01 - fundamentals
fundamentals
If someone claims to have the perfect programming language, he is either a fool or a salesman or both.
要是有人说有完美的编程语言,那这货要么是个傻der,要么是个卖课的,要么是个卖课的傻der。
– Bjarne Stroustrup, Inventor of C++
C++ 优劣
benefits 优势
-
C++ is fast
C++是编译型语言,python是解释型语言。
Get ready for the Python vs C++ speed showdown during Assignment 1! -
C++ is popular
许多公司和研究项目都使用 C++,并且在 C++ 中进行编码面试是很常见的 -
C++ is powerful
C++ brings you closer to the raw computing power that your computer has to offer
drawbacks 劣势
-
C++ is complex
· We will rely on the Stanford C++ libraries to provide a friendlier level of abstraction
· In the future, you may choose to explore the standard libraries -
C++ can be dangerous
"With great power comes great responsibility"
Comments 注解
-
Single-line comments
// Two forward slashes comment out the rest of the line cout << "Hello, World!" << endl; // everything past the double-slash is a comment -
Multi-line comments
/* This is a multi-line comment. * It begins and ends with an asterisk-slash. */
Includes 引用
-
Utilizing code written by other programmers is one of the most powerful things that you can do when writing code.
-
In order to make the compiler aware of other code libraries or other code files
that you want to use, you must include a header file. There are two ways that
you can do so:
#include <iostream>- Use of the angle bracket operators is usually reserved for code from the C++ Standard library
#include "console.h"- Use of the quotes is usually reserved for code from the Stanford C++ libraries, or code in files that you have written yourself
Console Output
- In C++, the way that you get information to the console is by using the cout keyword and angle bracket operators (<<).
- The endl is necessary to put the cursor on a different line. Here is an example with and without the endl keyword.
cout << "The answer to life, the universe, and everything is " << 42 << "." << endl;
Variables and Types
Variables
-
一个变量存储一个对应的值
A way for code to store infomation by associating a value with a name.
-
We will think of a variable as a
named container storing a value.
106 className
16.3 sundayTemp
- 变量是编程中最基础的部分之一
- 注意⚠️: c++ 使用驼峰式命名变量
Types
// int
int a = 1;
// double
double b = 3.14;
// string
string s = "hello";
// char
char c = 'A';
double a = 4.2; // ERROR! You cannot redifine a variable to be another type
int a = 12; // ERROR! You do not need the type when re-assigning a variable
a = 12; // this is okay, updates variable value
- In C++, all types must be explicitly defined when the variable is created, and a variable cannot change its type.
Functions and Parameters
Anatomy of a function
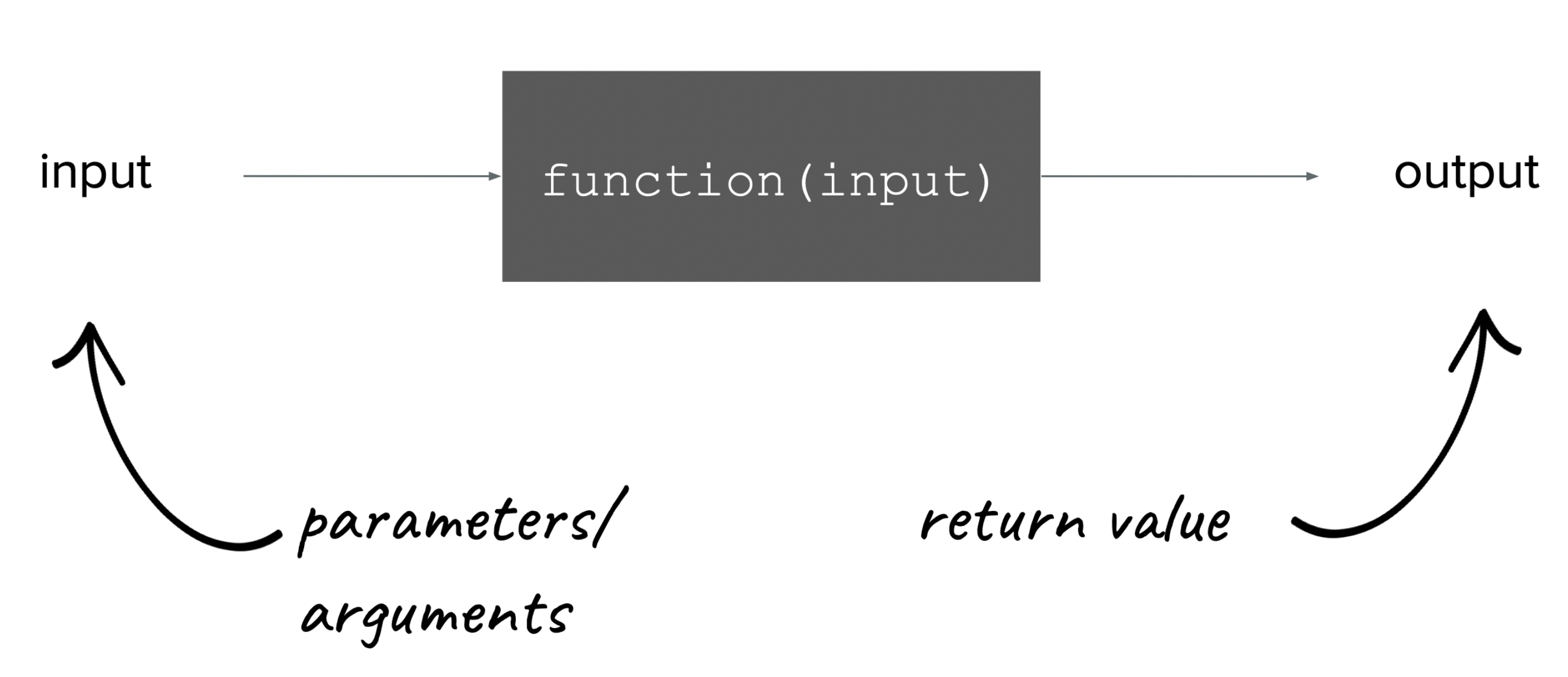
// function prototype
returnType functionName(varType parameter1, varType parameter2, ...);
// function defination
returnType functionName(varType parameter1, varType parameter2, ...) {
returnType variable = /* Some fancy code. */
/* Some more code to actually do things. */
return variable;
}
// example
double average(double a, double b){
double sum = a + b;
return sum / 2;
}
int main(){
double mid = average(10.6, 7.2);
cout << mid << endl;
return 0;
}

Pass by Value
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int doubleValue(int x) {
x *= 2;
return x;
}
int main() {
int myValue = 5;
int result = doubleValue(myValue);
cout << "myValue: " << myValue << " ";
cout << "result: " << result << endl;
}
// answer:
// myValue: 5 result: 10
Control Flow
Boolean Expressions
| Expression | Meaning | Operation | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| a < b | a is less than b | ||
| a <= b | a is less than or equal to b | a && b | Both a AND b are ture |
| a > b | a is greater than than b | a || b | Either a OR b are ture |
| a >= b | a is greater than or equal to b | !a | If a is true, returns false, and vice-versa |
| a == b | a is equal to b | ||
| a != b | a is not equal to b |
Conditional Statements
- The C++
ifstatement tests a boolean expression and runs a block of code if the expression istrue, and, optionally, runs a different block of code if the expression isfalse. Theifstatement has the following format:
if(expression) {
statements if expression is true
} else {
statements if expression is false
}
- Additional else if statements can be used to check for addtional conditions as well
if(expression1) {
statements if expression1 is true
} else if(expression2) {
statements if expression2 is false
} else {
statement if neither expression1 nor expression2 is true
}
while loops
- Loops allow you to repeat the execution of a certain block of code multiple times
whileloops are great when you want to continue executing something until a certain condition is met and you don't know exactly how many times you want to iterate for
// Execution continues until expression evaluates to false
while (expression) {
statement;
statement;
...
}
for loops
- for loops are great when you have a known, fixed number of times that you want to execute a block of code
/*
* The initializationStatement happens at the beginning of the loop, and initializes a variable. E.g., int i = 0.
*
* The testExpression is evaluated initially, and after each run through the loop, and if it is true, and the loop continues for another iteration. E.g., i < 3.
*
* The updateStatement happens after each loop, but before testExpression is evaluated. E.g., i++.
*/
for (initializationStatement; testExpression; updateStatement) {
statement;
statement;
...
}
Testing
Software and cathedrals are much the same – first we build them, then we pray.
– Sam Redwine



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号