递归不会超时]
耗时
20秒左右
分析
使用DFS,深度优先搜索。
实例
Step1:初始化
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
2 |
1 |
4 |
|
|
3 |
1 |
7 |
|
|
4 |
2 |
5 |
6 |
|
5 |
4 |
||
|
6 |
4 |
||
|
7 |
3 |
Step2:遍历1-7行
分别计算以每行为root节点的最大节点数;
节点数最多的行,就是root节点,即可得知答案。
源码
#include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <iterator> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::fstream; using std::map; using std::stringstream; using std::string; using std::vector; fstream fs("input.txt", fstream::in); fstream fout("output.txt", fstream::out); int get_int_from_next_line(); string get_string_from_next_line(); int get_result(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix); int get_max(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix, const int _child_row, const int _parent); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (fs.good()) { const int case_amount = get_int_from_next_line(); for (int i = 0; i < case_amount; ++i) { const int N = get_int_from_next_line(); // Step1: Init vector<vector<int> > matrix(N, vector<int>()); for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; ++j) { const string line = get_string_from_next_line(); int row = 0, column = 0; stringstream temp_stream(line); temp_stream >> row >> column; matrix[row-1].push_back(column-1); matrix[column-1].push_back(row-1); } const int result = get_result(matrix); fout << "Case #" << 1 + i << ": " << result << endl; } } fs.close(); fout.close(); return 0; } int get_int_from_next_line() { string line = ""; getline(fs, line); stringstream stream(line); int temp = 0; stream >> temp; return temp; } string get_string_from_next_line() { string line = ""; getline(fs, line); return line; } int get_result(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix) { int max = 0; for (int i = 0; i < _matrix.size(); ++i) { int result = get_max(_matrix, i, -1); if (max < result) max = result; } return _matrix.size() - max; } int get_max(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix, const int _child_row, const int _parent) { vector<int> children; for (int i = 0; i < _matrix[_child_row].size(); ++i) { if (_parent != _matrix[_child_row][i]) children.push_back(get_max(_matrix, _matrix[_child_row][i], _child_row)); } std::sort(children.begin(), children.end(), std::greater<int>()); if (children.size() < 2) return 1; else return 1 + children[0] + children[1]; }
解法3[很笨的方法,自作聪明了]
耗时
3分钟
分析
注意:
题目中给出了Full Binary Tree的定义,只要满足root的每一个子节点有2个或0个子节点。
题目中给出X-Y,说X距离root节点比Y近,没有用。
题目中给出树G没有环。
顶点V与n(n>=3)个点有边
1. 有1,2,3,…,N个顶点,根据输入的关系,初始化二维数组array[N][N]
例如:
1.1 默认初始值为-2
1.2 有边相连,则设置为-1
2 如果N=1直接返回0,N=2直接返回1;如果N>2,则预处理,设row表示第几行,row=0àN-1,即第row节点
如果row行只有一个-1,则继续,否则row++
row节点就是叶子节点,第column列为-1,设置array[row][column]=0,并将与该节点相连的另一个节点,对应的值设置为1,array[column][row]=1
3 设row表示第几行,row=0àN-1,即第row节点
3.0 bool isHasNegtiveOne = false; 表示是否含有-1
3.1 如果row行只有一个-1,则继续,否则跳到3.4;isHasNegtiveOne= true,假设array[row][column]==-1,如果第column行除了第row列没有-1,那么跳到3.2,否则跳到3.3
3.2 如果第column行,除了第row列,非-2的列的数目大于等于2,则
跳到3.2.1,否则跳到3.2.2
3.2.1 在column行选择最大的两列,假设最大两列的和为max,设置array[row][column] = 1 + max;跳到3.3
3.2.2 顶点row作为顶点column的父节点,column节点可以提供1个顶点给row节点,设置array[row][column] = 1;跳到3.3
3.3 如果第row行,除了第column列,非-2的列的数目大于等于2,则跳到3.3.1,否则跳到3.3.2
3.3.1 在row行选择最大的两列,例如下图,最大的两列为4和3,那么顶点column作为顶点row的父节点,row节点可以提供4+3+1个节点给column节点,设置array[column][row] = 8;跳到3.4
|
-2 |
4 |
-1 |
3 |
2 |
3.3.2 顶点column作为顶点row的父节点,row节点可以提供1个顶点给column节点,设置array[column][row] = 1;跳到3.4
3.4 row是否为最后一行,如果不是,则row++继续3.1,如果是,且isHasNegtiveOne为false,则跳到4,否则继续3
4 分别以每一个顶点作为root,计算最大的节点数目
5 删除节点数 = 总结点数 - 最大节点数目
实例
7
4 5 4 2 1 2 3 1 6 4 3 7
Step1:初始化
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
|
1 |
-2 |
-1 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
3 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-1 |
|
4 |
-2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-1 |
-1 |
-2 |
|
5 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
6 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
7 |
-2 |
-2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
Step2:预处理
对初始的array进行预处理
根据上图,5,6,7行都只有一个-1,例如第5行,存在边(5,4),分别设置array[4][3]=0, array[3][4]=1,即顶点5作为顶点4的孩子只能提供1个节点。
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
|
1 |
-2 |
-1 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
3 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
|
4 |
-2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
|
5 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
6 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
7 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
Step3: 遍历
根据上图,3,4行只有1个-1,例如第3行,array[2][0] == -1,可推出从顶点1到顶点3,顶点1作为3的父节点,由于顶点3只有一个孩子7,所以顶点3只能提供给顶点1,1个节点,设置array[0][2]=1,同理设置array[1][3]=3。
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
|
1 |
-2 |
-1 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
3 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
3 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
|
4 |
-2 |
-1 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
|
5 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
6 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
7 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
Step3: 遍历
根据上图,1,2,3,4行只有1个-1,例如第1行,array[0][1] == -1,可推出从顶点2到顶点1,顶点2作为1的父节点,顶点1只有顶点3一个孩子,那么顶点1只能提供顶点2, 1个节点,设置array[1][0]=1,同理设置array[0][1]=1,array[2][0]=1,array[3][1]=1。
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
|
1 |
-2 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
2 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
3 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
3 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
|
4 |
-2 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
|
5 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
6 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
7 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
Step4:
根据上图,每一行都不含有-1,计算每一个顶点作为root节点的最大节点数。
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
||
|
3 |
1 |
-2 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
5 |
2 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
3 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
3 |
3 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
|
3 |
4 |
-2 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
|
1 |
5 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
1 |
6 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
1 |
7 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
Step4:
节点2作为root节点,最多有5个节点,去掉2个节点即可。
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
||
|
3 |
1 |
-2 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
5 |
2 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
3 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
3 |
3 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
|
3 |
4 |
-2 |
1 |
-2 |
-2 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
|
1 |
5 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
1 |
6 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
|
1 |
7 |
-2 |
-2 |
0 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
-2 |
源码
#include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <iterator> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::fstream; using std::map; using std::stringstream; using std::string; using std::vector; fstream fs("input.txt", fstream::in); fstream fout("output.txt", fstream::out); int get_int_from_next_line(); string get_string_from_next_line(); int get_result(vector<vector<int> > _matrix); int get_max_children(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix, const int _row, const int _column); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (fs.good()) { const int case_amount = get_int_from_next_line(); for (int i = 0; i < case_amount; ++i) { const int N = get_int_from_next_line(); // Step1: Init vector<vector<int> > matrix(N, vector<int>(N, -2)); for (int j = 0; j < N - 1; ++j) { const string line = get_string_from_next_line(); int row = 0, column = 0; stringstream temp_stream(line); temp_stream >> row >> column; matrix[row-1][column-1] = -1; matrix[column-1][row-1] = -1; } const int result = get_result(matrix); fout << "Case #" << 1 + i << ": " << result << endl; } } fs.close(); fout.close(); return 0; } int get_int_from_next_line() { string line = ""; getline(fs, line); stringstream stream(line); int temp = 0; stream >> temp; return temp; } string get_string_from_next_line() { string line = ""; getline(fs, line); return line; } int get_result(vector<vector<int> > _matrix) { if (2 == _matrix.size()) { return 1; } else if (1 == _matrix.size()) { return 0; } // Step2: Preprocess for (int row = 0; row < _matrix.size(); ++row) { const int count_not_n2 = _matrix.size() - std::count(_matrix[row].begin(), _matrix[row].end(), -2); if (1 == count_not_n2) { const vector<int>::const_iterator it = std::find(_matrix[row].begin(), _matrix[row].end(), -1); const int column = it - _matrix[row].begin(); _matrix[row][column] = 0; _matrix[column][row] = 1; } } // Step3: loop while (true) { bool isHasNegtiveOne = false; for (int row = 0; row < _matrix.size(); ++row) { const int count_1 = std::count(_matrix[row].begin(), _matrix[row].end(), -1); if (0 < count_1) isHasNegtiveOne = true; if (1 == count_1) { const vector<int>::const_iterator r_it = std::find(_matrix[row].begin(), _matrix[row].end(), -1); const int column = r_it - _matrix[row].begin(); // Step: 3.1 { vector<int> column_vec = _matrix[column]; column_vec.erase(row + column_vec.begin()); const vector<int>::const_iterator c_it = std::find(column_vec.begin(), column_vec.end(), -1); if (c_it == column_vec.end()) { // Step: 3.2 const int column_max_children = get_max_children(_matrix, column, row); _matrix[row][column] = 1 + column_max_children; } } // Step: 3.3 // column as the parent, row as the child // calculate how many nodes can row have const int row_max_children = get_max_children(_matrix, row, column); _matrix[column][row] = 1 + row_max_children; } } if (!isHasNegtiveOne) break; } // Step: 4 int max = 0; for (int row = 0; row < _matrix.size(); ++row) { std::sort(_matrix[row].begin(), _matrix[row].end(), std::greater<int>()); int current_max = _matrix[row][0] + _matrix[row][1]; if (max < current_max) max = current_max; } return _matrix.size() - max - 1; } // column as the parent, row as the child // calculate how many nodes can row have int get_max_children(const vector<vector<int> > &_matrix, const int _row, const int _column) { int max_children = 0; // count of negtive 2 const int count_n2 = std::count(_matrix[_row].begin(), _matrix[_row].end(), -2); const int count_not_n2 = _matrix.size() - count_n2; if (2 >= count_not_n2) { // Step: 3.3 max_children = 0; } else { // Step: 3.2 // Find the max 2 of _matrix[_row] which can not be _matrix[_row][_column] vector<int> m_row = _matrix[_row]; m_row.erase(_column + m_row.begin()); std::sort(m_row.begin(), m_row.end(), std::greater<int>()); max_children = m_row[0] + m_row[1]; } return max_children; }
总结
DP+DFS需要1秒;纯DFS需要20秒,我的自作聪明的DP需要3分钟。算法很关键哇!
作者:loverszhaokai
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lovers
本文采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号