python· challenge1
ord(c)
Given a string of length one, return an integer representing the Unicode code point of the character when the argument is a unicode object, or the value of the byte when the argument is an 8-bit string. For example, ord('a') returns the integer 97, ord(u'\u2020')returns 8224. This is the inverse of chr() for 8-bit strings and of unichr() for unicode objects. If a unicode argument is given and Python was built with UCS2 Unicode, then the character’s code point must be in the range [0..65535] inclusive; otherwise the string length is two, and a TypeError will be raised.
chr(i)
Return a string of one character whose ASCII code is the integer i. For example, chr(97) returns the string 'a'. This is the inverse of ord(). The argument must be in the range [0..255], inclusive; ValueError will be raised if i is outside that range. See alsounichr().
range(start, stop[, step])
This is a versatile function to create lists containing arithmetic progressions. It is most often used in for loops. The arguments must be plain integers. If the step argument is omitted, it defaults to 1. If the start argument is omitted, it defaults to 0. The full form returns a list of plain integers [start, start + step, start + 2 * step, ...]. If step is positive, the last element is the largest start + i * step less than stop; if step is negative, the last element is the smallest start + i * step greater than stop. stepmust not be zero (or else ValueError is raised). Example:
>>> range(10)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> range(1, 11)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
>>> range(0, 30, 5)
[0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25]
>>> range(0, 10, 3)
[0, 3, 6, 9]
>>> range(0, -10, -1)
[0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, -8, -9]
>>> range(0)
[]
>>> range(1, 0)
[]
第一次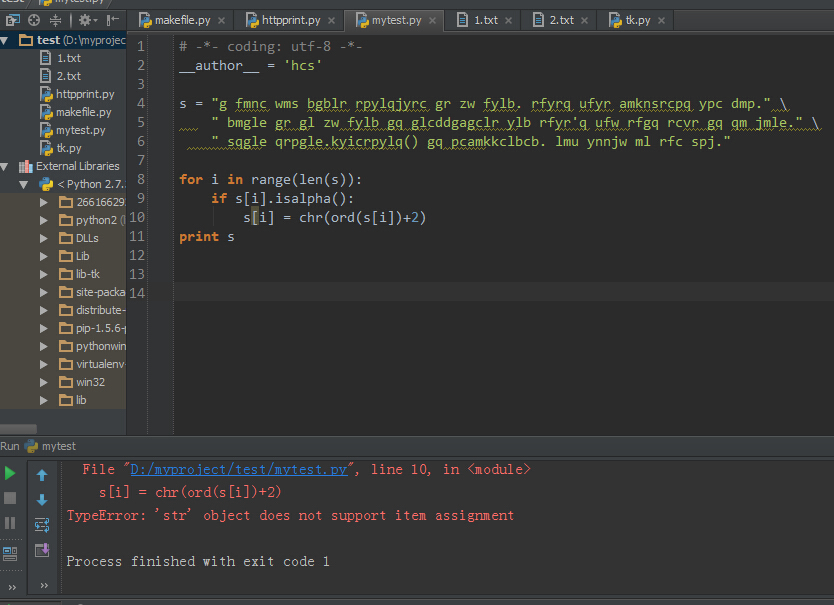
出现错误:
在SO上面找到答案:Python does not allow you to swap out characters in a string for another one; strings are immutable.
What you'll need to do is create a totally different string and return that instead.
重写代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- __author__ = 'hcs' s = "g fmnc wms bgblr rpylqjyrc gr zw fylb. rfyrq ufyr amknsrcpq ypc dmp." \ " bmgle gr gl zw fylb gq glcddgagclr ylb rfyr'q ufw rfgq rcvr gq qm jmle." \ " sqgle qrpgle.kyicrpylq() gq pcamkkclbcb. lmu ynnjw ml rfc spj." L = "" for i in range(len(s)): if s[i].isalpha(): if(ord(s[i])+2) <= ord('z'): L += (chr(ord(s[i])+2)) else: L += (chr(ord(s[i])+2-ord('z')+ord('a')-1)) else: L += s[i] print L
结果:i hope you didnt translate it by hand. thats what computers are for. doing it in by hand is inefficient and that's why this text is so long. using string.maketrans() is recommended. now apply on the url.
一个通用的程序
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 __author__ = 'hcs' 3 print'input the string' 4 s = raw_input() 5 print s 6 7 print'input the num' 8 j = int(input()) 9 print j 10 L = "" 11 for i in range(len(s)): 12 if s[i].isalpha(): 13 if(ord(s[i])+j) <= ord('z'): 14 L += (chr(ord(s[i])+j)) 15 else: 16 L += (chr(ord(s[i])+j-ord('z')+ord('a')-1)) 17 else: 18 L += s[i] 19 print L


