02 - Functions
functions


Thinking Recursively
Solving a problem with recursion requires two steps.
- First, determine how to solve the problem for simple cases. This is called the
basecase. - Second, determine how to break down larger cases into smaller instances. This is called the
recursivestep.
Summing Up Digits
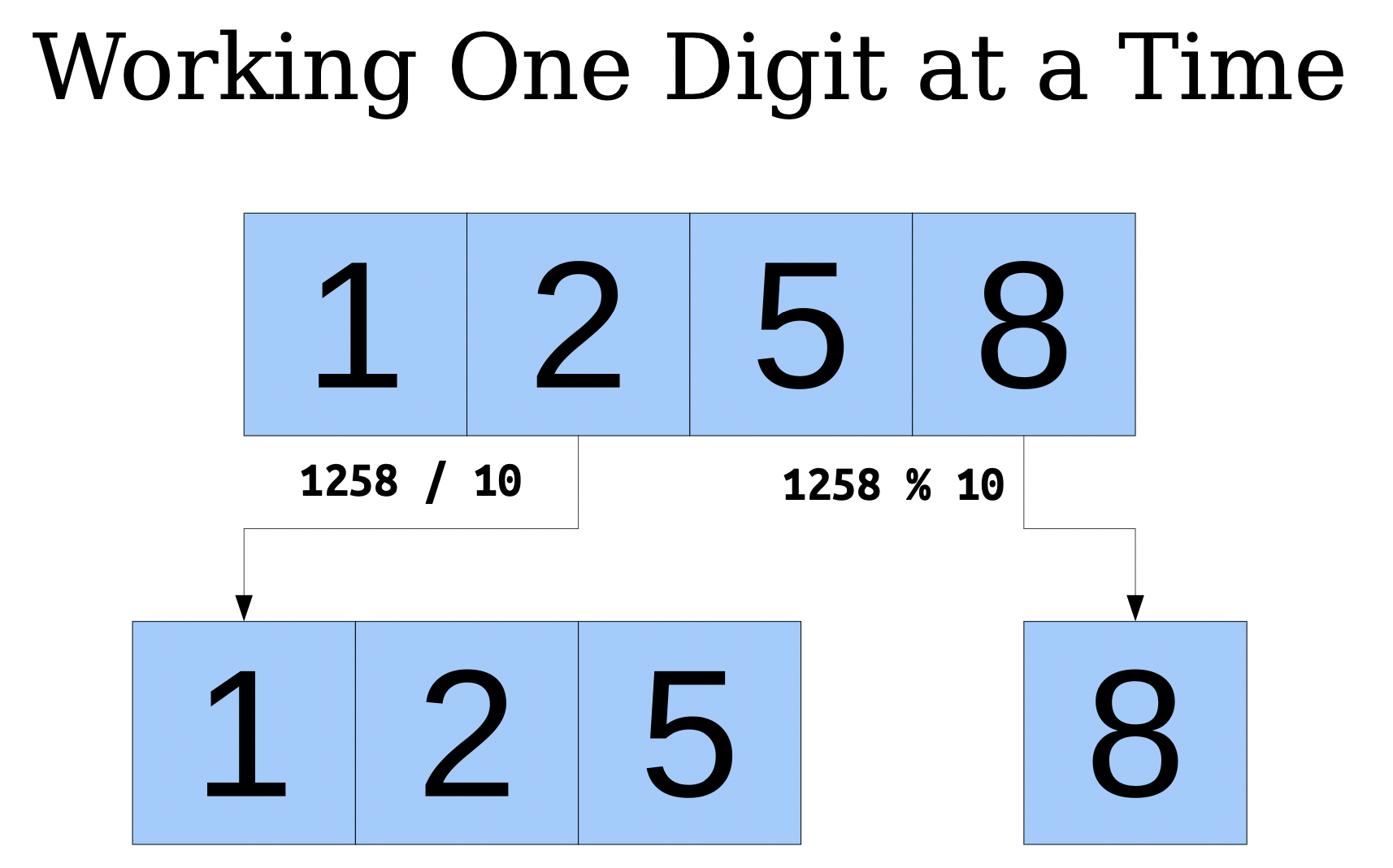
iteratively
int sumOfDigitsOf(int n){ int result = 0; while (n > 0){ result += (n % 10); n /= 10; } return result; } int main() { int n = getInteger("Enter an integer: "); int digitSum = sumOfDigitsOf(n); cout << n << " sums to " << digitSum << endl; return 0; }
recursively
int sumOfDigitsOfByRecursion(int n){ if (n < 10){ return n; } else { return sumOfDigitsOfByRecursion(n / 10) + (n % 10); } } int main() { cout << "Summing up digits by recursion" << endl; int n = getInteger("Enter an integer: "); int digitSum = sumOfDigitsOfByRecursion(n); cout << n << " sums to " << digitSum << endl; return 0; }
Factorials
- The number
n factorial, denotedn!, is n × (n – 1) × ... × 3 × 2 × 1
int factorial(int n){ if (n == 0) { return 1; } else { return n * factorial(n - 1); } } int main(){ int num = getInteger("Enter a integer: "); int factorialOfIt = factorial(num); cout << "Factorail of " << n << " is: " << factorail << endl; return 0; }
Digital Roots
- The
digital rootis the number you get by repeatedly summing the digits of a number until you’re down to a single digit.
Q: What is the digital root of 5?
A: 5 is a single digit, so the answer is 5.
Q: What is the digital root of 27?
A: 2 + 7 = 9.
The answer is 9.
Q: What is the digital root of 137?
A: 1 + 3 + 7 = 11.
1 + 1 = 2.
The answer is 2.
int digitalRoot(int n){ if(n < 10) { return n; } else { return digitalRoot(digitalRoot(n / 10) + (n % 10)); } } int main(){ int num = getInteger("Enter a integer: "); int result = digitalRoot(num); cout << "Digital root of " << n << " is: " << result << endl; return 0; }
Reverse a string
recurcively
string reverse(string s){ if (s.substr(1) == ""){ return s; } else { return reverse(s.substr(1)) + s[0]; } } int main(){ string s = getLine("Enter a string that you wanna reverse: "); string reversed = reverse(s); cout << "Reversed of " << s << " is: " << reversed << endl; }
Parameter Passing in C++
General principle: When passing a string into a function, use pass-by-reference unless you actually want a copy of the string.
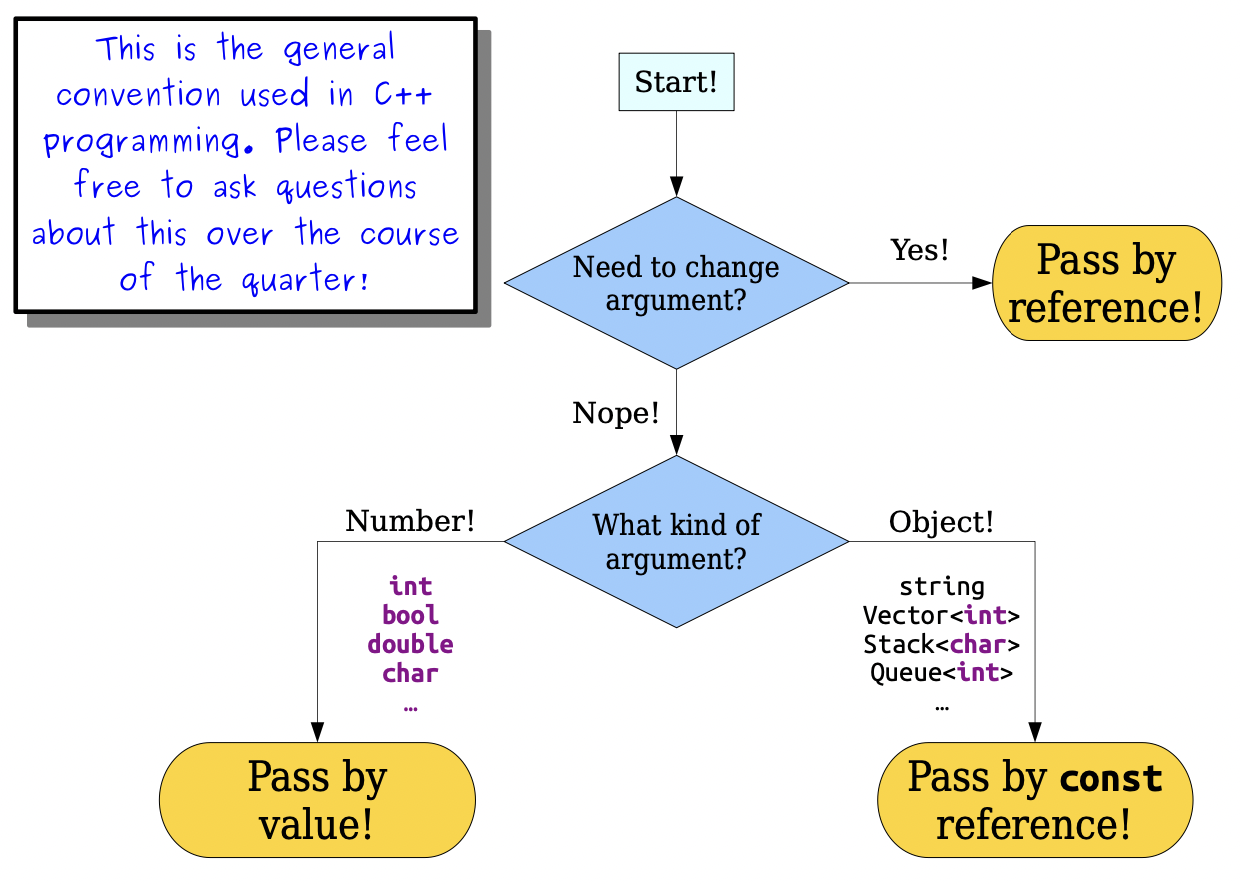
"Pass by value" (default behavior of parameters)
- The function
twiceOftakes the value of main’s variableaas input, but the change intwiceOfonly happens to a local copy nameda.
int twiceOf(int a){ return a *= 2; } int main(){ int num = 12; cout << twiceOf(num) << endl; return 0; } // the answer here is `12`
"Pass by reference" - &
- I like to think of the
&asa rope lasso that grabs the input parameter and drags it into the function call directly, rather than making a copy of its value and then leaving it in place.
int twiceOf(int& a){ return a *= 2; } int main(){ int a = 12; cout << twiceOf(a) << endl; return 0; } // the answer here is `24`
Pass-by-const-Reference
- If you want to look at, but not modify, a function parameter, pass it by
const reference: The “by reference” part avoids a copy. - The
const(constant) part means that the function can’t change that argument.
For example:
void proofreadLongEssay(const string& essay) { /* can read, but not change, the essay. */ }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~