Theano入门神经网络(一)
Theano是一个Python库,专门用于定义、优化、求值数学表达式,效率高,适用于多维数组。特别适合做机器学习。一般来说,使用时需要安装python和numpy.
首先回顾一下机器学习的东西,定义一个模型(函数)f(x;w) x为输入,w为模型参数,然后定义一个损失函数c(f),通过数据驱动在一堆模型函数中选择最优的函数就是训练training的过程,在机器学习中训练一般采用梯度下降法gradient descent.
使用theano来搭建机器学习(深度学习)框架,有以下优点:
1、 theano能够自动计算梯度
2、只需要两步骤就能搭建框架,定义函数和计算梯度。
一、 定义函数
步骤 0 宣告使用theano import theano
步骤 1 定义输入 x=theano.tensor.scalar()
步骤 2 定义输出 y=2*x
步骤3 定义fuction f = theano.function([x],y)
步骤 4 调用函数 print f(-2)
步骤1 定义输入变量
a = theano.tensor.scalar()
b =theano.tensor.matrix()
简化 import theano.tensor as T
步骤2 定义输出变量 需要和输入变量的关系
x1=T.matrix()
x2=T.matrix()
y1=x1*x2
y2=T.dot(x1,x2) #矩阵乘法
步骤3 申明函数
f= theano.function([x],y)
函数输入必须是list 带[]
example:
1 import theano 2 import theano.tensor as T 3 4 a= T.matrix() 5 b= T.matrix() 6 c = a*b 7 d = T.dot(a,b) 8 F1= theano.function([a,b],c) 9 F2= theano.function([a,b],d)
A=[[1,2],[3,4]] 10 B=[[2,4],[6,8]] #2*2矩阵 11 C=[[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]] #3*2矩阵 12 print F1(A,B) 13 print F2(C,B)
二、计算梯度
计算 dy/dx ,直接调用g=T.grad(y,x) y必须是一个标量 scalar
和梯度有关的三个例子:
example1 :标量对标量的导数
1 x= T.scalar('x') 2 y = x**2 3 g = T.grad(y,x) 4 f= theano.function([x],y) 5 f_prime=theano.function([x],g) 6 print f(-2) 7 print f_prime(-2)
example2 : 标量对向量的导数
x1= T.scalar() x2= T.scalar() y = x1*x2 g = T.grad(y,[x1,x2]) f= theano.function([x1,x2],y) f_prime=theano.function([x1,x2],g) print f(2,4) print f_prime(2,4)
example3 : 标量对矩阵的导数
A= T.matrix() B= T.matrix() C=A*B #不是矩阵乘法,是对于位置相乘 D=T.sum(C) g=T.grad(D,A) #注意D是求和 所以肯定是一个标量 但g是一个矩阵 y_prime=theano.function([A,B],g) A=[[1,2],[3,4]] B=[[2,4],[6,8]] print y_prime(A,B)
搭建神经网络
1 单个神经元

假设w b 已知。y=neuron(x;w,b)
1 import theano 2 import theano.tensor as T 3 import random 4 import numpy as np 5 6 x = T.vector() 7 w = T.vector() 8 b = T.scalar() 9 10 z= T.dot(w,x)+b 11 y= 1/(1+T.exp(-z)) 12 13 neuron =theano.function( 14 inputs=[x,w,b], 15 outputs=[y] 16 ) 17 18 w = [-1,1] 19 b=0 20 for i in range(100): 21 x = [random.random(),random.random()] 22 print x 23 print neuron(x,w,b)
但是运行出现错误 'TensorType(float32, vector) cannot store accurately value [0.4079584242156499, 0.7781482896772725], it would be represented as [ 0.40795842 0.77814829]. If you do not mind this precision loss, you can: 1) explicitly convert your data to a numpy array of dtype float32, or 2) set "allow_input_downcast=True" when calling "function".',
因此我们按照第一种方法,转换成a numpy array of dtype float32,将上述21行代码替换如下:
x=np.asarray([random.random(),random.random()], dtype = np.float32)
运行结果如下
[array(0.3996952772140503, dtype=float32)]
[ 0.12659253 0.45289889]
[array(0.5808603763580322, dtype=float32)]
[ 0.96148008 0.70698273]
[array(0.43671688437461853, dtype=float32)]
w,b应该也是参数 ,上述函数改为neuron(x),model 参数 wb 应该用shared variables,改进的代码
1 import theano 2 import theano.tensor as T 3 import random 4 import numpy as np 5 6 x = T.vector() 7 # share variables 参数!有值 8 w = theano.shared(np.array([1.,1.])) 9 b = theano.shared(0.) 10 11 z= T.dot(w,x)+b 12 y= 1/(1+T.exp(-z)) 13 14 neuron =theano.function( 15 inputs=[x], # x 作为输入 16 outputs=y 17 ) 18 19 w.set_value([0.1, 0.1]) #修改值 20 for i in range(100): 21 #x = [random.random(),random.random()] 22 x=np.asarray([random.random(),random.random()], dtype = np.float32) 23 print x 24 print w.get_value() #得到值 25 print neuron(x)
2 训练 training
定义一个损失函数C 计算C对每一个wi的偏导数 和b的偏导数
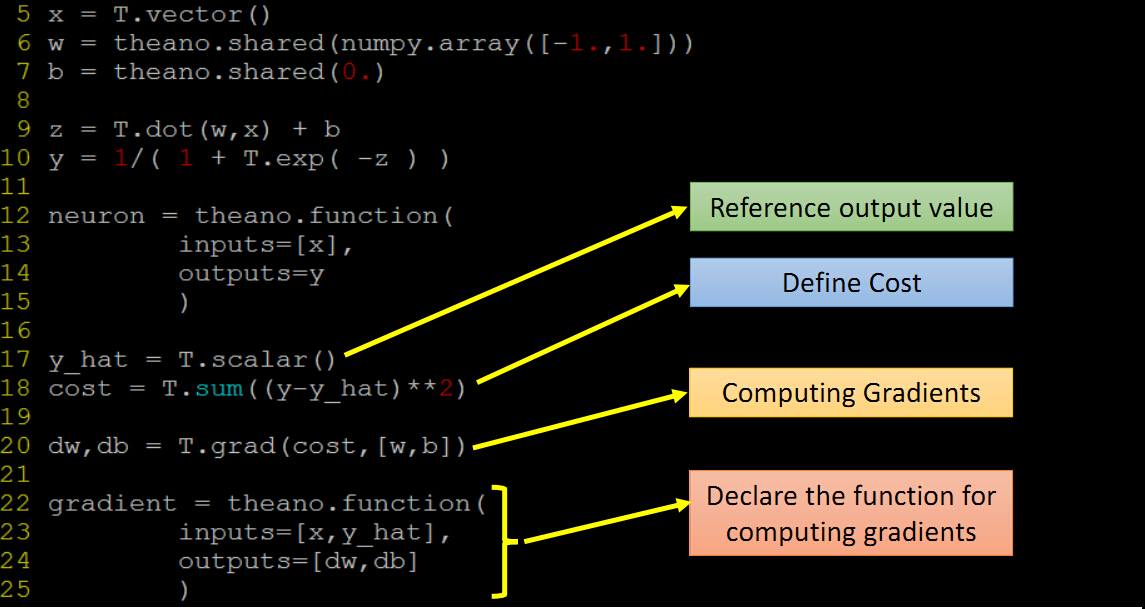
梯度下降 w1 = w1 -n*dc/dw1
常规:
dw, db =gradient(x,y_hat)
w.set_value(w.get_value()-0.1*dw)
b.set_value(b.get_value()-0.1*db)
改进:
gradient = theano.function(
inputs=[x,y_hat],
updates=[(w,w-0.1*dw),(b,b-0.1*db)]



