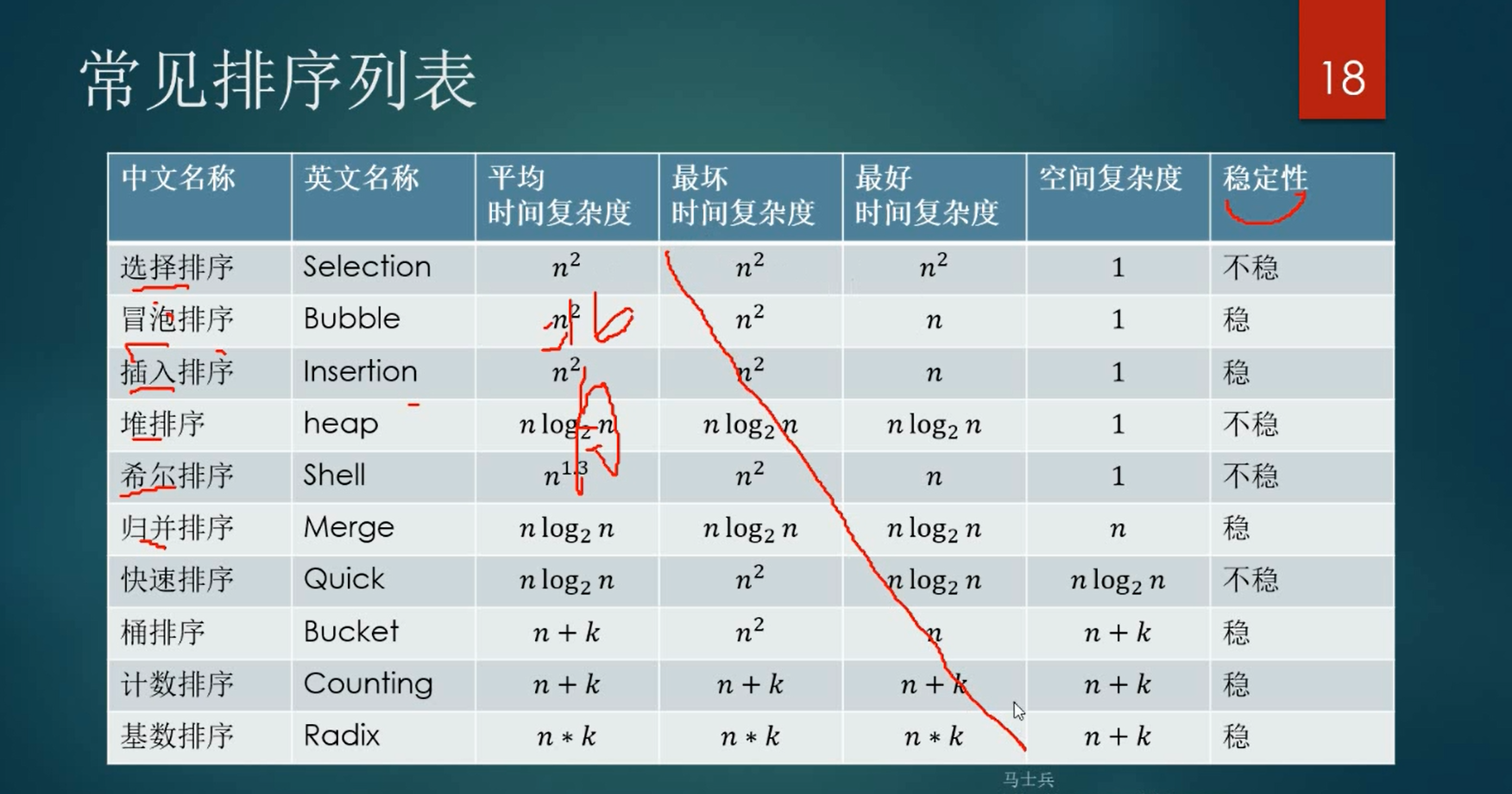
排序算法一计数排序
欢迎光临我的博客[http://poetize.cn],前端使用VUE2,聊天室使用VUE3,后台使用Spring Boot
简介
计数排序是一个非基于比较的排序算法,该算法于1954年由 Harold H. Seward 提出。
它的优势在于在对一定范围内的整数排序时,它的复杂度为Ο(n+k)(其中k是整数的范围),快于任何比较排序算法。
- count sort,以空间换时间
- 时间复杂度O(n)
- 空间复杂度O(max+n)max为要排序的数据中的最大值。
计数排序就是计算相同key的元素各有多少个,然后根据出现的次数累加而获得最终的位置信息。
计数排序有两个限制条件,
那就是存在一个正整数K,使得数组里面的所有元素的key值都不大于N,
key值都是非负整数。
1 class CountSort { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 int[] arr = {-2, -32, -1, 5, 0, 3, -1, 6, 4, 5}; 4 int a = 0; 5 int b = arr.length - 1; 6 arr=countSort(arr, 0, b); 7 } 8 9 private static int[] countSort(int[] arr, int a, int b) { 10 if (arr.length <= 1) return arr; 11 12 //寻找最大与最小值 13 int min = arr[0]; 14 int max = arr[0]; 15 for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { 16 if (min > arr[i]) min = arr[i]; 17 if (max < arr[i]) max = arr[i]; 18 } 19 20 //新数组 21 int[] finalarr = new int[arr.length]; 22 //count储存元素的个数 23 int[] count = new int[max - min + 1]; 24 25 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 26 count[arr[i] - min]++; 27 } 28 29 //将count中储存的数据转移至finalarr 30 int f = 0; 31 for (int i = 0; i < count.length; i++) { 32 for (int j = 0; j < count[i]; j++) { 33 finalarr[f++] = i + min; 34 } 35 } 36 return finalarr; 37 } 38 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号