并发编程补充--方法interrupted、isinterrupted详解
并发编程
interrupted()源码
/**
* Tests whether the current thread has been interrupted. The
* <i>interrupted status</i> of the thread is cleared by this method. In
* other words, if this method were to be called twice in succession, the
* second call would return false (unless the current thread were
* interrupted again, after the first call had cleared its interrupted
* status and before the second call had examined it).
*
* <p>A thread interruption ignored because a thread was not alive
* at the time of the interrupt will be reflected by this method
* returning false.
*
* @return <code>true</code> *if the current thread has been interrupted*;
* <code>false</code> otherwise.
* @see #isInterrupted()
* @revised 6.0
*/
public static boolean interrupted() {
return currentThread().isInterrupted(true);
}
重点看下方法上的注释:Tests whether the current thread has been interrupted。The
* interrupted status of the thread is cleared by this method。
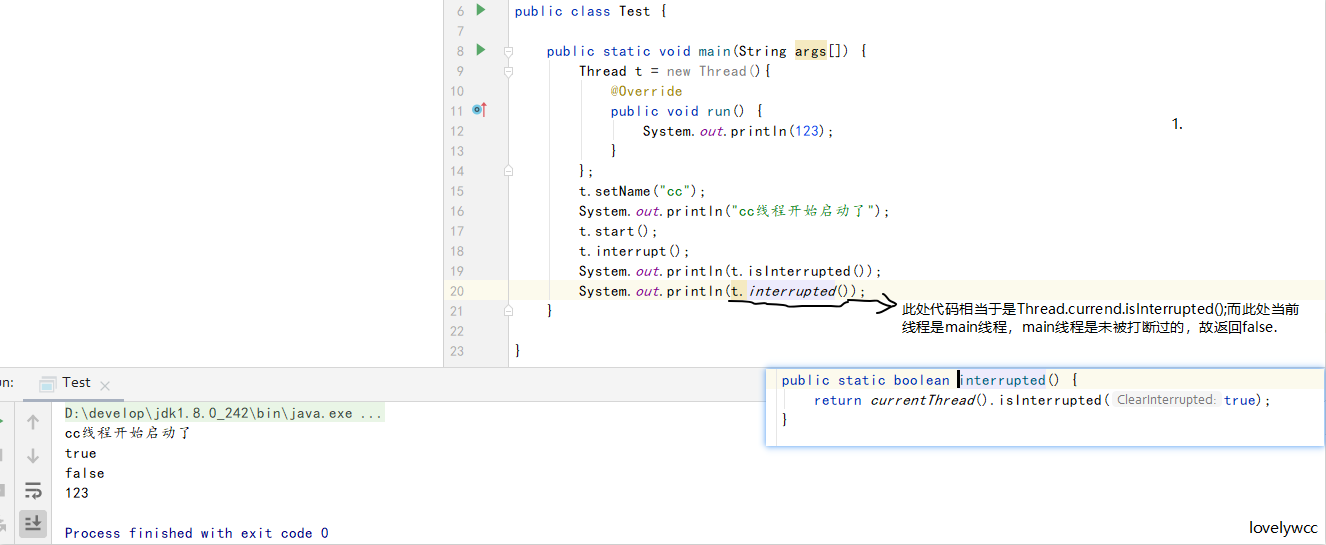
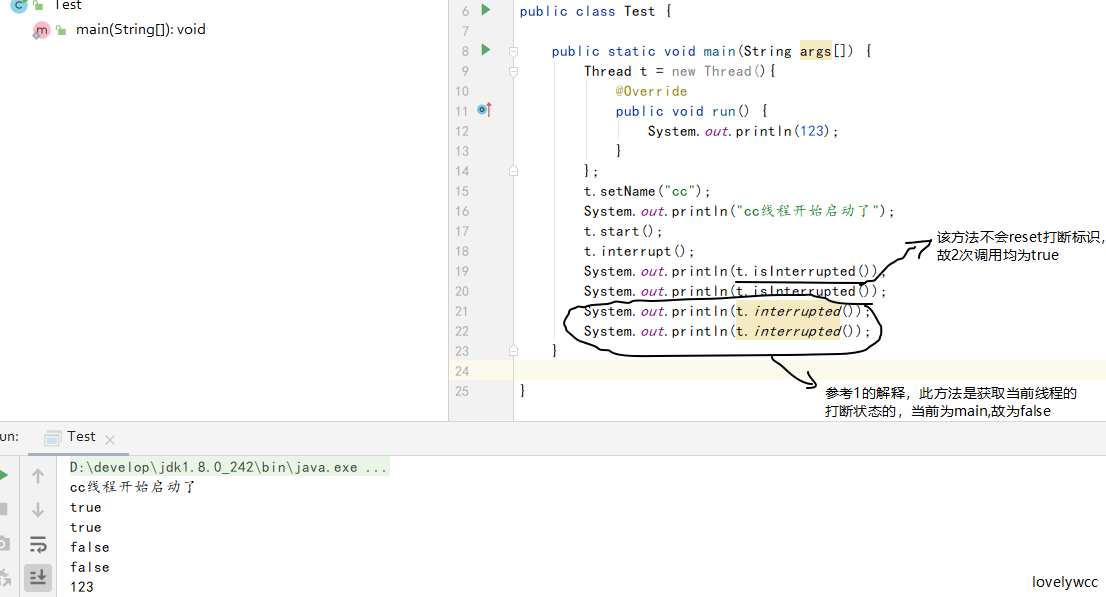
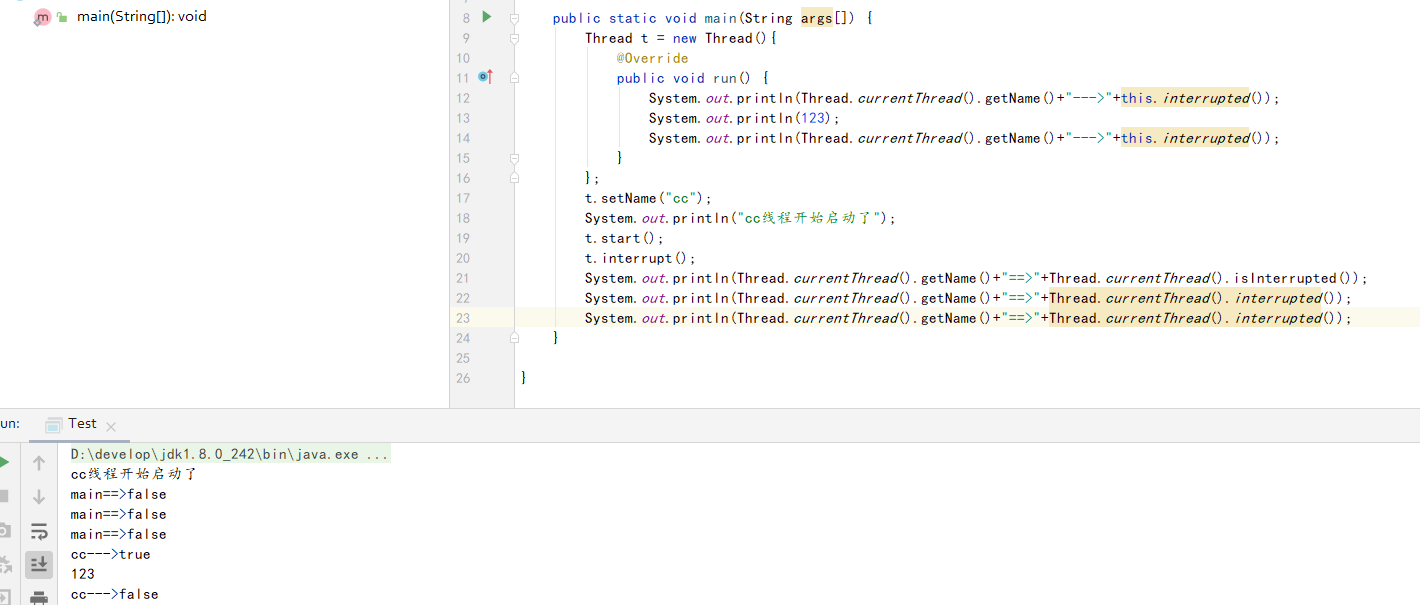
从上面两句话中,可得知,此方法返回的是当前线程是否被打断,如果是则为true,并且调用此方法后,interrupted status这种状态会被清除,清除逻辑是通过调用currentThread.isInterrupted()方法,并入参为true实现的
isInterrupted源码
/**
* Tests if some Thread has been interrupted. The interrupted state
* is reset or not based on the value of ClearInterrupted that is
* passed.
*/
private native boolean isInterrupted(boolean ClearInterrupted);
解读:调用isInterrupted方法时,会跟如入参ClearInterrupted决定是否重新设定interrupted state,true则重置,false则不执行,由于为本地方法,不能查看源码,但是根据源码注释是可以推断出来的,不传参会默认为false.
总结:
- interrupted()是静态方法:内部实现是调用的当前线程的isInterrupted(),并且会重置当前线程的中断状态
- isInterrupted()是实例方法,是调用该方法的对象所表示的那个线程的isInterrupted(),不会重置当前线程的中断状态
接下来进行代码展示环节
中断线程Interrupted的用处
线程状态
Java虚拟机将线程运行过程分成四种状态 。 (1) New 新生;(2) Runnable 可运行;(3) Blocked 阻塞;(4) Dead 死亡。
值得注意的是: 线程的可运行状态并不代表线程一定在运行(runnable != running ) 。 大家都知道:所有现代桌面和服务器操作系统都使用了抢占式的线程调度策略 。一旦线程开始执行,并不是总是保持持续运行状态的。当系统分给它的时间片(非常小的运行时间单位)用完以后,不管程序有没有执行完,线程被强制放弃CPU,进入就绪状态,直到下次被调度后开始继续执行。也就是说, Runnable可运行状态的线程处于两种可能的情况下:(1)占用CPU运行中,(2)等待调度的就绪状态。 这里要声明一下:处于等待调度的就绪状态线程和处于阻塞的线程是完全不同的。就绪的线程是因为时间片用完而放弃CPU,其随时都有可能再次获得CPU而运行,这一切取决于分时OS的线程调度策略。
在很多操作系统的专业术语中,这种因时间片用完而被剥夺CPU的情况我们叫做线程中断 。注意这和我们下面要将得中断线程是两个完全不同的概念。事实上,我们不可能通过应用程序来控制CPU的线程中断,除非我们能够自由调用OS的内核。
中断线程
一个正在运行的线程除了正常的时间片中断之外,能否被其他线程控制?或者说其他线程能否让指定线程放弃CPU或者提前结束运行? 除了线程同步机制之外,还有两种方法:
(1) Thread.stop(), Thread.suspend(), Thread.resume() 和Runtime.runFinalizersOnExit() 这些终止线程运行的方法 。这些方法已经被废弃,使用它们是极端不安全的。
(2) Thread.interrupt() 方法是很好的选择。但是使用的时候我们必须好好理解一下它的用处。
//无法中断正在运行的线程代码
class TestRunnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
while(true)
{
System.out.println( "Thread is running..." );
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();//去系统时间的毫秒数
while((System.currentTimeMillis()-time < 1000)) {
//程序循环1秒钟,不同于sleep(1000)会阻塞进程。
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Runnable r=new TestRunnable();
Thread th1=new Thread(r);
th1.start();
th1.interrupt();
}
}
//运行结果:一秒钟打印一次Thread is running...。程序没有终止的任何迹象
上面的代码说明interrupt()并没有中断一个正在运行的线程,或者说让一个running中的线程放弃CPU。那么interrupt到底中断什么。
首先我们看看interrupt究竟在干什么。
当我们调用th1.interrput()的时候,线程th1的中断状态(interrupted status) 会被置位。我们可以通过Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() 来检查这个布尔型的中断状态。
在Core Java中有这样一句话:"没有任何语言方面的需求要求一个被中断的程序应该终止。中断一个线程只是为了引起该线程的注意,被中断线程可以决定如何应对中断 "。好好体会这句话的含义,看看下面的代码:
//Interrupted的经典使用代码
public void run(){
try{
....
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()&& more work to do){
// do more work;
}
}catch(InterruptedException e){
// thread was interrupted during sleep or wait
}
finally{
// cleanup, if required
}
}
很显然,在上面代码中,while循环有一个决定因素就是需要不停的检查自己的中断状态。当外部线程调用该线程的interrupt 时,使得中断状态置位。这是该线程将终止循环,不在执行循环中的do more work了。
这说明: interrupt中断的是线程的某一部分业务逻辑,前提是线程需要检查自己的中断状态(isInterrupted())。
但是当th1被阻塞的时候,比如被Object.wait, Thread.join和Thread.sleep三种方法之一阻塞时。调用它的interrput()方法。可想而知,没有占用CPU运行的线程是不可能给自己的中断状态置位的。这就会产生一个InterruptedException异常。
//中断一个被阻塞的线程代码
class TestRunnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000000); //这个线程将被阻塞1000秒
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
//do more work and return.
}
}
}
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable tr=new TestRunnable();
Thread th1=new Thread(tr);
th1.start(); //开始执行分线程
while(true){
th1.interrupt(); //中断这个分线程
}
}
}
/*运行结果:
java.lang.InterruptedException: sleep interrupted
at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Native Method)
at TestRunnable.run(TestDemo2.java:4)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source)*/




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构